人髓核細胞分離、傳代培養方法的建立及意義
李大鵬,吳燕,黃永輝,蔣璐,孫繼芾,岳佳偉
(1江蘇大學附屬醫院,江蘇鎮江212001;2江蘇大學)
·論著·
人髓核細胞分離、傳代培養方法的建立及意義
李大鵬1,吳燕2,黃永輝1,蔣璐2,孫繼芾1,岳佳偉1
(1江蘇大學附屬醫院,江蘇鎮江212001;2江蘇大學)
目的建立一種體外分離、培養人髓核細胞(NPCs)的新方法,并探討其意義。方法采用0.2% Ⅱ型膠原酶消化法分離人正常NPCs,單層貼壁法進行傳代培養,倒置顯微鏡下觀察細胞形態。取第1、2、3代NPCs,采用CCK-8法檢測細胞增殖能力(以吸光度值表示),連續檢測12天。取第2代NPCs,采用免疫組化法檢測Ⅱ型膠原(Col-2)、細胞角蛋白18(KRT-18)、KRT-19、低氧誘導因子1α(HIF-1α)、葡萄糖轉運子1(GLUT-1)、Sox-9、聚集蛋白聚糖(ACAN)、CD24陽性表達率。結果分離的NPCs呈多角形或短梭形,類似于軟骨細胞;第4代以后,NPCs細胞突起延長,呈長梭形,生長緩慢,出現老化現象。NPCs生長曲線呈S形:1~2天細胞生長緩慢;3~7天細胞生長迅速,進入對數生長期;8天后進入平臺期,細胞增殖緩慢。連續培養12天,第1、2、3代NPCs相同時間點吸光度值比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。第2代NPCs中Col-2、KRT-18、KRT-19、HIF-1α、GLUT-1、Sox-9、ACAN、CD24陽性表達率均≥85.6%(85.6%~91.2%)。結論單純0.2% Ⅱ型膠原酶消化法及單層貼壁法可分離、培養人NPCs,并經免疫組化染色鑒定證實;傳代3代以內的NPCs細胞形態及增殖能力均無明顯改變,可作為椎間盤退變相關研究的種子細胞。
髓核細胞;Ⅱ型膠原酶消化法;單層貼壁法;細胞培養;椎間盤退變
Abstract:ObjectiveTo establish a new method for isolation and culture of human nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) in vitro and to explore its significance.MethodsHuman normal NPCs were isolated by type Ⅱ collagenase digestion, then were cultured and expanded in monolayer. Cell morphology was observed by inverted microscope; the proliferation ability (expressed as absorbance value) of passage 1, passage 2 and passage 3 NPCs were detected by CCK-8 assay for consecutive 12 days; the positive expression rates of type Ⅱ collagen (Col-2), cytokeratin 18 (KRT-18), KRT-19, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α(HIF-1α), glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1), Sox-9, aggrecan (ACAN), and CD24 in passage 2 NPCs were detected by immunohistochemistry.ResultsThe isolate human NPCs were polygonal or short spindle, similar to chondrocytes. However, the nucleus pulposus cells after passage 4 grew slowly, the protrusion of cells extended, and the cells were long spindle shape, all of these indicated the cells were aging. The growth curve of NPCs was S-shaped, cells grew slowly in 1-2 days, then grew into the logarithmic growth phase in 3-7 days, and after 8 days the cells proliferated slowly and entered the plateau. After consecutive 12-day culture, the difference of absorbance values at 450 nm among passage 1, passage 2 and passage 3 NPCs was not statistically significant at the same time point (allP>0.05). Immunohistochemical staining showed: the positive rates of Col-2, KRT-18, KRT-19, GLUT-1, HIF-1α, Sox-9, ACAN, and CD24 in passage 2 NPCs were no less than 85.6% (85.6%-91.2%).ConclusionsHuman NPCs can be effectively isolated by 0.2% type Ⅱ collagenase digestion method, and can be cultured by monolayer adherence method. The cells we cultured were identified as nucleus pulposus cells by immunohistochemistry. There are no significant changes in the morphological and proliferation abilities of NPCs within 3 generations, and could be used as seed cells for study of intervertebral disc degeneration.
Keywords: nucleus pulposus cells; type Ⅱ collagenase digestion; monolayer adherence; cell culture; intervertebral disc degeneration
下腰痛的主要原因之一為椎間盤退變[1,2]。椎間盤在結構上由纖維環、軟骨終板及髓核三部分組成[3,4]。目前研究認為,椎間盤退變始于髓核,髓核細胞(NPCs)的過早老化與凋亡使其數量減少、功能降低,使得聚集蛋白聚糖(ACAN)、Ⅱ型膠原(Col-2)等功能性細胞外基質的合成與分泌減少[5],進而引起髓核水分含量降低并失去其凝膠狀態,最終導致椎間盤生物學功能減退與喪失。椎間盤退變的生物學治療方法包括基因治療、細胞因子、干細胞移植、組織工程等[6,7],可恢復NPCs的數量及功能,延緩甚至逆轉椎間盤退變。2016年7~10月,本研究建立一種體外分離、培養人NPCs的新方法,并對其生物學特性進行鑒定,以期為椎間盤退變病因、機制及治療的相關基礎研究提供穩定的細胞來源。
1 材料與方法
1.1 材料 主要試劑:髓核細胞培養基(NPCM,美國Sciencell公司),Col-2(美國Gibco公司),胎牛血清(美國Sciencell公司),青霉素-鏈霉素(美國Sciencell公司),CCK-8試劑盒(上海翊圣生物科技有限公司),Col-2、細胞角蛋白18(KRT-18)抗體、KRT-19抗體、低氧誘導因子1α(HIF-1α)抗體(武漢博士德生物工程有限公司),鼠抗人葡萄糖轉運子1(GLUT-1)抗體、鼠抗人Sox-9抗體、鼠抗人CD24抗體、鼠抗人ACAN抗體(美國Santa Cruz公司),SABC-POD(小鼠/兔IgG)免疫組化試劑盒(武漢博士德生物工程有限公司)。主要儀器:細胞培養超凈臺(蘇州凈化設備有限公司),二氧化碳培養箱(美國Thermo公司),顯微鏡(德國Zeiss公司)。
1.2 人NPCs的分離及傳代培養 選擇1例因L2椎體爆裂骨折行L1/2髓核切除術及椎間融合術的患者(男性,20歲),術中根據Gries評分標準[8]未見椎間盤退變。將切取的髓核組織置于超凈臺上,PBS反復沖洗至組織無血污,去除纖維環組織,并將髓核組織剪碎至1 mm3大小的組織塊。加入不含胎牛血清的NPCM,1 500 r/min離心5 min,棄上清。加入0.2% Ⅱ型膠原酶10 mL,37 ℃恒溫震蕩消化4 h,1 500 r/min離心5 min,棄上清。加入含2%胎牛血清的NPCM 5 mL重懸細胞,以1×105個/mL接種至培養瓶中。37 ℃、5% CO2、飽和濕度條件下靜置培養3天,加入NPCM 5 mL;培養7天時第1次換液,待細胞融合至90%時進行傳代培養。本研究通過江蘇大學附屬醫院醫學倫理委員會審核,并與患者簽訂知情同意書。
1.3 NPCs生長情況觀察 ①貼壁情況及細胞形態:觀察細胞傳代培養后的貼壁情況,200倍倒置顯微鏡下觀察細胞形態。②細胞增殖能力:采用CCK-8法。取第1、2、3代生長狀態良好的NPCs,消化收集細胞,以1×104~2×104個/mL接種至96孔板,每孔100 μL。每天固定時間加入CCK-8溶液,每孔10 μL,孵育4 h后采用酶標儀檢測450 nm波長處的吸光度值,以吸光度值表示細胞增殖能力。實驗重復3次,連續檢測12天。
1.4 NPCs鑒定 采用免疫組化法。取第2代NPCs,加入胰蛋白酶消化,以1×105個/mL接種于24孔板, 每孔250 μL,細胞貼壁并融合至70%左右,給予4%多聚甲醛固定30 min。30% H2O2+純甲醇(1∶50混合)室溫浸泡30 min,蒸餾水沖洗2次;加入5% BSA封閉液,室溫條件下孵育20 min,甩去多余液體;滴加抗Col-2一抗,4 ℃過夜,PBS沖洗2 min×3次;滴加生物素化山羊抗小鼠(或兔)IgG,20~37 ℃條件下孵育20 min,PBS沖洗2 min×3次;滴加SABC試劑,37 ℃條件下孵育20 min,PBS沖洗5 min×4次;DAB顯色,蒸餾水洗滌。200倍顯微鏡下觀察染色情況及陽性表達位置,以細胞質或者細胞核染出現棕黃色視為陽性表達。每孔隨機選取3個視野,陽性表達率=陽性細胞數/總細胞數×100%,取平均值。參照上述方法分別檢測并計算細胞KRT-18、KRT-19、GLUT-1、HIF-1α、Sox-9、ACAN、CD24陽性表達率。
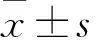
2 結果
2.1 NPCs生長情況 原代NPCs貼壁緩慢,培養4~5天開始有細胞貼壁,14天左右基本鋪滿瓶底;細胞形態呈多角形或短梭形,類似于軟骨細胞。傳代后細胞貼壁較快,12 h內即可貼壁生長,細胞生長迅速,仍呈短梭形;第4代以后,NPCs細胞突起延長,呈長梭形,生長緩慢,出現老化現象。
2.2 NPCs增殖能力 NPCs生長曲線呈S形:1~2天細胞生長緩慢;3~7天細胞生長迅速,進入對數生長期;8天后細胞增殖緩慢,進入平臺期。連續培養12天,第1、2、3代NPCs相同時間點吸光度值比較差異均無統計學意義(P均>0.05)。見表1。
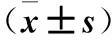
表1 第1、2、3代NPCs連續培養1~12天的吸光度值
2.3 NPCs免疫組化鑒定結果 NPCs中Col-2、KRT-18、KRT-19、GLUT-1、HIF-1α、Sox-9、ACAN、CD24陽性表達率分別為87.7%、88.1%、89.1%、85.6%、91.2%、90.1%、89.8%、87.0%。Col-2、KRT-18、KRT-19、GLUT-1、ACAN、CD24主要表達于NPCs的細胞質,HIF-1α主要表達于NPCs的細胞核,Sox-9在NPCs的細胞質和細胞核均有表達。見插頁Ⅰ圖1。
3 討論
目前NPCs分離培養應用最多的為酶消化法,酶消化法又可分為酶序貫消化法和單純Ⅱ型膠原酶消化法。前者先采用胰蛋白酶消化20~30 min,再予Ⅱ型膠原酶消化數小時,能分離出較多的細胞,但酶的聯合應用可加重細胞損傷,并增加污染概率。而單純Ⅱ型膠原酶消化法相對簡單實用,對細胞影響小,但各研究采用酶的濃度(0.025%~2%)及酶作用的時間不盡相同[9~11]。本研究選用Ⅱ型膠原酶的濃度為0.2%,消化時間為4 h,結果顯示獲取的NPCs貼壁較快,生長狀態良好。
NPCs的培養方法可分為三維培養法和單層貼壁培養法[12,13]。三維培養法利用藻酸鹽等材料構建三維空間,NPCs在三維空間內通過材料的孔隙通道獲取外界營養,該方法有利于NPCs維持軟骨樣細胞表型[14],但細胞增殖緩慢、不易觀察細胞形態等缺點限制了該方法的研究應用范圍。單層貼壁法培養的細胞增殖速度快,可在短期內獲得足量NPCs。本研究第1、2、3代的NPCs生長曲線呈S形, 3~7天細胞生長迅速迅速,進入對數生長期,此時細胞活力最佳,實驗時應盡量選擇此時對數生長期的細胞;而培養8天后NPCs生長曲線進入平臺期,細胞停止增殖,此時需進行消化傳代,否則細胞會發生形態改變,甚至死亡。但隨著傳代數的增加,細胞易出現去分化現象[15]。本研究結果表明,第4代后的NPCs細胞突起延長,呈長梭形,生長緩慢,出現老化現象,提示以NPCs為研究對象的相關研究應盡量選取第3代以內的細胞。
NPCs無特異性的細胞表面標識,其鑒定目前尚無統一標準[16,17]。首先,NPCs可表達軟骨細胞表型,如Col-2、ACAN、Sox-9,在正常NPCs表達均呈陽性。有研究認為,NPCs中ACAN/Col-2比值遠遠大于軟骨細胞,提示NPCs高表達ACAN[18]。其次,NPCs表達脊索細胞表型,如T基因、KRT-18、KRT-19、配對盒基因1等[19,20],這些基因高表達提示NPCs來源于胚胎發育過程中脊索細胞在椎間盤內的殘留。再次,NPCs可高表達環境相關性基因,如HIF-1α、GLUT-1、碳酸酐酶12、血管內皮細胞生長因子等。纖維環、軟骨終板、髓核均可表達HIF-1β,但僅有髓核表達HIF-1α[21]。另外,GLUT-1、碳酸酐酶12、血管內皮細胞生長因子受HIF-1α調控,三者在NPCs內高表達,但在纖維環及軟骨終板內不表達或低表達[22]。最后,NPCs高表達CD24、CD44、CD90等表面標識物[23],其中CD24被認為是NPCs特異性的表面標識物[24,25]。本研究免疫組化染色結果顯示,NPCs中Col-2、KRT-18、KRT-19、GLUT-1、HIF-1α、Sox-9、ACAN、CD24的陽性表達率均呈高表達(85.6%~91.2%),證明本研究分離、培養的細胞為NPCs。
綜上所述,單純0.2% Ⅱ型膠原酶消化法及單層貼壁法可分離、培養人NPCs;傳代3代以內的NPCs細胞形態及增殖能力均無明顯改變,可作為椎間盤退變相關研究的種子細胞。
[1] Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimaki J, et al. Does lumbar disc degeneration on magnetic resonance imaging associate with low back symptom severity in young finnish adults[J]. Spine, 2011,36(25):2180-2189.
[2] Feng C, Liu H, Yang M, et al. Disc cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration: causes and molecular pathways[J]. Cell Cycle, 2016,15(13):1674-1684.
[3] Le Maitre CL, Binch AL, Thorpe AA, et al. Degeneration of the intervertebral disc with new approaches for treating low back pain[J]. J Neurosurg Sci, 2015,59(1):47-61.
[4] Rim DC. Quantitative pfirrmann disc degeneration grading system to overcome the limitation of Pfirrmann disc degeneration grade[J]. Korean J Spine, 2016,13(1):1-8.
[5] Horner HA, Urban JP. 2001 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies: effect of nutrient supply on the viability of cells from the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc[J]. Spine, 2001,26(23):2543-2549.
[6] Zeckser J, Wolff M, Tucker J, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cell treatment for discogenic low back pain and disc degeneration[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2016(2016):3908389-3908401.
[7] Vasiliadis ES, Pneumaticos SG, Evangelopoulos DS, et al. Biologic treatment of mild and moderate intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Mol Med, 2014,20(1):400-409.
[8] Paesold G, Nerlich AG, Boos N. Biological treatment strategies for disc degeneration: potentials and shortcomings[J]. Eur Spine J, 2007,16(4):447-468.
[9] Wang F, Wu XT, Zhuang SY, et al. Ex vivo observation of human nucleus pulposus chondrocytes isolated from degenerated intervertebral discs[J]. Asian Spine J, 2011,5(2):73-81.
[10] Wang YY, Zhu QS, Wang YW, et al. Thymosin beta-4 recombinant adeno-associated virus enhances human nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and reduces cell apoptosis and senescence[J]. Chin Med J, 2015,128(11):1529-1535.
[11] Li ZY, Xiong SH, Hu M, et al. Knockdown epithelial membrane protein 1 suppresses human degenerative intervertebral disc-derived nucleus pulposus cell proliferation[J]. Cartilage, 2011,2(3):300-306.
[12] Gruber HE, Hanley EN Jr. Human disc cells in monolayer vs 3D culture: cell shape, division and matrix formation[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2000(1):1-5.
[13] Cheng CC, Uchiyama Y, Hiyama A, et al. PI3K/AKT regulates aggrecan gene expression by modulating Sox9 expression and activity in nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2009,221(3):668-676.
[14] Kluba T, Niemeyer T, Gaissmaier C, et al. Human anulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc: effect of degeneration and culture system on cell phenotype[J]. Spine, 2005,30(24):2743-2748.
[15] Mern DS, Thome C. Identification and characterization of human nucleus pulposus cell specific serotypes of adeno-associated virus for gene therapeutic approaches of intervertebral disc disorders[J]. BMC Muscul Dis, 2015(16):341-352.
[16] Risbud MV, Schoepflin ZR, Mwale F, et al. Defining the phenotype of young healthy nucleus pulposus cells: recommendations of the Spine Research Interest Group at the 2014 annual ORS meeting[J]. J Orthop Res, 2015,33(3):283-293.
[17] Rodrigues-Pinto R, Richardson SM, Hoyland JA. Identification of novel nucleus pulposus markers: interspecies variations and implications for cell-based therapiesfor intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2013,2(8):169-178.
[18] Clouet J, Grimandi G, Pot-Vaucel M, et al. Identification of phenotypic discriminating markers for intervertebral disc cells and articular chondrocytes[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2009,48(11):1447-1450.
[19] Minogue BM, Richardson SM, Zeef LA, et al. Characterization of the human nucleus pulposus cell phenotype and evaluation of novel marker gene expression to define adult stem cell differentiation[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010,62(12):3695-3705.
[20] Risbud MV, Schaer TP, Shapiro IM. Toward an understanding of the role of notochordal cells in the adult intervertebral disc: from discord to accord[J]. Dev Dyn, 2010,239(8):2141-2148.
[21] Rajpurohit R, Risbud MV, Ducheyne P, et al. Phenotypic characteristics of the nucleus pulposus: expression of hypoxia inducing factor-1, glucose transporter-1 and MMP-2[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2002,308(3):401-407.
[22] Richardson SM, Knowles R, Tyler J, et al. Expression of glucose transporters GLUT-1, GLUT-3, GLUT-9 and HIF-1alpha in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2008,129(4):503-511.
[23] Risbud MV, Guttapalli A, Tsai TT, et al. Evidence for skeletal progenitor cells in the degenerate human intervertebral disc[J]. Spine, 2007,32(23):2537-2544.
[24] Navone SE, Marfia G, Canzi L, et al. Expression of neural and neurotrophic markers in nucleus pulposus cells isolated from degenerated intervertebral disc[J]. J Orthop Res, 2012,30(9):1470-1477.
[25] Sakai D, Nakamura Y, Nakai T, et al. Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc[J]. Nat Commun, 2012(3):1264-1273.
Establishment and significance of separation and culture of human nucleus pulposus cells
LIDapeng1,WUYan,HUANGYonghui,JIANGLu,SUNJifu,YUEJiawei
(1AffiliatedHospitalofJiangsuUniversity,Zhenjiang212001,China)
國家自然科學基金資助項目(81601931);江蘇省自然科學基金資助項目(BK20150475)。
李大鵬(1981-),男,副主任醫師,研究方向為椎間盤退變的理論與治療。E-mail: lidapeng706@163.com
黃永輝(1966-),男,副教授,研究方向為椎間盤退變的理論與治療。E-mail: huangyh8855@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2017.32.001
R681.5
A
1002-266X(2017)32-0001-04
2016-11-12)

