拖拉機液壓傳動系統特性模型修正與參數辨識
程 準,魯植雄
拖拉機液壓傳動系統特性模型修正與參數辨識
程 準1,魯植雄2
(1. 南京林業大學汽車與交通工程學院,南京 210037;2. 南京農業大學工學院,南京 210031)
精準描述無級變速系統特性是拖拉機動力裝置設計和控制策略制定的前提,是節能減排和動力提高的關鍵。為解決拖拉機常用無級變速系統特性隨工況變化而導致原理論模型精度受限問題,該研究對受工況影響最為顯著的液壓傳動系統的調速和效率特性進行研究。采用臺架試驗獲取液壓傳動系統特性的樣本數據,基于偏最小二乘法對比不同工況對調速和效率特性的影響,結合原理論模型和改進的模擬退火算法,提出液壓傳動系統特性的模型修正及其參數辨識方法,并分別建立調速特性和效率特性的改進半經驗模型。結果表明,輸入轉速和輸出端負載轉矩對調速特性的影響程度分別為0.36和0.92;輸入轉速、輸出端負載轉矩和排量比對效率特性的影響程度分別為0.05、0.71和0.26;修正后模型參數較少,辨識容易,且精度高,估測值與實際值基本吻合(2參數調速特性半經驗模型的決定系數2為0.97、平均絕對百分比誤差為7.93%,5參數效率特性半經驗模型的決定系數2為0.93、平均絕對百分比誤差為2.50%)。研究以期為拖拉機等農業機械的動力傳動裝置的特性分析與評估、優化設計和控制策略制定提供依據和參考。
拖拉機;無級變速;調速特性;效率特性;參數辨識;半經驗模型
0 引 言
拖拉機是最為重要的農業作業機械之一[1-3],其作業工況惡劣復雜,這對拖拉機動力傳動系統提出了較高要求。液壓機械無級變速器(Hydro-Mechanical Continuously Variable Transmission,HMCVT)[4-6]和靜液壓傳動(Hydrostatic Transmission,HST)系統[7-9]是應用廣泛的先進拖拉機無級變速系統。
調速特性和效率特性是無級變速傳動系統的核心性能,對變速器的設計、性能評估以及控制策略制定等有著極為關鍵的作用。Macor等[10-11]研究指出HMCVT的優化設計復雜且具有較強的非線性特點,并采用粒子群算法進行多目標優化設計。Zhang等[12]采用非支配排序遺傳算法對行星排結構參數以及變速器傳動比進行優化。Sung等[13]采用網絡分析方法研究了12種HMCVT的調速特性。于今等[14]提出一種HMCVT系統,建立了調速特性和功率分流特性理論模型,并采用樣機試驗基于一定工況分析了系統調速特性以及效率特性等。李娟玲等[15]在Matlab環境下對研究所建立的調速特性和效率特性模型進行拖拉機HMCVT動態特性仿真分析與性能評估。Xia等[16]基于無級變速器工作原理推導得出了轉速、轉矩、效率等特性的變化關系式,并基于此分析了HMCVT的工作優點。Li等[17]采用改進的快速非支配排序遺傳算法對拖拉機HMCVT進行多目標優化,該方法具有相對更快的收斂速度。Dai等[18]研制了HMCVT多功能試驗臺,并對仿真模型進行了修正。王光明等[19]采用臺架試驗校準了基于Simulation X軟件搭建的HMCVT仿真平臺,并進行了特性分析與評估。孫景彬等[20]設計了一種遙控全向調平山地履帶拖拉機,整車傳動系統采用靜液壓驅動技術設計。此外,張明柱等[21-24]基于對HMCVT調速特性和效率特性的分析進而研究提升整車使用性能的控制策略。文獻[25]采用偏最小二乘法探究了不同類型因素對拖拉機無級變速系統動載荷特性的影響程度。文獻[26-27]采用改進的模擬退火算法分別進行了拖拉機驅動系統效率特性模型建立和車輛傳動系統優化設計研究。
綜上,目前對于無級變速系統(HST和HMCVT)已有一定的研究,且多集中于特性分析與評估、優化設計和控制策略制定。精準描述和解釋無級變速系統調速特性和效率特性是上述研究的必要前提。拖拉機無級變速系統由機械系統(主要包括定軸齒輪副和行星輪系)和液壓系統(主要為泵和馬達)組成。在傳動過程中,機械系統實際傳動特性與理論傳動特性基本吻合,但液壓系統受使用工況影響程度較大,這導致液壓系統實際傳動特性與理論傳動特性存在一定程度偏差。而在研發設計階段改進拖拉機無級變速系統特性模型精度較困難,只能在樣機制造后進行特性對比驗證,這會造成研發成本以及研發周期的增加。目前已有研究采用固定常數值或純理論表達式解釋系統特性,也有部分研究通過校準后的仿真模型進行特性數據獲取,但這些方法忽略了使用工況的影響,實測樣本數量有限,模型修正方法的應用效果有待改進,模型參數辨識的有效性相對較低等。
本文基于拖拉機液壓傳動系統試驗臺架,對其調速特性和效率特性分別開展多工況測試,采用偏最小二乘法分析特性影響因素,提出基于改進的模擬退火算法和理論模型的半經驗模型修正與參數辨識方法,對比驗證了修正后特性模型的精度,以期為拖拉機等農業機械及其他機械裝置中無級變速系統特性分析與評估、優化設計和控制策略制定提供直接性依據。
1 液壓傳動系統工作原理及試驗臺架
1.1 液壓傳動系統工作原理
液壓傳動系統總成主要包括泵、馬達、泵前齒輪、馬達后齒輪、離合器以及傳動軸。為匹配拖拉機HST和HMCVT的工作要求,本研究采用的傳動方案為:動力經柴油發動機輸出,通過泵前齒輪系統(傳動比分別為1和2)傳遞至“泵-馬達”系統,再通過馬達后齒輪系統(傳動比3)輸出(此時濕式離合器C0接合),見圖1。
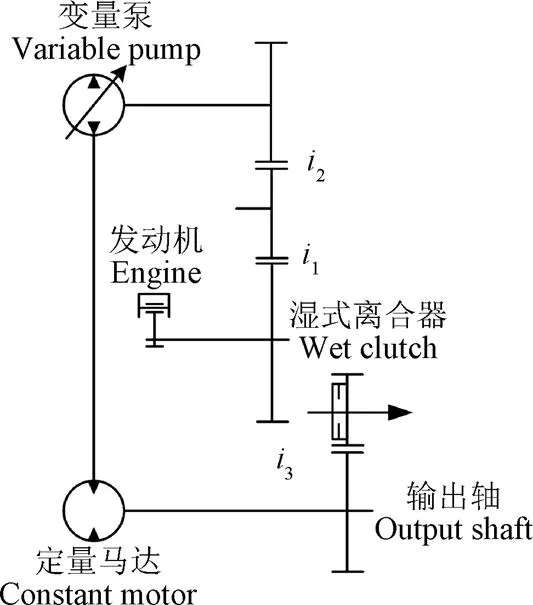
注:i1~i3為傳動比。
本文研究的變量泵-定量馬達系統采用容積調速回路,液壓傳動系統轉速和轉矩的關系式為:
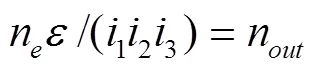

式中n為發動機轉速,r/min;為變量泵的排量比;0為其他傳動系總傳動比;n為液壓傳動系統輸出轉速,r/min;T、T、T分別為馬達輸出轉矩、液壓傳動系統輸出轉矩和拖拉機傳動系末端負載轉矩,N·m。
1.2 試驗臺架
本文研究所用的拖拉機泵-馬達系統為HPV-02型變量泵和HMF-02型定量馬達,排量皆為55 cm3/r,持續工作功率分別為75和93 kW,額定工作壓力為42 MPa,試驗臺架具體如圖2所示。
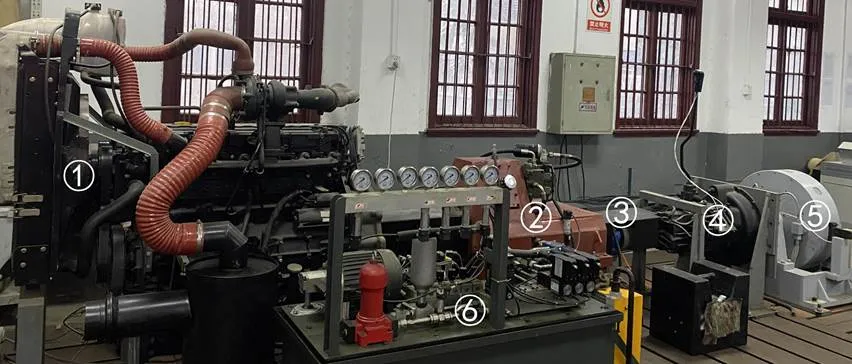
①發動機(道依茨TCD2013L062V)②液壓傳動系統③ZJ-5000A型轉速轉矩傳感器④副齒輪箱⑤DW250型電渦流測功機⑥液壓系統(實現潤滑、冷卻等功能)
發動機和液壓傳動系統的輸出端分別連接ZJ-2000A型和ZJ-5000A型轉速轉矩傳感器(中國江蘇蘭菱),其轉速量程分別為0~3 000和0~5 000 r/min,轉矩量程分別為0~2 000和0~4 000 N·m。對試驗臺架進行基本的性能測試試驗:固定發動機轉速,調節變量泵的排量比分別為0.200、0.250、0.300、0.375、0.500、0.625、0.750和1.000,測量發動機轉速和轉矩、液壓傳動系統轉速和排量比;固定發動機轉速、排量比和輸出端負載,濕式離合器連續接合和斷開3次,測量發動機轉速和輸出端負載。
根據試驗結果(見圖3),扭矩波動范圍約±2 N·m,轉速波動范圍約±3 r/min,輸出轉速與排量比正相關且排量比固定時輸出轉速平穩,試驗臺架的基本性能良好。
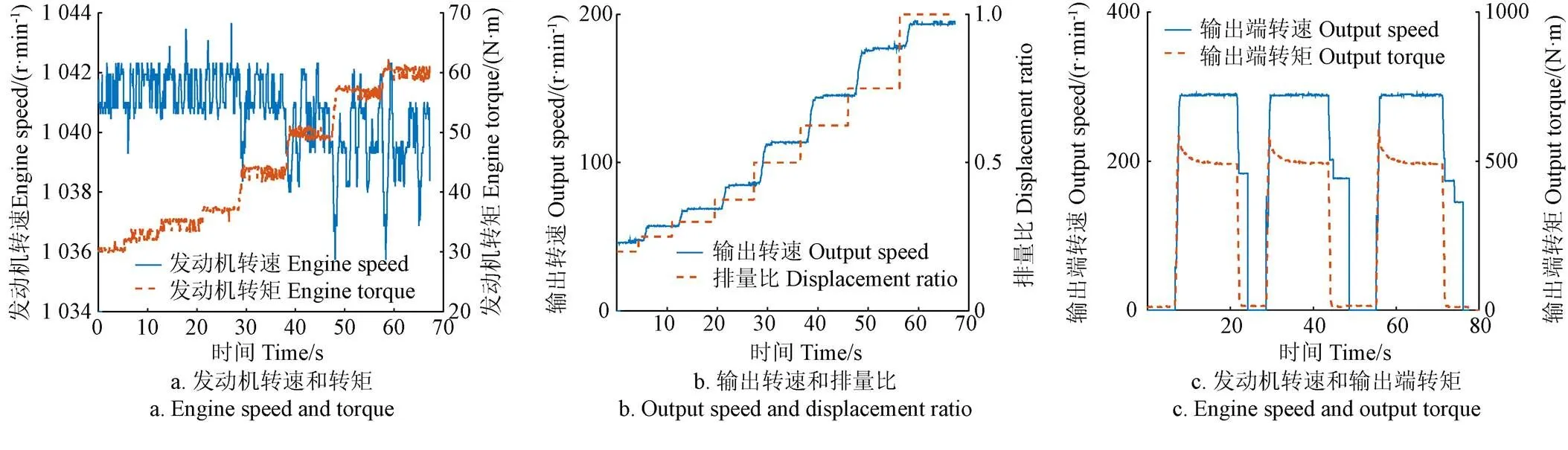
圖3 試驗臺架的基礎性能測試結果
2 調速特性及其影響因素分析
2.1 調速特性理論計算模型
采用傳動比變化特性表征調速特性。結合式(1),液壓傳動系統的傳動比(即調速特性理論計算模型)為

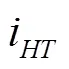
2.2 調速特性全因子試驗
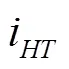
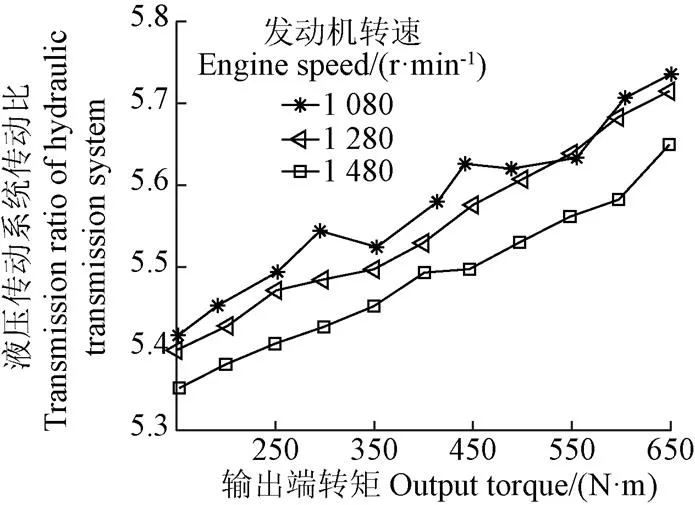
圖4 調速特性全因子試驗結果(排量比為1)
偏最小二乘法(Partial Least Squares,PLS)綜合了多元線性回歸、典型相關分析和主成分分析,能夠較好地解釋每一個自變量對因變量的影響程度。本文采用PLS以發動機轉速和輸出端負載轉矩為自變量對圖4結果進行分析,得到發動機轉速和輸出端負載轉矩對調速特性的影響程度(取絕對值)分別為0.36和0.92。輸出端負載轉矩對調速特性影響較大,而發動機轉速所引起的調速特性平均波動僅為1.65%,發動機轉速對調速特性影響較小,因此本文調速特性研究忽略發動機轉速影響。
2.3 輸出端負載轉矩和排量比的全因子試驗
由于柱塞式變量泵正偏和反偏時僅為系統旋轉方向不同,因此本文研究忽略變量泵正偏和反偏的影響,即不考慮排量比的正負性。試驗以輸出端負載轉矩(11水平,同2.2節)和排量比為因素,固定發動機轉速1 280 r/min。排量比變化范圍為0~1,排量比為0時,定量馬達不工作,因此除去該情況,以0.250為步長,考察0.500~0.750之間的調速特性規律,補充中間值0.625,共形成5個水平,分別為1.000、0.750、0.625、0.500和0.250。全因子試驗共獲得55組樣本數據,統計結果見圖5。
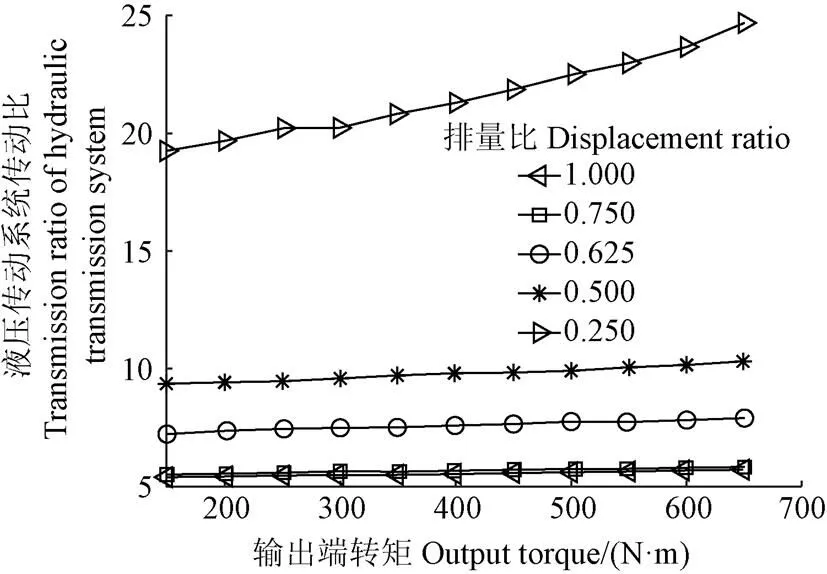
圖5 考慮負載轉矩和排量比的調速特性全因子試驗結果
觀察圖5可知,調速特性關于排量比和輸出端轉矩分別呈非線性和線性變化;相較于排量比,輸出端轉矩的影響程度較小;當排量比減小時,輸出端轉矩的影響程度也伴隨性增加。
3 效率特性及其影響因素分析
3.1 效率特性理論計算模型
常用的變量泵和定量馬達效率特性理論計算模型為
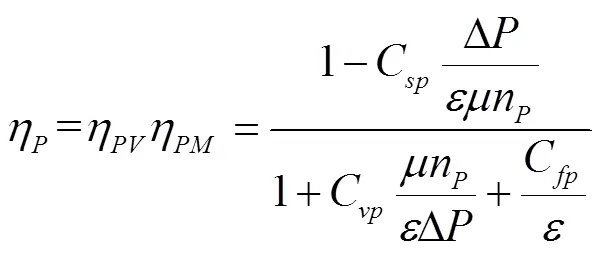

式中、、分別為變量泵效率、容積效率和機械效率;、、分別為變量泵層流泄漏系數、層流阻力系數和機械阻力系數;Δ為系統壓力差;為液壓油動力黏度;、分別為變量泵轉速和定量馬達轉速;、、分別為定量馬達效率、容積效率和機械效率;、、分別為定量馬達層流泄漏系數、層流阻力系數和機械阻力系數。
結合式(4)與式(5),效率特性主要與排量比、系統壓力差和輸入轉速有關。系統壓力差與負載轉矩正相關,所以效率特性與排量比、負載轉矩和輸入轉速有關。
3.2 效率特性全因子試驗
基于試驗臺架進行液壓傳動系統效率特性工況因素的全因子試驗。試驗因素取發動機轉速(3個水平,同2.2節)、輸出端負載轉矩(11個水平,同2.2節)和排量比(5個水平,同2.3節),共獲得165組樣本數據,統計結果見圖6。
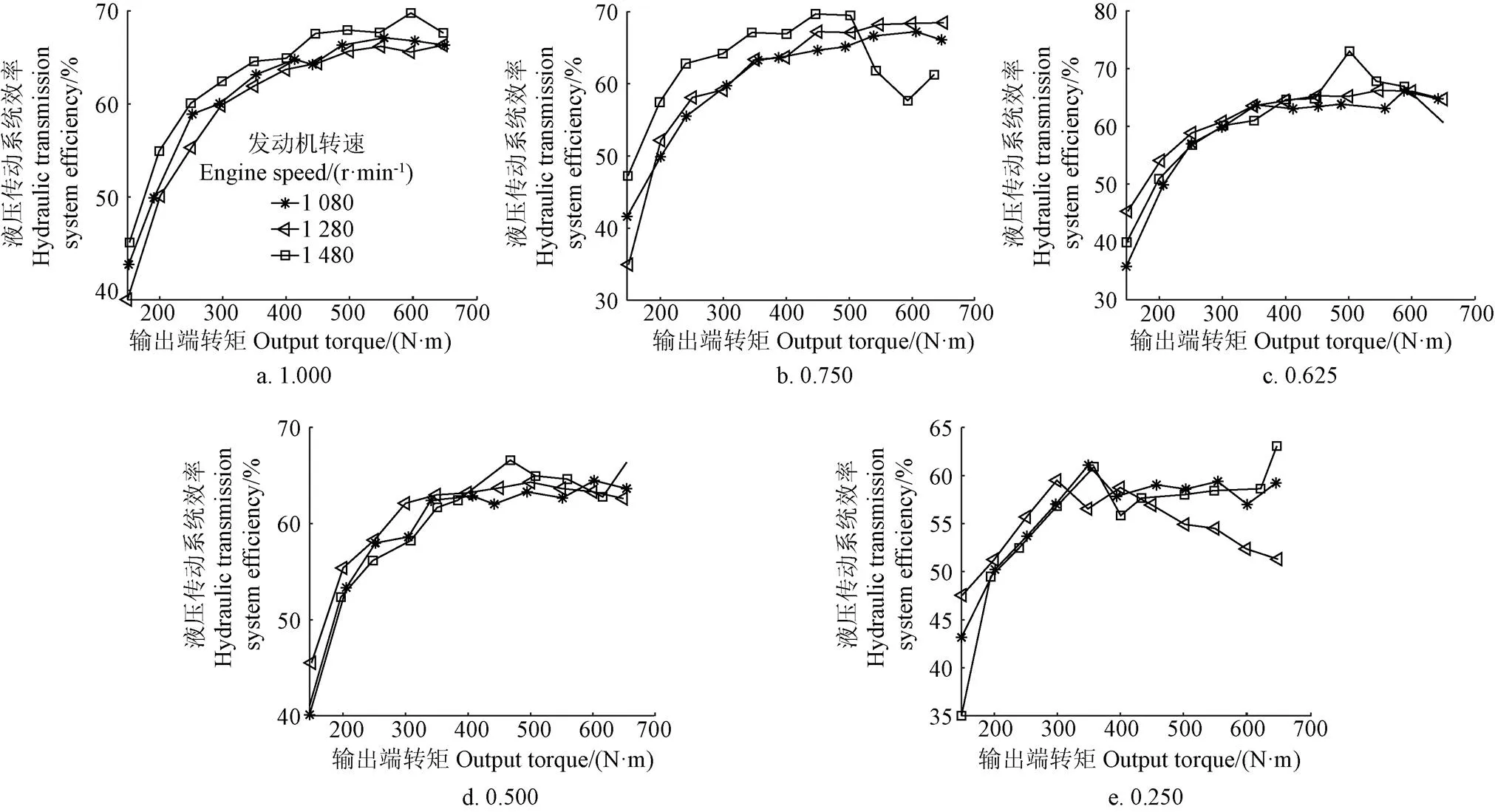
圖6 不同排量比下效率特性全因子試驗結果
采用PLS以發動機轉速、輸出端負載轉矩和排量比為自變量對圖6結果進行分析,得到發動機轉速、輸出端負載轉矩和排量比對效率特性的影響程度(取絕對值)分別為0.05、0.71和0.26。輸出端負載轉矩對效率特性影響程度大,其次為排量比,而發動機轉速影響較小。因此,本文效率特性研究忽略發動機轉速影響。
4 調速特性和效率特性模型修正與參數辨識
4.1 調速特性模型修正與參數辨識方法
結合調速特性實測數據(圖4和圖5)可知,同一排量比下液壓傳動系統傳動比與輸出端負載轉矩呈線性正相關,因此,可設調速特性修正模型為
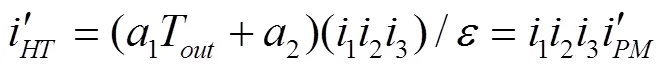
模擬退火算法應用Metropolis準則通過概率性方式獲取最優解,在決策變量較少的系統中應用效果較好[28]。參考文獻[29],考慮模擬退火算法的迭代過程主要依托于概率判定,且個體粒子的產生和擾動皆為隨機過程,本文對模擬退火算法建立外層循環,通過多次內層循環迭代獲取最終解。為進一步提高算法效率,減少計算次數,引入擾動次數自適應變化函數,見式(7)。
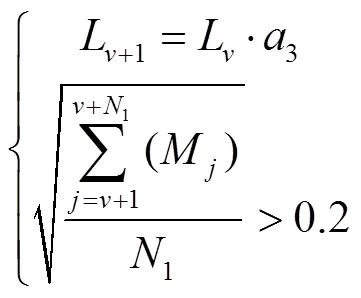
式中L為第次擾動函數周期性變更值;1為同一周期內層算法執行總次數;為周期數;M為同一周期第次內層算法執行后模型估測值和實測值的平均絕對百分比誤差;3為固定常數。
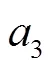
4.2 調速特性模型修正與參數辨識結果
外層循環200次的I-SA計算結果見圖7a,由圖7a可知第159次外層循環計算結果為最優解。內層循環的迭代過程見圖7b,根據最優解建立的液壓傳動系統調速特性模型計算結果見圖7c。
由圖7a可知,外層循環初期擾動次數相對較少,I-SA算法的解波動較大,隨后(擾動次數遞增)進入平穩狀態,外層循環第159次結果最優。由圖7b可知,該最優結果與實測值的平均絕對百分比誤差約7.93%。由圖7c可知,修正后模型與實際測量結果吻合度高,決定系數2約0.97,原理論模型與實際測量值之間的平均絕對百分比誤差約12.09%,修正后模型精度提升34.41%。
4.3 原理論效率特性模型參數辨識
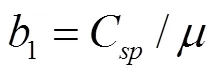
外層循環200次的I-SA算法結果見圖8a,由圖8a可知,第176次外層循環計算結果最優,內層循環的迭代過程見圖8b;根據最優解建立的液壓傳動系統效率特性模型計算結果見圖8c。

圖7 基于I-SA算法的調速特性修正模型參數辨識結果
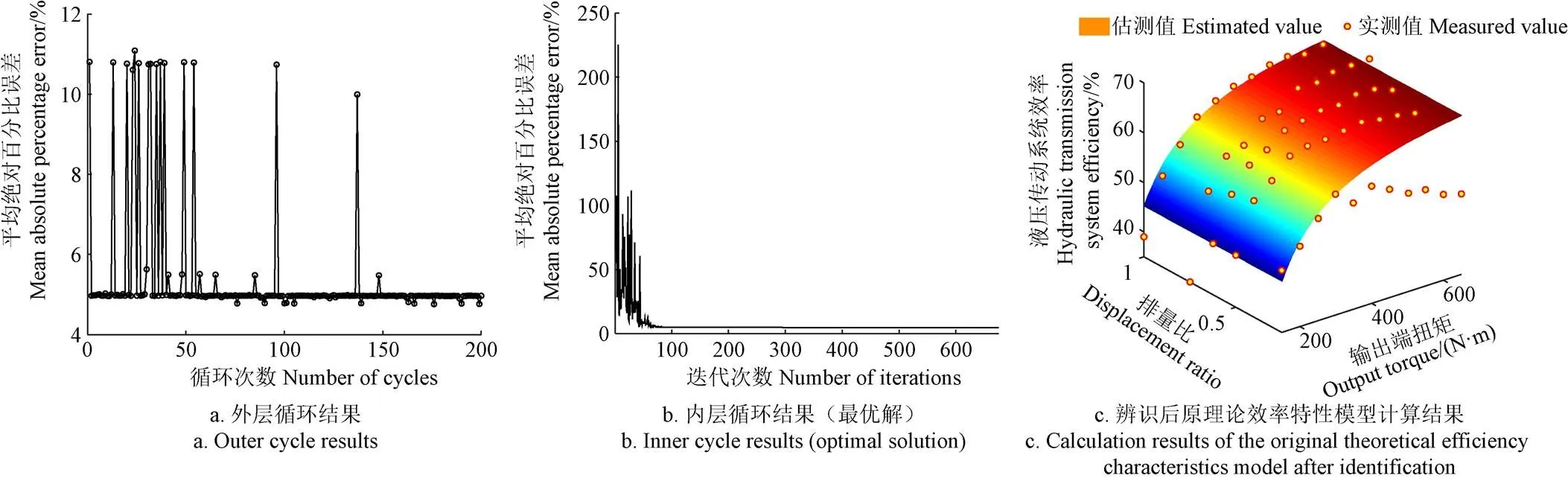
圖8 原理論效率特性模型參數辨識結果
由圖8a可知,外層循環初期擾動次數相對較少,I-SA算法的解波動較大,隨后(擾動次數遞增)進入平穩狀態。外層循環第176次結果最為優。由圖8b可知,內層循環初期的解波動明顯且數值較大,該最優結果與實測值的平均絕對百分比誤差約4.76%。由圖8c可知,辨識后原理論效率特性模型與實際測量結果吻合度一般,決定系數2約0.70,最大誤差約30.25%,辨識后原理論效率特性模型與實測結果有一定程度的誤差。
4.4 效率特性模型修正與對比
由于馬達為定量馬達,轉速影響可忽略,則式(5)輸出值基本僅由負載轉矩決定,且參數確定時模型單調性亦固定,因此定量馬達理論模型對效率特性變化的解釋有一定的局限性。變量泵理論模型(待辨識參數已合并)關于負載轉矩和排量比的偏微分分別為
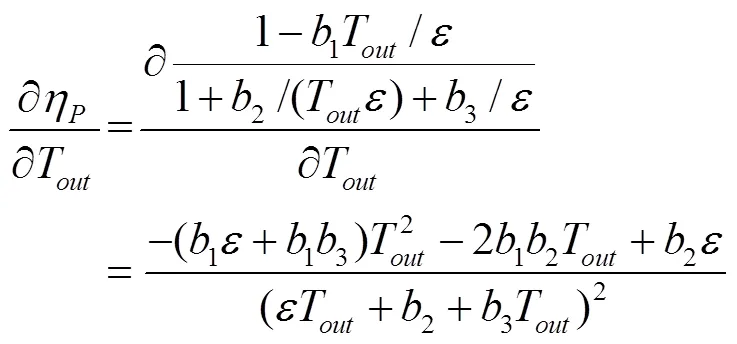
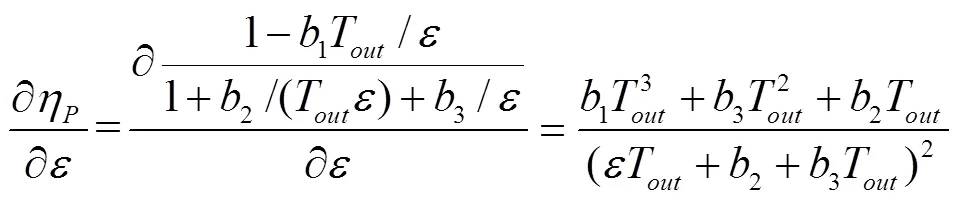
顯然式(8)和式(9)分母皆大于0,且隨排量比和負載轉矩增加而單調遞增。因此變量泵理論模型的變化特性基本由分子的變化規律所決定。結合試驗樣本數據以及PLS分析結果,負載轉矩和排量比皆與效率特性正相關,且隨負載轉矩和排量比的增大效率特性的變化率趨于平穩。式(8)和式(9)分子的最高階項分別為關于負載轉矩的2階項和3階項,因此分子的變化規律皆可設計為大于0且單調遞減(對應于效率特性遞增且變化率趨于平穩情況)。
綜上分析,在參數選擇合理的情況下,單獨的3參數變量泵理論模型可用來描述和解釋效率特性變化。采用4.1節的外層循環-I-SA算法對效率特性模型進行參數辨識,結果如下:外層循環第154次獲得最優解,平均絕對百分比誤差約13.92%,決定系數2約為?0.83,最大誤差約48.52%。
本文提出一種基于3參數理論模型的半經驗修正模型,先計算實際測量值與3參數理論模型估測值之間的誤差,再通過經驗方法枚舉出關于排量比的變化函數(作為不同類型的自變量)并進行相關系數分析,優選出相關系數最高的自變量并作為原理論模型的新增誤差補償項,進而形成4參數半經驗模型,其次計算實際測量值與4參數半經驗模型估測值之間的誤差,再通過經驗方法枚舉出關于負載轉矩的變化函數(作為不同類型的自變量)并進行相關系數分析,優選出相關系數最高的自變量并作為原理論模型的新增誤差補償項,進而形成5參數半經驗模型。改進半經驗修正模型建立方法流程見圖9。
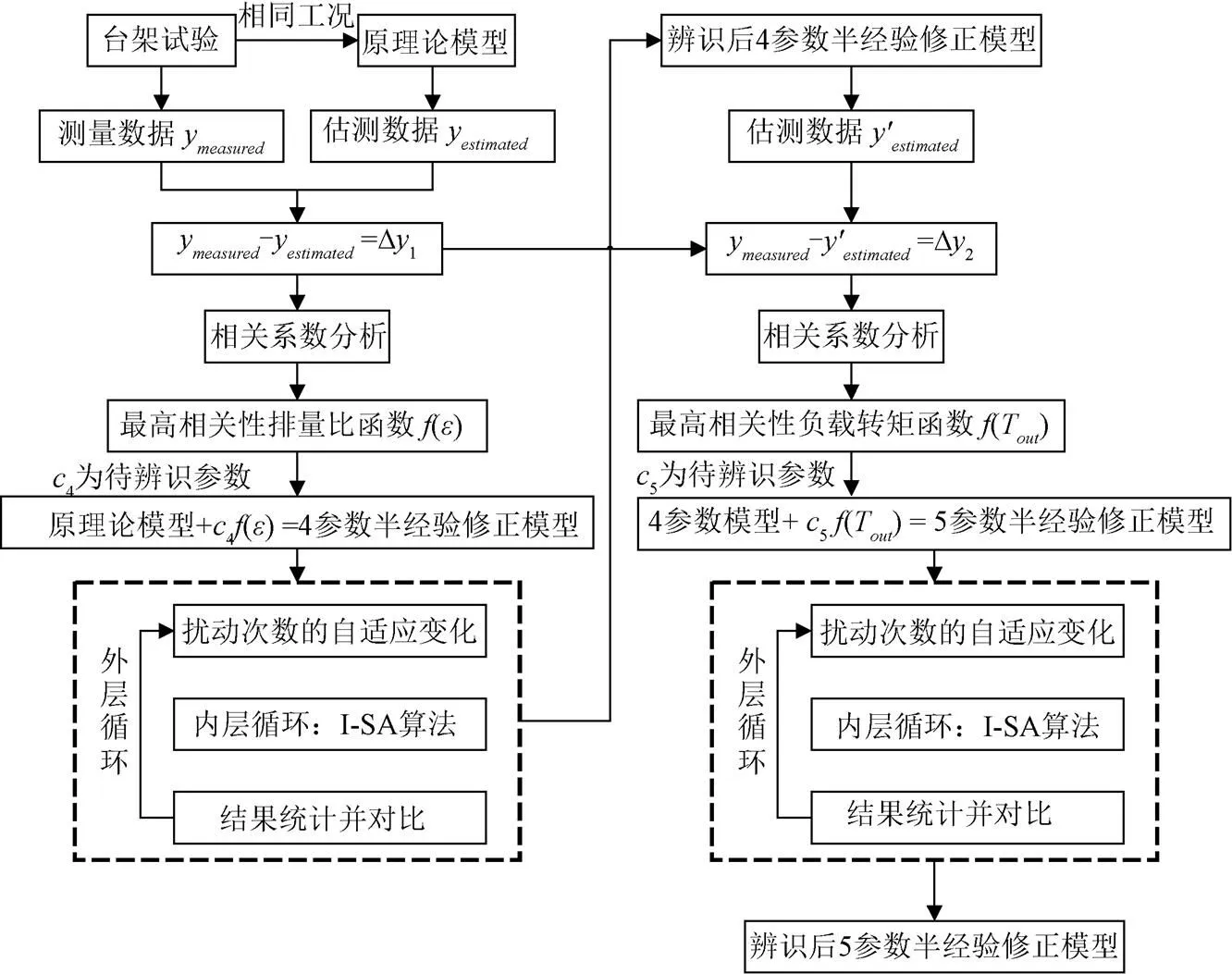
圖9 效率特性半經驗修正模型構建流程
本文研究以排量比和負載轉矩的冪函數(指數冪分別為1~3)、ln函數、exp函數和三角函數(sin、cos、tan)作為相關系數分析的自變量。原理論模型、3參數理論模型、4參數半經驗修正模型和5參數半經驗修正模型的辨識精度對比見表1。
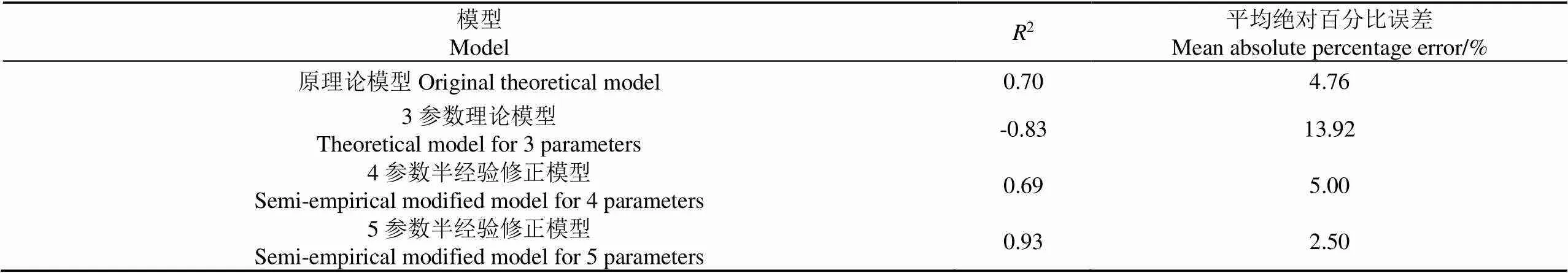
表1 不同模型辨識精度對比
由表1可知,本文提出的半經驗模型修正方法分2階段(階段1形成4參數半經驗修正模型,階段2形成5參數半經驗修正模型)進行持續性優化修正,第1階段引入關于排量比的相關函數,較原3參數理論模型平均絕對百分比誤差降低64.08%,決定系數提高183.13%;第2階段引入關于負載轉矩的相關函數,較第1階段修正模型(即4參數半經驗修正模型)平均絕對百分比誤差進一步降低50.00%,決定系數進一步提高34.78%。
5參數半經驗修正模型較原理論模型的平均絕對百分比誤差降低47.48%,決定系數提高32.86%。
5參數半經驗修正模型的辨識過程見圖10,其中外層循環200次的I-SA算法結果見圖10a,第138次外層循環計算結果最優,內層循環(即I-SA算法)的迭代過程見圖10b,根據最優解建立的液壓傳動系統效率特性模型計算結果見圖10c。
綜合對比圖8c和圖10c,修正后半經驗模型在估測精度以及液壓傳動系統效率特性變化規律的描述和解釋上有明顯提高。本文研究對象的效率特性在大排量和大負載工況下具有較大值,并往中小排量和中小負載工況呈梯度性非線性逐步下降。修正后模型對于小排量(排量比為0.25)工況下效率特性變化依舊有著高度吻合的解釋,而原理論模型解釋性差。
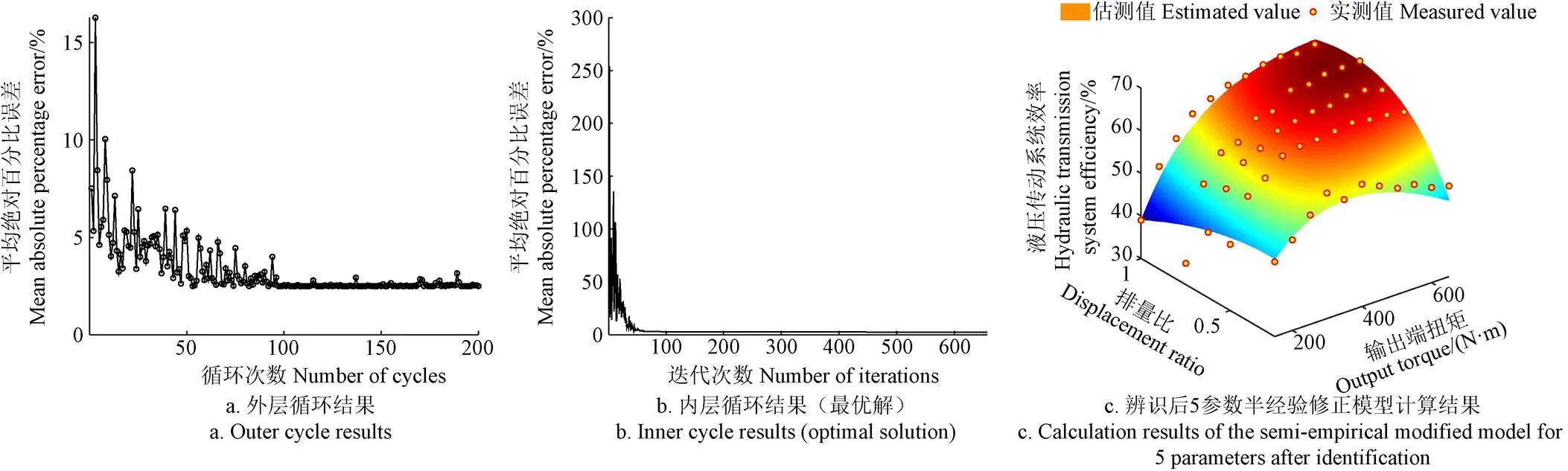
圖10 效率特性的5參數修正模型參數辨識結果
5 結 論
1)基于液壓傳動系統調速特性臺架試驗樣本數據,調速特性除與排量比有明顯關系外,還主要受負載轉矩的影響。修正后液壓傳動系統調速特性模型應為原理論模型與負載扭矩1階線性模型的乘積組合,修正后模型精度提升明顯,提高34.41%。
2)基于液壓傳動系統效率特性臺架試驗樣本數據,效率特性主要與排量比和負載轉矩有關。本文提出的改進半經驗修正模型建立方法有效修正了原理論模型,所建立的5參數半經驗修正模型的平均絕對百分比誤差較原理論模型降低47.48%,決定系數2達到0.93(提升32.86%),模型表征規律與實際測量值高度吻合,即在大排量和大負載工況下具有較大值,并往中小排量和中小負載工況呈梯度性非線性逐步下降,降幅逐步增加。
[1] Kalinichenko A, Havrysh V, Hruban V. Heat recovery systems for agricultural vehicles: utilization ways and their efficiency[J]. Agriculture, 2018, 8(12): 199.
[2] Cavallo E, Ferrari E, Bollani L, et al. Attitudes and behaviour of adopters of technological innovations in agricultural tractors: A case study in Italian agricultural system[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2014, 130: 44-54.
[3] 謝斌,武仲斌,毛恩榮. 農業拖拉機關鍵技術發展現狀與展望[J]. 農業機械學報,2018,49(8):1-17.
Xie Bin, Wu Zhongbin, Mao Enrong. Development and prospect of key technologies on agricultural tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(8): 1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 錢煜,程準,魯植雄. 重型拖拉機HMCVT的5因素換段品質逐步回歸優化研究[J]. 南京農業大學學報,2020,43(3):564-573.
Qian Yu, Cheng Zhun, Lu Zhixiong. Study on stepwise optimization of shift quality of heavy-duty tractor HMCVT based on five factors[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2020, 43(3): 564-573. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Zhao J, Xiao M H, Bartos P, et al. Dynamic engagement characteristics of wet clutch based on hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(5): 1377-1389.
[6] 于今,陳華,劉駿豪. 液壓機械無級變速器的變論域模糊PID速比跟蹤控制[J]. 中國機械工程,2019,30(10):1226-1232.
Yu Jin, Chen Hua, Liu Junhao. Speed ratio follow-up control of HMCVT based on variable universe fuzzy PID[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 30(10): 1226-1232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Liu Z, Zhang G, Chu G, et al. Design matching and dynamic performance test for an HST-Based drive system of a hillside crawler tractor[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(5): 466.
[8] Cheng Z, Lu Z X. Research on load disturbance based variable speed PID control and a novel denoising method based effect evaluation of HST for agricultural machinery[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(10): 960.
[9] 任軍華,尹叢勃,杜妍辰,等. 農用拖拉機HST與動力系統特性研究[J]. 農業裝備與車輛工程,2021,59(3):25-30.
Ren Junhua, Yin Congbo, Du Yanchen, et al. Study on characteristics of HST and power system of agricultural tractor[J]. Agricultural Equipment & Vehicle Engineering, 2021, 59(3): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] Macor A, Rossetti A. Optimization of hydro-mechanical power split transmissions[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2011, 46(12): 1901-1919.
[11] Rossetti A, Macor A. Multi-objective optimization of hydro-mechanical power split transmissions[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2013, 62: 112-128.
[12] Zhang Q, Sun D Y, Qin D T. Optimal parameters design method for power reflux hydro-mechanical transmission system[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part D-Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2019, 233(3): 585-594.
[13] Sung D, Hwang S, Kim H. Design of hydromechanical transmission using network analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part D-Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2005, 219(D1): 53-63.
[14] 于今,吳超宇,胡宇航,等. 新型混合式液壓機械復合變速器的特性分析[J]. 江蘇大學學報(自然科學版),2016,37(5):507-511.
Yu Jin, Wu Chaoyu, Hu Yuhang, et al. Characteristic analysis of a new compound HMCVT[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 37(5): 507-511. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李娟玲,劉連濤,肖茂華,等. 液壓機械無級變速箱動態特性研究[J]. 機械強度,2017,39(1):14-19.
Li Juanling, Liu Liantao, Xiao Maohua, et al. Research on dynamic characteristics of hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2017, 39(1): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] Xia Y, Sun D Y. Characteristic analysis on a new hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission system[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2018, 126: 457-467.
[17] Li J, Zhai Z Q, Song Z S, et al. Optimization of the transmission characteristics of an HMCVT for a high-powered tractor based on an improved NSGA-II algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part D-Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2022, 236(13): 09544070211067961.
[18] Dai H Z, Wan L R, Zeng Q L, et al. Method and test bench for hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission based on multi-level test and verification[J]. Machines, 2021, 9(12): 358.
[19] 王光明,朱思洪,史立新,等. 拖拉機液壓機械無級變速箱效率特性的仿真與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2013,29(15):42-48.
Wang Guangming, Zhu Sihong, Shi Lixin, et al. Simulation and experiment on efficiency characteristics of hydraulic mechanical continuously variable transmission for tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(15): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 孫景彬,楚國評,潘冠廷,等. 遙控全向調平山地履帶拖拉機設計與性能試驗[J]. 農業機械學報,2021,52(5):358-369.
Sun Jingbin, Chu Guoping, Pan Guanting, et al. Design and performance test of remote control omnidirectional leveling hillside crawler tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(5): 358-369. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 張明柱,王全勝,白東洋,等. 基于拖拉機整機效率最大化的液壓機械無級變速規律[J]. 農業工程學報,2016,32(21):74-78.
Zhang Mingzhu, Wang Quansheng, Bai Dongyang, et al. Speed changing law of hydro-mechanical CVT based on maximum efficiency of tractors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(21): 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 張明柱,王界中,王建華,等. 提高燃油經濟性的拖拉機變速控制策略[J]. 農業工程學報,2020,36(1):82-89.
Zhang Mingzhu, Wang Jiezhong, Wang Jianhua, et al. Speed changing control strategy for improving tractor fuel economy[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(1): 82-89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 夏光,夏巖,唐希雯,等. 采用滑轉率-阻力區間劃分法的拖拉機雙流傳動系統調速控制[J]. 農業工程學報,2021,37(3):47-55.
Xia Guang, Xia Yan, Tang Xiwen, et al. Speed regulation control of the dual-flow transmission system for a tractorusing slip rate-resistance interval division[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(3): 47-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 楊樹軍,褚捷豪,彭增雄,等. 液壓機械無級變速裝載機工況在線識別方法[J]. 農業工程學報,2022,38(4):1-11.
Yang Shujun, Chu Jiehao, Peng Zengxiong, et al. Online identification method for wheel loader working conditions with hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(4): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] Cheng Z, Lu Z X. Research on dynamic load characteristics of advanced variable speed drive system for agricultural machinery during engagement[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(2): 161.
[26] Cheng Z, Zhou H D, Lu Z X. A novel 10-parameter motor efficiency model based on I-SA and its comparative application of energy utilization efficiency in different driving modes for electric tractor[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(3): 362.
[27] Cheng Z. I-SA algorithm based optimization design and mode-switching strategy for a novel 3-axis-simpson dual-motor coupling drive system of PEV[J]. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2021, 12(4): 221.
[28] Cheng Z, Lu Z X. Research on the PID control of the ESP system of tractor based on improved AFSA and improved SA[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 148: 142-147.
[29] Cheng Z, Lu Z X. Two novel reconstruction methods of sparsity adaptive adjustment for road roughness compressive signal based on I-SA and GSM[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 171: 108915.
Model modification and parameter identification of tractor hydraulic transmission system characteristics
Cheng Zhun1, Lu Zhixiong2
(1.,,210037,;2.,,210031,)
An accurate identification of a continuously variable transmission (CVT) system can greatly contribute to the tractor power device and the control strategy, particularly to the energy saving and emission reduction for the power improvement. This study aims to improve the accuracy of the theoretical model, due to the variation of the characteristics for the common continuously variable speed system with the working conditions. Taking hydrostatic transmission (HST) and hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission (HMCVT) as the research objects, the speed regulation and efficiency characteristics of the hydraulic transmission system were determined under the working conditions (including engine speed, output load torque, and displacement ratio). The full-factor test was adopted to comprehensively analyze the hydraulic transmission system characteristics. Among them, the engine speed, output load torque, and displacement ratio were set at the 3-, 11-, and 5-levels, respectively. The samples of hydraulic transmission system characteristics were obtained by the bench test (including the test sample data of speed regulation characteristics and efficiency characteristics). The test bench was mainly composed of the variable pump, constant motor, diesel engine, wet clutch, several groups of gear devices and transmission shafts, as well as the speed torque sensors and the load device. Before that, the basic performance of the test bench was tested by the variable pump displacement ratio adjustment test (Test 1) and wet clutch test (Test 2). The influence degree of working conditions was compared using the partial least squares (PLS) method. Furthermore, the parameter identification and model correction of the hydraulic transmission system characteristics were proposed to combine the original theoretical model with the improved simulated annealing (I-SA). The simulated annealing was used as the inner cycle to construct the outer cycle. The disturbance number of the simulated annealing was improved to introduce an adaptive variation function. The results show that the speed regulation characteristics were closely related to the displacement ratio, depending mainly on the load torque, according to the bench test data from the hydraulic transmission system. PLS analysis showed that the influence degrees of the engine speed and output load torque (absolute value) were 0.36 and 0.92, respectively. The revised characteristics model of hydraulic transmission system speed regulation was the optimal combination of the original theoretical model and the first-order linear model of load torque. The accuracy of the revised model was significantly improved (34.41%) than before. The efficiency characteristics were mainly related to the displacement ratio and load torque, according to the bench test data of efficiency characteristics for the hydraulic transmission system. Among them, the influence degrees (absolute value) of the engine speed, output load torque, and displacement ratio were 0.05, 0.71, and 0.26, respectively. There was the limited accuracy of the original 6-parameter theoretical model (the mean absolute percentage error about 4.76%, and2about 0.70) after parameter identification, indicating the different overall change from the actual measurement. By contrast, the new semi-empirical modified model can be expected to effectively modify the original theoretical model. The mean absolute percentage error of the newly-developed 5-parameter semi-empirical modified model was improved by 47.48% than before, where the2was 0.93 (improved by 32.86%). The characterization of the new model was highly consistent with the actual measured values. Specifically, there was a large value in the conditions of large displacement and large load, indicating a divergent decline in the conditions of medium or small displacement and load, i.e., the gradually increased decline. Therefore, the I-SA algorithm can be expected to effectively serve as the engineering practice by introducing the outer cycle and the adaptive change of disturbance number. The reasonable design and control strategy can then be achieved in the correct speed regulation and efficiency characteristics model for the better performance of the tractor CVT system.
tractor; CVT; speed regulation characteristics; efficiency characteristics; parameter identification; semi-empirical model
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.19.004
S232.3
A
1002-6819(2022)-19-0033-08
程準,魯植雄. 拖拉機液壓傳動系統特性模型修正與參數辨識[J]. 農業工程學報,2022,38(19):33-41.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.19.004 http://www.tcsae.org
Cheng Zhun, Lu Zhixiong. Model modification and parameter identification of tractor hydraulic transmission system characteristics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(19): 33-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.19.004 http://www.tcsae.org
2022-04-26
2022-06-21
國家自然科學基金項目(52105063)
程準,博士,研究方向為車輛系統動力學與控制、農業機械裝備。Email:chengzhun38@163.com

