老年人群口腔缺牙現狀及修復現狀調查
王忠華 盛美春 鄭重陽
[摘要] 目的 探討老年人群口腔缺牙現狀及口腔修復的效果現狀。 方法 選取2018年7月~2019年7月期間在本院接受口腔健康檢查的182例湖州地區老年人群(年齡≥60周歲)為研究對象,記錄不同年齡段、性別及地區牙列缺失、牙列缺損率及修復現狀。 結果 182例入選者中,牙列缺失34例(18.68%),牙列缺損128例(70.33%);182例入選者中,牙列缺失修復率為91.18%,牙列缺損修復率為40.63%;女性組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率高于男性組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);不同性別間牙列缺失率、牙列缺失修復率、牙列缺損修復率及總口腔缺牙修復率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);高齡組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率高于低齡組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);不同年齡段間牙列缺失率、牙列缺失修復率、牙列缺損修復率及總口腔缺牙修復率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);城鎮組牙列缺損率、總口腔缺牙率均低于農村組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);城鎮組牙列缺損修復率與總口腔缺牙修復率均高于農村組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);不同地區牙列缺失率、牙列缺失修復率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);不同性別與年齡間口腔修復類型對比,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);不同地區口腔修復類型對比,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。 結論 老年人群牙列缺損率較高,但牙列缺損修復率較低,應積極加強健康宣教,以進一步提高其口腔保健意識。
[關鍵詞] 口腔缺牙;老年人群;口腔修復;健康宣教
[中圖分類號] R787? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] B? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)13-0147-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the status of tooth loss in oral cavity and effect status of oral rehabilitation in elderly population. Methods 182 elderly population(aged≥60 years old) in Huzhou who received oral health examination in our hospital from July 2018 to July 2019 were selected as the study subjects, and the dentition loss, dentition defect rate, and rehabilitation status in different age groups, genders and regions were recorded. Results Among the 182 candidates, 34(18.68%) candidates had dentition loss, and 128(70.33%) candidates had dentition defect; among the 182 candidates, the rehabilitation rate of dentition loss was 91.18%, the rehabilitation rate of dentition defect was 40.63%; the dentition defect rate and overall rate of tooth loss in oral cavity in the female group were higher than those in the male group, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05); there was no statistically significant difference in dentition loss rate, rehabilitation rate of dentition loss, rehabilitation rate of dentition defect, and overall rehabilitation rate of tooth loss in oral cavity between different genders(P>0.05); the dentition defect rate and overall rate of tooth loss in oral cavity in the elderly group were higher than those in the younger group, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05); there was no statistically significant difference in dentition loss rate, rehabilitation rate of dentition loss, rehabilitation rate of dentition defect, and overall rehabilitation rate of tooth loss in oral cavity between different age groups(P>0.05); the dentition defect rate and overall rate of tooth loss in oral cavity in the urban group were lower than those in the rural group, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05); the rehabilitation rate of dentition defect and overall rehabilitation rate of tooth loss in oral cavity in the urban group were higher than those in the rural group, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05); there was no statistically significant difference in dentition loss rate and rehabilitation rate of dentition loss in different regions(P>0.05); there was no statistically significant difference in the types of oral rehabilitation between different genders and ages(P>0.05); there was statistically significant difference in the types of oral rehabilitation in different regions(P<0.05). Conclusion The dentition defect rate in elderly population is higher, but the rehabilitation rate of dentition defect is lower. Health education shall be actively strengthened to further improve their awareness of oral health care.
[Key words] Tooth loss in oral cavity; Elderly population; Oral rehabilitation;Health education
口腔缺牙為口腔科發病率較高的疾病之一,包括牙列缺失和牙列缺損。口腔缺牙可對機體口腔功能產生不同程度的影響,嚴重影響患者的咀嚼功能,嚴重者可喪失咀嚼功能,對患者的身心健康及生活質量產生嚴重影響[1,2]。近年來,隨著我國人口老齡化的現狀日益嚴峻,老年人健康問題日益突出。老年人隨著機體功能的衰退,更易出現口腔健康問題[3,4]。因此,明確口腔缺牙現狀并采取對應干預措施,具有重要的臨床意義。本研究對本地區老年人群口腔缺牙現狀進行調查分析,以便為該地區老年人口腔缺牙防治干預提供參考資料,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
選取2018年7月~2019年7月期間在本院接受口腔健康檢查的182例老年人群(年齡≥60周歲)為研究對象。(1)納入標準:①常駐居民;②資料完整者;③年齡≥60周歲者。(2)排除標準:①甲狀腺功能紊亂者;②凝血功能障礙者;③合并嚴重心血管疾病者;④嚴重器官功能衰竭者;⑤合并嚴重感染性疾病者;⑥表達障礙或精神疾病者。其中男86例,女96例;年齡60~78歲,平均(68.36±2.87)歲;身體質量指數(Body mass index,BMI)(18.9~25.3)kg/m2,平均(22.17±1.18)kg/m2;職業:企業員工退休56例,公務人員退休69例,農民18例,其他39例;受教育程度:小學及以下12例,初中48例,高中87例,大專及以上35例。
1.2 方法
根據 WHO 口腔健康調查基本方法[5]的標準。詢問入選者年齡、受教育程度、BMI、職業、口腔衛生習慣、牙齒疾病史、合并慢性疾病等,由2名口腔醫師對其口腔情況給予檢查,即借助棉棒、口鏡等工具,對4個區域情況給予記錄,包括右下、右上、左下、左上,記錄口腔缺牙情況,尚且不記錄第三恒磨牙。若上頜和(或)下頜牙列全部缺失視作牙列缺失,若部分牙齒缺失促使恒牙牙列不完整視作牙列缺損。而后依據現場檢查結果及詢問修復病史對其義齒修復情況給予詳細記錄。
1.3觀察指標
比較不同性別牙列缺失率、牙列缺損率及修復率,不同年齡牙列缺失率、牙列缺損率及修復率,不同地區牙列缺失率、牙列缺損率及修復率。比較不同性別、年齡以及不同地區口腔修復類型。
1.4 統計學方法
采用SPSS19.0統計學軟件進行處理。計數資料以[n(%)]表示,組間比較采用χ2檢驗或Fisher精確概率法。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
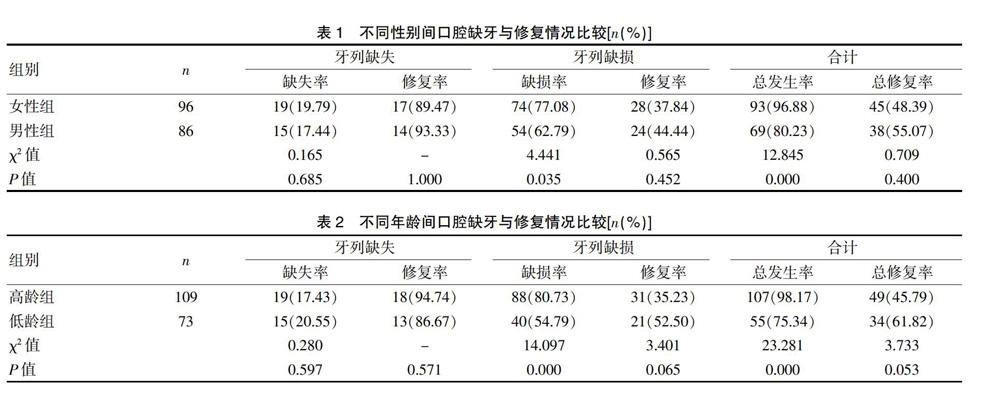
2.1 不同性別間口腔缺牙與修復情況比較
本研究182例入選者中,牙列缺失34例(18.68%),牙列缺失修復率為91.18%(31/34);牙列缺損128例(70.33%),牙列缺損修復率為40.63%(52/128);女性組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率高于男性組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);兩組牙列缺失率、牙列缺失修復率、牙列缺損修復率及總口腔缺牙修復率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表1。
2.2 不同年齡間口腔缺牙與修復情況比較
根據年齡分為70歲及以上年齡段為高齡組,60~69歲年齡段為低齡組進行比較,顯示高齡組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率高于低齡組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);兩組牙列缺失率、牙列缺失修復率、牙列缺損修復率及總口腔缺牙修復率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表2。
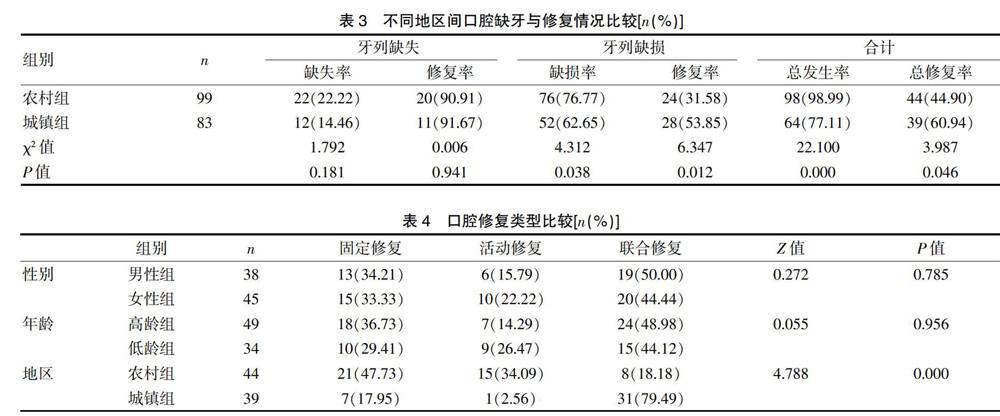
2.3 不同地區間口腔缺牙與修復情況比較
根據居住地區分為城鎮組和農村組,顯示城鎮組牙列缺損率、總口腔缺牙率均低于農村組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);城鎮組牙列缺損修復率與總口腔缺牙修復率均高于農村組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);兩組牙列缺失率、牙列缺失修復率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表3。
2.4 口腔修復類型比較
不同性別與年齡間口腔修復類型比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);不同地區口腔修復類型比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表4。
3 討論
牙列缺損和牙列缺失均為臨床發病率較高的一種口腔疾病,且受人口老齡化等多種因素的影響,促使其患病率呈現明顯上升態勢[5-6]。但不同地區口腔缺牙情況存在一定差異性,本研究182例入選者中,牙列缺失34例(18.68%),牙列缺損128例(70.33%),可見其對老年人群口腔健康影響極大。而口腔缺牙不僅對其咀嚼功能產生嚴重影響,還可對口腔頜系統健康及輔助發音的美觀性與功能性產生不同程度的影響,嚴重者可導致咀嚼功能完全喪失,將促使其生活質量明顯降低,而牙周病、齲齒為導致該類疾病發生的主要因素[7-9]。
有研究顯示[10-11],與老年女性相比,老年男性牙列完整率相對較高。本研究顯示,女性組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率高于男性組,究其原因為,老年女性群體機體激素水平產生的變化相對較大,雌激素水平的急劇下降更易導致牙周病、齲齒病等疾病發生[12]。有研究認為[13-14],年齡與牙列缺損率、牙列缺失率存在正相關。本研究結果顯示,高齡組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率高于低齡組。同時,農村地區對口腔保健、修復、治療的認知度普遍較差,加之生活習慣、經濟收入低等因素的影響,導致其口腔保護意識較差,而城鎮居民可通過網絡、電視、宣傳冊等多個途徑了解口腔健康知識,故自我保健意識較強,在日常生活中更加注重對自身牙齒的保護[15-17]。且本研究結果顯示,城鎮組牙列缺損率與總口腔缺牙率低于農村組,城鎮組牙列缺損修復率、口腔缺牙總修復率高于農村組。
現階段,隨著經濟條件及生活水平的提高,使老年人群對社會交往及美觀性的要求逐漸提升,一旦出現前牙缺失或者牙列缺失等情況,其一般會及時到院就診,進行義齒修復,而對于牙列缺損者,尤其對于部分后牙缺失者,則并不會引起高度重視[18-19]。且本研究結果顯示,本研究182例入選者中,牙列缺失修復率為91.18%,牙列缺損修復率為40.63%,與上述結果具有一致性。分析其原因如下:部分老年人群認為,隨著年齡的增長,口腔脫落幾顆牙齒屬于正常現象,還有人群易受自身身體素質、治療費用、時間等多方面因素的影響,未能及時進行口腔修復[20]。為此,臨床應積極開展社區口腔健康教育工作,使老年人群認識到牙齒缺失對其自身健康產生的不良影響及牙列缺損及時修復的重要性,以提高其疾病認知度,扭轉錯誤觀念,促使其義齒處于功能狀態。此外,不同地區老年人群對口腔修復類型的選擇具有一定差異性。本研究結果顯示,農村組口腔修復類型中固定修復占比明顯高于城鎮組,聯合修復低于城鎮組,究其原因,農村老年人群傾向于接受固定修復方式,其具有便捷等優勢,可在一定程度上幫助其恢復咀嚼功能,但口腔衛生難以處理;而城鎮老年人群義齒修復方式多為聯合修復,考慮更為全面,認為可能與口腔醫師建議存在一定關聯。
醫院應對有效資源給予充分利用,關注老年人群口腔缺牙情況及未及時修復的原因,并采取對應干預措施,以進一步促使其積極維持牙列完整,改善美觀,恢復咀嚼功能,提高修復率。此外,為方便老年人群就診,可進一步增加社區醫院內相關口腔醫療設施及醫療技術方面的建設,以保證老年人群口腔健康。
綜上,老年人群牙列缺損率較高,牙列缺損修復情況欠佳,存在一定口腔健康問題,應通過健康宣教等方式幫助其提高牙齒保健意識。
[參考文獻]
[1] 王喬齊,劉晨燕,馮劍穎,等. 杭州市濱江區低保老人缺牙狀況及口腔健康行為調查[J].中國現代醫學雜志,2015,25(34):73-76.
[2] 劉美娣,邱榮華. 口腔修復患者牙齒磨耗與牙列缺損狀況的調查分析[J]. 河北醫學,2015,21(8):1429-1432.
[3] 林天賜,黃達鴻,雷鳳翔,等. 老年種植修復患者牙科焦慮癥相關因素的調查研究[J].中華老年口腔醫學雜志,2018,16(4):229-233.
[4] 劉義,周卓君. 某醫院口腔疾病患者口腔健康觀念及就醫行為調查[J]. 預防醫學情報雜志,2018,34(2):235-237.
[5] World Health Organization. Oral health surveys-basic methods[M]. 4th ed. Geneva:Geneva:World Health Organization, 1997:1-48.
[6] 刀俊峰,宋光保,章錦才,等. 牙列缺損患者個性因素與種植術前焦慮狀況的相關性研究[J]. 口腔醫學,2014, 34(5):356-359.
[7] 陳青婭,黃茜,王黎. 口腔種植患者牙科焦慮的調查分析[J]. 國際口腔醫學雜志,2018,45(1):14-19.
[8] 戴東曉,李創,王毅,等. 應用正畸聯合口腔修復治療先天性缺牙的臨床效果分析[J].中國臨床醫生雜志,2017,45(3):93-95.
[9] Levorová J,Machoň V,Guha A,et al. Osteoarthrosis of temporomandibular joint related to the defects of posterior dentition: A retrospective study[J]. Prague Med Rep,2016,117(4):176-184.
[10] 萬哲,吳澤鈺,美力班·吐爾遜,等. 烏魯木齊市老年人口腔缺牙狀況的流行病學調查分析[J]. 中國美容醫學,2017,26(7):85-88.
[11] 夏鳳君,郭立娜. 呼市地區中老年人口腔缺牙及修復情況的流行病學調查[J]. 中國美容醫學,2017,26(1):107-109.
[12] 羅蓉,羅軍,夏羅英. 口腔種植修復在牙列缺失患者中的應用效果及對齦溝液中TNF-α、IL-6、IL-8的影響[J].上海口腔醫學,2017,26(3):324-327.
[13] 孟圓,劉雪楠,鄭樹國. 國內外口腔疾病負擔的現況和分析[J]. 中華口腔醫學雜志,2017,52(6):386-389.
[14] 劉佳鈺,陳卓凡,張慶元. 牙列缺損患者種植義齒修復的口腔健康影響程度量表研制[J].臨床口腔醫學雜志,2015,31(8):478-481.
[15] 韋彥鋒,劉艷春,白琴. 口腔種植修復與常規修復對牙列缺損患者的治療效果及預后影響[J]. 臨床和實驗醫學雜志,2017,16(21):2171-2173.
[16] Gezgin O,Botsali MS. Evaluation of teeth development in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients in mixed dentition by using medical image control systems[J]. Niger J Clin Pract,2018,21(2):156-162.
[17] Yoshitani M,Takayama Y,Yokoyama A. Significance of mandibular molar replacement with a dental implant:A theoretical study with nonlinear finite element analysis[J].Int J Paediatr Dent,2018,4(1):4.
[18] 蔣聰敏. 口腔種植修復牙列缺損的美學觀察及療效分析[J]. 中國傷殘醫學,2016,24(3):96-97.
[19] 楊婕. 口腔種植修復對牙列缺損患者咀嚼功能語言功能及治療滿意度的影響[J]. 河北醫學,2016,22(12):1979-1982.
[20] 戴東曉,李創,王毅,等.口腔修復對先天性缺牙患者的咀嚼功能及滿意度的影響[J].中國醫藥導刊,2015,17(11):1109-1110.
(收稿日期:2019-12-17)

