硫酸鹽侵蝕下軸心受壓鋼筋混凝土柱應力時變過程的數值分析
王佳林,左曉寶,馬強,殷光吉,湯玉娟
(南京理工大學 土木工程系,南京 210094)

硫酸鹽侵蝕下軸心受壓鋼筋混凝土柱應力時變過程的數值分析
王佳林,左曉寶,馬強,殷光吉,湯玉娟
(南京理工大學 土木工程系,南京 210094)
針對荷載和硫酸鹽耦合作用過程中鋼筋混凝土柱的應力分析問題,在已有混凝土內硫酸根離子擴散反應模型的基礎上,進一步給出了硫酸鹽侵蝕引起的混凝土損傷程度與硫酸根離子濃度及腐蝕時間之間的關系,建立了與損傷程度相關的混凝土腐蝕本構模型及軸壓混凝土柱截面應力的計算方法,并通過數值模擬分析了柱截面內硫酸根離子傳輸、腐蝕損傷程度變化、截面應變和應力分布規律。結果表明:硫酸根離子濃度和混凝土損傷程度在柱截面內呈梯度分布,且受二維交互效應的影響明顯;隨腐蝕時間的增加,截面損傷區逐漸向內移動且其寬度增加,而混凝土應力在損傷區呈先增加后逐漸降低、在未損傷區基本呈線性增加的趨勢。硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,軸壓混凝土柱截面應力發生了明顯的重分布現象。
混凝土;硫酸鹽侵蝕;軸心受壓;損傷;應力重分布
長期處于濱海、地下水及鹽漬土等侵蝕環境下的混凝土結構不僅承受各種荷載作用,還遭受硫酸鹽等環境介質的物理化學侵蝕,導致混凝土結構的安全性和耐久性降低[1-2]。硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,環境中的硫酸根離子經擴散而進入混凝土內部,與水泥水化產物發生化學反應,導致混凝土腐蝕損傷[3],造成其彈性模量、強度等宏觀力學性能降低。由于滲入的硫酸根離子濃度在混凝土內呈梯度分布[4],其內部損傷程度和力學性能發生不均勻變化。因此,荷載作用下混凝土結構或構件在硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,其截面力學性能發生不同程度的損傷退化,造成截面應力在損傷區降低、非損傷區上升,從而形成應力重分布現象,這種應力重分布規律與硫酸鹽侵蝕混凝土的損傷退化過程密切相關。
硫酸鹽侵蝕下混凝土損傷退化過程涉及離子傳輸、微結構演變及宏觀性能劣化等方面。目前,基于多孔介質傳輸理論或Fick定律,建立了硫酸根離子在混凝土中傳輸的模型,獲得了硫酸根離子在混凝土中的擴散反應規律[5-6];利用XRD、ESEM、EDS等微觀測試方法,研究了硫酸鹽侵蝕下混凝土等水泥基材料中侵蝕產物的生長特點及其微結構演變規律,揭示了硫酸鹽侵蝕混凝土微結構損傷機理[7-8];通過混凝土試件在硫酸鹽溶液中的腐蝕試驗,開展了試件在不同腐蝕時間的力學性能測試,獲得了混凝土強度、動彈性模量和泊松比等宏觀力學性能參數隨硫酸鹽濃度、腐蝕時間的變化規律[9-11];此外,人們還開展了硫酸侵蝕后混凝土抗壓實驗研究,獲得了不同腐蝕時間及應變速率等條件下混凝土本構模型[12-14]。上述研究主要揭示了硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中混凝土的損傷劣化機理及其強度、剛度等宏觀力學性能的退化規律,但對荷載和硫酸鹽侵蝕耦合作用過程中混凝土結構構件截面應力重分布及其演變過程的相關研究涉及較少。
應力重分布問題是混凝土結構分析與設計所關注的重要問題之一[15],筆者以硫酸鹽環境下軸向受壓混凝土為研究對象,針對混凝土試件在硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中的截面應力重分布問題,建立硫酸根離子在混凝土內的傳輸模型、混凝土損傷程度與硫酸根離子濃度和腐蝕時間之間的關系、考慮損傷程度影響的硫酸鹽侵蝕混凝土腐蝕本構模型,在此基礎上,建立硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中軸心受壓混凝土試件截面應力重分布過程的計算方法。
1 模型
1.1 擴散反應方程
(1)

Dc=[φ+ω(c,t)]Dc0
(2)

對于擴散反應方程(1),其初始和邊界條件為
(3)

cs=φsc0
(4)

(5)
(6)
式中:kv為化學反應速率常數;cCa為混凝土孔溶液中鈣離子濃度。
1.2 腐蝕損傷程度
(7)

通過積分求解,式(7)變為
(8)

圖1 混凝土腐蝕損傷程度與濃度及腐蝕時間的關系Fig.1 Relationship of concrete damage degree with sulfate concentration and corrosion time
1.3 腐蝕本構模型

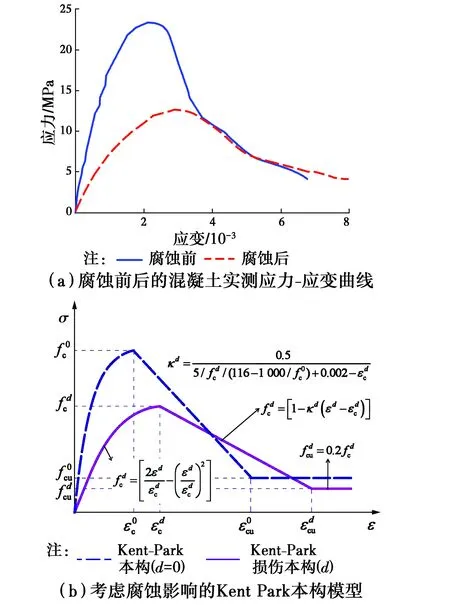
圖2 混凝土腐蝕損傷本構模型Fig.2 Damage constitutive model of theconcrete due to sulfate attac
(9)

(10)

(11)

(12)

(13)
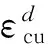
(14)
1.4 柱截面應力重分布

(15)
式中:N0為試件軸心受壓荷載;dx和dy分別為試件截面尺寸微分;Aur為縱向鋼筋截面面積;σs為縱向鋼筋應力,按鋼筋彈性強化本構模型確定[15]。
根據式(1)、式(6)、式(8)、式(9)和式(15),通過數值迭代法求解,可獲得硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中鋼筋混凝土柱截面應力分布隨損傷程度的變化規律。
2 數值求解
2.1 網格劃分


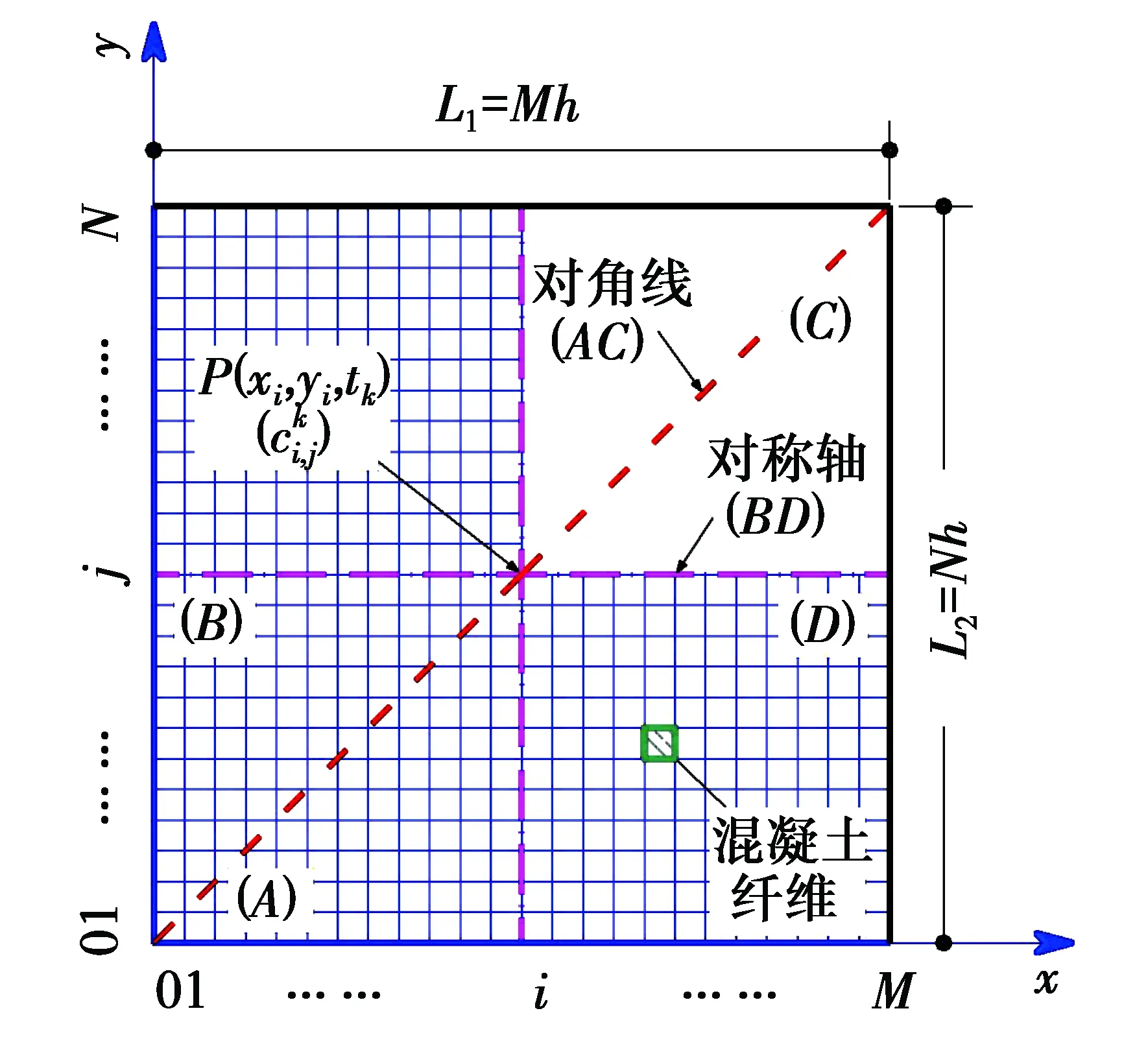
圖3 混凝土試件截面網格劃分Fig.3 Mesh of cross section of concrete specime
2.2 損傷程度計算
硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,混凝土損傷程度d(x,y,t)的計算式(8)是一個與硫酸根離子濃度相關的積分公式,需要按照圖3所示的網格劃分方法,進一步對式(8)進行數值離散。
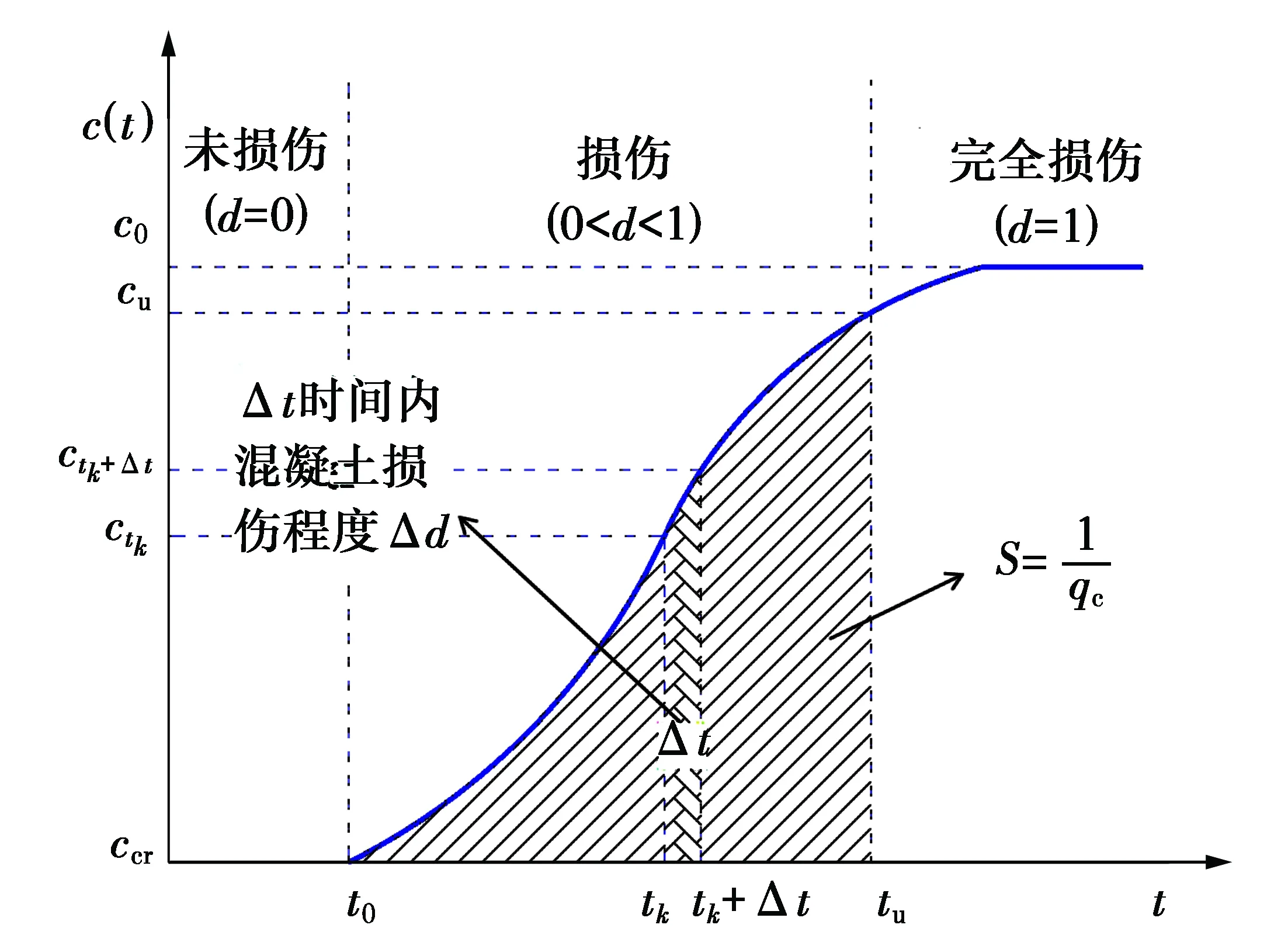
圖4 積分求解混凝土腐蝕損傷程度Fig.4 Integral calculation of concrete damage degre

(16)
式(16)表明,在腐蝕時間為tk時,混凝土試件截面位置(xi,yj)處的腐蝕損傷程度可通過圖4中的陰影區面積S表征。
(17)
即,試件截面 (xi,yj) 處的混凝土腐蝕損傷程度為
(18)

2.3 截面應力求解
(19)
式中:e為試件截面纖維網格單元;M×N為網格單元的數目;Ace為網格單元面積。

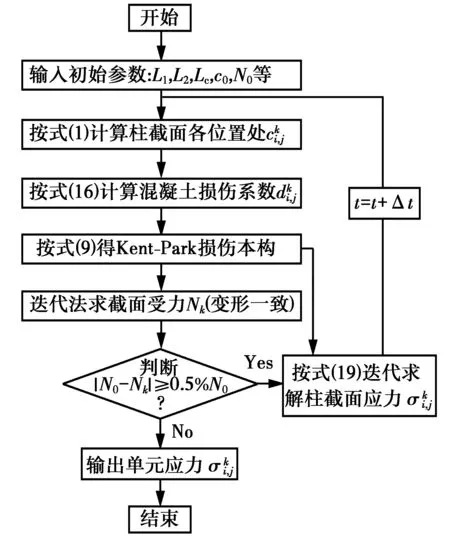
圖5 柱截面應力計算框圖Fig.5 Calculating flowchart of column section’s stres
值分析軸壓荷載和硫酸鹽耦合作用下鋼筋混凝土柱截面應力分布隨腐蝕時間的變化規律。
3 數值算例
3.1 初始參數

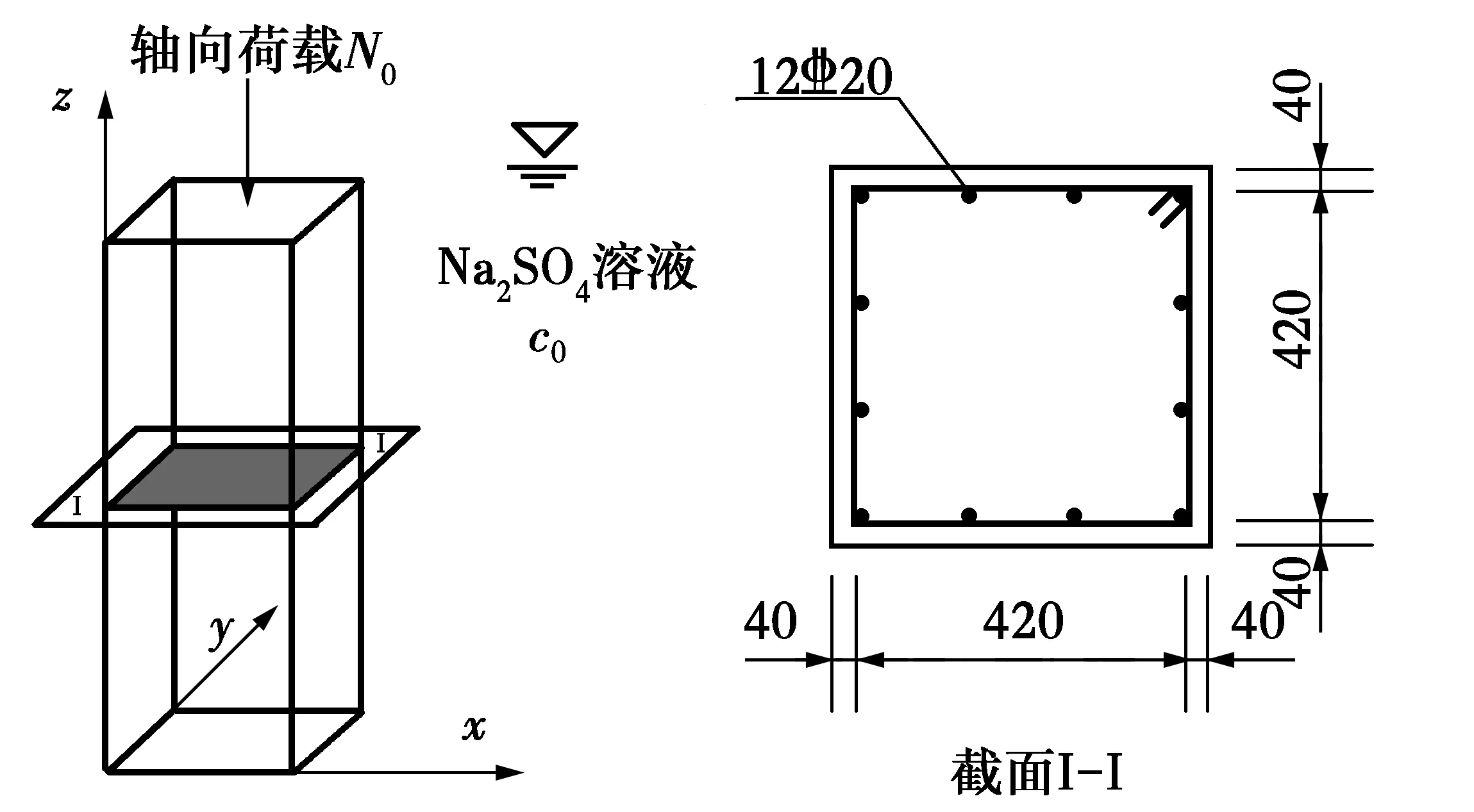
圖6 混凝土柱截面配筋Fig.6 Reinforced concrete column sectio
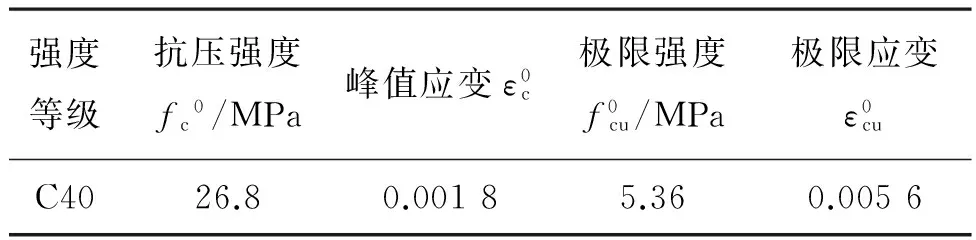
強度等級抗壓強度fc0/MPa峰值應變ε0c極限強度f0cu/MPa極限應變ε0cuC4026.80.00185.360.0056

表2 模型中的相關計算參數Table 2 Calculation parameters in the model
3.2 結果及分析
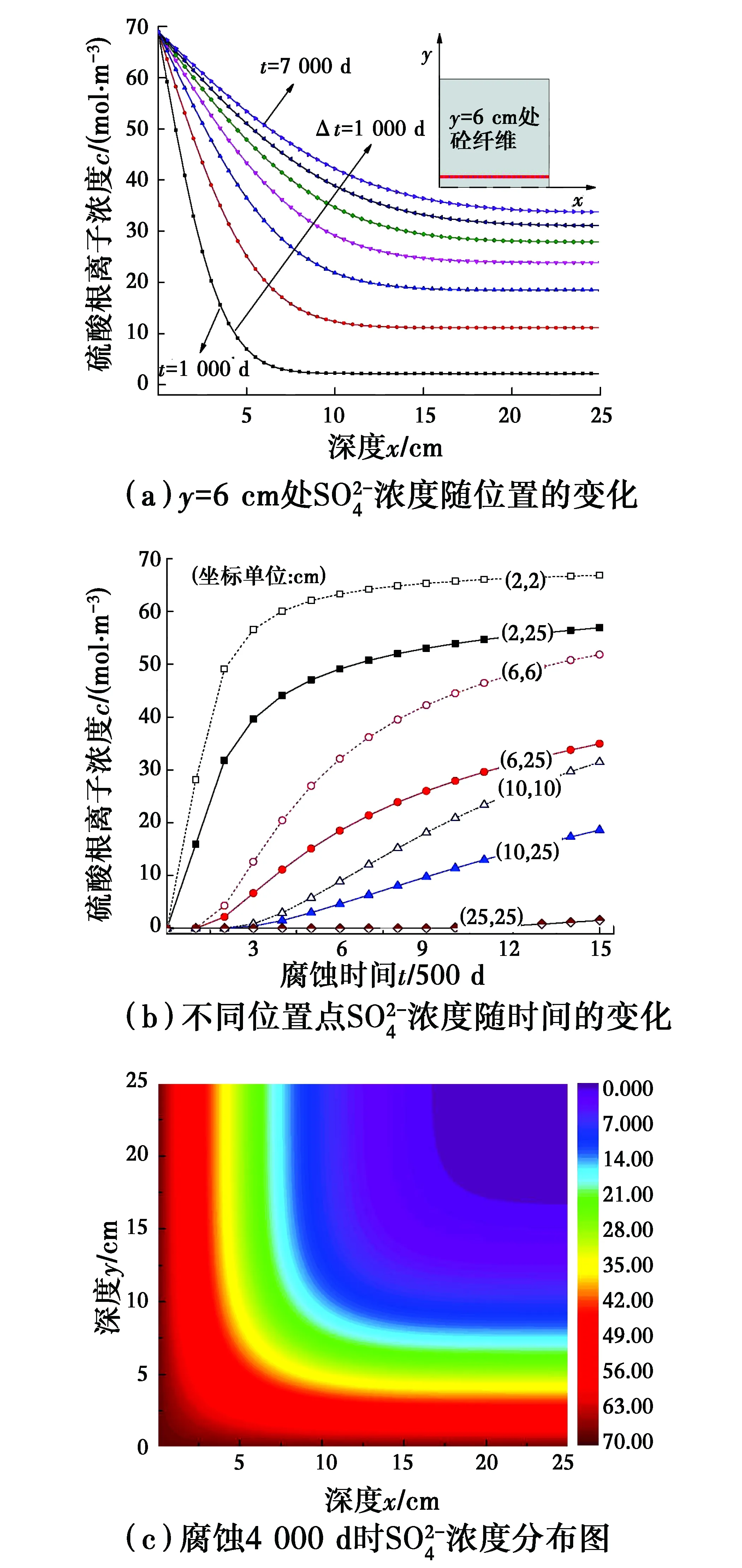
圖7 柱截面上硫酸根離子濃度隨截面位置與腐蝕時間的變化Fig.7 Time- and spatial-varying sulfate ion concentration in concrete column sectio
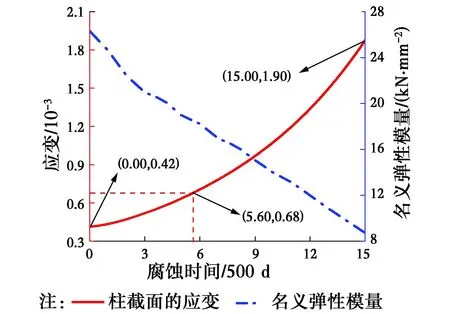
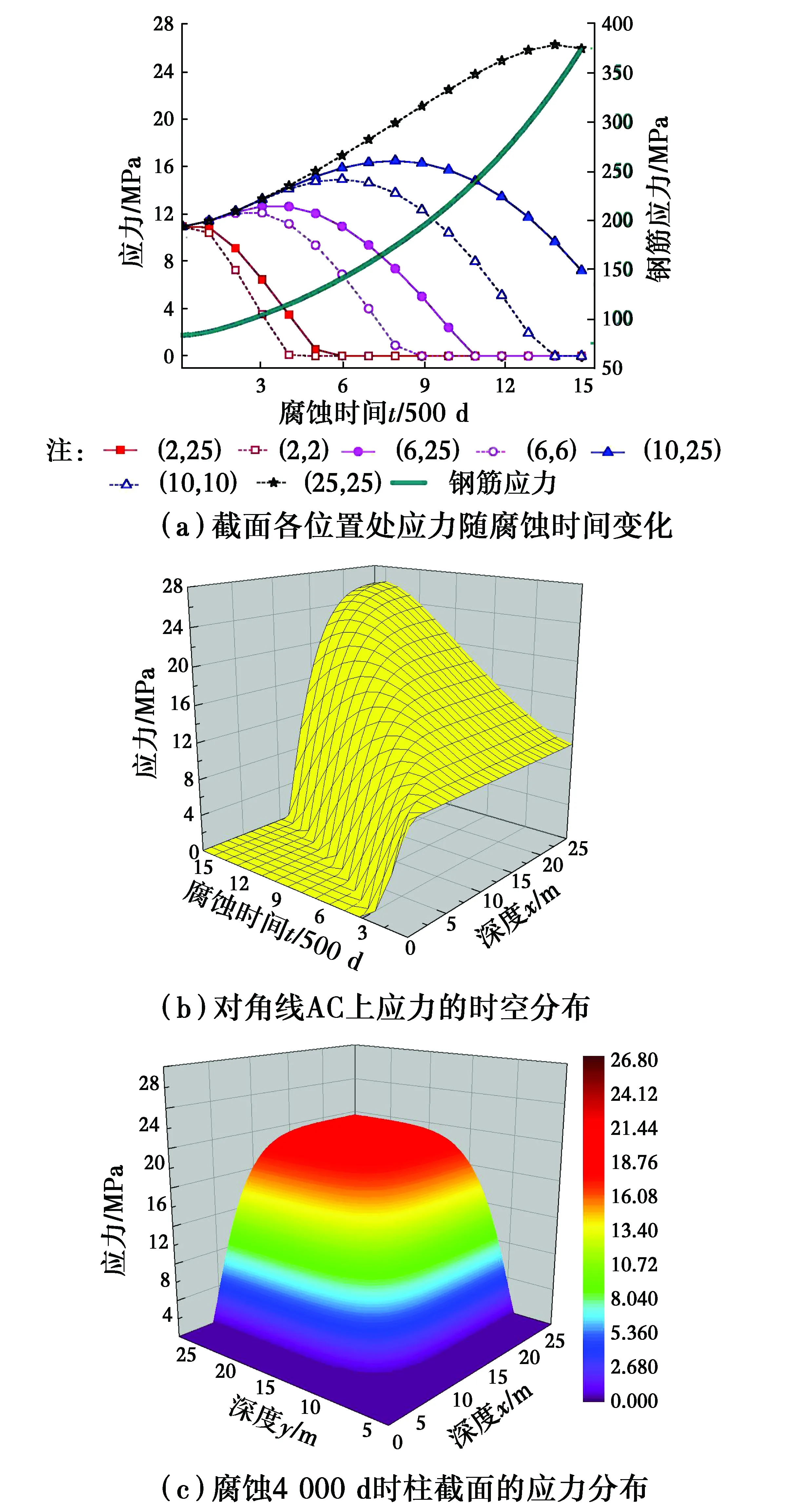
3.2.2 腐蝕損傷程度 硫酸鹽侵蝕下柱截面的損傷狀態含未損傷、損傷和剝落區,對應的混凝土損傷程度分別為d=0、0 圖8 混凝土腐蝕損傷程度隨截面位置與腐蝕時間的變化關系Fig.8 Time-and spatial-varying damage degree in concrete column sectio 3.2.3 應力應變曲線 圖9給出了腐蝕4 000 d時鋼筋混凝土柱截面不同位置處(d為各位置點的損傷程度)混凝土的應力應變曲線。從圖中可以看出,腐蝕4 000 d時,各位置處混凝土的應力應變曲線形狀基本一致,但峰值應力、峰值應變等參數隨d的變化而變化,其中,混凝土的峰值應力隨著d的增加而不斷減小,而峰值應變隨著d的增加而增大,如非對角線BC上點(10,25)(d=0.12)的峰值應力和峰值應變分別為23.58 MPa及1.93×10-3,而點(6,25)(d=0.53)的峰值應力和峰值應變分別為12.60 MPa及2.47×10-3,二者對比發現,前者混凝土的腐蝕損傷程度較小,其峰值應力是后者1.87倍,但峰值應變較后者小0.54×10-3。此外,從圖9中還可知,混凝土軟化段斜率隨d的增加而減小,最后變為0,而極限應變增大。 圖9 柱截面不同位置處的混凝土腐蝕損傷本構Fig.9 The concrete-corroded constitutive model at different positions of sectio 3.2.4 柱截面應變及名義彈性模量 在平截面假定的條件下,軸壓混凝土柱截面應變僅與腐蝕時間有關,圖10給出了硫酸鹽侵蝕混凝土柱截面應變隨腐蝕時間的變化規律。從圖中可以看出,在豎向荷載3 000 kN作用下,從硫酸鹽侵蝕前至腐蝕,混凝土柱截面應變從腐蝕前的0.42×10-3增加至腐蝕2 800 d時0.68×10-3,且其基本呈線性增加;而當腐蝕時間從2 800 d增加到7 500 d時,柱截面應變上升至1.90×10-3,超過混凝土的初始峰值應變(1.80×10-3),因此,在硫酸鹽侵蝕混凝土的后期,其柱截面應變增加明顯。此外,根據截面應變隨腐蝕時間的變化,可計算硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中混凝土名義彈性模量(E=N0A-1ε-1))隨腐蝕時間的變化情況,圖10表明,硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,混凝土的彈性模量隨腐蝕時間的增加而降低。 圖10 柱截面應變及混凝土名義彈性模量隨腐蝕時間的變化Fig.10 Change of the section strain and the elastic modulus of concrete with the corrosion tim 圖11 混凝土柱截面應力隨截面位置與腐蝕時間的變化Fig.11 Time-and spatial-varying stress in 通過數值模擬,研究了軸心受壓荷載和硫酸鹽侵蝕耦合作用下鋼筋混凝土柱截面內離子傳輸、腐蝕損傷演變、截面應變和應力的變化規律,結果表明: 1)硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,混凝土柱截面內硫酸根離子濃度呈梯度分布,且除了隨腐蝕時間的增加而增加外,還明顯受柱截面二維交互效應的影響。 2)在混凝土柱截面內存在硫酸鹽腐蝕損傷區,該腐蝕損傷區隨腐蝕時間逐漸向截面內部移動,且其寬度也逐漸增加。 3)在一定軸心受壓荷載作用下,混凝土柱截面應變隨腐蝕時間的增加而增加,且其名義彈性模量降低。 4)軸心受壓荷載作用下,柱截面鋼筋應力隨硫酸鹽腐蝕時間的增加而增加,而柱截面混凝土應力在未損傷區內隨腐蝕時間的增加而增加,但在損傷區內隨腐蝕時間的增加而呈現先增加后逐漸降低,可見,在硫酸鹽侵蝕過程中,鋼筋混凝土柱截面發生了明顯的應力重分布現象。 [1] JIANG L, NIU D T. Study of deterioration of concrete exposed to different types of sulfate solutions under drying-wetting cycles [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 117: 88-98. [2] 姚明博, 李鏡培. 混凝土灌注樁中混含硫酸鹽的時變分布規律[J]. 土木建筑與環境工程, 2015, 37(5): 95-100. YAO M B, LI J P. Theoretical analysis of the time-varying distribution behavior of bored pile internal mixed sulfate [J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2015, 37(5): 95-100. (in Chinese) [3] 殷光吉, 左曉寶, 孫偉, 等. 硫酸鹽侵蝕下水泥凈漿膨脹應變計算[J]. 工程力學, 2015, 32(9): 119-125. YIN G J, ZUO X B, SUN W, et al. Numerical simulation of the expansive strain in cement paste subjected to sulfate attack [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(9): 119-125. (in Chinese) [4] SUN C, CHEN J, ZHU J, et al. A new diffusion model of sulfate ions in concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 39: 39-45. [5] LORENTE S, YSSORCHE-CUBAYNES M P, AUGER J. Sulfate transfer through concrete: Migration and diffusion results [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2011, 33(7): 735-741. [6] TAI I, CAVALARO S H P, SEGURA I, et al. Alternative methodology to consider damage and expansions in external sulfate attack modeling [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2014, 63: 105-116. [7] LIU Z, DE SCHUTTER G, DENG D, et al. Micro-analysis of the role of interfacial transition zone in “salt weathering” on concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2010, 24(11): 2052-2059. [8] JIANG L, NIU D T, SUN Y Z, et al. Ultrasonic testing and microscopic analysis on concrete under sulfate attack and cyclic environment [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(12): 4723-4731. [9] YANG D Y, LUO J J. The damage of concrete under flexural loading and salt solution [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 36(4): 129-134. [10] SONG H, CHEN J K. Effect of damage evolution on poisson's ratio of concrete under sulfate attack [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2011, 24(3): 209-215. [11] MIRVALAD S, NOKKEN M. Studying thaumasite sulfate attack using compressive strength and ultrasonic pulse velocity [J]. Materials and Structures, 2016, 49(10): 4131-4146. [12] 梁詠寧, 袁迎曙. 硫酸鹽腐蝕后混凝土單軸受壓本構關系[J]. 哈爾濱工業大學學報, 2008, 40(4): 532-535. LIANG Y N, YUAN Y S. Constitutive relation of sulfate attacked concrete under uniaxial compression [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008, 40(4), 532-535. (in Chinese) [13] 劉漢昆, 李杰. 受侵蝕混凝土本構關系[J]. 建筑材料學報, 2011, 14(6): 736-741. LIU H K, LI J. Constitutive law of attacked concrete [J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2011, 14(6): 736-741. (in Chinese) [14] 鄒篤建, 劉鐵軍, 滕軍. 硫酸鈉侵蝕混凝土柱動態抗壓特性試驗研究[J]. 建筑材料學報, 2011, 14(6): 742-745. ZOU D J, LIU T J, TENG J. Research on dynamics compressive behavior of plain concrete columns suffering from sulfate attack [J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2011, 14(6): 742-745. (in Chinese) [15] 過鎮海. 鋼筋混凝土原理[M]. 北京: 清華大學出版社, 2013. GUO Z H. Reinforced concrete principle [J]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2013. (in Chinese) [16] ZUO X B, SUN W, YU C. Numerical investigation on expansive volume strain in concrete subjected to sulfate attack [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 36(4): 404-410. [17] 左曉寶, 孫偉. 硫酸鹽侵蝕下的混凝土損傷破壞全過程[J]. 硅酸鹽學報, 2009, 37(7): 1063-1067. ZUO X B, SUN W. Full process analysis of damage and failure of concrete subjected to external sulfate attack [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 37(7): 1063-1067. (in Chinese) [18] BONTEMPI F, BIONDINI F, DAN M F, et al. Cellular automata approach to durability analysis of concrete structures in aggressive environments [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering,2004,130(11): 1724-1737. [19] SCOTT B D, PARK R, PRIESTLEY M J N. Stress-strain behavior of concrete confined by overlapping hoops at low and high strain rates [J]. ACI Journal, 1982, 79(2): 13-27. [20] 陸金甫. 偏微分方程數值解法[M]. 北京: 清華大學出版社, 2004. LU J F. Numerical methods for partial differential equations [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. (in Chinese) [21] ZUO X B, SUN W, LI H, et al. Modeling of diffusion-reaction behavior of sulfate ion in concrete under sulfate environments [J]. Computers and Concrete, An International Journal, 2012, 10(1): 47-51. 2017-05-25 National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 51378262, 51778297); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20141396) Numericalanalysisontime-varyingprocessofstressinreinforcedconcretecolumnsubjectedtoaxialcompressionandsulfateattack WangJialin,ZuoXiaobao,MaQiang,YinGuangji,TangYujuan (Department of Civil Engineering, Nanjing University of Science & Technology, Nanjing 210094, P. R. China) In order to investigate the stress responses of reinforced concrete column subjected to the couplings of axial compression and sulfate attack, this paper applied an existed diffusion-reaction equation of sulfation in concrete to obtain a relationship between the sulfate-induced damage degree and the ion concentration and the corrosion time. On the basis, a concrete-corroded constitutive model related to the damage degree and a calculating approach for stress responses of concrete under the couplings of axial compression and sulfate attack were proposed. Through numerical solution on these models, the changes of sulfate ion concentration, damage degree, strain and stress in concrete with the corrosion time were analyzed. Results show that the sulfate ion concentration and damage degree has a gradient distribution in concrete, and they are obviously influenced by the two-dimensional interactions in the cross section. With the increase of corrosion time, the damage zone gradually moves inward the cross section, and its width has a gradual increase, and the stress in the damage zone increases firstly and then has a gradual decrease, but in the no damage zone, the stress has a basically linear increase. In the process of sulfate attack, there produces the stress redistribution in concrete under axial compression. concrete; sulfate attack; axial compression; damage; stress redistribution 10.11835/j.issn.1674-4764.2018.01.005 TU375.3 A 1674-4764(2018)01-0030-09 2017-05-25 國家自然科學基金 (51378262、51778297);江蘇省自然科學基金 (BK20141396) 王佳林(1994-),男,主要從事混凝土材料與結構研究,E-mail:jialinwang1994@163.com。 左曉寶(通信作者),男,教授,博士生導師,E-mail:xbzuo@sina.com。 AuthorbriefWang Jialin (1994- ), main research interests: concrete materials and concrete structures,E-mail:jialinwang1994@163.com. Zuo Xiaobao(corresponding author), professor, doctoral supervisor,E-mail:xbzuo@sina.com. (編輯 胡英奎)

4 結論

