PRPS2對肺癌細胞體外生長、增殖和體內成瘤的影響及其機制
顧鴻莉,宋衛峰,王靜玨,蔡訊,李琦
(上海交通大學附屬第一人民醫院,上海200080)
PRPS2對肺癌細胞體外生長、增殖和體內成瘤的影響及其機制
顧鴻莉,宋衛峰,王靜玨,蔡訊,李琦
(上海交通大學附屬第一人民醫院,上海200080)
目的探討磷酸核糖焦磷酸合成酶2(PRPS2)對肺癌細胞體外生長、增殖和體內成瘤的影響及其機制。方法將體外培養的肺癌A549細胞隨機分為對照組、Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組,分別感染scramble序列慢病毒及能夠沉默PRPS2基因表達的慢病毒Lenti-sh1、Lenti-sh2,作用時間均為12 h,結果顯示Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組PRPS2 mRNA及蛋白表達均低于對照組(P均<0.05),說明慢病毒可抑制A549細胞PRPS2基因表達,該分組及處理方法可用于以下研究。采用克隆形成實驗檢測三組細胞形成的克隆數量,CCK-8法檢測細胞增殖能力(吸光度值),流式細胞術檢測細胞周期,RT-PCR法及Western blotting法檢測Wnt信號通路中的關鍵基因β-連環蛋白(β-catenin)、APC、糖原合成酶激酶3β(Gsk-3β)mRNA和蛋白表達。將18只裸鼠隨機分成3組,分別接種對照組、Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞,每組6只;接種6周時剝離瘤體稱重,并測量體積。結果Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞形成的克隆數量均少于對照組(P均<0.05);培養72、96 h時,Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞吸光度值均低于同時間點對照組(P均<0.05)。Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組G0/G1期細胞比例均高于對照組,S期、G2/M期細胞比例均低于對照組(P均<0.05)。Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組Wnt信號通路中的關鍵基因β-catenin、APC mRNA和蛋白相對表達量均低于對照組,Gsk-3β mRNA和蛋白相對表達量均高于對照組(P均<0.05)。接種對照組細胞的裸鼠瘤體質量及體積均大于接種Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞的裸鼠(P均<0.05)。結論沉默PRPS2基因可抑制肺癌細胞的體外生長、增殖,減弱體內成瘤能力;調控Wnt信號通路可能是其作用機制。
肺癌;磷酸核糖焦磷酸合成酶2;細胞增殖;細胞周期;體外成瘤能力
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the role of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 2 (PRPS2) in lung cancer cell proliferation, tumor growth in vitro, and tumorigenic ability in vivo.MethodsLung cancer A549 cells cultured in vitro were divided into 3 groups: the control group (scramble control shRNA lentivirus infecting cells for 12 h), Lenti-sh1 group (lentivirus Lenti-sh1 infecting cells for 12 h) and Lenti-sh2 group (lentivirus Lenti-sh2 infecting cells for 12 h). These results indicated that the mRNA and protein expression levels of PRPS2 were effectively reduced in the control group as compared with that of the other two groups (bothP<0.05). These results indicated that the expression levels of PRPS2 were reduced by PRPS2 shRNA lentivirus in A549 lung cancer cells. Colony formation assay was used to detect the clone number of three groups. The cell proliferation rate was evaluated by a CCK8 assay and cell cycle was detected by flow cytometry. RT-PCR and Western blotting were used to detect the mRNA and protein expression levels of APC, β-catenin, Gsk3β in A549 cells of WNT signaling pathway. Tumors were generated by subcutaneously injecting lung cancer A549 cells from the control, Lenti-sh1 and Lenti-sh2 groups into the right forelimb axillaries of Balb/c nude mice (each group contained 6 mice). The mice were sacrificed at the 6th week to evaluate the weight and volume of tumors.ResultsCompared with the control group, the number of cell colonies in the Lenti-sh1and Lenti-sh2 groups were reduced (P<0.05). The absorbance value of the Lenti-sh1and Lenti-sh2 groups at 72 and 96h was lower than that of the control group (P<0.05). A significantly higher percentage of cells accumulated in the G0/G1phase of the cell cycle in the Lenti-sh1and Lenti-sh2 groups as compared with that of the control group. However, the percentage of cells in the S and G2/M phase was lower than that of the control group (allP<0.05). The mRNA and protein levels of APC and β-catenin in the Lenti-sh1and Lenti-sh2 groups were lower than that of the control group but the mRNA and protein levels of Gsk-3β were higher than that of the control group (allP<0.05). The tumor weight and volumes of the the Lenti-sh1and Lenti-sh2 groups decreased significantly as compared with those of the control group (bothP<0.05).ConclusionSilencing PRPS2 gene may suppress lung cancer growth, proliferation in vitro, and tumorigenic ability in vivo by regulating the WNT signaling pathway.
Keywords: lung carcinoma; phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 2; cell proliferation; cell cycle; tumorigenic ability in vitro
肺癌是呼吸系統常見惡性腫瘤,發生機制尚未明確。磷酸核糖焦磷酸合成酶(PRPS)是核苷酸合成過程的關鍵酶,由PRPS基因家族編碼[1]。PRPS2基因作為髓細胞增生原癌基因(c-myc)的作用靶點,其表達水平隨c-myc表達降低而下降。c-myc基因表達下調可誘導多種細胞凋亡[2],參與腫瘤的發生、發展,提示PRPS2可能與腫瘤細胞的增殖及凋亡有關。2015年9月~2016年4月,本研究觀察了PRPS2對肺癌細胞增殖和腫瘤生長的調控作用,現分析結果并探討其機制。
1 材料
肺癌細胞株A549(下稱A549細胞)購自中科院上海細胞庫。18只BALB/c裸鼠購自上海SLAC實驗動物公司,5周齡,平均體質量15 g。Bradford蛋白濃度檢測試劑盒、CCK-8試劑盒購自上海碧云天生物科技有限公司。Annexin V-FITC/PI細胞周期檢測試劑盒購自凱杰生物工程有限公司。PRPS2-shRNA慢病毒載體購自上海吉凱基因科技有限公司。
2 方法與結果
2.1 體外實驗
2.1.1 細胞培養及分組處理 將A549細胞培養于含有10% FBS、100 U/mL鏈霉素、100 U/mL青霉素的RPMI 1640培養基,取對數生長期細胞隨機分為對照組、Lenti-sh1組及Lenti-sh2組。對照組感染表達scramble序列的慢病毒,Lenti-sh1組感染能夠沉默PRPS2基因表達的慢病毒Lenti-sh1,Lenti-sh2組感染能夠沉默PRPS2基因表達的慢病毒Lenti-sh2,作用時間均為12 h。
2.1.2 細胞PRPS2表達檢測 ① PRPS2 mRNA表達檢測:采用RT-PCR法。取各組細胞逆轉錄為cDNA。PCR體系為50 μL,包括25 μL MasterMix、上下游引物各0.5 μL、cDNA模板5 μL、去離子水19 μL。PCR條件:95 ℃、15 s,60 ℃、30 s,共40個循環。引物序列由上海生工生物工程股份有限公司合成。以酶標儀檢測PRPS2 mRNA擴增產物電泳條帶的吸光度(A)值,以GAPDH為內參,計算目的基因相對表達量。②PRPS2蛋白表達檢測:采用Western blotting法。取三組細胞,采用RIPA細胞裂解液冰上裂解30 min,加入相應比例蛋白上樣緩沖液,沸水浴10 min;分別取30 μg蛋白加預制膠,50 V恒壓下電泳;待樣本中溴酚藍跑至濃縮膠與分離膠分界線時,切換至120 V恒壓;溴酚藍跑至膠板底部時,400 mA恒流將蛋白樣本轉至PVDF膜上;加入PRPS2一抗,37 ℃孵育4 h;加入二抗孵育過夜;ECL液顯影,Quantity One 1-D分析軟件對蛋白質印跡條帶進行定量,計算目的蛋白相對表達量。結果顯示,對照組、Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組PRPS2 mRNA相對表達量分別為1.00±0.23、0.35±0.01、0.30±0.03,PRPS2蛋白相對表達量分別為1.00±0.01、0.64±0.04、0.52±0.02,Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組均低于對照組(P均<0.05);說明慢病毒可以抑制A549細胞PRPS2基因及蛋白表達。該分組及處理方法可用于以下研究。
2.1.3 細胞形成克隆數量檢測 采用克隆形成實驗。將三組細胞分別消化并制備單細胞懸液,顯微鏡下計數。以密度為500個/孔接種于6孔板,每2天換1次液。細胞培養9天時用移液器去除培養基并用PBS洗1遍,每孔中加入500 μL 4%多聚甲醛固定10 min;吸去多聚甲醛,PBS清洗1遍,每孔加入500 μL結晶紫染色液,常溫下染色5 min;吸去染色液, PBS清洗3遍,顯微鏡下觀察拍照,統計三組細胞形成的克隆數量。結果顯示,對照組、Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞形成的克隆數量分別為(144±19)、(57±14)、(64±21)個,Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組均少于對照組(P均<0.05)。
2.1.4 細胞增殖能力檢測 采用CCK-8法。將三組細胞分別制備成單細胞懸液,顯微鏡下計數。以密度為1×103個/孔接種于96孔板,分別在培養0、12、24、48、72、96 h時加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,繼續培養1 h,在酶標儀上測定450 nm處A值。結果顯示,培養72、96 h時,Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞A值均低于對照組(P均<0.05)。見表1。
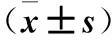
表1 三組各時間點細胞增殖能力比較
注:與對照組同時間點比較,*P<0.05。
2.1.5 細胞周期檢測 采用流式細胞術。將三組細胞分別制備成單細胞懸液,4 ℃下300 g離心5 min,收集細胞并用預冷的PBS洗滌細胞2次。分別用流式管收集1×104~5×104個細胞,加入100 μL 1×Binding Buffer重懸細胞成為單細胞懸液;分別加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC和5 μL PI Staining Solution,輕輕混勻,室溫避光反應10 min;分別加入400 μL 1×Binding Buffer,用移液器輕輕吹打、混勻,放置于冰上,1 h內采用流式細胞儀檢測細胞周期。結果顯示,Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組G0/G1期細胞比例均高于對照組,S期、G2/M期細胞比例均低于對照組(P均<0.05)。見表2。
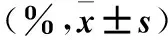
表2 三組細胞周期中各期細胞比例比較
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05。
2.1.6 APC、β-連環蛋白(β-catenin)、糖原合成酶激酶3β(Gsk-3β)mRNA和蛋白表達檢測 采用RT-PCR法、Western blotting法。具體方法參照2.1.2。結果顯示,Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組Wnt信號通路中的關鍵基因APC、β-catenin mRNA和蛋白相對表達量均低于對照組,Gsk-3β mRNA和蛋白相對表達量均高于對照組(P均<0.05)。見表3。
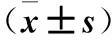
表3 三組APC、β-catenin、Gsk-3β mRNA和蛋白相對表達量比較
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05。
2.2 體內實驗 將2.1.1中三組細胞采用胰蛋白酶進行消化,調整細胞數量后重懸為單細胞懸液。將18只裸鼠隨機分成3組,每組6只;采用注射器在右前腋窩下分別注射對照組、Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞(體積為300 mL,數量為1×107個)。細胞接種6周時采用斷頸法處死荷瘤小鼠,用手術剪和鑷子剝離瘤體稱重并測量體積。結果顯示,接種對照組、Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞的裸鼠瘤體質量分別為(0.94±0.17)、(0.31±0.09)、(0.33±0.11)g,瘤體體積分別為(0.76±0.12)、(0.25±0.10)、(0.32±0.12)cm2,接種對照組細胞的裸鼠瘤體質量及體積均大于接種Lenti-sh1組、Lenti-sh2組細胞的裸鼠(P均<0.05)。
3 討論
腫瘤細胞的無限增殖依靠充足的蛋白質、糖類物質以及核酸的合成,代謝相關產物如核酸對腫瘤細胞的生長、增殖等發揮重要的調控作用[7,8]。核酸合成過程中的關鍵酶通過調節核酸的合成速度調控腫瘤細胞的生長、增殖。磷酸核糖焦磷酸(PRPP)合成的關鍵酶PRPS2是耦合蛋白質和核苷酸生物合成的限速酶之一,其在細胞內的濃度受到嚴格調控,生理狀態下其濃度一般較低,參與嘌呤核苷酸與嘧啶核苷酸的從頭合成和補救合成,以及某些核苷酸類輔酶如輔酶Ⅰ和輔酶Ⅱ,某些氨基酸如組氨酸和色氨酸的合成[9,10]。研究發現,PRPS2能促進癌基因c-myc轉錄,進而促進腫瘤細胞內的核苷酸合成[11]。PRPS2功能缺失延遲體內c-myc依賴的腫瘤細胞的啟動和維持,敲除PRPS2基因可抑制腫瘤進展[12]。5-磷酸核糖是嘌呤、嘧啶、吡啶核苷酸生成通路中的關鍵物質[4,5]。PRPS2在催化ATP和5-磷酸核糖合成PRPP的過程中發揮重要作用[13~15]。研究發現,PRPS2在結直腸癌、多形性膠質母細胞瘤、急性淋巴細胞白血病等癌組織及細胞中高表達[6],可促進腫瘤的發生、發展。但PRPS2與肺癌發生、發展的關系鮮見報道。
本研究首先以A549細胞為研究對象,采用慢病毒介導的RNA干擾技術沉默 PRPS2表達,結果顯示通過慢病毒Lenti-sh1、Lenti-sh2沉默PRPS2基因表達的肺癌細胞形成的克隆數量減少,增殖受到抑制,細胞周期明顯阻滯。進一步采用裸鼠成瘤實驗在體內驗證PRPS2對肺癌生長的調控作用,結果顯示沉默PRPS2表達的A549細胞成瘤能力明顯減弱。以上結果均說明,沉默PRPS2基因表達可抑制肺癌的發生及發展。Wnt信號通路在肺癌生長和轉移過程中發揮重要作用,但它的上游調節因子仍有待闡明。APC、β-catenin、GSK-3β是Wnt信號通路中的關鍵基因,共同介導細胞的增殖和凋亡過程[3]。本研究結果顯示,沉默PRPS2基因的肺癌細胞Gsk-3β mRNA和蛋白表達均增加,APC及β-catenin表達均降低;提示PRPS2可能通過調控Wnt信號通路而發揮作用。
綜上所述,沉默PRPS2基因可抑制肺癌細胞的體外生長、增殖,減弱體內成瘤能力;調控Wnt信號通路可能是其作用機制。
[1] Robusto M, Fang M, Asselta R, et al. The expanding spectrum of PRPS1-associated phenotypes: three novel mutations segregating with X-linked hearing loss and mild peripheral neuropathy[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2015,23(6):766-773.
[2] Annava S, Grachtchouk V, Wheeler LJ, et al. Direct role of nucleotide metabolism in C-MYC-dependent proliferation of melanoma cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2008,7(15):2392-2400.
[3] Kase S, Sugio K, Yamazaki K, et al. Expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in human non-small cell lung cancer and the clinical significance[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2000,6(12):4789-4796.
[4] Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, et al. The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells[J]. Cell, 2011,147(4):759-772.
[5] Iizasa T, Taira M, Shimada H, et al. Molecular cloning and sequencing of human cDNA for phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase subunit Ⅱ[J]. FEBS Letters, 1989,244(1):47-50.
[6] Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011,11(2):85-95.
[7] Green CD, Martin DW Jr. A direct, stimulating effect of cyclic GMP on purified phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase and its antagonism by cyclic AMP[J]. Cell, 1974,2(4):241-245.
[8] Ward PS, Thompson CB. Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate[J]. Cancer Cell, 2012, 21(3):297-308.
[9] Jimenez A, Santos MA, Revuelta JL. Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase activity affects growth and riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii[J]. BMC Biotechnol, 2008(8):67.
[10] Eriksen TA, Kadziola A, Bentsen AK, et al. Structural basis for the function of Bacillus subtilis phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthetase[J]. Nat Struct Biol, 2000,7(4):303-308.
[11] Tong X, Zhao F, Thompson CB. The molecular determinants of de novo nucleotide biosynthesis in cancer cells[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2009,19(1):32-37.
[12] Zhang F, Patel DM, Colavita K, et al. Arginylation regulates purine nucleotide biosynthesis by enhancing the activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthase[J]. Nat Commun, 2015(6):7517.
[13] Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG. 5-fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2003,3(5):330-338.
[14] Fridman A, Saha A, Chan A, et al. Cell cycle regulation of purine synthesis by phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate and inorganic phosphate[J]. Biochem J, 2013,454(1):91-99.
[15] Berger F, Ramirez-Hernandez MH, Ziegler M. The new life of a centenarian: signalling functions of NAD(P)[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2004,29(3):111-118.
Effects of PRPS2 on lung cancer cell proliferation, tumor growth in vitro,and tumorigenic ability in vivo
GUHongli,SONGWeifeng,WANGJingjue,CAIXun,LIQi
(ShanghaiGeneralHospitalofShanghaiJiaotongUniversitySchoolofMedicine,Shanghai200080,China)
上海市自然科學基金資助項目(15ZR1433600)。
顧鴻莉(1981-),女,主治醫師,研究方向為肺癌及胃腸道腫瘤的個體化綜合治療。E-mail: titaghl@sina.com
李琦(1974-),男,主任醫師,研究方向為惡性腫瘤多學科綜合治療。E-mail: leeqi2001@hotmail.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2017.32.006
R734.2
A
1002-266X(2017)32-0021-04
2017-04-22)

