重癥超聲在AECOPD機械通氣中的應用
陳小雅 曾金華 高坤華
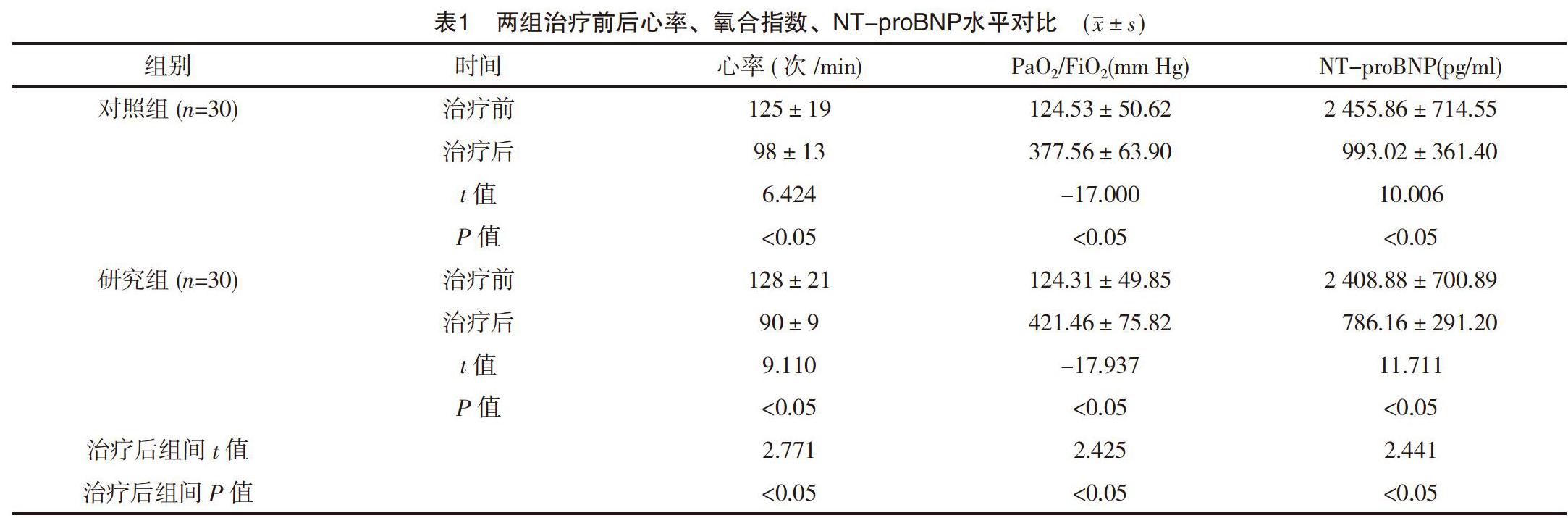
【摘要】 目的:評估重癥超聲在慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期(AECOPD)機械通氣中的應用價值。方法:選取筆者所在醫院2017年2月-2019年3月ICU收治的60例AECOPD患者為研究對象,將其隨機分為對照組和研究組,每組30例。對照組通過傳統方法測量CVP指導氣管插管機械通氣后補液治療,研究組通過重癥超聲測量下腔靜脈擴張指數、膈肌位移(DE)和膈肌收縮速度等指導機械通氣后補液治療。比較兩組治療前后心率、氧合指數(PaO2/FiO2)、腦利鈉肽前體(NT-proBNP)水平,拔管時間、不良事件發生率及死亡率。結果:治療后研究組心率低于對照組,PaO2/FiO2高于對照組,NT-proBNP水平低于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組拔管時間短于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組重新插管率、呼吸機相關性肺炎(VAP)發生率均低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。兩組死亡率比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論:針對AECOPD重癥患者,ICU治療期間采用重癥超聲指導液體治療可顯著改善患者心功能水平,通過對DE和膈肌收縮速度的觀察有效指導拔管,并減少不良事件發生和死亡,建議廣泛采用。
【關鍵詞】 重癥超聲; 慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期; 多普勒超聲心動圖; 膈肌收縮速度
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.24.021 文獻標識碼 B 文章編號 1674-6805(2019)24-00-03
【Abstract】 Objective:To evaluate the application value of severe ultrasound in mechanical ventilation of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(AECOPD).Method:From February 2017 to March 2019,60 cases of AECOPD patients admitted to ICU of our hospital were selected as research objects,and they were randomly divided into control group and study group,with 30 cases in each group.In the control group,CVP was measured by traditional method to guide rehydration therapy after mechanical ventilation of endotracheal intubation.In the study group,the dilation index of inferior vena cava,diaphragm displacement(DE) and diaphragm contraction velocity were measured by severe ultrasound to guide rehydration therapy after mechanical ventilation.The heart rate,oxygenation index(PaO2/FiO2),brain natriuretic peptide precursor(NT-proBNP) level,extubation time,incidence of adverse events and mortality were compared between the two groups before and after treatment.Result:After treatment,the heart rate of the study group was lower than that of the control group,PaO2/FiO2 was higher than that of the control group,and NT-proBNP level was lower than that of the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The extubation time of the study group was shorter than that of the control group,and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The reintubation rate and the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia(VAP) in the study group were lower than those in the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).There was no significant difference in mortality between the two groups(P>0.05).Conclusion:For severe patients with AECOPD,the use of severe ultrasound-guided fluid therapy during ICU treatment can significantly improve the level of cardiac function of patients.The observation of DE and diaphragm contraction velocity can effectively guide extubation,and reduces adverse events and death,which is recommended to be widely adopted.
綜上所述,針對AECOPD等重癥患者,ICU治療期間采用重癥超聲指導液體治療可顯著改善患者心功能水平,通過對下腔靜脈擴張指數、DE和膈肌收縮速度的觀察有效指導拔管,并減少不良事件發生和死亡,建議廣泛采用。
參考文獻
[1]趙慧靜,王元元.重癥超聲診斷方案在機械通氣患者撤機中的應用價值評價[J].臨床醫藥文獻雜志,2018,5(66):108,110.
[2]龔仕金,宋佳,張海翔.重癥超聲:脫機過程中一種有用的評估工具[J].浙江醫學,2017,39(3):149-151,155.
[3]方軍,李冰冰,潘曉潔,等.重癥超聲診斷方案在機械通氣患者撤機中的應用[J].海南醫學,2017,27(8):1265-1267.
[4]劉婧,朱莉.PICCO監測技術聯合重癥超聲在感染性休克患者液體復蘇中的應用[J].中外醫療,2018,37(33):179-181.
[5]陳衛挺,趙佳麗,陳英姿,等.床旁超聲定位鼻胃管在機械通氣危重患者中的應用[J].中國鄉村醫藥,2018,25(9):11-12.
[6]張聲,張衛星,林影芯.超聲膈肌功能評估在指導重癥COPD機械通氣患者撤機中的應用[J].臨床醫學工程,2017,24(8):1051-1052.
[7]楊旻,李惠,尹路,等.床旁肺部超聲在重癥患者機械通氣脫機評估中的應用價值[J].中國急救醫學,2017,37(11):1000-1004.
[8] Shi L,Zhu B J,Xu M L,et al.Selection of AECOPD-specific immunomodulatory biomarkers by integrating genomics and proteomics with clinical informatics[J].Cell Biology and Toxicology,2018,34(2):109-123.
[9] Song Y L,Chen W,Chen R C,et al.The optimum timing to wean invasive ventilation for patients with AECOPD or COPD with pulmonary infection[J].International Journal of Chronic Obstructive,2016,11(1):535.
[10] Jing Z,Chun C,Ning S,et al.Systemic Inflammatory Marker CRP Was Better Predictor of Readmission for AECOPD Than Sputum Inflammatory Markers[J].Archivos De Bronconeumologia,2016,52(3):138-144.
[11]付黎明,王華.床旁超聲對急診重癥監護病房機械通氣合并氣胸患者的應用價值[J].臨床薈萃,2018,33(2):157-159.
[12]陸建紅,謝波,姬曉偉,等.床旁超聲在不同機械通氣模式和膈肌萎縮中的應用[J].浙江臨床醫學2017,19(8):1431-1433.
[13]馬少林,朱曉萍.機械通氣與膈肌萎縮[J].國際呼吸雜志,2012,32(1):70-72.
(收稿日期:2019-04-16) (本文編輯:桑茹南)

