Does delaying ureteral stent placement lead to higher rates of preoperative acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy?
INTRODUCTION
Acute renal colic is one of the most common reasons for pregnant women to be hospitalized for non-obstetric reasons. The incidence of renal colic during pregnancy is about 1 in 1500[1]. Renal colic may cause adverse maternal and fetal outcomes, such as premature delivery, premature rupture of membranes, urinary tract infection and sepsis, pregnancy loss and preeclampsia[2-4].
The main causes of renal colic in pregnancy are urinary stones and hydronephrosis.Several anatomical and physiological changes occur during pregnancy and may affect the entire urinary system. Antenatal hydronephrosis and hydroureter are the result of compression of the ureter at the pelvic brim due to the growing uterus and smooth muscle relaxation induced by elevated progesterone levels[5,6]. Moreover, the secretion of placental 1, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol and parathyroid hormone are reduced, resulting in transient hypercalciuria during pregnancy. These substances in the urine combine with each other and obstruction of the urinary tract leads to the deposition of crystals in the urine in the poorly drained area, thereby forming stones[7]. The above may cause acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy. Acute pyelonephritis is a manifestation of infection of the upper urinary tract and kidneys.Most cases of pyelonephritis occur during the second and third trimesters. Pregnant women are at risk for both medical and obstetric complications resulting from pyelonephritis.
越來越多的教師已經開始嘗試使用新型電子軟件來布置英語作業,利用免費的英語學習APP拓展資源、輔助教學,使用軟件聽音模仿的比例高達83.94%。(見表1-4)
The clinical features of acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy include fever (> 38°C), chills, low back pain, nausea, vomiting, or costal and spinal angle pain, with or without typical symptoms of cystitis. Pregnant women require special attention when they develop acute pyelonephritis. Acute pyelonephritis not only adversely affects pregnant women, but also causes anemia, renal insufficiency or respiratory insufficiency; It also affects the fetus[8].
Conservative treatment is effective in 70%-80% of patients with renal colic during pregnancy[9]. Pregnant women who develop a stone may need three types of medication: painkillers, antibiotics and anesthesic drugs. Patients with simple renal colic without other complications should be given antispasmodic, analgesic and antiinfective treatment, and if necessary, uterine contraction suppression treatment should be given[10]. However, when conservative treatment is ineffective, active surgical intervention is necessary[5]. Surgical methods include ureteroscopy, ureteroscopic lithotripsy, surgery, and nephrostomy[1].
At present, few studies have investigated the relationship between operation time and the clinical outcome of the mother and child. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to compare the effects of early surgery (less than 48 h from onset of renal colic to surgery) or delayed surgery (more than 48 h from onset of renal colic to surgery) in patients diagnosed with renal colic during pregnancy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
A retrospective study of all pregnant women with the diagnosis of renal colic admitted to The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2019 was performed. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was reviewed and approved by the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University Institutional Review Board (Approval No. V1.0). Diagnosis of renal colic was as follows: left or right low back pain, with or without fever, frequent urination, urgency, hematuria,obvious percussive pain in the kidney area, and B-ultrasound confirmed stones or hydronephrosis on the affected side. The patients diagnosed with renal colic met the following criteria: percussion pain in the renal area, and B-ultrasound revealed hydronephrosis. Two hundred and twelve patients were diagnosed with renal colic.Patients with complications (such as diabetes, hypertension, immune system diseases,) were excluded. All patients initially underwent conservative treatment, including hydration, pain relief and antibiotic treatment if necessary. If conservative treatment failed, patients with persistent renal colic, febrile urinary tract infection, sepsis, acute renal failure, or single kidney with obstruction, surgical intervention was necessary.The surgical method evaluated in this study was ureteral stent placement. Ureteroscopy was generally performed before ureteral stent placement. Among the 102 eligible patients who underwent surgery, two patients did not have follow-up data.Therefore a total of 100 patients were included in the study.
Time to ureteral stent placement (TTU), was defined as the period from diagnosis of renal colic to surgery. The median TTU in our hospital was 48 h. The patients were divided into two groups according to the TTU, the early TTU (< 48 h,= 42) and delayed TTU (≥ 48 h,= 58) groups. The demographic (age, BMI [body mass index],gestation) and clinical characteristics including history of stones, laboratory examination such as white blood cell (WBC) count and C-reactive protein (CRP),imaging data (stone size, stone location, and hydronephrosis), clinical outcome(PANP, preoperative fetal obstetric complications, UTI after surgery, newborn weight,cesarean section rate and preterm delivery), length of hospital stay (LOS) and total charges were compared between the two groups. Acute pyelonephritis was suggested by the presence of flank pain, nausea/vomiting, fever (> 38 °C or 100.4 °F), and/or costovertebral angle tenderness, with or without typical symptoms of cystitis, or was confirmed by the presence of bacteriuria in the setting of these symptoms. The diagnosis was confirmed if the patient met the following three criteria: renal colic,fever, and positive urine culture. Once acute pyelonephritis was diagnosed, broad spectrum intravenous antibiotics (Cephalosporin-based therapy) were administered immediately for about 7-10 d after surgery. If a susceptibility test was carried out before treatment, we used antibiotics sensitive to bacteria according to the susceptibility test results. Fetal obstetric complications were defined as premature delivery,threatened premature delivery, premature rupture of membranes, or fetal loss. UTI after surgery was defined as patients who underwent surgery for renal colic and were re-admitted to the hospital for UTI after surgery.
Parametric distributed numerical data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.Non-parametric distributed continuous variables are presented as interquartile ranges(Q1, Q3). Categorical data are presented as numbers and percentages. T tests and Mann-Whitney U tests were used to evaluate the difference between quantitative measurements that had non-parametric distribution. Chi-squared tests were used for categorical data. The associations of preoperative and operative characteristics with the TTU and with acute pyelonephritis were evaluated using Pearson χtests.
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS 26.0 software (SPSS, Mac). The α value was set at 0.05, and all statistical tests were 2-tailed. A logistic regression model was used to test whether the risk factors were related to the outcome variables.
RESULTS
Among 212 patients with renal colic in pregnancy, 102 patients underwent surgery.Due to missing data in 2 women, 100 pregnant women with renal colic were included in this study. If conservative treatment failed or the patient developed any of the following conditions, surgical intervention was required: clinical indications included all situations that require emergency intervention for patients with non-pregnant stones, such as isolated renal obstruction, bilateral obstruction, deterioration of renal function, intractable symptoms and related urosepsis.
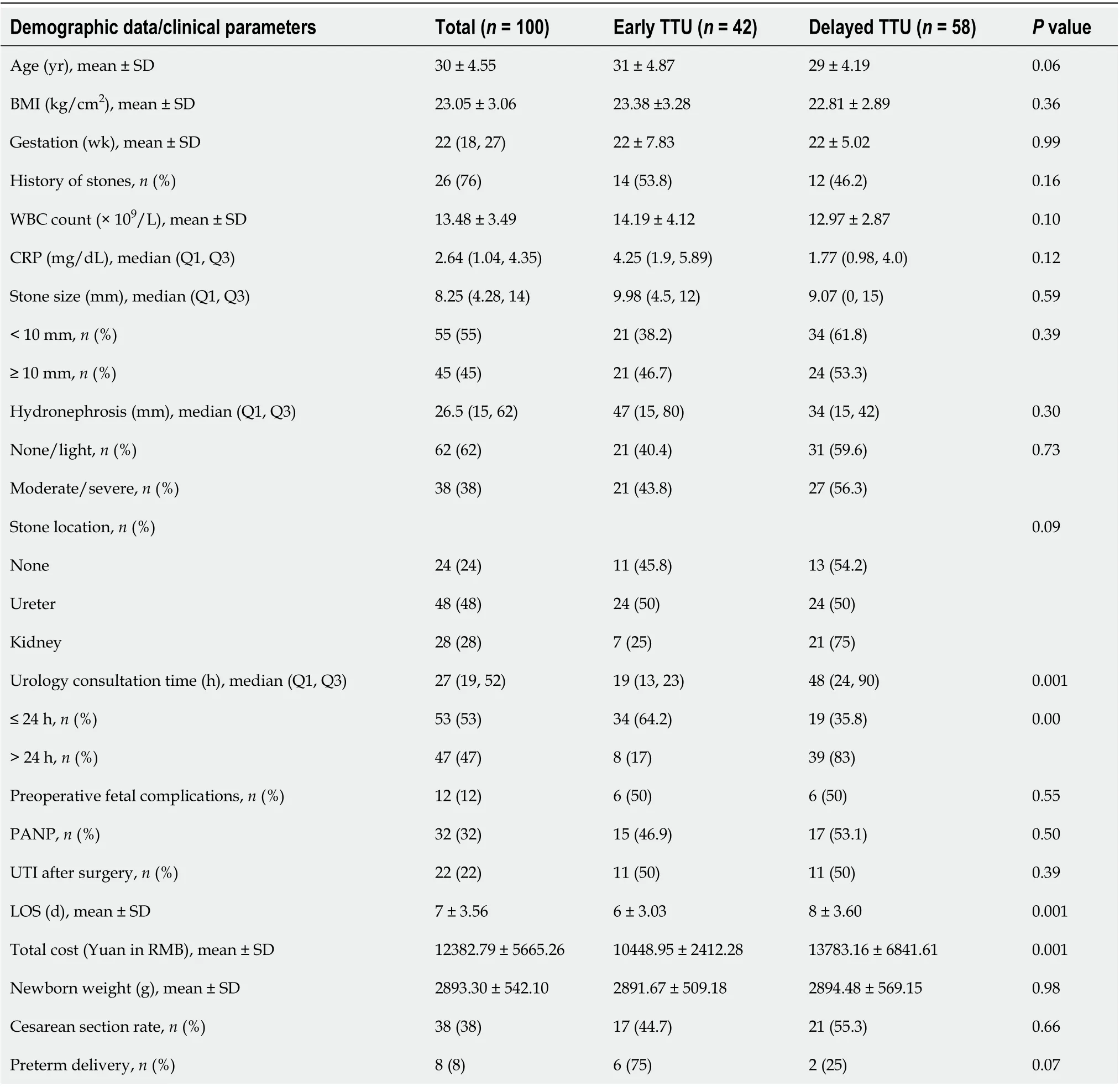
The characteristics of patients in the early and delayed surgery groups are listed in Table 1. The median age was 30 years and median gestation was 22 wk. The median surgery time was 48 h. Forty-two patients (42%) underwent early surgery and 58 patients (58%) underwent delayed surgery. There were no differences in basic information such as age, BMI, gestation, and history of stones between the two groups.There was no significant difference with regard to WBC count and CRP when laboratory examination data were compared. In addition, there was no significant difference in stone size, stone location, and hydronephrosis between the groups when the imaging data were compared. In terms of clinical outcome, there was a significant difference in the length of hospital stay between the two groups (7 d9 d), but there was no difference in preoperative-fetal complications, PANP, UTI, total cost, newborn weight, cesarean section rate, and preterm delivery between the two groups. We found that the timeliness of consultation was related to the time of surgical intervention. The consultation time in early surgery group was 19 h, which was significantly earlier than that in the delayed surgery group (48 h) (Table 1).
China
1)在涂有W3.5金剛石研磨膏的鑄鐵上將焊件試樣接頭部位磨平,分別采用W3.5及W1.5的金剛石研磨膏將試樣在拋光機上拋光,以拋光面上無明顯劃痕為宜。
Using local data, we have identified the association between time to ureteral stent placement and clinical outcomes, and analyzed the risk factors for preoperative acute pyelonephritis in pregnant women with renal colic during pregnancy. Delayed surgery does not affect clinical outcomes, but leads to longer hospital stay. Time from pain to hospitalization and the location of the stones are risk factors for preoperative acute pyelonephritis. Our research will have important significance in the clinic.
Renal colic symptoms were eliminated after surgery in all patients. Laboratory data were also improved (Table 4). As the patients’ creatinine levels were normal before and after surgery, creatinine levels were not compared.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we assessed the relationship between the timing of surgery and clinical outcomes of the mother and child in pregnant patients with renal colic. The results showed that longer TTU was not associated with an increased risk of complications or adverse outcomes when surgery was performed within 48 h of presentation. The timeliness of surgery was closely related to urology consultation. Nevertheless, the length of hospital stay in patients with early surgical intervention was significantly shortened. Furthermore, we analyzed the relationship between acute pyelonephritis and the timing of surgical intervention and found time from pain to admission and the location of stones were risk factors for acute pyelonephritis caused by renal colic during pregnancy. Taken together, these results suggest that it is unlikely that the timing of surgery affected the risk of complications and adverse outcomes if performed within a reasonable time frame.
The timing of surgery is very important due to the impact of surgical emergencies and their complications. Previous studies showed that a delay in appendectomy within 24 h of presentation was not associated with increased risk of complicated appendicitis or surgical site infections[11,12]. Both early and delayed laparoscopic common bile duct exploration are safe and effective for the treatment of common bile duct stone-related non-severe acute cholangitis during emergent admissions[13]. Renal colic during pregnancy is an acute abdomen caused by non-obstetric reasons, and there are few reports on the timing of surgery.
對于中小零售企業電子商務商業運營模式運行管理體系而言,顧客界面是較為關鍵的組成元素,主要涉及目標客戶、管理渠道以及服務與品牌建設等,從而維護相應產品信息和服務對象,一定程度上在網絡中樹立關鍵的企業品牌形象,為后續服務管理工作的全面開展奠定基礎。
The median time from admission to surgical intervention in pregnant patients with renal colic was 48 h. Based on this, we divided the patients into the early and delayed intervention groups, with 42% in the early intervention group and 58% in the delayed intervention group. The results showed that the 48-h delay from admission to surgery was not associated with an increased risk of poor clinical outcome in the mother and child. There was no difference in the effect of early and delayed surgery [see Table 4].Management of renal colic as an urgent rather than emergency procedure wasreasonable during pregnancy. We found that timeliness of intervention was related to the urology consultation. This is consistent with previous research that the availability of specialists to perform the necessary procedures has been implicated in delays in acute stone intervention[14,15]. Faw[16] reported that patients who were stented within 6, 10, and 14 h of admission had more expeditious urologic consults compared with their counterparts, indicating that early urologic consultation is vital to ensure prompt intervention.
當混凝土保護層厚度達不到標準或澆筑質量較差時,鋼筋會發生銹蝕,主要是由于其保護層受二氧化碳侵蝕,大大降低了鋼筋堿度,鐵離子與水分與氧氣產生化學反應,使混凝土出現膨脹應力,同時銹跡滲透到混凝土表面。此外,因銹蝕問題致使鋼筋有效面積減少,混凝土與鋼筋之間的融合力降低,結構承載力出現較大程度的下降,會加劇混凝土鋼筋銹蝕,使結構遭到破壞。
Pyelonephritis is a severe complication of pregnancy. It has been estimated that as many as 20% of women with severe pyelonephritis develop complications that include septic shock syndrome or its variants, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS)[17-19]. We further analyzed the risk factors for PANP, time from pain to admission and stone location, and we found that stone location was closely related to PANP. According to our data analysis, most of the patients with delayed visits were transferred to our hospital due to poor results after treatment in another hospital,which may be the reason for pyelonephritis. Therefore, we should strengthen the management of patients referred from other hospitals, and active intervention is necessary. When patients with suspected acute pyelonephritis are admitted to our hospital, empirical antibiotic use is very important to control the disease.
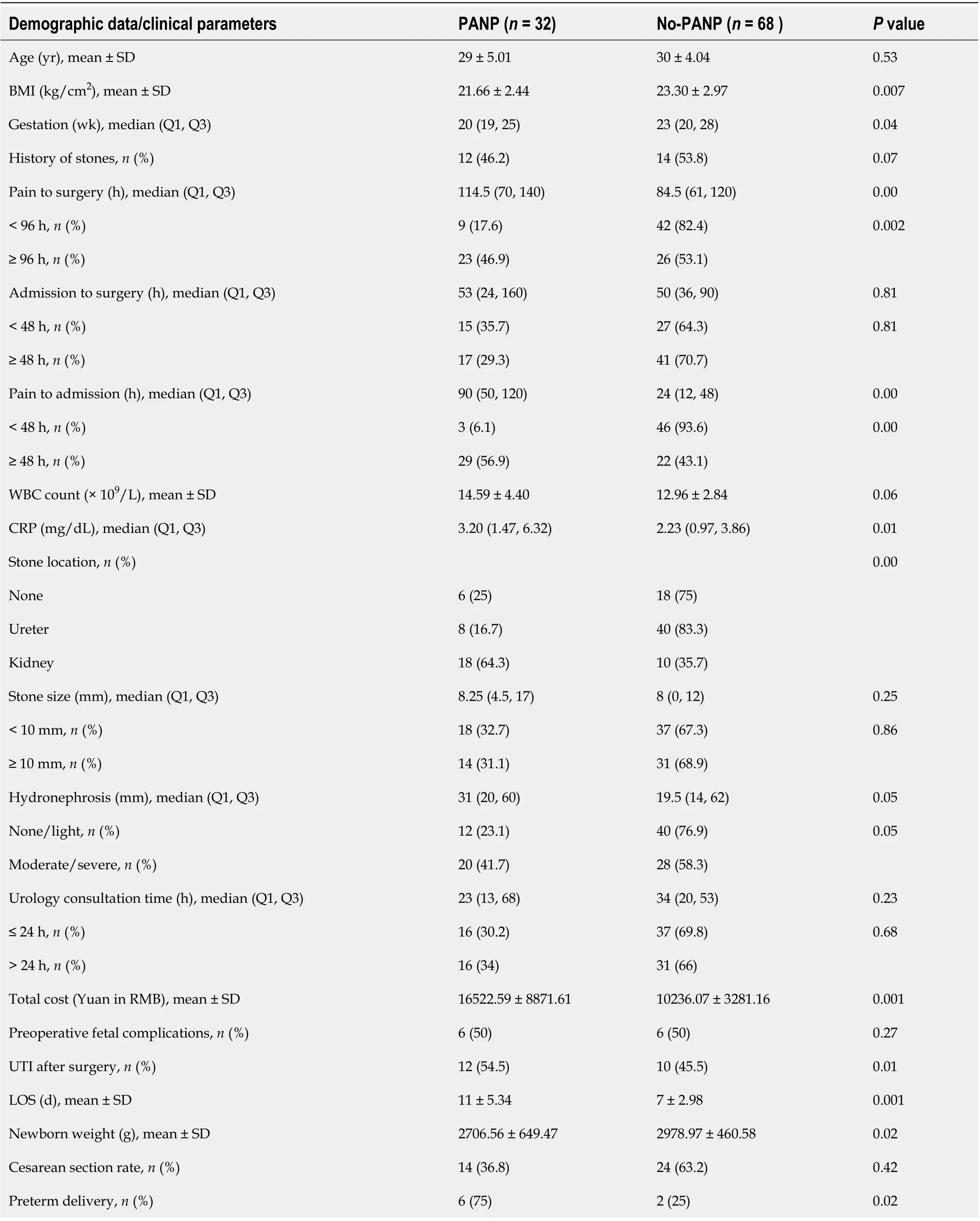

PANP was closely related to re-admission to hospital due to UTI after surgery and premature delivery in our study. This was consistent with previous research[22,23].Chen[24] found ureteral stent placement was a risk factor for PANP. Patients with PANP developed UTI after surgery (OR 3.48, 95%CI: 1.31-9.28), which was reported in our previous studies[25]. Therefore, active anti-infection treatment is required during the perioperative period to avoid adverse outcomes in such patients.
It is known that pyelonephritis is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. An 18-year retrospective study included more than 500000 singleton pregnancies in a large health care system in the United States. The results showed that among 2894 women with pyelonephritis during pregnancy, the preterm birth rate (mainly at 33-36 wk) was higher than those without pyelonephritis (10.3%7.9%, OR 1.3, 95%CI: 1.2-1.5)[26]. The incidence of preterm birth was 8%, and 75% of preterm pregnant women suffered preoperative acute pyelonephritis (OR 7.62, 95%CI: 1.44-40.19).
In addition to the implications for patient health outcomes, our data also suggest an economic benefit with timely intervention. Delayed surgery (≥ 48 h) can lead to longer hospital stay, but did not increase hospitalization costs. The increase in hospitalization costs was mainly related to preoperative acute pyelonephritis. In conclusion, both early and delayed surgery are safe and effective for the treatment of renal colic during pregnancy. Early surgery is recommended for patients with pyelonephritis as it tends to decrease costs and reduce mother and child complications.
The limitation of the current study is its relatively small sample size and lack of patients with very severe complications. Therefore, a large cohort study and randomized controlled trials are needed to validate our findings. We also did not evaluate the degree of pain, which may be an important factor leading to timely intervention of surgery. Despite these limitations, we believe that our findings can still help obstetricians and urologists provide patient consultation.
CONCLUSION
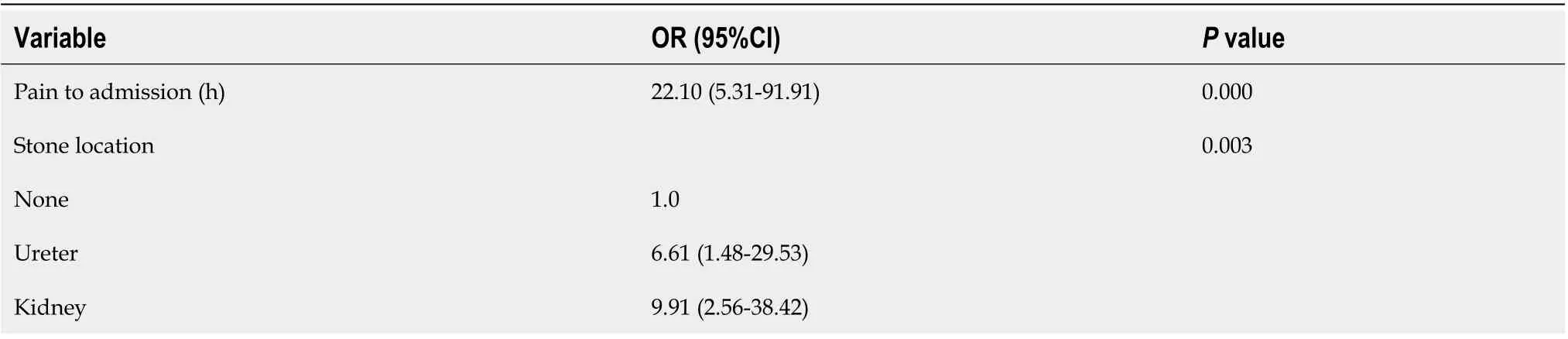
In univariate analyses, increased risk of PANP was associated with BMI, gestation,time from pain to admission, time from pain to surgery, hydronephrosis and stone location (Table 2). Multivariate analysis showed that stone location and time from pain to admission were closely related to PANP (Table 3).
時值冬季,天氣逐漸寒冷,寶寶稍不注意“小肚子”就會著涼,尤其是年齡較小的寶寶,拉起肚子來往往讓寶媽們措手不及又心疼不已。
Pregnancy with renal colic may cause pyelonephritis, decreased renal function,systemic infection and even shock in pregnant women, and cause premature birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes.
When surgery is necessary, the relationship between timing of the operation and the outcome of the mother and child are not known.
白砂糖添加量確定為12%,姜水比為1∶1,姜汁添加量為14%時,在檸檬酸添加量分別為0.125%,0.375%,0.625%,0.875%,1.125%時設計單因素試驗,進行感官評價。
To investigate the association between time to ureteral stent placement and clinical outcomes of patients with renal colic during pregnancy.
Thanks for the cases provided by the Medical Records Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University.
In this retrospective study, pregnant women with renal colic who underwent surgery were studied. Maternal preoperative acute pyelonephritis (PANP), pregnancy outcome, and length of hospital stay (LOS) were compared between the two groups.
PANP was closely related to hospitalization costs, re-admission to hospital due to urinary tract infection after surgery and premature delivery. Multivariate analysis showed that stone location and time from pain to admission were related to PANP.
Both early and delayed surgery are safe and effective for the treatment of renal colic during pregnancy. Early surgery may be superior to a delayed procedure due to shorter LOS. For pregnant patients with renal colic, delayed surgery within 48 h is not related to the clinical outcome of the mother and child. However, the time from pain to hospital admission was related to PANP.
Delayed surgery does not affect clinical outcomes, but leads to longer hospital stay.Time from pain to hospitalization and location of the stones are risk factors for preoperative acute pyelonephritis. Our research will have important significance in the clinic.
舞蹈節目的民間文化元素與公共文化服務實踐 ……………………………………………………………………… 廖智享(3/67)
綜上所述,應用集束化護理措施,能夠顯著降低呼吸機相關性肺炎患者的機械通氣時間、呼吸機相性肺炎發生率,并有助于提高護理質量與患者滿意度,值得臨床廣泛推行。
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年3期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年3期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Mycoplasma hominis meningitis after operative neurosurgery: A case report and review of literature
- Recurrence of sigmoid colon cancer–derived anal metastasis: A case report and review of literature
- New method to remove tibial intramedullary nail through original suprapatellar incision: A case report
- Metastasis to the thyroid gland from primary breast cancer presenting as diffuse goiter: A case report and review of literature
- Gastric submucosal lesion caused by an embedded fish bone: A case report
- Epibulbar osseous choristoma: Two case reports
