Effects of sunlight on the eye
Zhen-Zhen Liu*, Shao-Fan Chen2*, Tong-Yong Yu*, Guo-Shu Ma2, Xiang-Yu Huang2, De-Ying Yu, Hao-Tian Lin
1State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China 2Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Eye-protection Lamp, Guangdong Guangyang Electric Appliance Co., Ltd., Zhongshan 528415, Guangdong Province, China Co-first authors:Zhen-Zhen Liu, Shao-Fan Chen, and Tong-Yong Yu.
Abstract
?KEYWORDS:sunlight; ultraviolet light; ocular structure; oxidative stress; DNA damage
INTRODUCTION
Sunlight is a proportion of electromagnetic radiation from the sun, which includes cosmic, γ, X-ray, UVC (200-280 nm), UVB (290-320 nm), UVA (321-400 nm), visible light and infrared radiation[1]. Blue light (400 nm-480 nm) is a part of the visible light included in sunlight and carries high energy that may trigger molecular changes in cells[2]. Ultraviolet light (200-400 nm) carries higher energy than visible light, and high dose exposure to UV leads to direct cellular damage.
The eye is the organ that perceives the light and transmits the signal to the cerebral cortex. In the eye, sunlight is known to contribute to impact various ocular structures. When sunlight reaches the eye, different wavelengths of light will be absorbed by different structures (Figure 1). The wavelengths below 300 nm are mostly absorbed by the cornea, while the aqueous humor can absorb only a little light between 300 nm and 340 nm[3]. In addition, the wavelengths below 400 nm are mostly absorbed by crystalline lens, while the wavelengths between 400 nm and 1355 nm are mostly absorbed by retina and uvea[4]. Sunlight can change the composition of the cell molecules in the specific ocular tissue, affecting its homeostasis and function. Sunlight can affect the function of the eye through the cumulative effects of light or the acute exposure to high dose of sunlight.
This article focuses on the recent knowledge on effects of sunlight on different ocular structures, such as cornea, anterior chamber, lens, retina, and optical nerve. We also summarized how to prevent sunlight related ocular diseases.
Sunlight-induced Ocular Pathologies
ConjunctivaandcorneaConjunctiva and cornea are at the outermost layer of the eyeball, which is mostly affected by light below 300 nm. Pterygium is an ocular disease, caused by hyperplasia of bulbar conjunctiva. According to a study, chronic UV exposure is associated with pterygium development, of which etiology remains unclear[5]. Pinguecula, fibro-fatty degeneration in bulbar conjunctiva, is related to UV exposure, while Fuchs Flecks is the earlist indicator[6]. The similar histopathological change has been found between these diseases[7]. According to some researches, direct phototoxic effects on DNA, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), local inflammation and disorder anti-apoptosis process may contribute to the development of pterygium by DNA damage, tissue damage, cells proliferation and cell migration[5,8-10]. Moreover, pterygium develops mostly on the nasal limbus of the bulbar conjunctiva, because the light at the temporal limbus passes through the aqueous and arrive at the opposing corneal side, which is near the nasal limbus[11].
Photokeratitis is a punctate staining of corneal epithelium and, with symptoms of ocular pain, tearing, conjunctival chemosis, blepharospasm, and deterioration of vision, due to the acute exposure to the UVB and UVC[12-13], namely, ‘snow blindness’ from natural UV exposure and ‘welder’s flash’ from artificial UV exposure[13]. The sign occurs after up to 6h exposure and disappears spontaneously in 24-72h depending on the UV damage[14]. According to animal experiments, it was indicated that supra-threshold UVB exposure results in disordered shedding process and increased corneal epithelial apoptosis due to activation of potassium channel[14-15]. The detachment of corneal epithelium results in pain due to the exposure of corneal nerve endings.
Additionally, a study of Labrador Canadians stated that the severity of climatic droplet keratopathy is dependent on UV exposure[15]. Moreover UV exposure is one of the etiological factors of ocular surface squamous neoplasia, which is precancerous dysplasia and cancerous epithelial lesions at the cornea and conjunctiva[11]. One explanation is that UV exposure causes telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations, which contributes to aberrant overexpression of telomerase and carcinoma development[16].
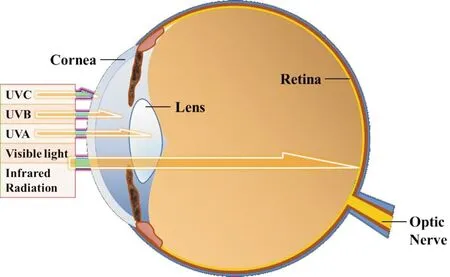
Figure1AdiagramshowingtheopticalradiationwithdifferentwavelengthabsorbedbydifferentocularstructuresSunlight goes through various refractive medium before it reaches the retina. Light with specific wavelength has the greatest impact on the ocular tissue with the highest absorption ratio (orange arrow). They can also affect other structure of the eye for they can reaches to other structure with little dose.
AnteriorchamberGlaucoma, a common disease with hypertension of ocular pressure mainly caused by an aqueous outflow disorder, is primarily associated with oxidative stress. Exposure to UV can induce oxidative stressviathe production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which is induced by activation of riboflavin, tryptophan, and porphyrin[17]. Generally, most ocular tissues possess integrated anti-oxidative equipment to protect ocular cells from ROS. However, some ocular tissues, for example, the trabecular meshwork, that are poorly equipped with anti-oxidant defense due to their location with indirect exposure to UV and a lower oxygen compartment, can be easily damaged by ROS[18]. The accumulations of ROS and free radicals could lead to macromolecule damage including mtDNA, DNA and protein damage, which could further induce mitochondrial damage and apoptosis, that resulting in alternation of the trabecular meshwork structure[18]. Consequently, the alternation of the structure and increase of aqueous humor may give contributions to the occurrence of primary open-angle glaucoma, a kind of irreversible blindness.
LensThe lens is a part of the transparent refractive pathway. However, it can become opaque due to the degeneration of lens proteins. There are studies stating that the increasing level of UVB is related to the disability-adjusted life year rates of cataracts[19-20], which may be associated with 25-hydroxy vitamin D[21]. A study conducted in Hongkong indicated that an increased proportion of men spent 5 or more hours outdoors per day, developed cortical cataracts at ages 40-50, compared to men spent less time outdoors[22]. It showed that the increased risk of cortical cataracts is related to the accumulation of UVB, while it showed no correlation between nuclear cataracts and UVB exposure or between cataracts and UVA exposure[23]. Another interesting study has found that the increased risk of cortical cataract with UVB exposure is limited in men, while there is no association between cortical cataract and UVB exposure among women[24]. Nevertheless, several epidemiological studies showed sufficient evidence to support that UVB exposure contributes to the occurrence of cortical cataracts, while there is insufficient evidence to support those as for nuclear cataracts and posterior sub-capsular cataracts[23-25]. According to an experiment, UVB exposure can induce anterior cortical cataract and posterior cortical cataract[26]. This is because UV exposure results in energy-dependent sodium-potassium ATPase damage. The disrupted sodium-potassium balance contributes to the swelling lens epithelial cells and cortical fibers, which ruptures and causes vacuolization, thus leading to cortical opacities[26]. UV exposure induces oxidation, cross-linking, cleavage and deamination of crystallin proteins, resulting in their aggregation, which develops cataract ultimately[27]. In recent year, some studies have found that blue light makes contributions on the generation of ROS in the mitochondria of lens epithelial cell, which may induce the development of cataracts[28-29]. Another study have reported that the oxidative stress is association with the pathogenesis of age-related cataract for the antioxidants can slow down the onset and development of cataract[30].
RetinaLight goes through the eyeball and is projected on the retina, which is a receptor of light signals due to cone cells and rod cells. A study showed that retinal pigment epithelium cells are observed to undergo time dependent apoptosis, caused by UVC[31]. Exposure to UV may induce DNA damage and activate the MAPK pathway, which is associated with programmed cell death. A study also demonstrated that sunlight is associated with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD) by ROS[32]. Surprisingly, according to the meta-analyse, several epidemiological studies has demonstrated that UV exposure has no association with AMD[33]. Therefore, the relationship between sun exposure and AMD is still being argued. More larege population of randomized controlled trials should be done to make sure the relationship between sun exposure and AMD. Another researh has reported that patients with blue-blocking intraocular lens can inhibit the AMD development[34]. According to the animal experiment, blue light at 400-500 nm wavelength, induces photochemical damage to retinal pigment epithelium cells[35], which may also activate the MAPK and NF-κB signal pathways by regulating the pathological cytokines expression of retinal pigment epithelium[36].
In addition to retinal pigment epithelium,sunlight can also affect the retinal vessel, which will increase the risk of blindness. According to animal experiments, the processes of both hyaloid vessel regression and angiogenesis are regulated by direct and melanopsin-dependent light responses, which are important for regulating the development of ocular vessels and retinal neuron number[37]. With increasing VEGF derived from a higher number of neuron, the vascular development is out of control in response to the increased demand of oxygen[37]. This experiment suggests that the liability of retinal vasculopathy is related to the amount of light received during retinal development. In other words, the fetal light may also regulate eye development. The sunlight can make influence on the retina not only through cumulative effect, but also through acute exposure. A study has demonstrated that foveal cone photoreceptor mosaic disturbances can be found after acute solar exposure[38].
OpticalNerveConductionOptical nerve conduction is not a component of the eyeball, but it plays an important role in the formation of light sensation in the cerebral cortex. This part is composed of the neuron, with abundance of mitochondria. Most of the short wavelength light, ranging from 400 nm to 480 nm, which can be absorbed by chromophores, located in mitochondria. It is suggested that short wavelength light may have a great influence on mitochondria, which is enriched in retinal ganglion cell. The first stop in the optical nerve conduction is the retinal ganglion cell, which is located in retina, and receives information from rod cells and cone cells[39]. Short wavelength light has a negative effect on mitochondria due to cumulative mutation of the mtDNA, which affects the respiratory chain by decreasing the output of ATP and increasing the production of ROS[40-42]. Consequently, the number of mitochondria in retinal ganglion cells decreases, leading to neuron death due to the absence of ATP and accumulation of ROS induced oxidative stress. Eventually, optic nerve conduction has been affected by short wavelength light.
PreventionsforSunlight-inducedOcularDamagesThe invisible threat to eyes caused by ultraviolet and blue light from the sun should not be underestimated. Children are particularly susceptible to these harmful lights because their pupils are larger, and their refractive media are more transparent. WHO estimates that 80% of a person’s lifetime exposure to ultraviolet light occurs before the age of 18[43]. Exposure to ultraviolet light and blue light produces cumulative effects over a lifetime. Considering that life expectancy is increasing, this increases the chance for cumulative effects to develop in tissues and lead to age-related pathology. Overexposure to sunlight, especially before adolescent age, may increase oxidative stress in various eye tissues, leading to the development of severe ocular pathology, such as AMD, glaucoma and cataract in old age[43].
Table1Mechanismsandpreventionsforsunlight-inducedoculardamages
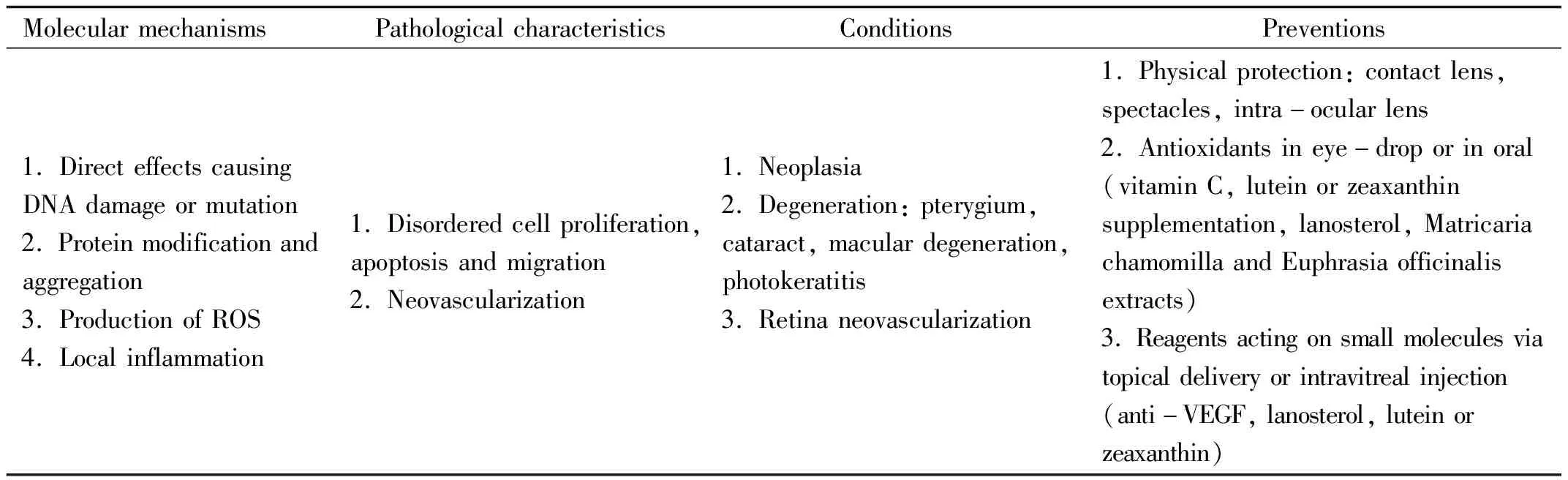
MolecularmechanismsPathologicalcharacteristicsConditionsPreventions1.DirecteffectscausingDNAdamageormutation2.Proteinmodificationandaggregation3.ProductionofROS4.Localinflammation1.Disorderedcellproliferation,apoptosisandmigration2.Neovascularization1.Neoplasia2.Degeneration:pterygium,cataract,maculardegeneration,photokeratitis3.Retinaneovascularization1.Physicalprotection:contactlens,spectacles,intra-ocularlens2.Antioxidantsineye-droporinoral(vitaminC,luteinorzeaxanthinsupplementation,lanosterol,MatricariachamomillaandEuphrasiaofficinalisextracts)3.Reagentsactingonsmallmoleculesviatopicaldeliveryorintravitrealinjection(anti-VEGF,lanosterol,luteinorzeaxanthin)
ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
According to the mechanism that sunlight lead to ocular disease, we can put forward some suggestions to protect ocular tissue from sunlight. First, physical protection, including sunglasses, clear spectacles or contact lenses, wide brim hats, and absorbing films for side windows in cars could be used to block UV below 400 nm[44]. What is more, another research on patients with blue-blocking intraocular lens after removing cataract showed that the blue-blocking intraocular lens can protect the retinal pigment epithelium from AMD development[34].
Secondly, we can use eye-drops or oral supplements that contain antioxidants to protect the eye from oxidative stress, such as vitamin C, lutein or zeaxanthin supplementation, lanosterol, Matricaria chamomilla and Euphrasia officinalis extracts. Vitamin C may neutralize superoxide radicals and provide protection to the retina from light-induced damage[45]. An intresting study has indicated that lutein or zeaxanthin supplementation can work on senile cataractviaprotecting the lens from oxidative damageinvitro[46]. Lutein and zeaxanthin were also demonstrated in other researches on retinal pigment epithelial cells to reduce oxidative damage and play an important role in regulating the MAPK pathway[47-48]. For corneal epithelial cells, eye drop containing matricaria chamomilla and Euphrasia officinalis extracts seems to take similar effect against the oxidative damage[49].
Last but not least, small molecules regulating the sunlight-activated signaling pathways can also be utilized to protect sunlight-induced damages. Anti-VEGF reagentsviatopical delivery or intravitreal injection were shown to attenuate retinal neovascularization[50]. Lanosterol eyedrop could prevent lens protein aggregation caused by sunlight-induced modification[51].
CONCLUSION
As a part of solar electromagnetic radiation, sunlight covers almost all wavelengths of light. The wavelength of light is negatively correlated with energy. The higher the energy of light, the more harmful it is to cells.Extensive exposure to sunlight may cause alternation of large molecular, including DNA and protein, or lead to production of ROS and/or aberrant proliferation, apoptosis and migration of cells. These pathological changes may result in various ocular conditions, including corneal or conjunctival neoplasia, pterygium, cataract and age-related macular degeneration. Accordingly, physical protection, topical and/or oral antioxidants and small molecules blocking sunlight-induced signal pathways could be used independently or combinedly to prevent and reduce sunlight-induced ocular damages (Table 1).

