新疆護生亞健康現狀及影響因素
蔣昕 王晶 方瑤 張濤濤 帕提古麗·哈力別亞提 李楊春
摘要:目的? 調查新疆護生的亞健康現狀,分析其影響因素。方法? 采用便利整群抽樣法于2018年4月選取新疆醫科大學、石河子大學及克拉瑪依厚博學院2016級、2017級本、專科440名護生,根據亞健康狀況調查問卷(SHSQ-25)分為健康狀態和亞健康狀態,比較不同健康狀態護生的一般資料、生活事件,并分析亞健康的影響因素。結果? 共423名護生,亞健康問卷得分0~66分,平均得分(26.84±12.91)分,有108名護生存在亞健康狀態,檢出率為25.53%。不同健康狀態護生的學校、學歷、學習壓力比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。不同健康狀態護生的負性事件、工作學習中的問題、社交及其他問題得分比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。多因素Logistic回歸分析顯示,學校、學習壓力、社交及其他問題是亞健康的影響因素(P<0.05)。結論? 新疆護生亞健康檢出率較高,受多種因素影響,學校應積極開展健康教育,指導護生樹立健康生活理念,正確應對生活或學習中的壓力。
關鍵詞:護生;亞健康;影響因素
中圖分類號:R181.3+7? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.03.036
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)03-0120-02
Sub-health Status and Influencing Factors of Nursing Students in Xinjiang
JIANG Xin,WANG Jing,FANG Yao,ZHANG Tao-tao,Partiguli·Halebiate,LI Yang-chun
(School of Nursing,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830011,Xinjiang,China)
Abstract:Objective? To investigate the sub-health status of Xinjiang nursing students and analyze its influencing factors.Methods? Using convenient cluster sampling method, in April 2018, 440 nursing students from Xinjiang Medical University, Shihezi University, and Karamay University College were selected in 2016 and 2017. They were divided into health according to the sub-health questionnaire (SHSQ-25) State and sub-health state, compare the general information and life events of nursing students with different health states, and analyze the influencing factors of sub-health.Results? A total of 423 nursing students had a sub-health questionnaire score of 0 to 66, with an average score of (26.84±12.91) points. There were 108 nursing students who survived in a sub-health state with a detection rate of 25.53%.There were statistically significant differences in the school, education, and study pressure of nursing students of different health states (P<0.05). The scores of negative events, work-learning problems, social and other problems of nursing students in different health states were statistically significant(P<0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that school, learning stress, social and other issues were influencing factors of sub-health(P<0.05). Conclusion? The high rate of sub-health detection of nursing students in Xinjiang is affected by many factors. Schools should actively carry out health education, guide nursing students to establish a healthy life concept, and correctly cope with the pressure of life or study.
Key words:Nursing students;Sub-health;Influencing factors
亞健康狀態(sub-health state)是獨立于健康與疾病的一種狀態,學習、生活、社交等各方面壓力增加使亞健康狀態的人數不斷上升。亞健康已被證實與心血管疾病等慢性非傳染性疾病密切相關[1]。有研究表明[2],36.56%的湘西大學生已步入亞健康行列。因此做好亞健康管理,有利于提高大學生生活質量。本研究通過了解新疆護生的亞健康現狀,探究其影響因素,并提出針對性建議,從而改善大學生亞健康狀態,現報道如下。
1對象與方法
1.1研究對象? 采用便利整群抽樣法于2018年4月選取新疆醫科大學、石河子大學及克拉瑪依厚博學院2016級、2017級本、專科440名護生。
1.2方法? 采用問卷調查方式,內容包括:①一般資料:學校、學歷、年級、性別、民族、城鄉、是否獨生子女及學習壓力。②亞健康狀況調查問卷(SHSQ-25)[3]:包括疲勞、精神、免疫、胃腸道及心血管癥狀5個方面,共25個條目,分數≥35分即診斷為亞健康狀態。③生活事件:分為正、負性事件、家庭、工作學習、社交及其他問題5個類別,共13個條目計13分,得分越高表明目前面對的生活事件越多。
1.3統計學分析? 采用SPSS 21.0統計學軟件進行數據分析。計量資料以(x±s)表示,采用t檢驗;計數資料以(n)表示,采用?字2檢驗。以P<0.05表示差異有統計學意義。
2結果
2.1亞健康情況? 共發放440份問卷,回收有效問卷423份,有效率為96.14%。亞健康問卷得分0~66分,平均得分(26.84±12.91)分。有108名護生存在亞健康狀態,檢出率為25.53%。
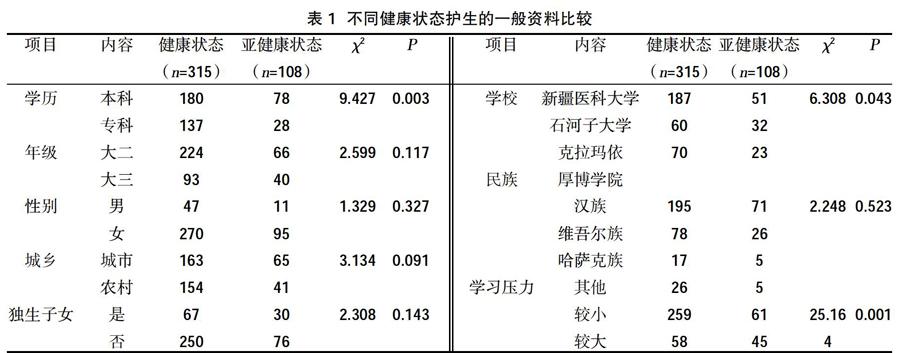
2.2不同健康狀態護生的一般資料比較? 不同健康狀態護生的學校、學歷、學習壓力比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);不同健康狀態護生的年級、性別、城鄉、民族、是否獨生子女比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),見表1。
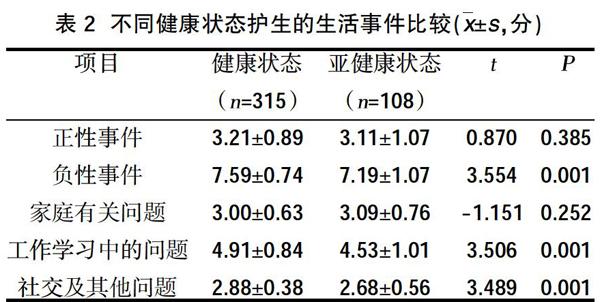
2.2不同健康狀態護生的生活事件比較? 不同健康狀態護生的負性事件、工作學習中的問題、社交及其他問題得分比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表2。
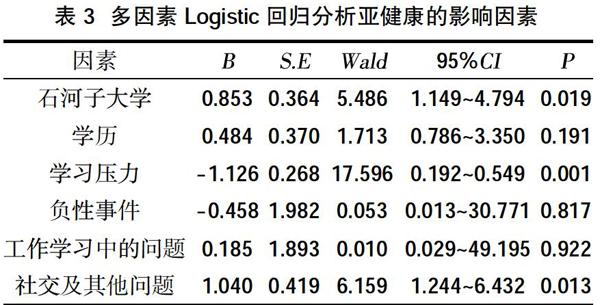
2.3多因素Logistic回歸分析亞健康的影響因素? 學校、學習壓力、社交及其他問題是亞健康的影響因素(P<0.05),見表3。
3討論
3.1亞健康現狀? 本研究結果顯示,護生亞健康問卷平均分(26.84±12.91)分,低于亞健康診斷標準(≥35分)[3],可見新疆護生基本處于健康狀態,但仍有108名護生存在亞健康狀態,檢出率為25.53%(108/423),高于蒙世佼等[4]對醫務人員群體亞健康檢出率的14.30%,其差異可能與調研時間臨近期末考試有關,緊張的情緒與氛圍可能導致亞健康的發生。本研究中石河子大學護生的檢出率高于克拉瑪依厚博學院和新疆醫科大學,這可能與院校間課程安排和考試時間不同有關。本科護生亞健康檢出率高于專科,感到學習壓力較大的護生高于感到學習壓力較小的護生,其原因可能是本科護生面臨較多的壓力源。多因素Logistic回歸分析顯示,學校、學習壓力、社交及其他問題為亞健康的影響因素。可能原因為石河子大學調研期間正處于期末考試階段,護生課業壓力較重,可能出現熬夜復習、飲食不規律、睡眠不足等情況,易導致亞健康現象的發生。而克拉瑪依學院屬于新疆醫科大學的分校區之一,課程進度及考試安排基本一致,可能成為二者亞健康檢出率無差別的原因。壓力是一種心理應激,直接影響護生的身心健康情況。護生體驗到的學習壓力越大,越可能出現自信心受挫等情緒,導致出現健康問題。大學生由于社會經驗不足,自我保護意識薄弱,易出現社交及其他問題,因此應引起學校廣泛關注。
3.2合理建議? 學生要善于發揮溝通作用,向老師或好友訴說心事,緩解內心焦慮、緊張等消極情緒。高校體育課是大學生參加體育運動、促進身體健康的重要途徑。在面臨繁重學習任務的同時,學生應注重勞逸結合,積極參加感興趣的文體活動,培養廣泛的興趣愛好。另外,高校應重視體育學科的發展,適當開展文體活動,激發學生興趣,使其自覺投身至健身行列中。針對學生社會經驗淺、防范意識差的社交問題,學校可通過開展防詐騙專題教育、印發知識手冊、真實案例分享等方式使學生熟知常見詐騙手段,將安全意識落到實處。
參考文獻:
[1]Kupaev V,Bofisov O,Marutina E,et a1.Integration of suboptimal health status and endothelial dysfunction as a new aspect for risk evaluation of cardiovascular disease[J].EPMA J,2016,7(1):19.
[2]宋曉英,楊婉麗,雷云霓,等.湘西大學生亞健康現狀及影響因素分析[J].社區醫學雜志,2016,14(18):11-14.
[3]Yan YX,Liu YQ,Li M,et al.Development and Evaluation of a Questionnaire for Measuring Suboptimal Health Status in Urban Chinese[J].Journal of Epidemiology,2009,19(6):333-341.
[4]蒙世佼,閆宇翔,劉佑琴,等.醫務人員亞健康狀態及其影響因素的研究[J].中國全科醫學,2013,16(1):6l-64.
收稿日期:2019-10-29;修回日期:2019-11-09
編輯/杜帆

