樺木酸對人胃癌SGC-7901細胞自噬的影響
郭旭,何孟奇,張偉偉,沈洋,黃鑫,孟令雪,邵淑麗
樺木酸對人胃癌SGC-7901細胞自噬的影響
郭旭1,何孟奇1,張偉偉1,2,沈洋1,黃鑫1,孟令雪1,邵淑麗1,2
(齊齊哈爾大學 1. 生命科學與農林學院,2. 抗性基因工程與寒地生物多樣性保護黑龍江省重點實驗室,黑龍江 齊齊哈爾 161006)
通過不同梯度濃度的樺木酸處理SGC-7901細胞,研究樺木酸對細胞自噬相關基因表達的影響,從而確定樺木酸在胃癌細胞內與自噬的關聯.將人胃癌SGC-7091細胞分為5組,其中3組設置樺木酸的濃度梯度分別為10,20,30 mg/L,使用經典抗癌藥物氟尿嘧啶(5-Fu)作為陽性對照組,使用0 mmol/L樺木酸為陰性對照組,每組3個復孔,處理細胞48 h,用qRT-PCR和Western blot方法檢測樺木酸對人胃癌SGC-7091細胞自噬相關基因mRNA和蛋白表達的影響,使用免疫熒光法定位并檢測SGC-7091細胞內的蛋白.與陰性對照組相比,梯度樺木酸處理組的細胞中-Ⅱ,mRNA和蛋白的表達均顯著升高(<0.01),-Ⅰ蛋白的表達明顯降低(<0.05).同時激光共聚焦的結果顯示高濃度樺木酸誘導蛋白在細胞質內的聚集現象.在設置的梯度濃度范圍內,樺木酸能誘導人胃癌SGC-7091細胞發生自噬,且呈劑量依賴性,濃度升高誘導效果也升高.
樺木酸;人胃癌SGC-7901細胞;細胞自噬
2020年全球新增癌癥病例約1 930萬例,癌癥死亡近1 000萬例(均不包括非黑素瘤皮膚癌),其中胃癌分別占新增和死亡病例數的5.6%,7.7%[1],其誘發因素多,復發率高[2],早期診斷極為復雜,絕大部分患者在胃癌早期無癥狀,出現腹痛等癥狀時已是晚期.外科手術及藥物輔助治療仍是早期胃癌最主要的治療方式.由于大多數胃癌病例被診斷時已處于局部晚期甚至轉移階段,限制了根治性手術的適用性,且多半患者預后差,需化療予以緩解[3].而目前的幾種主流化療藥物(如氟尿嘧啶、順鉑等)毒副作用較大,在治療腫瘤的同時對患者自身正常組織也造成傷害,且礙于胃癌的獨特性,其對化學療法普遍不敏感.因此研發特異性強、副作用小的化療藥物刻不容緩.
自噬是一種細胞營養匱乏導致的應激所誘導的分解代謝降解過程,大多數情況是一種細胞保護措施[4],指細胞在特定因素(如饑餓)刺激下,調動自噬相關蛋白分解自身物質,抵抗外來干擾,以維持內環境穩定的樞紐.但如果自噬過程調用頻繁,破壞原本細胞的生理結構,則也會引發細胞凋亡.通過引發癌細胞自噬進而殺滅癌細胞是化療藥物的一種作用方式.研究表明,多種藥物可通過誘導自噬引發細胞凋亡[5-7].
樺木酸(Betulinic acid,BA)是一種五環三萜類化合物,可從白樺樹、三葉樹和棗樹中提取[8].樺木酸具有廣泛的生物活性[9-13],在誘導細胞凋亡時也伴隨著自噬.樺木酸會通過抑制人宮頸癌細胞[14]、口腔鱗狀細胞癌[15]、乳腺癌[16]、白血病細胞[17]等的G0/G1期來抑制細胞增殖和誘導細胞凋亡,也會在骨髓瘤細胞[18]、大腸癌細胞[19]、肝癌細胞[20]中通過誘導自噬來介導細胞凋亡.
但目前樺木酸對SGC-7901細胞自噬方面的研究還未見報道.本研究在體外添加樺木酸后對自噬相關指標進行檢測,完善樺木酸在胃癌自噬方面的研究,并為后續實驗提供理論基礎.
1 材料與方法
1.1 材料與試劑
人胃癌SGC-7901細胞株(中國醫學科學院腫瘤研究所).
RPMI-1640培養基干粉(Gibico);胎牛血清(Biological Iudustries);樺木酸(北京漢博生物有限公司);Trizol(上海生工生物工程股份有限公司);反轉錄及RT-PCR Mixture(寶生物工程(大連)有限公司);,-Ⅰ,-Ⅱ一抗,兔二抗(北京博奧森生物技術有限公司).
1.2 細胞培養及藥物處理
用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培養基在標準細胞培養箱內(37 ℃,5%CO2)培養人胃癌SGC-7901細胞,每1~2 d傳代1次.細胞培養至對數生長期后,將細胞分為5組,設置3個梯度濃度,分別為10,20,30 mg/L,每組3個復孔,0 mg/L處理組作為陰性對照,70 μm/L的5-FU處理組作為陽性對照,處理48 h后收集細胞進行相應檢測.
1.3 qRT-PCR檢測自噬相關基因mRNA的表達
收集各組細胞,通過Trizol法提取RNA并進行反轉錄,隨后使用cDNA作為模板,進行qRT-PCR檢測,結果見表1.所有結果以2-△△Ct方法計算.

表1 熒光定量引物
1.4 Western blot檢測自噬相關基因的蛋白表達
分別培養6瓶細胞,根據梯度濃度分別處理48 h后,收集細胞并提總蛋白,SDS-PAGE電泳后進行轉膜,使用5%的脫脂奶封閉1 h,再按照蛋白大小進行剪膜,隨后分別使用,-Ⅰ,-Ⅱ一抗(均按1∶500進行稀釋)孵育對應的PVDF膜,4 ℃下孵育過夜;第2天回收所有一抗,TBST洗膜3次,棄凈TBST后使用兔二抗(1∶1 000稀釋)室溫搖床下避光孵育1 h,再使用TBST洗膜3次,最后通過奧德賽掃膜儀掃描條帶并分析處理.
1.5 免疫熒光檢測人胃癌SGC-7901細胞自噬
分別培養6皿細胞,待細胞數合適時,根據梯度濃度設置處理細胞48 h,處理結束后使用甲醇進行固定處理.固定結束后清洗甲醇,標準封閉液封閉1 h.一抗4 ℃過夜,TBST洗3次;二抗避光孵育1 h,TBST洗3次.隨后使用20 μL的DAPI孵育3~8 min,再使用PBST洗3次.清洗完畢后,滴加一滴抗熒光淬滅封片液,激光共聚焦顯微鏡下拍照.
1.6 統計學處理
2 結果
2.1 qRT-PCR檢測樺木酸對自噬相關基因mRNA表達的影響
和的mRNA表達量見表2.由表2可見,與陰性對照組相比,隨著樺木酸的質量濃度梯度升高,和的mRNA表達逐步升高,當樺木酸濃度為30 mg/L時,和的mRNA表達量最高,5-FU陽性對照處理組與10 mg/L處理組結果相似.結果表明,樺木酸上調了人胃癌SGC-7901細胞中的,基因mRNA的表達.
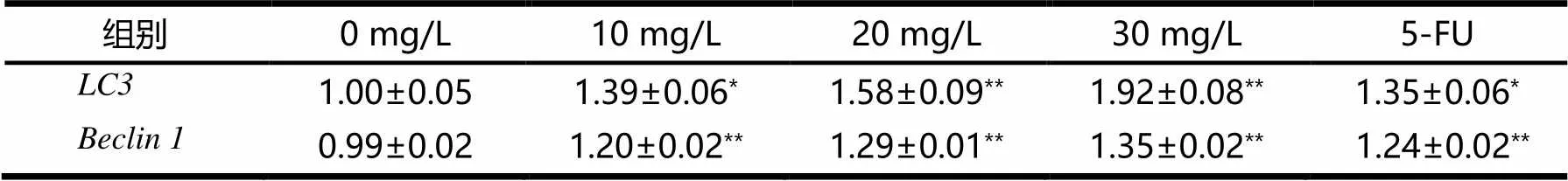
表2 LC3和Beclin 1的mRNA表達量
2.2 Western blot檢測樺木酸對自噬相關基因蛋白表達的影響
不同濃度樺木酸對人胃癌SGC-7901細胞自噬相關,蛋白表達影響見表3和圖1.由表3和圖1可見,在3組梯度濃度處理組中-Ⅱ,蛋白表達水平梯度遞增(<0.01),而-Ⅰ蛋白表達水平則隨濃度梯度變化遞減(<0.01),-Ⅱ/-Ⅰ比值隨濃度梯度變化遞增(<0.01).10 mg/mL樺木酸處理的效果與陽性對照組的效果相似.結果表明,樺木酸通過調控-Ⅱ,蛋白表達促進胃癌SGC-7901細胞自噬.

表3 樺木酸對Beclin 1,LC3-Ⅰ,LC3-Ⅱ蛋白水平的影響
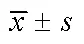

圖1 樺木酸對Beclin 1,LC3-Ⅰ,LC3-Ⅱ蛋白水平的影響(n=3)
2.3 樺木酸對人胃癌SGC-7901細胞中LC3蛋白定位的影響
通過激光共聚焦顯微鏡觀察蛋白在胃癌SGC-7901細胞內的定位及表達變化(見圖2).鑒于30 mg/L的樺木酸處理細胞后細胞死亡過于明顯,不利于鏡下觀察和染色,因此選擇20 mg/L的質量濃度進行處理,48 h后蛋白在細胞質內的聚集現象顯著,5-FU陽性對照組與20 mg/L處理組有相似結果.結果表明,樺木酸的處理誘導胃癌SGC-7901細胞發生自噬.
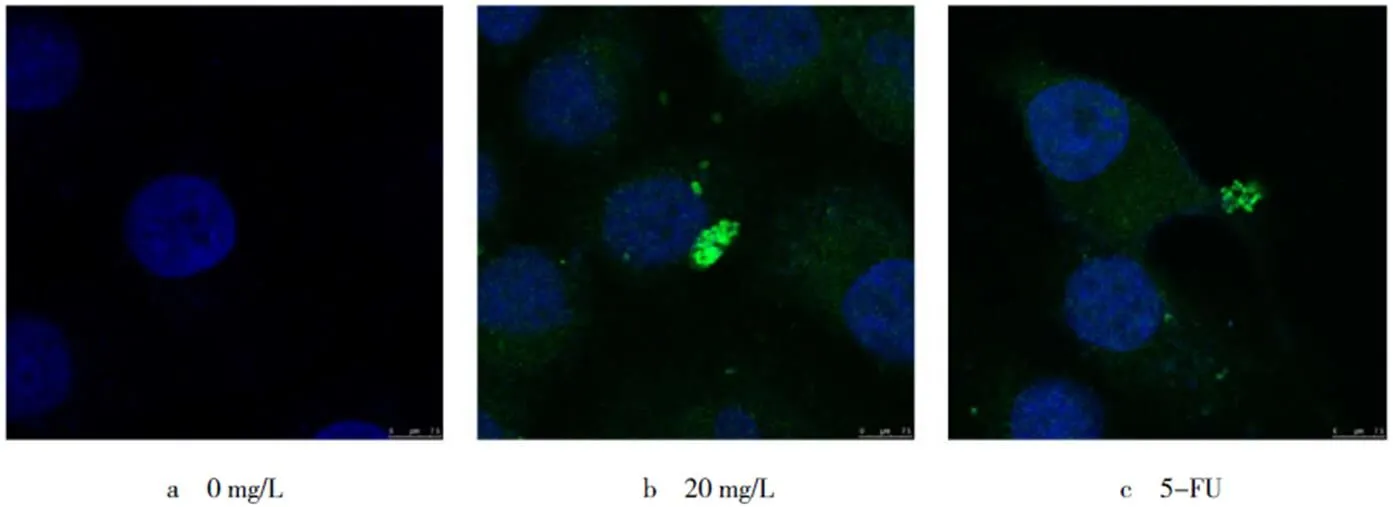
圖2 樺木酸處理細胞48 h,LC3的細胞內定位(bar=100 μm,n=3)
3 討論
細胞保護性自噬是應對化療藥物和放射治療的重要反應.在大多數情況下,抗癌治療中,自噬作用會支持癌細胞的存活;然而在某些情況下,它也會促進細胞死亡.因此,調節自噬有可能成為提高化療和放療療效的策略之一.此外,自噬調節劑和傳統治療方法的結合可能使癌細胞對癌癥治療敏感.有越來越多的臨床前證據表明,靶向誘導自噬,利用其細胞自身功能瓦解腫瘤,其毒副作用相對較小,在聯合治療中的作用也較為明顯[21-22].如褪黑素對胃腸癌細胞的自噬具有調節作用,可通過聯合用藥增加胃腸癌細胞對藥物的敏感性[23];脫落酸在膠質母細胞瘤細胞中可通過誘導腫瘤細胞自噬來抑制腫瘤的生長[24].樺木酸作為一種天然產物藥物,已有研究表明其對人類肺癌、乳腺癌、結腸癌等均具有明顯的細胞毒性[25-29].本實驗研究證明,樺木酸可誘導人胃癌SGC-7901細胞自噬.
自噬的誘導途徑有很多,其中自噬相關基因和是自噬過程的主要調節劑,許多自噬調控蛋白通過與的不同結構域或氨基酸發生直接或間接結合,形成蛋白復合體,進而調控自噬水平[30].而的功能主要參與了自噬小體的形成,饑餓時,核會被SIRT1(sirtuin 1)脫乙酰化,并與TP53INP2一起重新分布到細胞質中,以引發自噬[31].在自噬過程中,樺木酸可能通過觸發細胞內的上游自噬信號(如PI3K/AKT/mTOR信號通路)來介導和的表達變化,同時樺木酸也可能通過對細胞內原本自噬信號的破壞,導致細胞自噬失調,進而引發腫瘤細胞的過度自噬行為,導致細胞死亡.
本實驗5-FU為陽性對照組,證明隨著樺木酸濃度的增加,自噬標志基因、mRNA和蛋白的表達量增加,但是-Ⅰ蛋白表達量減少.通過激光共聚焦顯微鏡觀察蛋白在胃癌SGC-7901細胞質內形成點狀聚集增多,證明樺木酸的處理誘導了胃癌SGC-7901細胞發生自噬.研究結果為樺木酸的開發利用提供了實驗依據.綜上所述,樺木酸通過對自噬標志基因和的調節,調控胃癌細胞SGC-7901自噬的發生.
[1] SUNG H,FERLAY J,SIEGEL R L,et al.Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2021,7(31):209-249.
[2] CHENG X J,LIN J C,TU S P.Etiology and Prevention of Gastric Cancer[J].Gastrointest Tumors,2016,3(1):25-36.
[3] FUJITANI K,YANG H K,MIZUSAWA J,et al.Gastrectomy plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric cancer with a single non-curable factor(REGATTA):a phase 3,randomised controlled trial[J].Lancet Oncol,2016,17(3):309-318.
[4] LEVINE B,KROEMER G.Biological Functions of Autophagy Genes:A Disease Perspective[J].Cell,2019,176(1-2):11-42.
[5] DU Y,SHAO S L,JIAO K H,et al.Effects of hedyotis diffusa on mitochondrial membrane potential and expressions of apoptosis-related genes in human gastric cancer cell line MNK-45[J].,2020,36(2):171-175.
[6] XU J,PAN Y,LIU Y,et al.A review of anti-tumour effects of ginsenoside in gastrointestinal cancer[J].J Pharm Pharmacol,2021,72(10):1292-1301.
[7] JIN X,SUN P P,HONG Y,et al.Puerarin induces apoptosis in A549 cells[J].,2017,33(5):466-469.
[8] DUBEY K K,GOEL N.Evaluation and optimization of downstream process parameters for extraction of betulinic acid from the bark of Ziziphus jujubae L[J].Scientific World Journal,2013(1):e469674.
[9] COSTA J F,BARBOSA-FILHO J M,MAIA G L,et al.Potent anti-inflammatory activity of betulinic acid treatment in a model of lethal endotoxemia[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2014,23(2):469-474.
[10] HONG E H,SONG J H,KANG K B,et al.Anti-Influenza Activity of Betulinic Acid from Zizyphus jujuba on Influenza A/PR/8 Virus[J].Biomol Ther(Seoul),2015,23(4):345-349.
[11] LUO C,HUANG C,ZHU L,et al.Betulinic Acid Ameliorates the T-2 Toxin-Triggered Intestinal Impairment in Mice by Inhibiting Inflammation and Mucosal Barrier Dysfunction through the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway[J].Toxins(Basel),2020,12(12):794.
[12] QIAN K,YU D,CHEN C H,et al.Anti-AIDS agents.78.Design,synthesis,metabolic stability assessment,and antiviral evaluation of novel betulinic acid derivatives as potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus(HIV)agents[J].J Med Chem,2009,52(10):3248-3258.
[13] QUAN H Y,KIM D Y,KIM S J,et al.Betulinic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver by inhibiting SREBP1 activity via the AMPK-mTOR-SREBP signaling pathway[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2013,85(9):1330-1340.
[14] XU T,PANG Q,WANG Y,et al.Betulinic acid induces apoptosis by regulating PI3K/Akt signaling and mitochondrial pathways in human cervical cancer cells[J].Int J Mol Med,2017,40(6):1669-1678.
[15] SHEN H,LIU L,YANG Y,et al.Betulinic Acid Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Modulating ROS-Regulated p53 Signaling[J].Oncol Res,2017,25(7):1141-1152.
[16] FOO J B,SAIFUL YAZAN L,TOR Y S,et al.Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by betulinic acid-rich fraction from Dillenia suffruticosa root in MCF-7 cells involved p53/p21 and mitochondrial signalling pathway[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2015,166:270-278.
[17] CHEN Z,WU Q,CHEN Y,et al.Effects of betulinic acid on proliferation and apoptosis in Jurkat cells and its in vitro mechanism[J].J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci,2008,28(6):634-638.
[18] YANG L J,CHEN Y,HE J,et al.Betulinic acid inhibits autophagic flux and induces apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells in vitro[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2012,33(12):1542-1548.
[19] WANG S,WANG K,ZHANG C,et al.Overaccumulation of p53-mediated autophagy protects against betulinic acid-induced apoptotic cell death in colorectal cancer cells[J].Cell Death Dis,2017,8(10):e3087.
[20] LIU W P,LI S L,QU Z L,et al.Betulinic acid induces autophagy-mediated apoptosis through suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Am J Transl Res,2019(11):6952-6964.
[21] MOKARRAM P,ALBOKASHY M,ZARGHOONI M,et al.New frontiers in the treatment of colorectal cancer:Autophagy and the unfolded protein response as promising targets[J].Autophagy,2017,13(5):781-819.
[22] DJAVAHERI-MERGNY M,GIURIATO S,TSCHAN M P,et al.Therapeutic Modulation of Autophagy in Leukaemia and Lymphoma[J].Cells,2019,8(2):103.
[23] POURHANIFEH M H,MEHRZADI S,KAMALI M,et al.Melatonin and gastrointestinal cancers:Current evidence based on underlying signaling pathways[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2020,886:e173471.
[24] ZHOU N,WEI Z,QI Z,et al.Abscisic Acid-Induced Autophagy Selectively via MAPK/JNK Signalling Pathway in Glioblastoma[J].Cell Mol Neurobiol,2021,41(4):813-826.
[25] CHINTHARLAPALLI S,PAPINENI S,LEI P,et al.Betulinic acid inhibits colon cancer cell and tumor growth and induces proteasome-dependent and -independent downregulation of specificity proteins(Sp)transcription factors[J].BMC Cancer,2011,11:371.
[26] CHINTHARLAPALLI S,PAPINENI S,RAMAIAH S K,et al.Betulinic acid inhibits prostate cancer growth through inhibition of specificity protein transcription factors[J].Cancer Res,2007,67(6):2816-2823.
[27] HSU T I,WANG M C,CHEN S Y,et al.Betulinic acid decreases specificity protein 1(Sp1)level via increasing the sumoylation of sp1 to inhibit lung cancer growth[J].Mol Pharmacol,2012,82(6):1115-1128.
[28] LI L,DU Y,KONG X,et al.Lamin B1 is a novel therapeutic target of betulinic acid in pancreatic cancer[J].Clin Cancer Res,2013,19(17):4651-4661.
[29] REINER T,PARRONDO R,DE LAS POZAS A,et al.Betulinic acid selectively increases protein degradation and enhances prostate cancer-specific apoptosis:possible role for inhibition of deubiquitinase activity[J].PLoS One,2013,8(2):e56234.
[30] KANG R,ZEH H J,LOTZE M T,et al.The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis[J].Cell Death Differ,2011,18(4):571-580.
[31] SHIM M S,NETTESHEIM A,HIRT J,et al.The autophagic proteintranslocates to the nucleus and localizes in the nucleolus associated to NUFIP1 in response to cyclic mechanical stress[J].Autophagy,2020,16(7):1248-1261.
Effects of betulinic acid on autophagy of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells
GUO Xu1,HE Mengqi1,ZHANG Weiwei1,2,SHEN Yang1,HUANG Xin1,MENG Lingxue1,SHAO Shuli1,2
(1. School of Life Sciences,Agriculture and Forestry,2. Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Resistance Gene Engineering and Protection of Biodiversity in Cold Areas,Qiqihar University,Qiqihar 161006,China)
SGC-7901 cells were treated with betulinic acid at different concentrations to study the effect of betulinic acid on the expression of autophagy related genes,so as to determine the association between betulinic acid and autophagy in gastric cancer cells.Human gastric cancer SGC-7091 cells were divided into 5 groups.The concentration gradients of betulinic acid in the three groups were 10,20,30 mg/L,respectively.The classic drug 5-fluorouracil(5-Fu)was used as the positive control group,and 0 mmol/L betulinic acid was used as the negative control group.Each group had three replicates and the cells were treated for 48 h,then qRT-PCR and Western blot were used to detect the effects of betulinic acid on mRNA and protein expression of autophagy related genes in human gastric cancer SGC-7091 cells.protein in SGC-7091 cells was localized by immune of luorescence.Compared with the negative control group,the mRNA and protein expressions of-Ⅱ andwere significantly increased(<0.01),and the protein expression of-Ⅰwas significantly decreased(<0.05).Confocal laser microscopy showed that high concentration of betulinic acid inducedprotein aggregation in cytoplasm.In the gradient concentration range,betulinic acid can induce autophagy in human gastric cancer SGC-7091 cells in a dose-dependent manner,and the induction effect increased with the increase of concentration.
betulinic acid;human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells;autophagy
Q2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9831.2022.06.013
1007-9831(2022)06-0075-05
2022-02-26
齊齊哈爾大學黑龍江省教育廳基本業務專項重點項目(135109104);黑龍江省高教強省優勢特色學科——玉米“糧頭食尾”重點項目(LTSW201737);黑龍江省省屬高等學校基本科研業務費科研項目(YSTSXK201809)——植物性食品加工技術特色學科專項;2020年齊齊哈爾大學研究生創新科研項目(YJSCX2020046)
郭旭(1997-),男,黑龍江哈爾濱人,在讀碩士研究生,從事腫瘤細胞基因表達調控研究.E-mail:757011379@qq.com
邵淑麗(1962-),女,黑龍江齊齊哈爾人,教授,博士,從事基因表達調控研究.E-mail:shshl32@163.com

