THE VON NEUMANN PARADOX FOR THE EULER EQUATIONS?
(王麗)
Department of Arts and Sciences,Shanghai Dianji University,Shanghai 201306,China
E-mail:wangli@sdju.edu.cn
Abstract The reflection of a weak shock wave is considered using a shock polar.We present a sufficient condition under which the von Neumann paradox appears for the Euler equations.In an attempt to resolve the von Neumann paradox for the Euler equations,two new types of reflection configuration,one called the von Neumann reflection(vNR)and the other called the Guderley reflection(GR),are observed in numerical calculations.Finally,we obtain that GR is a reasonable configuration and vNR is an unreasonable configuration to resolve the von Neumann paradox.
Key words von Neumann paradox;shock polar;Guderley reflection;von Neumann reflection
1 Introduction
The phenomenon of shock wave reflection was first reported by Ernst Mach[1]in 1878.In his experiments,he discovered two types of shock wave reflection configurations:regular reflection(RR)and irregular reflection(IR).Mach reflection(MR)is the main wave configuration among the various ones in IR,and it was systematically investigated by von Neumann[2]in 1943.According to the three shock theory(3ST)proposed by von Neumann,the wave configuration in the Mach reflection consists of three shocks and a contact discontinuity.When the incident shock is strong,the above mentioned theoretical result coincides well with experiments.However,for sufficiently weak shock,an interesting phenomenon has been found:there is no MR solution according to 3ST,but experimental results[3,4]and numerical results[5–7]show that there exists a wave configuration similar to the MR configuration.This phenomenon was suggested by Guderley[8],who concluded that a supersonic patch exists behind the triple point.Such a discrepancy was called the von Neumann paradox,and it has been studied by many authors[9].In this paper,we present a sufficient condition under which the von Neumann paradox appears for the Euler equations.
The first serious attempt to simulate numerical shock wave reflection under the conditions of the von Neumann paradox was undertaken by Colella and Henderson[3]using a secondorder accurate scheme.They hypothesized that the reflected shock wave degenerated into a continuous compression wave near the triple point.This type of reflection configuration is now referred to as vNR.However,Olim and Dewey[10]showed that experiments comply with this hypothesis only when Ms<1.05,or for a wedge angle θw<10°.In[11],Lai and Sheng proved that the reflection configuration in which the Mach shock is smoothly merged into the incident shock at a point and where the wave behind this point is smooth is a mathematically impossible flow pattern for the two-dimensional(2D)self-similar potential flow equation and the 2D self-similar Euler equations.In this paper,we conduct numerical calculations using the Euler equations to confirm the unreasonableness of vNR in order to resolve the von Neumann paradox.
In 1947,Guderley[8]proposed a modified Mach reflection.He added a centered expansion fan and a supersonic path behind the triple point.He also demonstrated that the local structures consisting of three shocks,a centered expansion fan and a contact discontinuity are possible.Calculations performed by Vasilev[12]confirmed the principal points of Guderley’s solution.Tesdall and Hunter[13]conducted numerical calculations using a simplified model based on the two-dimensional Burger’s equation.Tesdall et al.[14]performed similar calculations using the model of the nonlinear wave system.This new type of reflection configuration is now referred to as GR.Numerous experiments and numerical calculations that were reported in[15–20]confirmed the reasonableness of GR for resolving the von Neumann paradox.Lai and Sheng[21]confirmed the reasonableness of GR mathematically for the two-dimensional(2D)self-similar potential flow equation.In this paper,we conduct numerical calculations using the Euler equations to confirm the reasonableness of GR for resolving the von Neumann paradox.
The paper is organized as follows:in Section 2,we present a sufficient condition under which the von Neumann paradox appears for the Euler equations.In Section 3,we study vNR in numerical calculations and confirm that vNR is an unreasonable configuration for resolving the von Neumann paradox.In Section 4,we study GR in numerical calculations and confirm that GR is a reasonable configuration for resolving the von Neumann paradox.
2 The Sufficient Condition Under Which the von Neumann Paradox Appears for the Euler Equations
The 3ST is the analytical model for describing the flow field near the triple point of a Mach reflection(MR).The wave configuration and some associated parameters of an MR are shown in Figure 1.
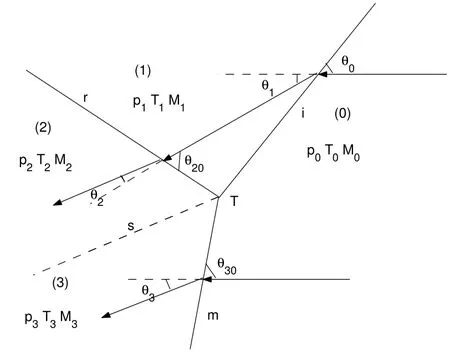
Figure 1
The MR consists of the incident shock wave,i,the reflected shock wave,r,the Mach stem,m,and one slipstream,s.These four discontinuities meet at a single point,known as the triple point,T.The flow field is divided into four regions:(0),(1),(2)and(3).Here,piis the flow pressure,Tiis the flow temperature,Miis the Mach number(i=0,1,2,3),θ0,θ20,θ30are the incident angles of the flow,and θj(j=1,2,3)are the deflected angles of the flow[22].In virtue of the conservation equations across an oblique shock wave,together with appropriate boundary conditions,we get[23,24]that
(i)Across the incident shock wave i:
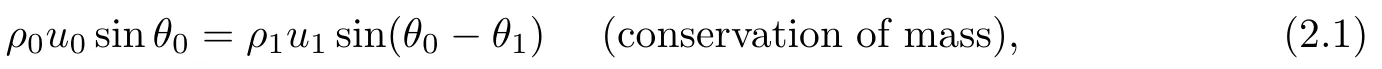
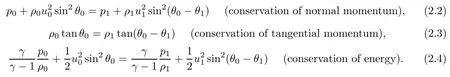
(ii)Across the reflected shock wave r:
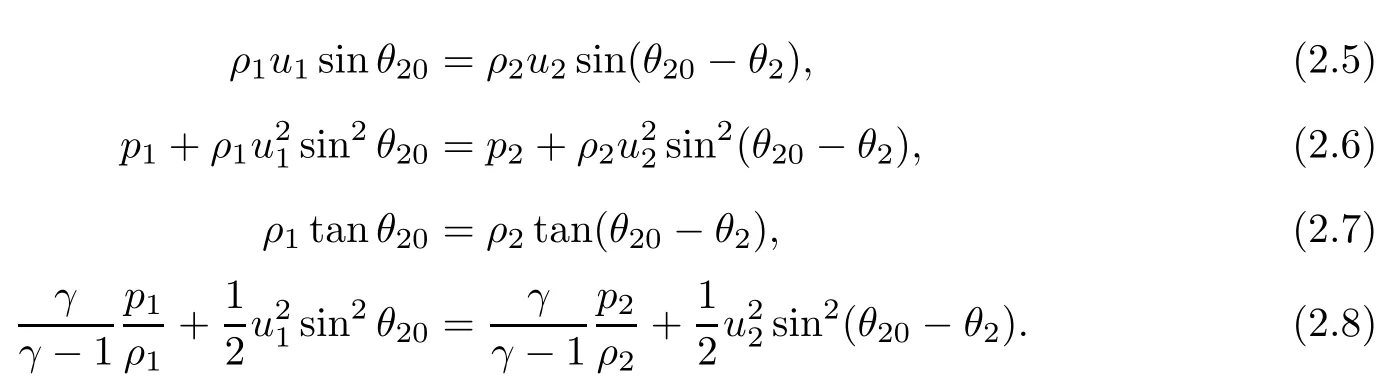
(iii)Across the Mach stem m:

In addition to these equations,there are also two boundary conditions which arise from the fact that state(2)and(3)are separated by a contact surface across which the pressure remains constant,that is,[22],

Furthermore,if the flow is assumed to be inviscid and if the contact surface is assumed to be infinitely thin,that is,a slipstream,then the flows on both sides of the slipstream are parallel,that is,

Using the expression for the Mach numberwhere γ is the adiabatic exponent and R is the specific gas constant,the eight parameters of equations(2.1)–(2.4)become p0,p1,T0,T1,M0,M1,θ0and θ1.Given p0,T0,M0and θ0,by solving the equations(2.1)–(2.4),we have
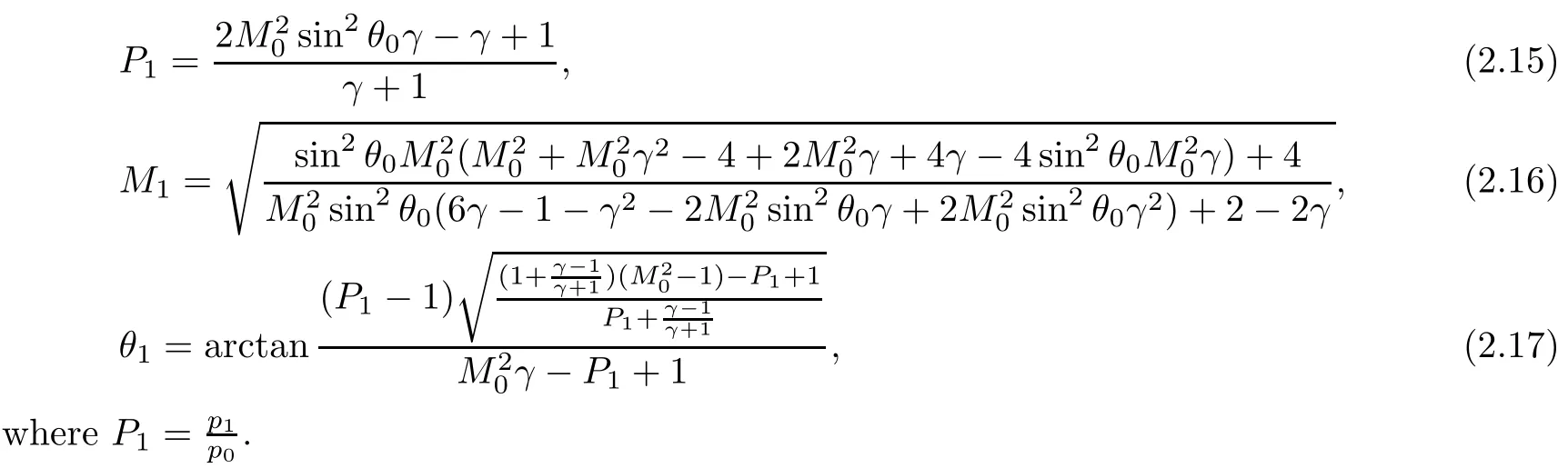
When the shock is weak,there are initial conditions for which the 3ST does not provide any solution.In what follows,we give the sufficient condition under which the von Neumann paradox occurs.It is worth mentioning that the condition we propose here is a sufficient but not a necessary one.
Theorem 2.1When the flow field(0)satisfiesand 1.18≤M0≤1.32,the von Neumann paradox takes place,where Ms=M0sinθ0is the Mach number of the shock wave.
ProofFor the convenience,we use the polar coordinates(P,θ),whereThe equation of the I-polar is
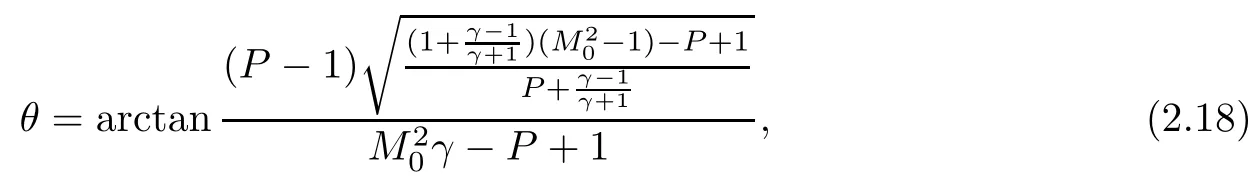
the equation of the left bench of the R-polar is
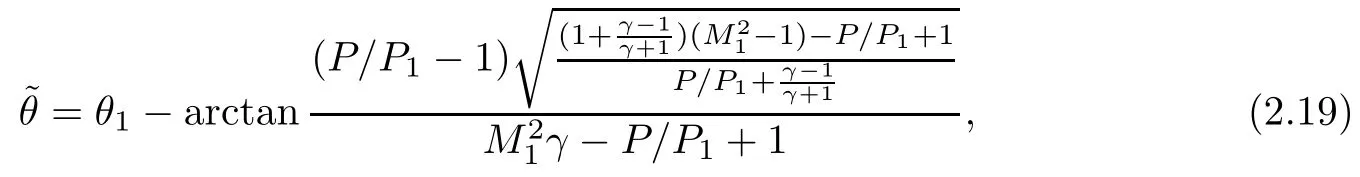
and the equation of the right bench of the R-polar is
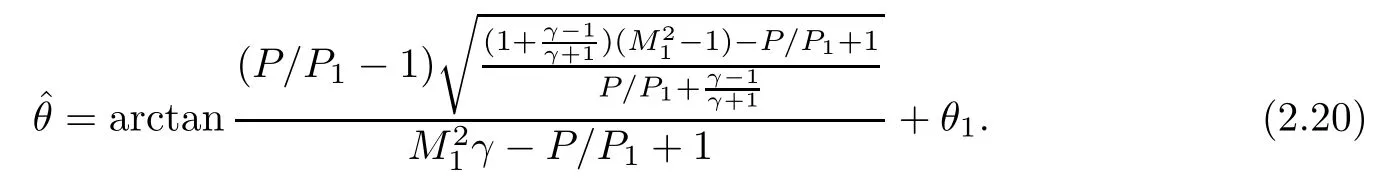
We will show that the R-polar is inside the I-polar wholly for the condition proposed in Theorem 2.1;see Figure 2.Thus the 3ST does not provide any solution and the von Neumann paradox occurs.

Figure 2 (=,γ=,M0=1.2)
Using(2.15)–(2.17),we obtain
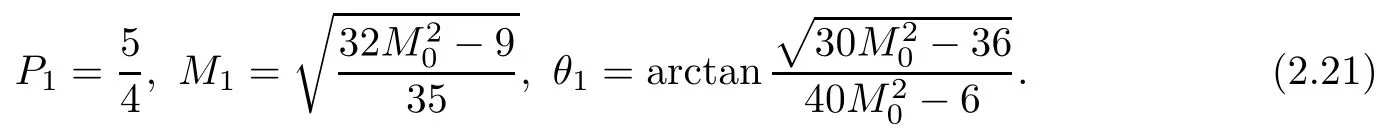
Inserting(2.21)into(2.18)–(2.20),we get
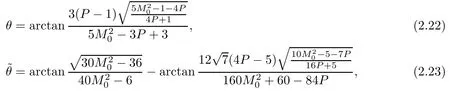
and
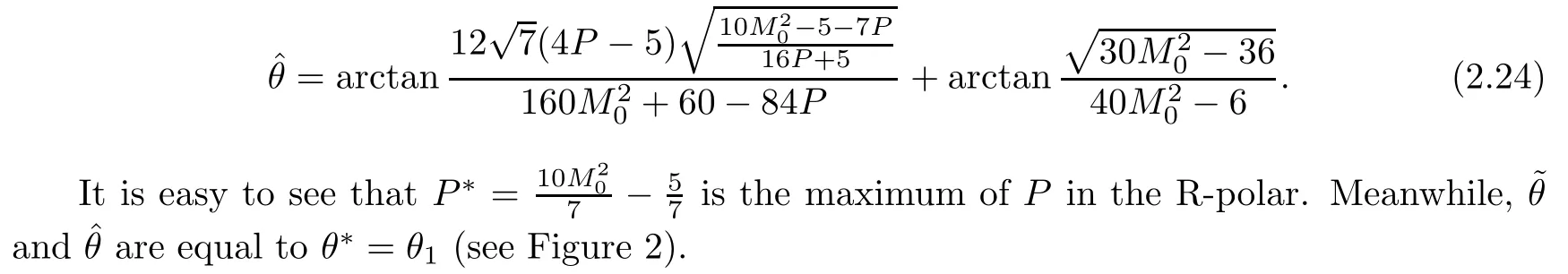
Proposition 2.2Whenthe R-polar does not intersect either the P-axis or the I-polar.
Firstly,we prove that the R-polar does not intersect the P-axis whenDifferentiating(2.23)with respect to P,we have

we see that the minimum value of the objective function is 0.0198(rounded to 4 decimal places),which is positive and occurs when M0=1.32.The relationship betweenand M0and the minimum point of the functionare displayed in Figure 3.
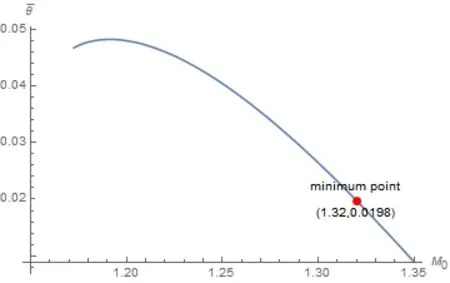
Figure 3

Figure 4

3 Unreasonableness of vNR to Resolve the von Neumann Paradox
In order to resolve the von Neumann paradox,Colella and Henderson investigated,numerically,the weak-shock wave reflection domain,and found that there were cases in which there was no apparent discontinuity in the slope between the incident shock wave and the Mach stem and that the reflected shock wave degenerated near the triple point to a band of compression wave(see Figure 5).
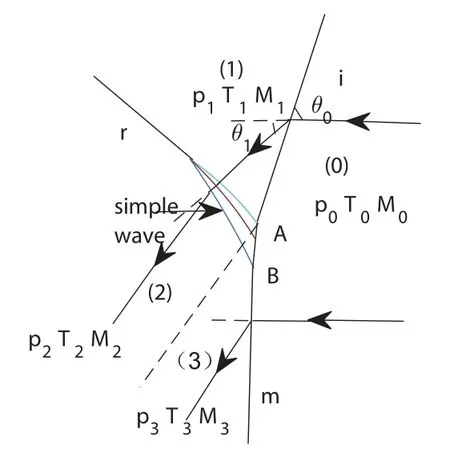
Figure 5
Next,we will show that the vNR is an unreasonable configuration for resolving the von Neumann paradox.In what follows,we also suppose that the flow field(0)satisfies=6/5,γ=and 1.18≤M0≤1.32,where Ms=M0sinθ0is the Mach number of the shock wave.
From Figure 5,we see that states(1)and(3)connect with state(0)via the incident shock wave i and the mach stem m,respectively,and state(2)connects with state(1)via a band of compression wave near the triple point.For convenience,we use the polar coordinates(P,θ),where P=.As is known,states(1)and(3)connect with state(0)via the I-polar defined by(2.22),and state(2)connects with state(1)via the epicycloid[23]

where ν(M)is given by the following expression:
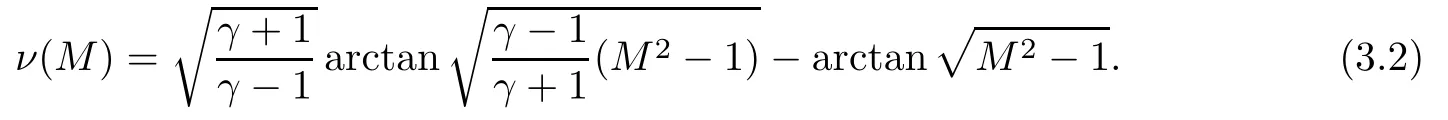
The total pressures on both sides of the compression wave are the same,hence

Theorem 3.1When the flow field(0)satisfiesand 1.18≤M0≤1.32,the vNR is an unreasonable configuration for resolving the von Neumann paradox,where Ms=M0sinθ0is the Mach number of the shock wave.
ProofOn the basis of the above analysis,if we can prove that the I-polar defined by(2.22)cannot intersect with the epicycloid defined by(3.4)when(see Figure 6),the proof of Theorem 3.1 is finished.
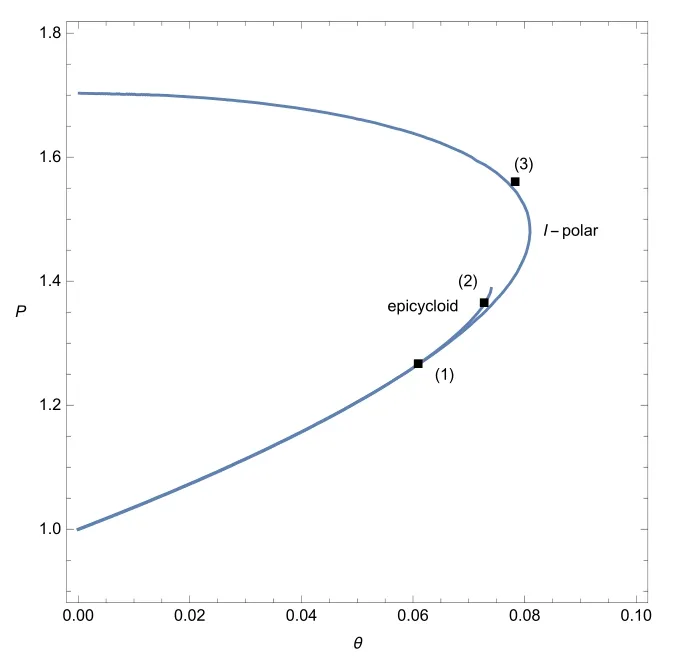
Figure 6 (=,γ=,M0=1.25)
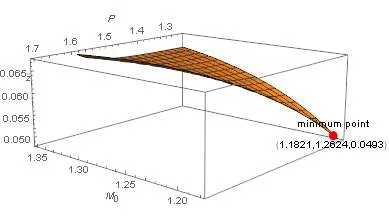
Figure 7

4 Reasonableness of GR to Resolve the von Neumann Paradox
In order to resolve the von Neumann paradox,Guderley[8]proposed a modified Mach reflection.He added a centered expansion fan and a supersonic path behind the triple point.Many researchers have supported the above idea through experiment,numerical calculation or theoretical analysis[11–20].This type of reflection configuration is now referred to as GR(see Figure 8).Next,we will show that GR is a reasonable configuration for resolving the von Neumann paradox.In what follows,we also suppose that the flow field(0)satisfiesand 1.18≤M0≤1.32,where Ms=M0sinθ0is the Mach number of shock wave.

Figure 8
According to the oblique shock theory,we have
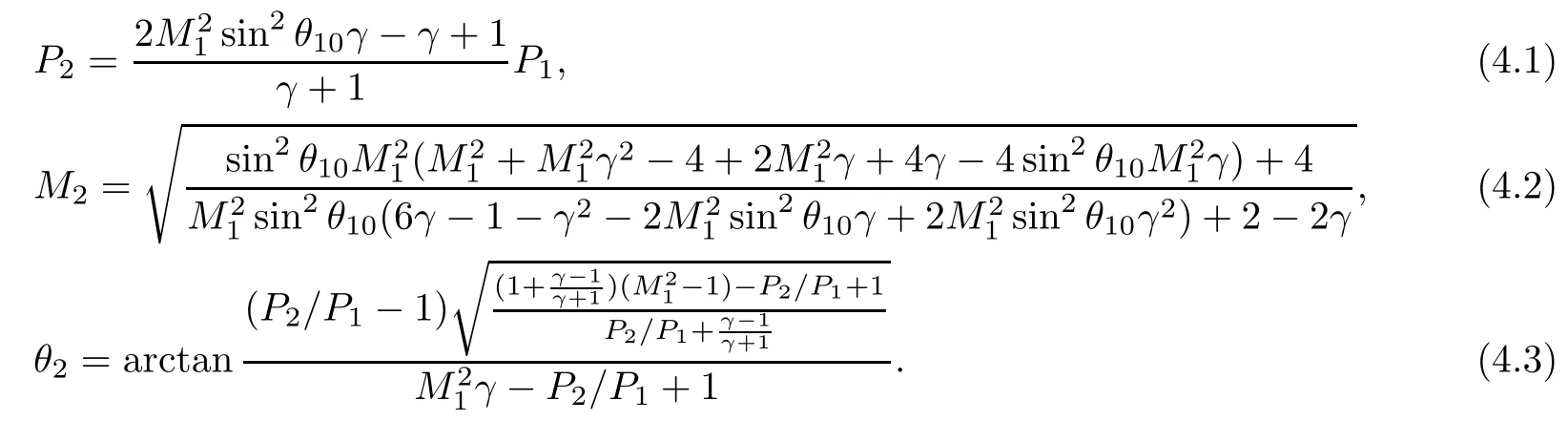
For our convenience,we use the polar coordinates(P,θ),whereAs is well known,states(1)and(4)connect with state(0)via the I-polar defined by(2.22),state(2)connects with state(1)via the R-polar defined by(2.24),and state(3)connects with state(2)via the epicycloid[23]
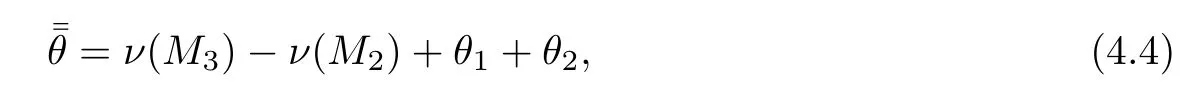
where ν(M)is given by the following expression:
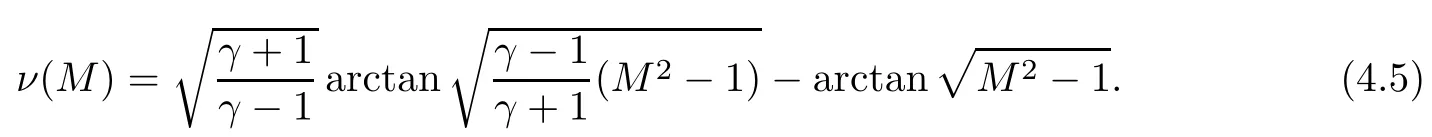
The total pressures on both sides of the compression wave are the same,hence

For closing the 4 wave theory,we require the following:

In virtue of(4.4)–(4.8),we have

From Figure 8,we know that on both sides of the slip line,P3=P4,where(i=3,4).
Theorem 4.1When the flow field(0)satisfiesand 1.18≤M0≤1.32,the GR is a reasonable configuration for resolving the von Neumann paradox,where Ms=M0sinθ0is the Mach number of the shock wave.
ProofOn the basis of the above analysis,if we can prove that the I-polar defined by(2.22)can intersect with the epicycloid defined by(4.9)(see Figure 9),the proof of Theorem 4.1 is finished.
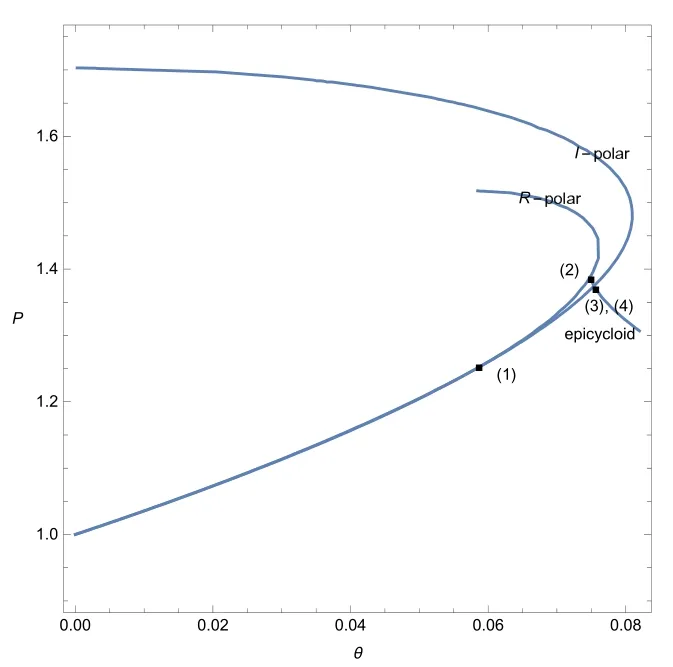
Figure 9 (=,γ=,M0=1.25)

Figure 10
From(4.9),we get
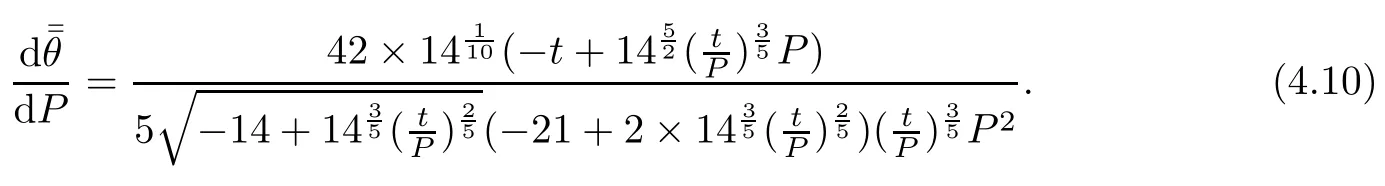
Solving a nonlinear programming problem

This finishes the proof of Theorem 4.1. □
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2021年3期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2021年3期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- ANALYSIS OF THE GENOMIC DISTANCE BETWEEN BAT CORONAVIRUS RATG13 AND SARS-COV-2 REVEALS MULTIPLE ORIGINS OF COVID-19?
- DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF A DELAYED HIV INFECTION MODEL WITH CTL IMMUNE RESPONSE AND ANTIBODY IMMUNE RESPONSE?
- BILINEAR SPECTRAL MULTIPLIERS ON HEISENBERG GROUPS?
- ON SCHWARZ-PICK TYPE INEQUALITY FOR MAPPINGS SATISFYING POISSON DIFFERENTIAL INEQUALITY?
- EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF THE GLOBAL L1 SOLUTION OF THE EULER EQUATIONS FOR CHAPLYGIN GAS?
- UNIQUENESS OF THE INVERSE TRANSMISSION SCATTERING WITH A CONDUCTIVE BOUNDARY CONDITION?
