顱內外血管狹窄程度與頸內動脈系統短暫性腦缺血發作的相關性分析
劉 瑞
?
顱內外血管狹窄程度與頸內動脈系統短暫性腦缺血發作的相關性分析
劉 瑞
【摘要】目的 探討顱內外血管狹窄程度與頸內動脈系統短暫性腦缺血發作次數與持續時間的關系。方法 對130 例頸內動脈TIA患者的全腦血管造影(DSA)進行分析,觀察TIA患者的發作與頸內動脈顱內外段血管有無狹窄及狹窄程度的關系。結果 130例中有血管狹窄94 例(占72.3%)。頸內動脈顱外段狹窄 32例(占34.1%),顱內段狹窄16 例(占17.0%),大腦中動脈狹窄38 例(占40.4%),大腦前動脈狹窄8例(占8.5%)。其中頻發TIA 44例,有血管狹窄35例,其中輕中度血管狹窄10例,重度狹窄血管25例。非頻發組血管狹窄的有59例,其中輕中度血管狹窄38例,重度狹窄21例,兩組患者比較說明TIA發生次數與血管狹窄程度有關。TIA發作持續時間<10 min的58例患者中無血管狹窄15例,輕中度狹窄19例,重度狹窄24例;發作持續時間為10~59 min的65例患者中無血管狹窄17例,輕中度狹窄27例,重度狹窄21例;≥60 min的7例患者中無血管狹窄4例,輕中度狹窄3例,重度狹窄0例。數據表明癥狀持續時間與血管狹窄的程度無相關性。結論 頸內動脈TIA大多存在血管狹窄,TIA發作次數與血管狹窄程度有相關性,而發作持續時間與血管狹窄程度差異無統計學意義。
【關鍵詞】短暫性腦缺血發作;血管狹窄程度;全腦血管造影
Objective To study intracranial vascular stenosis degree and internal carotid artery system transient ischemic attack frequency and duration of the relationship. Methods 130 cases of patients with internal carotid artery TIA cerebral angiography(DSA)were analyzed,and observation of patients with TIA attacks and the relationship between internal carotid artery stenosis and the degree of stenosi. Results In 130 patients with 94 cases of vascular stenosis (72.3%). 32 cases of extracranial internal carotid artery stenosis (34.1%),16 cases of intracranial internal carotid artery stenosis (17.0%),38 cases of middle cerebral artery stenosis(40.4%),8 cases of cerebral artery stenosis before(8.5%). Recurrent TIA of 44 cases,35 cases of vascular stenosis,including 10 patients with mild-to-moderate vascular stenosis,25 cases of severe stenosis vessels. Don't frequent set of vascular stenosis in 59 cases,38 patients with mild-to-moderate vascular stenosis,21 cases of severe stenosis,two groups of patients with vascular stenosis degree was statistically significant. Patients with TIA onset duration<10 minutes of 58 cases,15 cases without vascular stenosis,19 patients with mildto-moderate stenosis,24 cases of severe stenosis. Onset duration of 10 to 59 minutes of 65 cases,17 cases without vascular stenosis,27 patients with mild-to-moderate narrow,21 cases of severe stenosis. Onset duration 60 minutes of 7 cases,4 cases of vascular stenosis,3 cases of mild-to-moderate narrow,0 cases of severe stenosis. TIA onset duration and vascular stenosis degree has no statistical significance. Conclusion There is a correlation between the frequency of TIA attack and the degree of vascular stenosis,and the duration of attack is not related to the degree of vascular stenosis in the carotid artery TIA.
【Key words】 Transient ischemic attack,Degree of vascular stenosis,Total cerebral angiography
短暫性腦缺血發作(TIA)是神經內科急癥,可作為腦卒中的早期預警。有研究顯示[1]TIA后90 d內再發卒中的機率為10% ~15%,但王擁軍發表的一項9萬多人的全國調查顯示,國人對TIA的知曉率、規范診治率、有效控制率均較低。國內外研究[2]已有證實TIA與顱內外血管狹窄有關,血管狹窄程度與TIA發作頻率存在關系。本研究于 2010年8月~2015年6月對 130 例行DSA的TIA患者分析以探討顱內外血管狹窄程度與頸內動脈TIA的發作頻率及發作持續時間的關系。
1 對象與方法
1.1對象
選取鄭州人民醫院2010年8月~2015年6月行腦血管造影的TIA患者130 例,男 76 例,女54 例,年齡31~78歲,平均(62.3±8.0)歲。均符合第四屆腦血管病學術會議制定的診斷標準。其中24 h內發作次數≥2次為頻發TIA,共44例。合并高血壓 69 例 ,糖尿病21 例,冠心病 14 例,吸煙 35 例,高脂血癥28 例。
1.2方法
研究對象均行DSA檢查,并由鄭州人民醫院介入醫學科專科大夫進行檢查讀片,觀察顱內外大血管有無狹窄,狹窄程度的計算采用北美癥狀性頸動脈外科實驗(NASCET)[1]。血管的確定:腦血管造影能解釋癥狀的血管有無病變,如能解釋發作時的癥狀即入研究組,不能解釋癥狀的排除。
1.3統計學方法
將所有數據輸入SPSS 18.0軟件進行分析,組間率的比較采χ2檢驗,以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1頸內動脈系統TIA患者的DSA
130例中有血管狹窄94 例(占72.31% )。頸內動脈顱外段狹窄 32例(占34.04%),顱內段狹窄16 例(占17.02%),大腦中動脈狹窄38例(占40.42%),大腦前動脈狹窄8例(占8.51%)。
2.2頻發TIA的DSA檢查結果
頻發TIA患者有44例,有血管狹窄的35例(占79.55%),其中輕中度血管狹窄10例(占28.57%),重度狹窄血管25例(占71.42%),血管閉塞的患者2例(占5.71%),無血管狹窄的患者9例(占20.45%)。
2.3兩組患者血管狹窄程度比較
頻發組有血管狹窄的為35例,輕中度血管狹窄10例,重度狹窄血管25例。非頻發組59例中輕中度血管狹窄38例,重度狹窄21例。血管狹窄程度比較,差異有統計學意義(χ2=11.289,P <0.05)見表1。
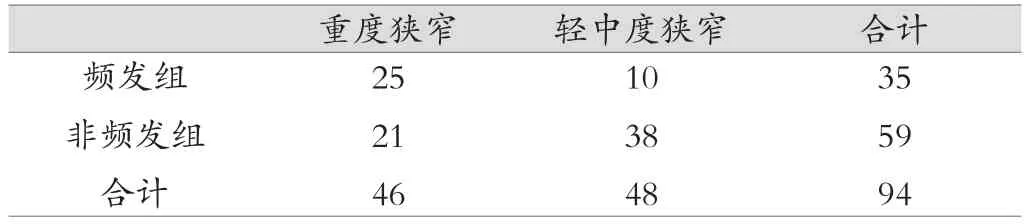
表1 兩組TIA患者血管狹窄程度比較
2.4TIA發作持續時間與血管狹窄程度關系
TIA發作持續時間<10 min的58例患者中無血管狹窄15例,輕中度狹窄19例,重度狹窄24例;發作持續時間為10~59 min的65例患者中無血管狹窄17例,輕中度狹窄27例,重度狹窄21例;≥60 min的7例患者中無血管狹窄4例,輕中度狹窄3例,重度狹窄0例。TIA發作持續時間與血管狹窄程度的比較,差異無統計學意義(χ2=6.287 P=0.179)見表2。
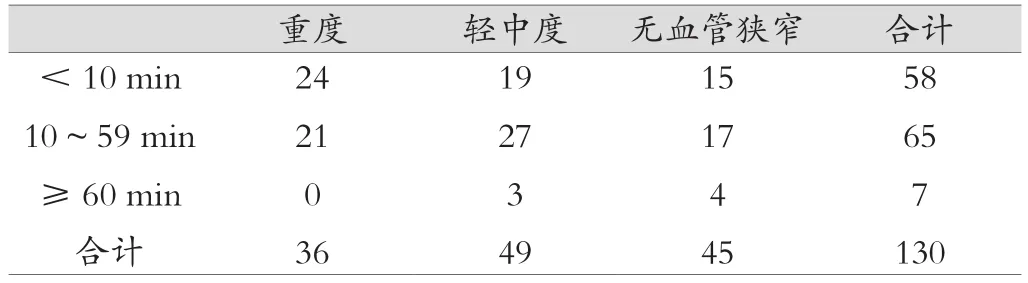
表2 癥狀持續時間與血管狹窄程度關系
3 討論
短暫性腦缺血發作(TIA)是腦、脊髓、視網膜的局灶性缺血引起的短暫性神經功能障礙,是比較常見的缺血性腦血管病。TIA的發病機制有很多假說,本研究中血管狹窄占72.3%,表明腦動脈狹窄可能是導致頸內TIA的重要發病原因[3]。動脈粥樣硬化是導致動脈狹窄的常見原因[4]。本研究表明頸內動脈血管狹窄65.39%為顱外段起始處,這與動脈分叉處血流動力學容易在外界因素影響下紊亂有關,極易形成微血栓,微栓子在流體力學選擇性壓力下進入下一級別的血管,如果病變區、交界區、遠端側枝循環尚可或微栓子數量少,沒有超過腦組織清除力,不會導致腦細胞壞死,臨床表現為一過性腦缺血發作,所以頸內動脈系統TIA可發現很多合并腦血管的狹窄,同時血管狹窄程度越重的情況下在外界誘因下如,低血壓、發熱、腹瀉等更容易發生[5]血流動力學改變,容易誘發TIA發作,容易形成腦梗死,因此本研究顯示重度血管狹窄下TIA發作次數較輕中度血管狹窄增加。另外即使狹窄血管無明顯內膜不穩定性,在血管重度狹窄的基礎下亦在外界因素影響下容易形成血流動力學改變,狹窄血管及其代償血管供血區的腦組織短暫性供血不足而缺血缺氧,引起臨床癥狀的發作,可以解釋重度血管狹窄下TIA發作次數較輕中度血管狹窄增加。
本研究示血管狹窄程度不會影響頸內動脈TIA發作持續時間,一方面可能為代償血管的側枝循環有個體差異,即使有些患者的血管局限性狹窄達到重度程度,但代償支的血管側枝循環豐富,可以很快代償,從而使臨床癥狀持續時間很短暫。另一方面可能為狹窄出內膜穩定性的差異,即使重度血管狹窄但形成的微栓子數量有限,容易被清除,因此臨床發作時間可以很短。總之,大多數頸內動脈系統短暫性腦缺血發作常伴有腦血管狹窄,血管狹窄程度不影響TIA的發作持續時間,影響TIA發作的次數,如不及時治療易引起腦梗死[6-8]。因此對于TIA應爭取及早明確血管狹窄并行個體化診療,減少腦卒中發生率。
參考文獻
[1]黃維,畢齊. 短暫性腦缺血發作新進展[J]. 中國卒中雜志,2014,9(10):874-879.
[2]王姝瑾,張維法,李青. 短暫性腦缺血發作與顱內外血管狹窄的相關性研究[J]. 中國綜合臨床,2015,14(3):236-238.
[3]朱曉波,張宏偉,李舟,等. 短暫性腦缺血發作與顱內外血管狹窄相關性分析[J]. 中國誤診學雜志,2011,11(4):825-826.
[4]蔣鋒,劉惠祥,高嶸,等. 頸動脈狹窄頸動脈內膜剝脫術32例分析[J]. 江蘇醫藥,2015,41(20):2476-2477.
[5]Person S,KappelleLJ,Klijn CJ. Limb-shaking transient ischemic attacks in patients with internal carotid artery occlusion:a case control study[J]. Brain,2010,133(Pt 3):915-922.
[6]Wever KE,Menting TP,Rovers Metal,et al. Ischemic preconditioning in the animal kidney,a systematic review and metaanalysis[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(2):e32296.
[7]Naraynan SV,Dave KR,Perez Pinzon. Ischemic preconditioning and clinical senarios[J]. Curr Opin Neurol,2013,26(1): 1-7.
[8]于永鵬,遲相林. 缺血性腦血管病發病機制的再認識[J]. 中華腦科疾病與康復雜志(電子版),2013,3(5):53-57.
【中圖分類號】R743.31
【文獻標識碼】A
【文章編號】1674-9316(2016)08-0045-02
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9316.2016.08.030
作者單位:鄭州人民醫院神經內科,河南 鄭州 450000
Correlation Analysis Between the Degree of Intracranial Vascular Stenosis and Transient Ischemic Attack of Internal Carotid Artery System
LIU Rui Neurology Department,People's Hospital of Zhengzhou,Zhengzhou He'nan 450000,China
【Abstract】

