BISAP與APACHEⅡ評分系統評估急性胰腺炎嚴重程度及臟器功能不全的臨床價值
高楠 李銳 丁一心 沈佳慶 肖坤廷 陳衛昌
·論著·
BISAP與APACHEⅡ評分系統評估急性胰腺炎嚴重程度及臟器功能不全的臨床價值
高楠 李銳 丁一心 沈佳慶 肖坤廷 陳衛昌
目的探討BISAP、APACHEⅡ評分系統評估急性胰腺炎(AP)嚴重程度及臟器功能不全的臨床價值。方法 回顧性分析2012年1月至2014年12月間蘇州大學附屬第一醫院消化內科收治的185例AP患者的臨床資料。根據BISAP評分,將≥3分患者歸為高分組,<3分為低分組;根據APACHEⅡ評分,將≥8分患者歸為高分組,<8分為低分組。按中華醫學會消化病學分會胰腺病學組制定的標準將患者分為輕癥AP(MAP)、中度重癥AP(MSAP)、重癥AP(SAP )。比較MSAP+SAP組與MAP組兩評分系統的差異;高分組與低分組之間MSAP+SAP發生率的差異。應用ROC曲線下面積(AUC)評價BISAP及APACHEⅡ評分對AP嚴重程度和并發臟器功能不全的預測價值。結果 185例患者中MAP 101例,MSAP 76例,SAP 8例。MSAP中出現臟器功能不全25例,8例SAP患者均并發臟器功能不全。MSAP+SAP組與MAP組的BISAP評分分別為(1.43±0.89)、(0.38±0.61)分;APACHEⅡ評分為(2.45±1.36)、(0.87±0.62)分,MSAP+SAP組顯著高于MAP組,差異均有統計學意義(P值均<0.01)。BISAP低分組137例中MSAP+SAP患者47例(34.3%),高分組48例中MSAP+SAP患者37例(77.0%);APACHEⅡ低分組153例中MSAP+SAP患者56例(36.6%),高分組32例中MSAP+SAP患者28例(87.5%)。高分組的MSAP+SAP患者例數均顯著高于低分組,差異有統計學意義(P值均<0.01)。BISAP、APACHEⅡ評分預測AP病情嚴重程度的AUC分別為0.804 (95%CI0.738~0.870)、0.794(95%CI0.725~0.863);預測臟器功能不全的AUC分別為0.758(95%CI0.686~0.830)、0.781(95%CI0.710~0.852)。兩種評分系統間的差異無統計學意義。結論 BISAP評分對AP嚴重程度及預后的評估價值與APACHEⅡ評分系統相同,但其指標少,24 h內可采集,值得在臨床推廣應用。
胰腺炎; 疾病嚴重程度指數; BISAP評分; APACHⅡ評分; 預后
急性胰腺炎(AP)是常見的消化系統疾病,大部分為輕癥,病程呈自限性,但仍有相當比例患者為重癥,出現嚴重的全身炎性反應綜合征(SIRS)及不同程度的臟器功能不全,住院時間長,臨床總體病死率5%~10%[1]。因此病情評估、預測臟器功能不全對AP早期診治、改善預后具有十分重要的意義。BISAP評分系統是2008年出現的一種較新的AP評分系統[2-3],主要特點是簡單易行,已在國外多項大樣本的回顧性研究中得到證實。本研究回顧性分析185例AP住院病例的臨床資料, 探討BISAP評分及APACHEⅡ評分對AP嚴重程度的評估價值及其與臟器功能不全的相關性。
資料與方法
一、病例資料
收集2012年1月至2014年12月間蘇州大學附屬第一醫院消化內科185例AP住院患者資料,AP診斷及分型均符合中華醫學會消化病學分會胰腺病學組制定的標準[4]。輕癥急性胰腺炎(MAP)為符合AP診斷標準且滿足以下情況之一:無臟器衰竭、無局部或全身并發癥,Ranson評分<3分,APACHEⅡ評分<8分,BISAP評分<3分,MCTSI評分<4分;中度重癥急性胰腺炎(MSAP)為符合AP診斷標準且急性期滿足下列情況之一:Ranson評分≥3分,APACHEⅡ評分≥8分,BISAP評分≥3分,MCTSI評分≥4分,可有一過性(<48 h)的器官功能障礙,恢復期出現需要干預的假性囊腫、胰瘺或胰周膿腫等;重癥急性胰腺炎(SAP)為符合AP診斷標準且伴有持續性(>48 h)器官功能障礙(單器官或多器官)。器官功能不全評估采用Marshall評分[5],當某器官評分≥2分時定義為該器官存在功能不全。本組患者均無手術及病死。排除標準:(1)資料不完整的患者;(2)非病情原因自動出院患者。
二、研究方法
記錄患者的性別、年齡、腹部癥狀持續時間、生命體征以及實驗室檢查結果,以CT表現評估胰腺局部并發癥和有無胸膜滲出,24 h內應用BISAP評分系統和APACHEⅡ評分系統進行評分。APACHEⅡ評分由急性生理學評分、年齡評分、慢性健康狀況評分組成,最后得分為三者之和。理論最高分為71分,分值越高提示病情越重。本研究將≥8分患者歸為高分組,<8分為低分組。BISAP評分系統[2]包括尿素氮、意識障礙、SIRS、年齡和胸膜滲出5項內容。BISAP≥3分的AP患者有發展成SAP及發生并發癥的高風險性[6]。本研究將≥3分患者歸為高分組,<3分為低分組。
三、統計學處理
結 果
一、一般情況
185例AP患者中男性92例(49.7%),女性93例(50.3%)。病因:膽源性157例(84.9%),酒精性13例(7%),高脂血癥性7例(3.78%),暴飲暴食5例(2.7%),特發性3例(1.62%)。MAP 101例,MSAP 76例,SAP 8例。MSAP中出現胰腺外臟器功能不全25例,其中肝功能不全19例次,呼吸功能不全22例次,腎功能不全5例次;SAP患者均同時并發肝、腎及呼吸功能不全。
二、BISAP及APACHEⅡ評分與AP嚴重程度的關系
MSAP+SAP組與MAP組的BISAP評分分別為(1.43±0.89)、(0.38±0.61)分,MSAP+SAP組顯著高于MAP組,差異有統計學意義(H=6.31,P<0.01);APACHEⅡ評分分別為(2.45±1.36)、(0.87±0.62)分,差異也有統計學意義(H=7.48,P<0.01)。
三、高分組和低分組的MSAP+SAP發生率
BISAP低分組137例中MSAP+SAP患者47例(34.3%);高分組48例中MSAP+SAP患者37例(77.0%)。高分組MSAP+SAP發生率顯著高于低分組,差異有統計學意義(χ2=15.14,P<0.01)。
APACHEⅡ低分組153例中MSAP+SAP患者56例(36.6%);高分組32例中MSAP+SAP患者28例(87.5%)。高分組MSAP+SAP發生率顯著高于低分組,差異有統計學意義(χ2=28.73,P<0.01)。
四、BISAP及APACHEⅡ評分預測AP嚴重程度及臟器功能不全的比較
BISAP、APACHEⅡ評分預測AP病情嚴重程度的AUC分別為0.804(95%CI0.738~0.870)、0.794(95%CI0.725~0.863);預測臟器功能不全的AUC分別為0.758(95%CI0.686~0.830)、0.781(95%CI0.710~0.852)(圖1)。兩種評分系統間的差異無統計學意義。
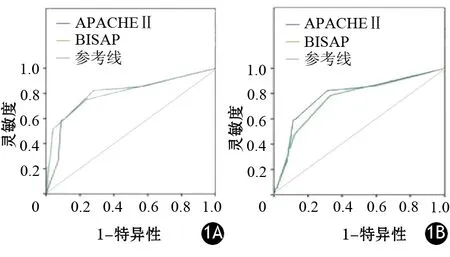
圖1 兩種評分系統預測AP嚴重程度(1A)及臟器功能不全(1B)的ROC曲線
討 論
理想的評分系統應該具有簡便、在疾病的早期能對病情嚴重程度進行評估以及能夠對病情的整個過程進行監測,并且可反復進行等特點。
APACHEⅡ的監測指標有12項,能早期對AP的嚴重程度和預后做出預測,在臨床治療中有一定的指導意義。該評分系統可在患者入院時及入院后任何時間進行病情嚴重程度的反復評估。但指標比較繁瑣,需要搜集大量的數據,計算復雜。
BISAP評分系統是于2008年出現的一種新的評分系統,經大規模的研究證實,其對AP住院患者的病死率有很好的預測價值。它僅由5項指標組成,源于體格檢查、生命體征、實驗室檢查及影像學檢查,包含了Glasgow昏迷指標及全身炎癥反應綜合征評分,所需收集的資料在臨床實踐中簡單易得,與傳統評分標準相比更注重機體對損傷的免疫應答及年齡因素[6],且入院24 h即可評分,可更早地評估病情。
本研究結果顯示,BISAP評分系統及APACHEⅡ評分系統對AP嚴重程度及臟器功能不全的預測能力相似,與Shabbir等[8]的研究結果一致。因BISAP評分的參數易于獲得,計算簡單,可以早期預測SAP,更應在臨床推廣應用。
[1] 曹均強,湯禮軍.急性胰腺炎治療方式的研究進展[J].中華消化外科雜志,2014,13(11):913-918.
[2] Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Revision of the Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis (3rd revision). 2008.
[3] 鄒金艷,林軍,易三鳳,等.BISAP、Ranson′s、APACHE Ⅱ和CTSI評分系統在急性胰腺炎評估中的價值[J].中華消化外科雜志,2014,13(1):39-43.
[4] 中華醫學會消化學分會胰腺疾病學分組.中國急性胰腺炎診治指南(2013年,上海).中華胰腺病雜志,2013,13(2);73-76.
[5] Baddeley RNB, Skipworth JRA, Pereira SP. Acute pancreatitis. Medicine, 2011, 39: 108-115.
[6] Papachristou GI, Muddana V, Yadav D, et al. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson′s, APACHEⅡ, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol, 2010, 105(2): 435-441.
[7] Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology, 1982, 143:29-36.
[8] Shabbir S, Jamal S, Khaliq T, et al. Comparison of BISAP Score with Ranson′s Score in Determining the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015, 25(5): 328-331.
(本文編輯:呂芳萍)
·讀者·作者·編者·
本刊可直接用縮寫的常用詞匯
作者對下列一些常用詞匯可直接用縮寫,即在論文中第一次出現時,可以不標注中文
ADP 腺苷二磷酸
AEP 急性水腫性胰腺炎
AFP 甲胎蛋白
Alb 白蛋白
ALP 堿性磷酸酶
ALT 丙氨酸氨基轉移酶
AMP 腺苷一磷酸
ANP 急性壞死性胰腺炎
AP 急性胰腺炎
ARDS 急性呼吸窘迫綜合征
AST 天冬氨酸氨基轉移酶
ATP 腺苷三磷酸
BP 血壓
BUN 血尿素氮
BSA 牛血清蛋白
CCK 縮膽囊素
CCK-8 細胞增殖-毒性檢驗
CEA 癌胚抗原
CP 慢性胰腺炎
CT X線計算機斷層攝影術
CRP C-反應蛋白
DAB 二氨基聯苯胺
DAPI 4,6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚二鹽酸
DBil 直接膽紅素
DC 樹突狀細胞
DMSO 二甲基亞砜
EGF 表皮生長因子
ELISA 酶聯免疫吸附測定
ENBD 內鏡鼻膽管引流
ERCP 內鏡下逆行胰膽管造影
EST 內鏡下乳頭括約肌切開術
EUS 內鏡超聲
EUS-FNA EUS引導下細針穿刺活檢
EUS-FNI EUS引導下細針注射
FITC 異硫氰酸熒光素
γ-GT γ-谷氨酰轉移酶
Hb 血紅蛋白
HE 蘇木素-伊紅
HRP 辣根過氧化物酶
IBil 間接膽紅素
IFN 干擾素
IL 白細胞介素
iRNA RNA干擾
LDH 乳酸脫氫酶
MAP 輕癥急性胰腺炎
MRCP 磁共振膽胰管造影
MRI 磁共振成像
MODS 多器官功能不全綜合征
MOF 多器官功能衰竭
MPO 髓過氧化物酶
MSCs 骨髓間充質干細胞
MTT 四甲基偶氮唑藍
NF-κB 核因子-κB
NK 自然殺傷細胞
NO 一氧化氮
PaCO2動脈血二氧化碳分壓
PaO2動脈血氧分壓
PBS 磷酸鹽緩沖液
PD 胰十二指腸切除術
PDAC 胰腺導管腺癌
PET 正電子發射計算機斷層掃描
PLT 血小板
PPPD 保留幽門的胰十二指腸切除術
PSC 胰腺星狀細胞
RBC 紅細胞
RT-PCR 逆轉錄-聚合酶鏈反應
SAP 重癥急性胰腺炎
shRNA 小發夾RNA
siRNA 小干擾RNA
SIRS 全身炎癥反應綜合征
TBil 總膽紅素
TC 總膽固醇
TG 三酰甘油
TGF 轉化生長因子
TNF 腫瘤壞死因子
TP 總蛋白
WBC 白細胞
VEGF 血管內皮生長因子
BISAP and APACHEⅡ scores in predicting the severity and organ failure of patients with acute pancreatitis
GaoNan,LiRui,DingYixin,ShenJiaqing,XiaoKuntin,ChenWeichang.DepartmentofGastroenterology,FirstAffiliatedHospitalofSoochowUniversity,Suzhou215006,China
Correspondingauthor:LiRui,Email: 13771725877@163.com
Objective To evaluate the clinical value of bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis (BISAP) and APACHEⅡ score in predicting the severity and organ failure of acute pancreatitis (AP). Methods One hundred eighty-five patients of AP admitted to Department of Gastroenterology of First affiliated Hospital of Soochow University from January 2012 to December 2014 were studied retrospectively. According to BISAP score, patients who were ≥3 points were considered as high risk group, while <3 points were considered as low risk group. According to APACHEⅡ score, patients who were ≥8 points were considered as high risk group, while <8 points were considered as low risk group. According to the criteria of Pancreatic Diseases Group of Chinese Society of Gastroenterology of Chinese Medical Association, the patients were diagnosed as mild acute pancreatitis (MAP), moderately severe acute pancreatitis (MSAP), and severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). The BISAP, APACHEⅡ scores were calculated and compared between MAP group and MSAP+SAP group, respectively. The incidence of MSAP+SAP between high risk group and low risk group was also compared. The area of ROC curve (AUC)was used to evaluate the ability of BISAP and APACHEⅡ scoring system for predicting the severity of AP and the multiple organ dysfunction syndromes (MODS). Results Among 185 patients, MAP was identified in 101 patients, MSAP in 76 patients and SAP in 8 patients. Twenty-five MSAP patients developed organ dysfunction, and all the 8 SAP patients developed organ dysfunction. The BISAP scores of MSAP+SAP group and MAP group were (1.43±0.89), (0.38±0.61), and APACHⅡ scores were (2.45±1.36), (0.87±0.62), the scores of MSAP+SAP group were significantly higher than those in MAP group (P<0.01). In the 137 patients of low risk BISAP group, there were 47 MSAP+SAP patients (34.3%), while in the 48 patients of high risk BISAP group, there were 37 MSAP+SAP patients (77.0%); in the 153 patients of low risk APACHEⅡ group, there were 56 MSAP+SAP patients (36.6%), while in the 32 patients of high risk APACHEⅡ group,there were 28 MSAP+SAP patients (87.5%); the incidence of MSAP+SAP patients was significantly higher in high risk group than that in low risk group (P<0.01). The AUC of BISAP, APACHEⅡ for MSAP+MAP was 0.804 (95%CI0.738~0.870), 0.794(95%CI0.725~0.863), and the AUC for organ dysfunction was 0.758 (95%CI0.686~0.830), 0.781 (95%CI0.710~0.852), and the difference between BISAP and APACHEⅡ was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Conclusions The BISAP has the prediction ability for AP severity and prognosis similar to APACHEⅡ, and it consists of only 5 parameters and can be completed in the first 24 h of admission, therefore it is worth of clinical application.
Pancreatitis; Severity of illness index; BISAP score; APACHⅡ score; Prognosis
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2015.06.009
215006 江蘇蘇州,蘇州大學附屬第一醫院消化內科
李銳,Email: 13771725877@163.com
2015-04-20)

