High directional multi-beam organic laser
HAO Ya-ru, DENG Zhao-qi
(Zhongshan Institute,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Zhongshan 528402,China)
Abstract: The advantages of organic lasers with DFB distributed feedback structures have attracted much attention, however, there are few reports on the principle of multi-beam organic lasers using high-order Bragg feedback. Different from single-waveguide or single-beam lasers implemented by low-order Bragg feedback in the past, high-order Bragg feedback is introduced into a planar organic semiconductor waveguide to produce red and blue multi-beam organic lasers in this paper. Using a fourth-order Bragg feedback and PVK∶DCJTI film, a three-beam red laser is realized with an exit angle of ±53° and 0.5°. A four-beam blue laser is implemented using a fifth-order Bragg feedback and PS∶DSA-ph film with exit angles of ±18° and ±75°. The relationship between higher-order Bragg grating feedback and device characteristics is studied by combination of plane waveguide and grating coupling. The results show that the theoretically calculated beam coupling angle is consistent with the actual test, which provides guidance for the design of multi-beam organic laser devices to some extent.
Key words: organic laser;Bragg scattering;grating coupling
1 Introduction
Since the discovery of high optical-gain and stimulated-emission properties in organic thin films based on small molecules and polymers, the solid-state organic lasers have been extensively explored due to their broad wavelength tunability throughout the visible spectrum and low-cost device fabrication possibility[1-2]. Different from traditional solid-state lasers[3-5], optically pumped organic lasers have been demonstrated in various resonator geometries such as waveguides[6]and microcavities[7], and the most promising structure is the distributed feedback resonator(DFB)[8-10]. By imposing a periodic surface corrugation(i.e. one-dimension grating structure) on the organic film, one may realize DFB that will reflect propagating waveguide modes without forming high-quality end facets.
Lasing occurs when the Bragg condition is satisfied:
mλ=2Λneff,
(1)
where,λis the light wavelength in vacuum,Λis the structure period, m is an integer that represents the diffraction order, andneffis the effective refractive index of waveguide. First-order(m=1) and second-order(m=2) feedbacks have been usually exploited to obtain edge-emitting and surface-emitting lasers[9-11], respectively, while higher-order(m>2) feedback has not come into sight, because out-coupled laser power represents a loss mechanism and thus increases the oscillation threshold[10]. But the disadvantages of higher-order feedback can't conceal their potential for the application. W.Holzer showed the stimulated emission condition of TE and TM mode[9], and Minghuan Liu pointed the emission angle of high-order DFB HPDLC lasers were in good agreement with theoretical calculations[12], however there are inadequate investigations on the cause of higher-order lasers from combination of waveguide modes and emission angles.
In this study, we realize red and blue multi-beam organic lasers by incorporating fourth-order and fifth-order Bragg scattering into planar organic semiconductor waveguides, respectively. Furthermore, a combination of plane waveguide and grating coupling theories help us understand the behaviors of our multi-beam devices, and provide guidance for their further design.
2 Experiment
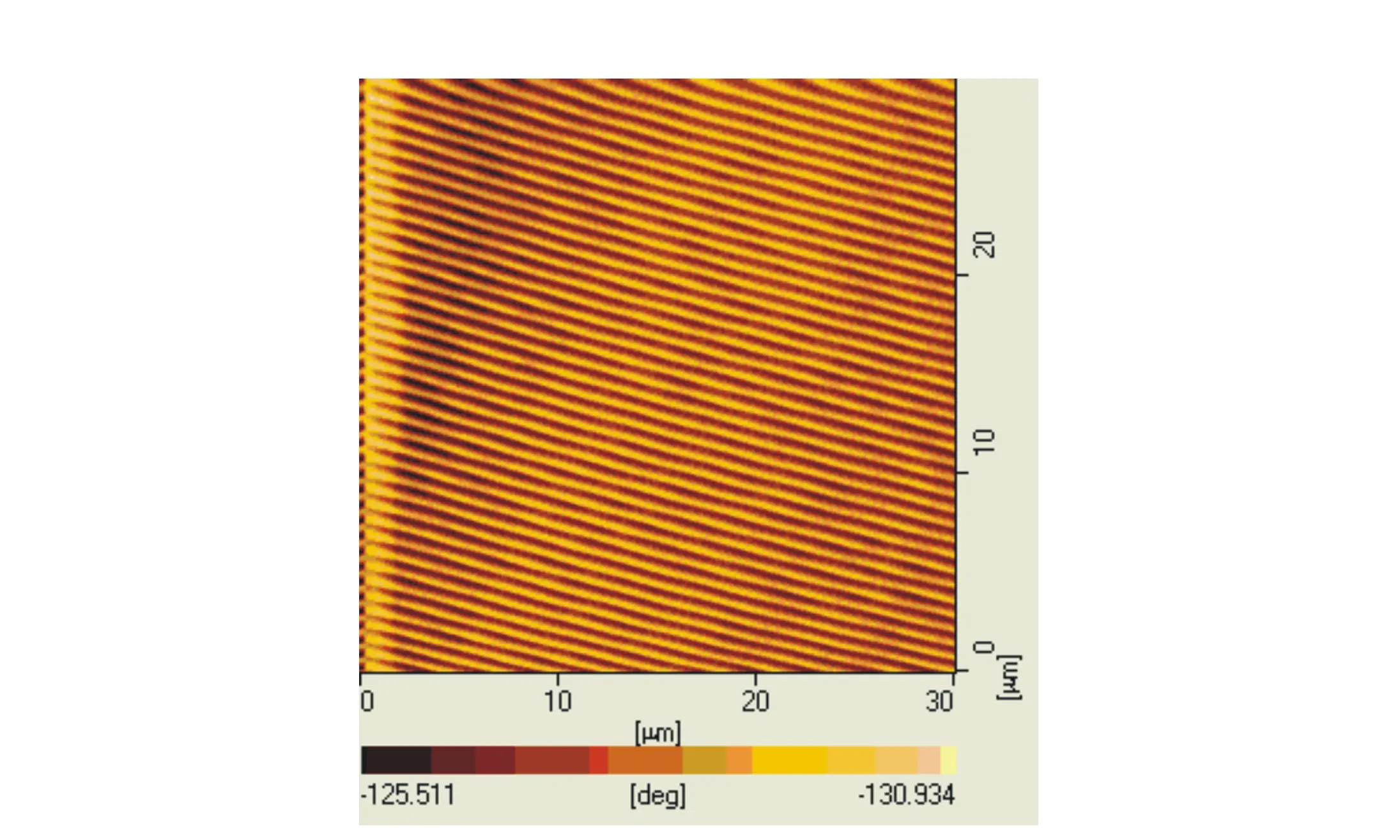
Fig.1 DFB structure(Λ=740 nm) scanned by atomic force microscope
A flexible substrate with periodical acrylic coating(Λ=740 nm) was fabricated followed Ref.[13], with difference that the substrate here was polycarbonate, which structure is shown in Fig.1. Then dye as the emissive dopant was doped in film-forming polymer materials by chlorobenzene solution. The dye doped polymer films were then spin-coated onto the flexible substrate. The laser structures were optically pumped with 5 ns pulses by a frequency-tripled Nd-YAG laser(Spectra-Physics) atλp=355 nm with a 10 Hz repetition rate. The output pulse energy of pump laser was controlled using neutral-density filters. An adjustable slit and a cylindrical lens were used before the beam splitter in order to shape the beam into a narrow stripe with dimensions of 3 mm×0.5 mm on the sample film. Then films were pumped at an angle incidence with the long axis of pump beam perpendicular to grating groove. The output signals were detected by a fiber-coupled CCD spectrometer(JY Spex CCD3000, the max resolution is 0.025 nm). The pumped energies from laser were measured using a calibrated laser power and energy meter(Gentec).
3 Results and Discussions
Firstly, we pay attention to the red multi-beam laser emission. The doped polymer films are composed of red fluorescence DCJTI doped PVK. The doping concentration was approximately 2%(by weight). The absorption and photoluminescence spectra are shown in Fig.2. The average film thickness was about 500 nm. Here we choose PVK as the film-forming material since its refractive index is suited to make the whole device′s parameters satisfy the Bragg condition.

Fig.2 Absorption and photoluminescence spectra of the PVK∶DCJTI film
The characteristics of red multi-beam laser formed on a flexible grating are shown in Fig.3. A photograph of the far field pattern is shown in the inset, from which we can obviously see 3 red laser beam emissions along ±53° and 0.5°, respectively. Every beam was centered near 613 nm and all exhibited typical laser characteristics are as follows:(i)monochromatic emission with a narrow full width at half maximum(FWHM) of 0.2 nm, (ii)strongly polarized emission with a ratio of 200∶1 for light polarized parallel to the grating, (iii)the typical fan-shaped beam profile of a 1D DFB resonator and (iv)clear threshold behavior. The output emission intensity integrated over all wavelengths as a function of pump intensity in PVK∶DCJTI film is shown in Fig.4, from which the threshold of laser is obtained to be 0.02 mJ/pulse.
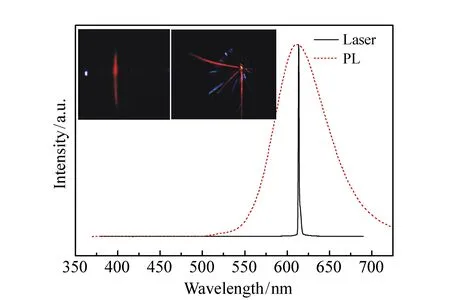
Fig.3 Emission spectra of PVK∶DCJTI system pumped by optically pulsed laser at above lasing threshold. The inset shows the photograph of the far field pattern
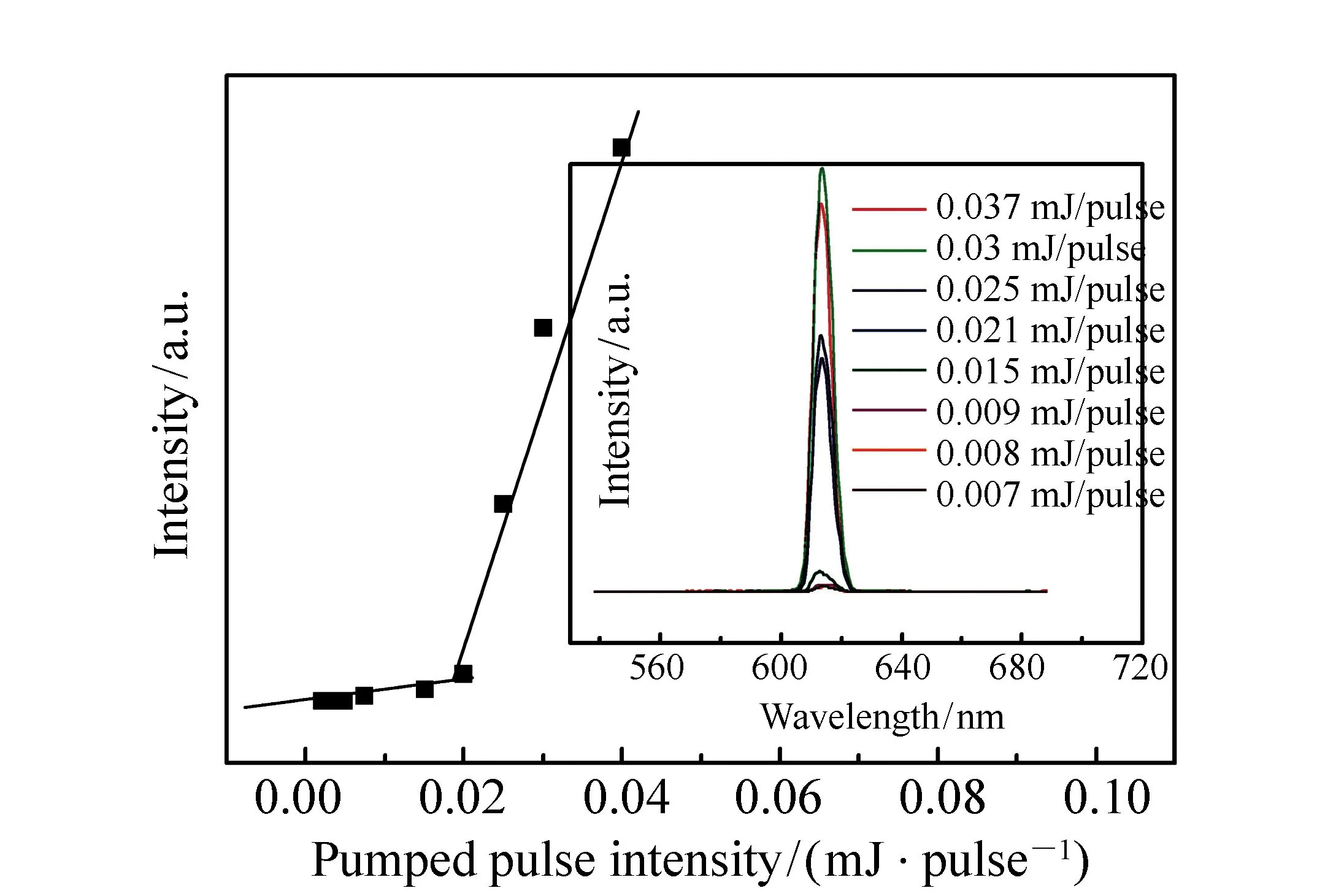
Fig.4 Output emission intensity integrated over all wavelengths as a function of pump intensity for PVK∶DCJTI film, from which we get the threshold of laser is 0.02 mJ/pulse. The inset shows the emission spectra of PVK∶DCJTI system pumped by optically pulsed laser at different pump intensity
In order to understand these results, the standard Helmholz equations were solved to model the modes in our asymmetric waveguide, formed by substrate-PVK∶DCJTI-air. The equation for waveguide modes is given as Ref.[14]
2k0nfhcosα-2φ13-2φ12=2mπ ,
(2)
wherek0is the free space wave vector,nfis refractive index of core layer(polymer film here),his polymer film thickness,αis the angle of propagation,mis an integer,φ12andφ13are the phase changes on reflection from the polymer/air interface and polymer/substrate interface, respectively. For a given thickness of polymer layer in an asymmetric waveguide, the guided modes have a distinct propagation angle, and the light at a certain wavelength can only propagate as a guided mode at one angle. The propagation of the guided mode in z-direction is entirely determined by the wave-vector componentkz=nfsinαk0=neffk0. Therefore, the guided mode propagated in z-direction likes a plane wave in a bulk material with refractive indexneff, which is so called effective refractive index. Then the solutions of equation (2) can be denoted by using discrete effective refractive indexes. The phase changes can be substituted by the Fresnel formula and never need to be calculated in the derivation solution.
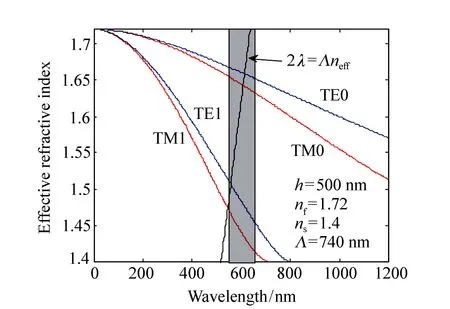
Fig.5 Graphical determination of the possible oscillation wavelengths for the DFB laser(PVK∶DCJTI) in a multimode optical waveguide. Curves show the effective refractive index of the various TE and TM waveguide modes as a function of wavelength. The shaded region shows the approximate wavelength range over which the DCJTI exhibits gain. Intersection of the straight line with the dispersion curves describes the possible oscillation wavelengths
Easily, the solutions of equation (2) can be visualized as Fig.5. Here, the dispersion curves for the various modes of guide effective refractive index as a function of wavelength is schematically given. The shaded region marks the approximate wavelength range over which the DCJTI exhibits gain. Also shown is the straight line given by 2λ=Λneff, which denotes the fourth order Bragg scattering. The points of intersection of straight line with dispersion curves specify the wavelengths at which DFB operation can occur. As we see, only TE0mode is observed experimentally, whereas the other modes can not arrive at the threshold due to small gain. As shown in Fig.5, the PVK∶DCJTI system has satisfied the fourth-order Bragg condition.
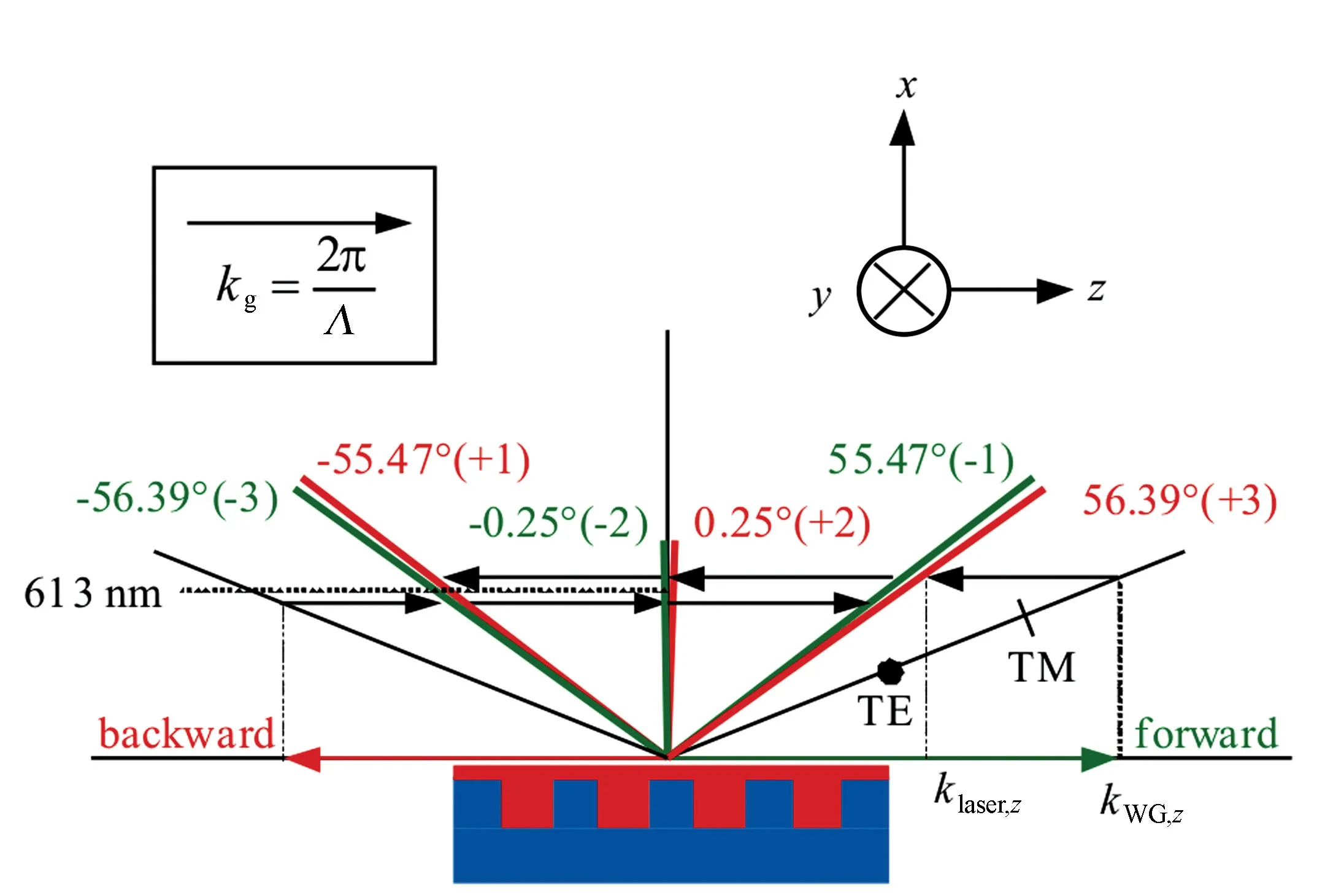
Fig.6 Grating coupling process between the waveguide mode and laser emission under the fourth Bragg condition
In order to understand the physical mechanism of coupling waveguide modes to laser light in the certain emission angles, the grating coupling condition should be considered.
kWG,z±lkg=klaser,z,
(3)


Fig.7 Output emission intensity integrated over all wavelengths as a function of pump intensity for PS∶DSA-ph film. The inset shows the emission spectra of PS∶DSA-ph system pumped by optically pulsed laser at different pump intensity
On the basis of strategy described above, the blue multi-beam laser was also realized in the PS∶DSA-Ph system by incorporating fifth Bragg scattering. The average film thickness was about 500 nm. Absorption and photoluminescence spectra of PS∶DSA-ph is similar with Ref.[15]. Likewise, all typical laser characteristics are also exhibited in
the blue multi-beam device. Fig.7 shows the dependence of laser output as a function of input energy with a threshold at 0.05 mJ/pulse. The lasing spectrum at 473 nm with a FWHM of 0.32 nm is shown in the inset of Fig.7. It can be seen that there are four-beam emission along about ±18° and ±75°, respectively. The calculated emission angles are approximately ±18.51° and ±73.09°, which are corresponding to the experiment results well, respectively. Besides the fifth-order laser emission in PS∶DSA-Ph film, low-order emission has not been observed, for lower-order diffraction never satisfy the Bragg condition.
4 Conclusions
In conclusion, a three-beam red organic laser with emission angles of ±53° and 0.5° and a four-beam blue organic laser with emission angles of ±18° and ±75° were realized by applying fourth-order and fifth-order Bragg scattering in emissive layer respectively. By coupling mechanism of the planar waveguide and the grating, the relationship between the feedback of the high-order Bragg grating and the device characteristics was studied. The theoretical calculations were in good agreement with the experimental results. It can be seen that the used Bragg grating plays an important role in realizing multi-beam emission of organic lasers. This opens a way to the design and development of high performance multi-beam organic lasers. The further study of coupling relationship between different periodic gratings and different emission wavelength materials has been on the agenda, including accurately tuning the emission wavelength, emission angle and intensity of multi-beam organic lasers.

