番茄穴盤苗組織-N閾值的初步研究
梁 歡, 尚慶茂
(農業部園藝作物生物學與種質創制重點實驗室,中國農業科學院蔬菜花卉研究所,北京 100081)
梁 歡, 尚慶茂*
(農業部園藝作物生物學與種質創制重點實驗室,中國農業科學院蔬菜花卉研究所,北京 100081)


多孔一體式穴盤育苗具有節能、省力、適合機械化操作、生產效率高等顯著特點,是我國蔬菜集約化育苗的主要形式。與傳統營養缽育苗相比,穴盤育苗采用的人工混配輕型基質,通氣孔隙度增大,單株基質容量減小,管理不當極易導致幼苗礦質養分盈虧,實時準確判斷蔬菜穴盤苗養分狀況對壯苗育成至關重要。目前,蔬菜礦質營養診斷方法主要分為培養介質(包括土壤和人工混配基質)分析法和組織分析法[1-2],介質分析僅能反映根系可從介質獲得的潛在營養水平,分析結果常因取樣方法、貯存條件和養分提取技術而產生偏差。組織分析剔除了介質特性、環境因素對礦質養分吸收的影響,更能直接反映植株礦質營養狀況,研究與應用也更加廣泛。

1 材料與方法
1.1 試驗材料
共采集了番茄17個品種,‘中雜9號’(Zhongza 9)、‘中雜15號’(Zhongza 15)、‘中雜101號’(Zhongza 101)、‘中雜105號’(Zhongza 105)、‘中雜106號’(Zhongza 106)、‘中雜108號’(Zhongza 108)、‘中雜109號’(Zhongza 109)、‘美櫻2號’(Meiying 2)、‘北京櫻桃番茄’(Beijing cherry tomato)來自中國農業科學院蔬菜花卉研究所。‘佳紅4號’(Jiahong 9)、‘佳紅5號’(Jiahong 5)、‘佳粉18號’(Jiafen 18)、‘硬粉8號’(Yingfen 8)、‘仙客1號’(Xianke 1)、‘仙客5號’(Xianke 5)、‘京丹紅小果’(Jingdan red cherry tomato)、‘京丹黃小果’(Jingdan yellow cherry tomato)來自北京京研益農科技發展中心。

化學測定所用試劑均購自國藥集團化學試劑北京有限公司,AR級。
1.2 試驗設計
1.3 測定方法
每重復隨機選取番茄穴盤苗25株,將下胚軸、莖(子葉節至頂端生長點)、各葉位葉柄和葉片分別取樣,剪成1 cm小段(下胚軸、莖、葉柄)或1 cm×1 cm小塊(葉片),壓蒜器榨取汁液,收集至1.5 mL離心管,4℃冰箱保存備測。
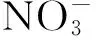
采用Microsoft Excel 2003和SAS 9.2進行統計分析。
2 結果與分析



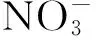
3 討論
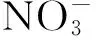
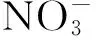
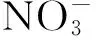
4 結論
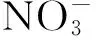

表4 番茄穴盤苗不同組織-N閾值
[1] Prado R D M, Caione G. Plant analysis[J]. Soil Fertility, 2012, 115-134.
[2] Hartz T K, Smith R F, LeStrange Metal. On-farm monitoring of soil and crop nitrogen status by nitrate-selective electrode[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1993, 24(19-20): 2607-2615.
[3] Peng S, García F V, Laza R Cetal. Adjustment for specific leaf weight improves chlorophyll meter's estimate of rice leaf nitrogen concentration[J]. Agronomy Journal, 1993, 85(5): 987-990.
[4] Gianquinto G, Sambo P, Borsato D. Determination of SPAD threshold values for the optimisation of nitrogen supply in processing tomato[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2004, 700: 159-166.
[5] Sandoval-Villa M, Wood C W, Guertal E A. Tomato leaf chlorophyll meter readings as affected by variety, nitrogen form, and nighttime nutrient solution strength[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2002, 25(10): 2129-2142.
[6] Fontes P C R, Araujo C. Use of a chlorophyll meter and plant visual aspect for nitrogen management in tomato fertigation[J]. Journal of Applied Horticulture, 2006, 8(1): 8-11.
[7] 張延麗, 田吉林, 翟丙年, 諸海濤. 不同施氮水平下黃瓜葉片 SPAD 值與硝態氮含量及硝酸還原酶活性的關系[J]. 西北農林科技大學學報(自然科學版), 2009, 37(1): 189-193. Zhang Y L, Tian J L, Zhai B N, Zhu H T. Relationship between leaf SPAD values and the nitrate content and nitrate reductase activity in cucumber at different nitrogen rates[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(1): 189-193.
[8] 范燕萍, 余讓才, 陳建勛,楊瑞陶. 氮素營養脅迫對匙葉天南星生長及光合特性的影響[J]. 園藝學報, 2000, 27(4): 297-299. Fan Y P, Yu R C, Chen J X, Yang R T. Effects of nitrogen nutrition stress on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of spathiphyllum palls hort[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2000, 27(4): 297-299.
[9] 毛罕平, 徐貴力, 李萍萍. 番茄缺素葉片的圖像特征提取和優化選擇研究[J]. 農業工程學報, 2003, 19(2): 133-136. Mao H P, Xu G L, Li P P. Extracting and selecting features of leaf images for diagnosis nutrient deficiency diseases in tomatoes[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2003, 19(2):133-136.
[10] 柴阿麗, 李寶聚, 王倩, 等. 基于計算機視覺技術的番茄葉片葉綠素含量的檢測[J].園藝學報, 2009, 36(1): 45-52. Chai A L, Li B J, Wang Qetal. Detecting chlorophyll content of tomato leaves with technology of computer vision[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2009, 36(1): 45-52.
[11] Leigh R A, Johnston A E. Nitrogen concentrations in field-grown spring barley: an examination of the usefulness of expressing concentrations on the basis of tissue water[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science, 1985, 105(2): 397-406.
[12] Huett D, Rose G. Diagnostic nitrogen concentrations for tomatoes grown in sand culture[J]. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 1988, 28(3): 401-409.
[13] Hochmuth G J. Efficiency ranges for nitrate-nitrogen and potassium for vegetable petiole sap quick tests[J]. Horttechnology, 1994, 4(3): 218-222.
[14] 張衛建, 黃丕生, 陸士龍. 單季中稻體內氮營養水平診斷研究[J]. 江蘇農業學報, 1996, 12(3): 15-19. Zhang W J, Huang P S, Lu S L. Studies on rapid determination of plant nitrogen status in single crop midseason rice[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Science, 1996, 12(3): 15-19.
[15] 李文才, 林振武, 湯玉瑋. 硝酸還原酶的研究-Ⅴ. 棉花硝酸還原酶活力與NO3-N含量的關系[J]. 作物學報, 1983, 9(2): 93-97. Li W C, Lin Z W, Tang Y W. Studies on nitrate reductase Ⅴ.Relation of nitrate reductase activity to nitrate content in cotton[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1983, 9(2): 93-97.
[16] Olsen J K, Lyons D J. Petiole sap nitrate is better than total nitrogen in dried leaf for indicating nitrogen status and yield responsiveness of capsicum in subtropical Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 1994, 34(6): 835-843.
[17] 周阮寶, 谷麗萍, 茆敦俊, 周嘉槐. 介紹兩種簡易測定硝態氮的比色方法[J]. 植物生理學通訊, 1991, 27(4): 299-301. Zhou R B, Gu L P, Mao D J, Zhou J H. Two simple colorimetric methods for NO3-N[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1991, 27(4): 299-301.
[18] 王西娜, 王朝輝, 陳寶明, 李生秀. 不同品種菠菜葉柄和葉片的硝態氮含量及其與植株生長的關系[J]. 植物營養與肥料學報, 2005, 11(5): 675-681. Wang X N, Wang C H, Chen B M, Li S X. Nitrate accumulation in petiole and blade of different spinach cultivars and its relation to plant growth[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(5): 675-681.
[19] 姚建武, 艾紹英, 柯玉詩, 等. 幾個菜心品種硝酸鹽累積差異的研究[J]. 土壤與環境, 2002, 11(3): 255-257. Yao J W, Ai S Y, Ke Y Setal. Differences of nitrate accumulation among some Chinese flowering cabbage varieties[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2002, 11(3): 255-257.
[20] 劉麗, 甘志軍, 王憲澤. 植物氮代謝硝酸還原酶水平調控機制的研究進展[J]. 西北植物學報, 2004, 24(7): 1355-1361. Liu L, Gan Z J, Wang X Z. Advances of studies on the regulation of nitrate metabolism of plants at nitrate reductase level[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2004, 24(7): 1355-1361.
[21] Farneselli M, Tei F, Simonne E. Reliability of petiole sap test for N nutritional status assessing in processing tomato[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2014, 37(2): 270-278.

[23] 柳勇, 何江華, 杜應瓊, 等. 施氮, 鉀和鉬對菠菜不同生長階段硝態氮積累影響研究初報[J]. 植物營養與肥料學報, 2005, 11(3): 363-368. Liu Y, He J H, Du Y Qetal. Effects of N, K and Mo application on the nitrate accumulation at different growth stages of spinach[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(3): 363-368.
[24] 周根娣, 盧善玲. 磷鉀肥、 光照、 貯藏加工對蔬菜硝酸鹽含量的影響[J]. 上海農業學報, 1991, 7(2): 53-56. Zhou G D, Lu S L. Effects of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, shining, storage and processing on nitrate content in vegetable[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 1991, 7(2): 53-56.
[25] 楊暹, 關佩聰. 氮鉀營養與花椰菜氮素代謝和產量的初步研究[J]. 華南農業大學學報, 1994, 15(1): 85-90. Yang X, Guan P C. The preliminaru study on the relationship between N K nutrition and nitrogen metabolism, curd yied in cauliflower(Brassicaoleraceavar.botrytisL.)[J]. Journal of South China Agriculture University, 1994, 15(1): 85-90.
[26] 齊炳林, 曹翠玲, 王菲, 等. 磷脅迫對豇豆幼苗硝酸還原酶活性和硝態氮含量的影響[J]. 干旱地區農業研究, 2010, 28(1): 147-151. Qi B L, Cao C L, Wang Fetal. Influence of low phosphorus on nitrate reductive activity and NO3-N content in cowpa seedling[J]. Agriculture Research in the Arid Areas, 2010, 28(1): 147-151.
[27] 馬光恕, 廉華, 王彥宏, 等. 磷素不同用量對萵苣硝酸鹽積累的影響[J]. 中國土壤與肥料, 2009,(4): 68-70. Ma G S, Lian H, Wang Y Hetal. Effects of different amount phosphorus elements on the nitrate accumulation of lettuce[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2009,(4): 68-70.
[28] Proietti S, Moscatello S, Leccese Aetal. The effect of growing spinach(SpinaciaoleraceaL.) at two light intensities on the amounts of oxalate, ascorbate and nitrate in their leaves[J]. Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 2004, 79(4): 606-609.
[29] Liu W K, Yang Q C. Effects of short-term treatment with various light intensities and hydroponic solutions on nitrate concentration of lettuce[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica(Section B-Soil and Plant Science), 2012, 62(2): 109-113.
[30] 許振柱, 周廣勝. 植物氮代謝及其環境調節研究進展[J]. 應用生態學報, 2004, 15(3): 511-516. Xu Z Z, Zhou G S. Research advance in nitrogen metabolism of plant and its environmental regulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(3): 511-516.

[32] Zhao C, Liang J, He Jetal. Effects of elevated temperature and nitrogen fertilization on nitrogen metabolism and nutrient status of two coniferous species[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2012, 58(6): 772-782.

LIANG Huan, SHANG Qing-mao*
(KeyLaboratoryofBiologyandGeneticImprovementofHorticulturalCrops,MinistryofAgriculture;InstituteofVegetablesandFlowers,ChineseAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Beijing100081,China)


2014-02-17 接受日期: 2014-10-16 網絡出版日期: 2015-02-04
國家自然科學基金項目(31172001); 現代農業產業技術體系建設專項資金(CARS-25); 公益性行業科研專項(201303014); 中國農業科學院科技創新工程(CAAS-ASTIP-IVFCAAS)資助。
梁歡(1990—),女,山西臨汾人,碩士研究生,主要從事蔬菜苗期發育調控方面的研究。E-mail:lianghuanconf@126.com * 通信作者 E-mail:shangqingmao@caas.cn
S625.5+4; S641.2
A
1008-505X(2015)03-0709-10

