EP/CE聯合與不聯合紫杉醇方案治療復合性小細胞肺癌的臨床價值*
周嬋 李月雅 楊等霞 王心悅 王晶 劉竹君 李凱
·臨床研究與應用·
EP/CE聯合與不聯合紫杉醇方案治療復合性小細胞肺癌的臨床價值*
周嬋 李月雅 楊等霞 王心悅 王晶 劉竹君 李凱
目的:通過觀察三藥(紫杉醇+順鉑/卡鉑+依托鉑苷)和雙藥方案(順鉑/卡鉑+依托鉑苷)一線治療復合性小細胞肺癌(combined small-cell lung CSCLC)的療效及不良反應,比較兩者的有效和安全性。方法:回顧性分析天津醫科大學腫瘤醫院2000年7月至2013年4月收治的62例經病理證實的復合性小細胞肺癌患者資料(19例接受三藥、43例接受雙藥治療),隨時評價不良反應,每2周期評價療效。結果:三藥與雙藥方案的有效率分別為90%和53%,差異有統計學意義(P=0.033),疾病控制率分別為100%和86%,差異無統計學意義(P=0.212)。兩組的中位無進展生存期(PFS)分別為10.5個月和8.9個月、中位生存時間(OS)分別為24.0個月和17.5個月,差異均無統計學意義(P=0.484;P=0.457)。三藥方案組中Ⅳ度骨髓抑制和因嚴重的不良反應終止原方案治療的發生率均高于雙藥方案組,差異有統計學意義(P=0.034;P=0.006)。結論:需慎用TEP/TCE等三藥方案治療CSCLC,順鉑/卡鉑+依托鉑苷暫時仍應為其一線治療標準方案。
復合性小細胞肺癌 化療 生存分析 不良反應
依2004年WHO肺及胸膜腫瘤的病理分類,復合性小細胞肺癌(combined small-cell lung cancer, CSCLC)被歸類為小細胞肺癌的一種亞型,即小細胞肺癌(small cell lung cancer,SCLC)中復合非小細胞肺
癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)成分的一類腫瘤,其復合成分通常為腺癌、鱗癌、大細胞神經內分泌癌、巨細胞癌和梭形細胞癌等[1],其中腺癌居多[2]。CSCLC僅約占SCLC的25%~30%[3-4],但其既對化療具抗拒性、又兼有SCLC生長快的特點,臨床治療中十分棘手,目前尚無標準化療,治療暫同于SCLC,但其預后常較單純SCLC差[5-6]。目前多將CSCLC抗拒標準化療的原因歸咎于其中的NSCLC成分。由于其中的絕大多數復合成分為腺癌,國內、外有在標準EP化療方案基礎上增加紫杉醇的完成[7],但能否較雙藥方案更優仍未達成共識。本文回顧分析了天津醫科大學腫瘤醫院2006年7月至2013年4月收治的62例經病理確診、隨訪資料完整的初治CSCLC,依所用化療分為三藥(紫杉醇+鉑類+依托鉑苷)和雙藥方案(鉑類+依托鉑苷)兩組,比較兩種方案的短期療效、生存獲益以及不良反應。
1 材料與方法
1.1一般資料
收集本院2000年7月至2013年4月臨床資料完整的62例CSCLC患者資料。入選標準:1)經病理學或細胞學證實的CSCLC患者;2)未接受過化療、放療和手術治療;3)未患過其他惡性腫瘤;4)具影像學上可測量的病灶;5)年齡18~80歲,治療前患者KPS評分≥60;6)治療前血、尿常規、電解質、肝腎功能、心電圖基本正常。其中男性49例,女性13例,男女比例為3.85:1;年齡34~79歲,中位年齡60歲;吸煙者51例;TNM分期Ⅰ期5例、Ⅱ期4例、Ⅲ期26例、Ⅳ期27例。比較兩組患者各項基線資料,差異均無統計學意義(表1)。
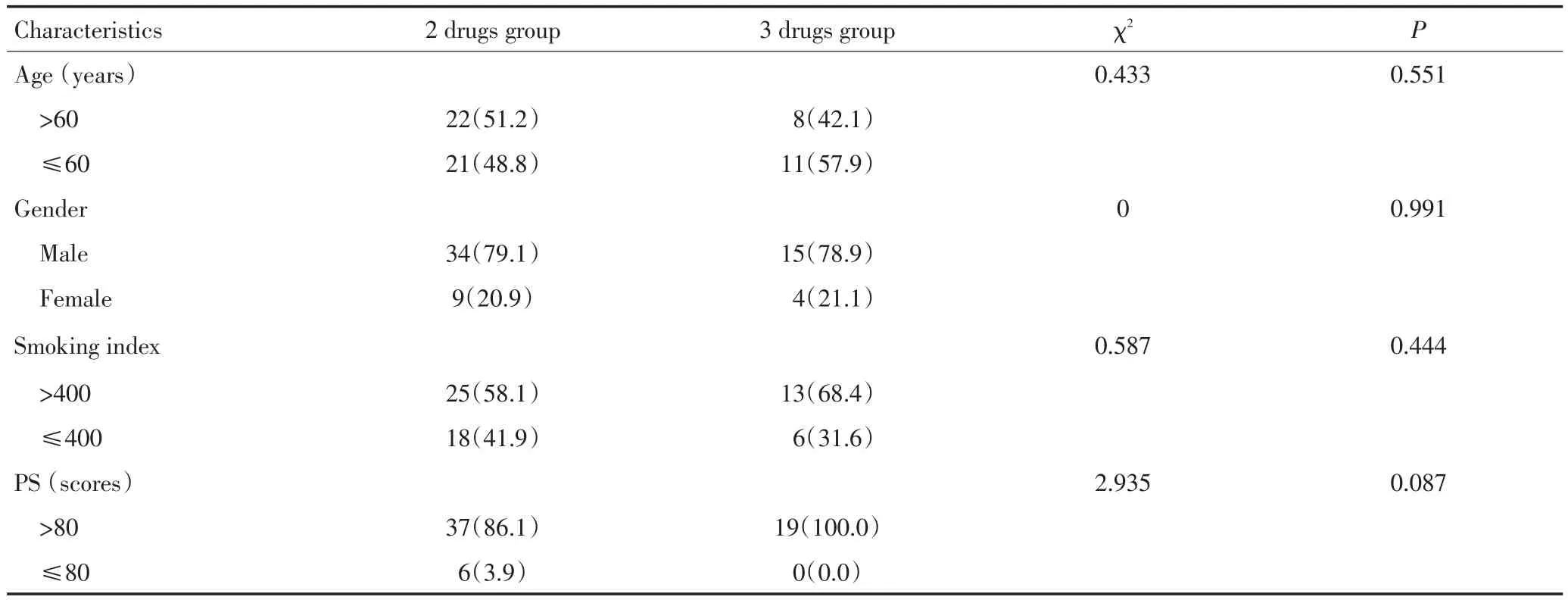
表162 例患者一般情況比較n(%)Table 1General condition of 62 lung cancer patients[n(%)]
1.2治療方法
Ⅰ~Ⅱ期和T1~3N2的Ⅲa期的15例患者行肺葉切除術+淋巴結清掃術、術后分別給予三藥方案或雙藥方案化療,其余患者行放、化療或單純化療。62例患者中,19例接受三藥方案,為紫杉醇135 mg/m2第1天,順鉑25 mg/m2靜脈滴注第1~3天或卡鉑AUC=5靜脈滴注第1天,依托泊苷100 mg/m2靜脈滴注第1~3天;43例接受雙藥方案,為順鉑25 mg/m2靜脈滴注第1~3天或卡鉑AUC=5靜脈滴注第1天,依托泊苷100 mg/m2靜脈滴注第1~3天。兩方案均以21天為1個周期、至少完成2個周期。部分患者在2~4周期化療間期給予胸部放療50 Gy/25次、化療結束后給予腦預防照射30 Gy/10次。
1.3評價療效
按照RECIST1.1版評價近期療效,分為完全緩解(complete response,CR)、部分緩解(partial response,PR)、疾病穩定(stable disease,SD)和疾病進展(progressive disease,PD);以CR+PR計算有效率(objective response rate,ORR)、CR+PR+SD計算疾病控制率(disease control rate,DCR)。無進展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)指患者開始用藥至疾病進展或死亡的時間,生存期(overall survival,OS)指化療開始至死亡或末次隨訪時間。不良反應參照WHO化療藥物急性與亞急性毒性表現及分度標準分為0~Ⅵ度評價。
1.4統計學方法
應用SPSS 13.0軟件進行統計學分析。計量資料用均數±標準差(±s)表示,組間比較采用兩樣本均數t檢驗;計數資料用率表示,組間比較采用χ2檢驗,PFS和OS采用Kaplan-Meier檢驗。α=0.05為顯著性檢驗水準,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
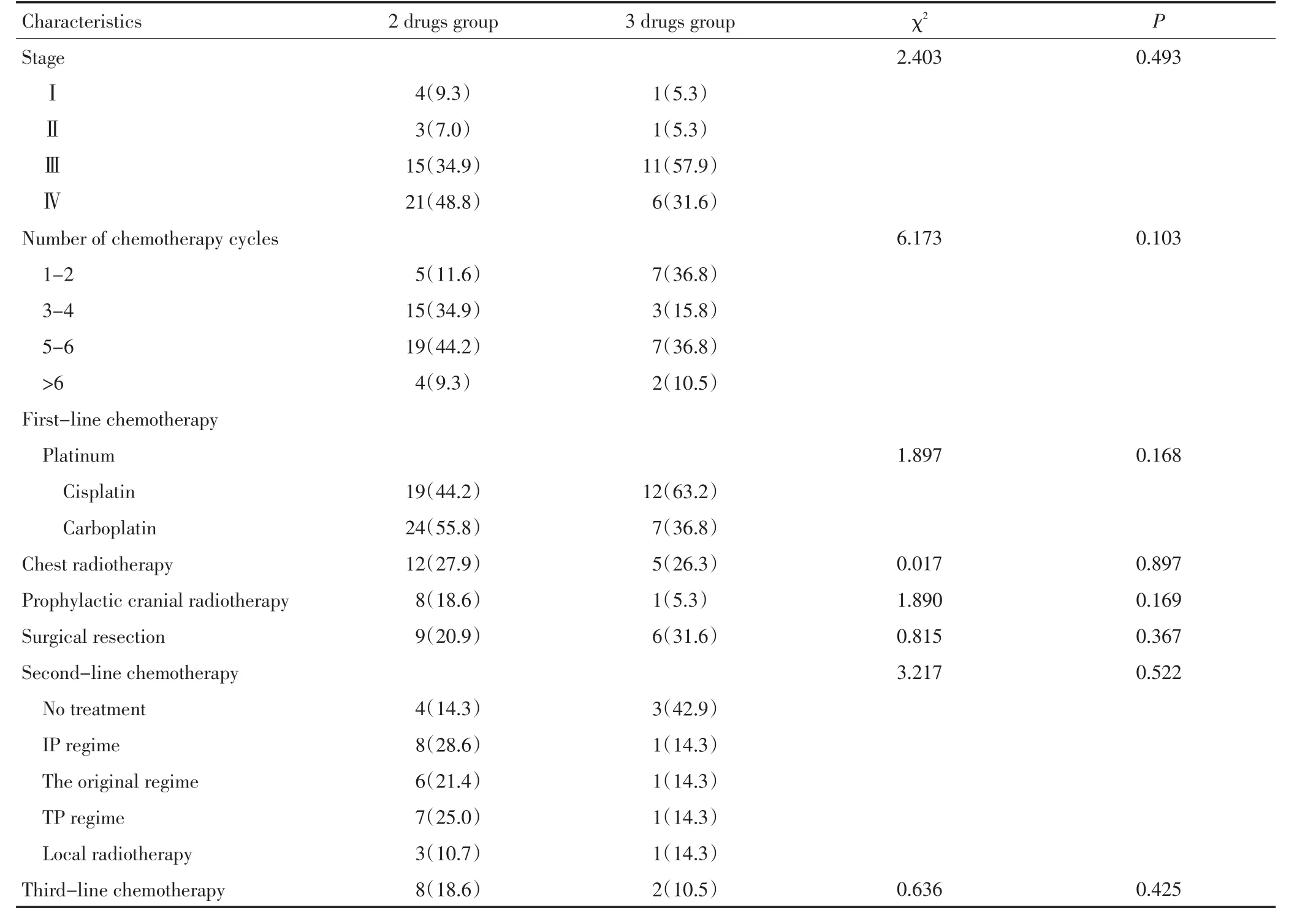
表162 例患者一般情況比較n(%)(續表1)Table 1General condition of 62 lung cancer patients[n(%)]
2 結果
2.1近期療效
所有病例的化療周期數均≥2,三藥和雙藥方案組的有效率差異有統計學意義(90%vs.53%,P= 0.033,χ2=4.552),疾病控制率差異無統計學意義(100%vs.86%,P=0.212,χ2=1.558)。到末次隨訪62例患者均隨訪到PFS和OS。三藥組中位PFS略長于雙藥組,差異無統計學意義(10.5 vs.9.8,P=0.484,χ2= 0.489,圖1);其中位OS也略長于雙藥組,差異亦無統計學意義(24.0 vs.17.5,P=0.457,χ2=0.554)(圖2)。Ⅲ~Ⅳ期的患者中三藥與雙藥方案組中位PFS的差異有統計學意義(19.5 vs.7.6,P=0.071,χ2=3.259,圖3)、中位OS差異無統計學意義(22.8 vs.14.3,P= 0.269,χ2=1.224,圖4)。
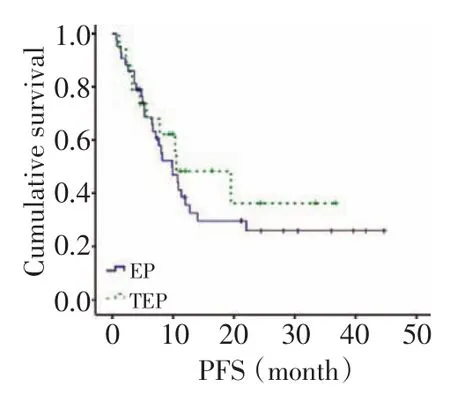
圖1 兩組患者的無進展生存Figure 1Progression-free survival(PFS)of patients in both groups
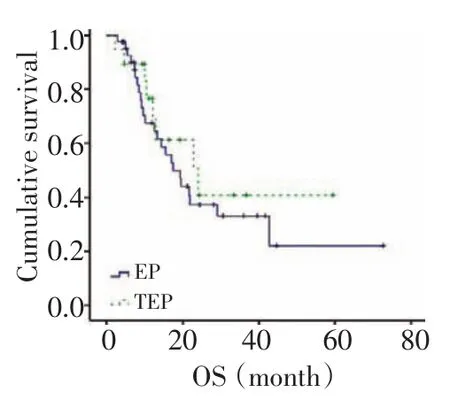
圖2 兩組患者的總生存Figure 2Overall survival(OS)of patients in both groups
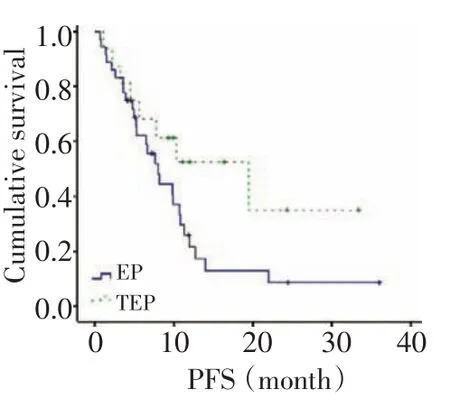
圖3 Ⅲ~Ⅳ期患者的無進展生存Figure 3PFS of patients with stagesⅢtoⅣ
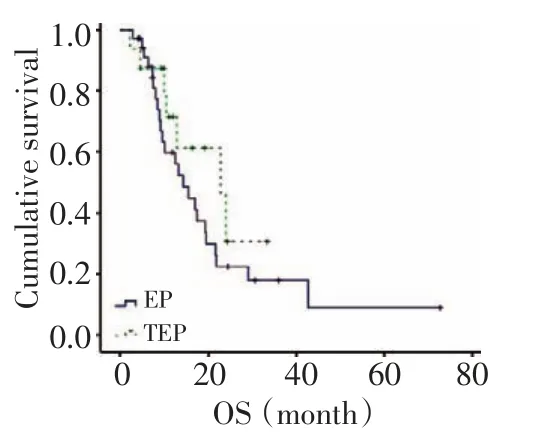
圖4 Ⅲ~Ⅳ期患者的總生存Figure 4OS of patients with stagesⅢtoⅣ
2.2預后因素分析
對表1中的各項行單因素分析,結果提示KPS評分>80分、確診時無淋巴結及遠處轉移、Ⅰ~Ⅱ期患者及接受手術治療、腦預防照射的患者生存時間較長。將上述因素輸入Cox比例回歸風險模型進行多因素分析,結果顯示確診時KPS評分、是否淋巴結或遠處轉移及是否行腦預防照射為影響預后的獨立因素(表2)。

表2 影響62例患者生存因素的Cox比例風險回歸分析Table 2Cox regression analysis of the factors affecting the survival rate of 62 patients
2.3安全性評價
毒性Ⅰ~Ⅱ度,為可逆性。三藥方案皮疹、腹瀉的發生率均高于雙藥方案,差異無統計學意義(10.5%vs.0%,P=0.09,χ2=4.677);其Ⅳ度骨髓抑制發生率高于雙藥方案組,差異有統計學意義(26.3%vs. 7.0%,P=0.036,χ2=4.385);三藥組患者因不良反應而中斷原方案化療的發生率高于雙藥組(31.6%vs. 4.7%,P=0.004,χ2=8.502),主要因不良反應而更換治療方案(31.6%vs.4.7%,P=0.004,χ2=8.502),而雙藥組主要因疾病進展更換化療方案(32.6%vs.5.3%,P= 0.021,χ2=5.353)。
3 討論
SCLC對化療敏感、一線化療常可奏效。但易耐藥復發、成為難治性腫瘤。其中CSCLC即對標準化療不敏感、預后差[5-6],常見于重度吸煙、男性、60歲以上者[2]。目前通常采用SCLC的標準EP方案,最常見改為三藥治,以抑制兩種成分。羅潔等[8]評估了NIP(長春瑞濱25 mg/m2第1、8天,異環磷酰胺1.2 mg/m2第1~3天,順鉑25 mg/m2第1~3天)與EP(依托泊苷100 mg/m2第1~3天,順鉑25 mg/m2第1~3天)方案一線治療復合性小細胞肺癌的療效和不良反應,發現其并不能取代EP方案。
由于CSCLC中最常見的復合成分為腺癌[2],人們又嘗試在標準治療方案中加入治療腺癌的有效藥物。由于紫杉醇治療腺癌等NSCLC的有效率達22%~47%[9-10],本院從2005年開始使用紫杉醇+鉑類+依托鉑苷三藥聯合化療,以求增加劑量強度及抗瘤譜覆蓋。本研究共收集了2 371例小細胞肺癌病例中62例隨訪資料完整的CSCLC(2.6%),發生率與既往報道相符。對比三藥和雙藥方案一線治療CSCLC的療效及不良反應顯示,兩者ORR分別為90%和53%差異有統計學意義,但DCR分別為100%和86%,差異無統計學意義。兩組的PFS分別為11.86和12.14個,OS分別為17.65和18.01個月,差異亦均無統計學意義。這提示三藥方案可取得較好的短期療效,卻未改善長期生存。多因素分析也顯示僅確診時的KPS評分、淋巴結和遠處轉移及腦預防照射為影響CSCLC預后的獨立因素;但亞組分析卻顯示,在Ⅲ~Ⅳ期的患者中雙藥與三藥方案組的PFS分別為10.95和8.20個月(P=0.071),OS分別為10.2和17.621個月(P=0.089),差異有統計學意義,提示三藥方案仍可能為分期較晚、腫瘤負荷較大者帶來臨床獲益。進一步分析發現,雙藥方案組因疾病進展更換化療方案的概率達30%、明顯高于三藥方案組(32.6%vs.5.3%,P=0.021),提示CSCLC對EP/CE雙
藥方案耐藥率較高,常因腫瘤進展而失敗。而三藥方案組因Ⅳ度骨髓抑制等嚴重不良反應而停止化療或更換方案的比例均高于雙藥方案組,差異具有統計學意義(P=0.004)。其不良反應與既往報道紫杉醇毒性一致,顯然與加入此藥有關,并因此導致了31.6%的患者無法耐受不良反應而終止原治療方案;15.8%的患者拒絕繼續化療,從而無法獲益,顯然也影響了PFS和OS。因此,在治療CSCLC時需謹慎使用TEP/TEC方案,合理選擇新添加的藥物及減少不良反應是三藥化療中亟待解決的問題。另外,紫杉類治療腺癌療效良好、對CSCLC中的腺癌成分是否具同等效力,研究發現CSCLC中的腺癌成分與小細胞癌細胞具有基因同源性[11-12],提示其可能不同于NSCLC中的腺癌,而具有更多SCLC的生物特性,甚至與SCLC細胞同源。目前利用深度測序的方法比較、分析CSCLC中腺癌成分與NSCLC中腺癌的基因表達差別,相信研究結果將對闡明CSCLC中兩種成分的聯系及針對基因變化篩選最佳化療藥物提供幫助。總之,TEP/TCE等三藥方案顯示了提高療效的潛力,但目前仍難取代順鉑/卡鉑+依托鉑苷等成為治療CSCLC的標準治療。
由于本研究只是一項回顧性研究,且樣本量較小,對于CSCLC的最佳化療方案尚需開展前瞻性的大樣本隨機對照試驗來進一步研究。
1Travis WD,Brambilla E,Muller-Hermelink HK,et al.Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Lung,Pleura,Thymus and Heart[M].Lyon:IARC Press.2004:31-34.
2Lu HY,Mao WM,Cheng QY,et al.Mutation status of epidermal growth factor receptor and clinical features of patients with combined small cell lung cancer who received surgical treatment[J].Oncology Letters,2012,3(6):1288-1292.
3Nicholson SA,Beasley MB,Brambilla E,et al.Small cell lung carcinoma(SCLC):a clinicopathologic study of 100 cases with surgical specimens[J].American Journal of Surgical Pathology,2002,26(9):1184-97.
4Wagner PL,Kitabayashi N,Chen YT,et al.Combined small cell lung carcinomas:genotypic and immunophenotypic analysis of the separate morphologic Components[J].American Journal of Clinical Pathology,2009,131(3):376-382.
5Wang XY,Jiang RC,LI K.Prognostic significance of pretreatment laboratory parameters in combined small-cell lung cancer[J].Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics,2014,69(3):633-640.
6Sehested M,Hirsch FR,Osterlind K,et al.Morphologic variations of small cell lung cancer.A histopathologic study of pretreatment and posttreatment specimens in 104 patients[J].Cancer,1986,57(4):804-807.
7Zhu YY,Ge W,Xu HL,et al.The effect of Paclitaxe combined with Cisplatin and Etoposide comparing with Cisplatin and Etoposide on patients with small cell lung cancer:a systematic review[J]. China Medical Herald,2014,11(13):62-66.
8Luo J,Li AW,Wu FY.Navelbine-ifosfamide-cisplatin versusetoposide-cisplatin as the first-line treatment of advanced combined small-cell lung cancer:retrospective analysis of 167 case[J].Tumor,2012,32(3):194-198.[羅潔,李愛武,吳鳳英,等.NIP與EP方案一線治療167例晚期復合性小細胞肺癌的回顧性分析[J].腫瘤,2012,32(3):194-198.]
9Zhang S,Zhang QC,Jiang SJ.Effect of trichostatin A and paclitaxel on the proliferation and apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Chinese Medical Journal,2013,126(1):129-134.
10 Rigsa JR.Taxane-platinum combinations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer:a review[J].Oncologist,2004,9(Suppl 2):16-23.
11 Wagner PL,KitabayashiN,Chen YT,et al.Combined small cell lung carcinomas:genotypic and immunophenotypic analysis of the separate morphologic components[J].American Journal of Clinical Pathology,2009,131(3):376-382.
12 Fukui T,Tsuta K,Furuta K,et al.Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status and clinicopathological features of combined small cell carcinoma with adenocarcino a of the lung[J].Cancer Science,2007,98(11):1714-1719.
(2014-10-07收稿)
(2014-11-06修回)
(編輯:楊紅欣)
Comparison of therapeutic efficacy of different chemotherapeutic regimens on combined small cell lung cancer
Chan ZHOU,Yueya LI,Dengxia YANG,Xinyue WANG,Jing WANG,Zhujun LIU,Kai LI
Kai LI;E-mail:likai5@medmail.com.cn
Objective:To compare the therapeutic and adverse effects of chemotherapeutic regimen based on three drugs(taxol+ carboplatin/cisplatin+etoposide)and two drugs(carboplatin/cisplatin+etoposide)on the combined small cell lung cancer(CSCLC). Methods:A retrospective study was conducted based on the data of 62 CSCLC patients who were admitted to and treated at Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital between July 2000 and April 2013.Of the 62 patients,19 received the three-drug regimen and 43 received the two-drug regimen.All patients received at least two cycles of chemotherapy and completed follow-up procedures.For each patient,the therapeutic efficacy was evaluated every two cycles,and toxicity was evaluated every cycle.Results:The response rates between the three-drug and two-drug groups were statistically significant(90%vs.53%,P=0.033).However,no statistical differences were observed in the disease control rate between the two groups(100%vs.86%,P=0.212).The three-drug regimen could induce a better median progression-free survival compared with the two-drug regimen,but with no statistical significance(10.5% vs.9.8%,P=0.484).Similarly,no statistical differences were noted in the median overall survival between the three-drug and two-drug groups(24.0%vs.17.5%,P=0.457).The incidence rates of grade IV bone marrow depression and the termination of the original regimen owing to severe adverse reactions were both significantly higher in the three-drug group than in the two-drug group(26.3%vs. 7.0%,P=0.036;31.6%vs.14.7%,P=0.004).Conclusion:The two-drug regimen had almost the same survival rate and lower toxicity compared with the three-drug regimen.When using the TEP/TCE regimen,a close attention should be focused on its adverse reactions. The findings of this work showed that the two-agent regimen should be one of the standard treatments for CSCLC.
combined small-cell lung cancer,chemotherapy,survival analysis,adverse reactions

10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.20141670
天津醫科大學腫瘤醫院肺部腫瘤內科,國家腫瘤臨床醫學研究中心,天津市腫瘤防治重點實驗室,天津市肺癌診治中心(天津市300060)
*本文課題受國家自然科學基金項目(編號:81372517)及天津市科委面上課題(編號:11JCYBJC11300)資助
李凱likai5@medmail.com.cn
Medical Department of Pulmonary Neoplasms,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin Lung Cancer Center,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Tianjin 300060,China
This work was supported by grants from the General Program of Tianjin Science and Technology Commission(No.:11JCYBJC11300)and the Natural Science Foundation of China(No.:81372517)
周嬋專業方向為肺部腫瘤的綜合治療與基礎研究。
E-mail:wifytal@sina.com

