基于卷積模型的核信號仿真
邵瑋豪 梁勇飛 楊朝文 左晶鑫 宋云


NaI(Tl)探測器因具有探測效率高和成本低等優點,常被用于核輻射能譜測量和核輻射監管等領域. 由于實驗條件等的限制,研究人員往往較難獲取理想的實驗核信號,雖然可以借助探測器的仿真信號來實現研究目的,但是常規的探測器單指數或雙指數模型和實際采集到的核信號模型存在一定的差異,需要一種更為精準的數學模型對探測器輸出信號進行描述. 我們通過對探測器信號形成過程分析,將探測器視為線性時不變系統,探測器各個部分響應的總卷積即為輸出的核信號模型. 本文建立的探測器輸出信號卷積模型,結合實測伽瑪源的幅度分布規律和相鄰脈沖時間間隔分布規律,可以提供更精確的NaI(Tl)探測器輸出信號,以便用于伽瑪能譜測量算法研究; 通過調節脈沖間隔時間大小,可以仿真不同計數下探測器輸出信號的堆積情形,以便用于堆積信號還原算法研究. 經過與伽瑪輻射源的對比測試,該仿真信號與真實探測器輸出信號一致,既避免了研究人員接觸放射源,提高輻射防護安全性,又為開展數字化核信號處理算法研究及能譜算法研究提供了極大的便利性.
NaI(Tl)探測器; 卷積模型; 仿真核信號
TL8A2023.014003
收稿日期: 2022-08-07
基金項目: 國家自然科學基金(U1967205)
作者簡介: 邵瑋豪(1996-), 男, 山西永濟人, 碩士研究生, 研究方向為核信號獲取與處理. E-mail: 249804801@qq.com
通訊作者: 梁勇飛. E-mail: liangyf@scu.edu.cn
Simulation nuclear signal generation program based on convolution model
SHAO Wei-Hao, LIANG Yong-Fei, YANG Chao-Wen, ZUO Jing-Xin, SONG Yun
(College of Physics, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
Due to the advantages of high detection efficiency and low cost, NaI(Tl) detectors are often used in the fields of nuclear radiation energy spectrum measurement and nuclear radiation supervision. Due to the limitations of experimental conditions, it is often difficult for researchers to obtain the ideal experimental nuclear signal. Although the simulation signal of the detector can be used to achieve the research purpose, there are certain differences between the conventional detector single exponential or double exponential model and the actual nuclear signal model, and a more accurate mathematical model is needed to describe the detector output signal. Through the analysis of the detector signal formation process, the detector is regarded as a linear time-invariant system, and the total convolution of the responses of each part of the detector is the output kernel signal model. Through the established detector output signal convolution model, combined with the amplitude distribution law of the measured gamma source and the adjacent pulse time interval distribution law, a more accurate NaI(Tl) detector output signal can be provided for use in gamma energy research on spectral measurement algorithms. By adjusting the pulse interval time, the accumulation situation of the detector output signal under different counts can be simulated, so as to be used for the research of the accumulation signal reduction algorithm. After the comparison test with the gamma radiation source, the simulated signal is consistent with the output signal of the real detector, which not only prevents researchers from contacting the radioactive source and improves the safety of radiation protection, but also provides great convenience for the research of digital nuclear signal processing algorithm and energy spectrum algorithm.
NaI(Tl) scintillator detector; Convolution model; Simulation nuclear signal
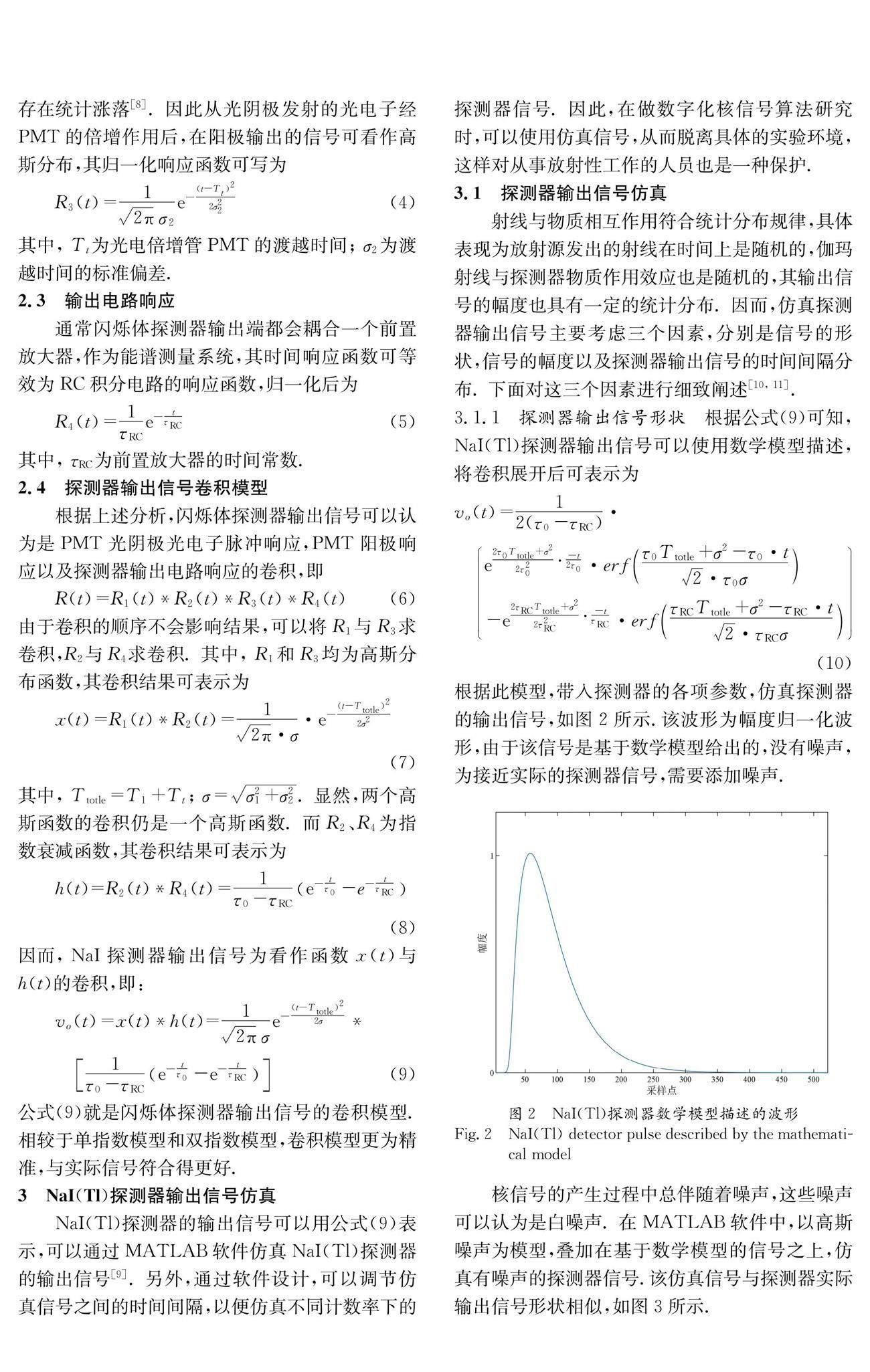
1 引 言NaI(Tl)探測器因具有探測效率高和成本低等優點,常被用于核輻射能譜測量和核輻射監管等領域. 由于實驗條件等的限制,研究人員獲取所需的實驗信號往往需要花費大量的時間,因此常借助探測器的仿真信號來實現研究目的. 實現核信號的仿真,需要解決三個方面的問題,分別是探測器輸出信號的數學模型,信號的幅度及相鄰核信號的間隔時間[1]. 對于閃爍體探測器,通常采用單指數或者雙指數模型進行近似表述[2-4],但是這一模型不夠準確,在數字核信號處理算法上往往無法還原真實核信號的處理結果.
本文通過對NaI(Tl)探測器在伽瑪射線作用后產生信號的過程分析,得到更為精準的核信號數學模型,結合核信號幅度規律和相鄰核信號間隔時間規律,通過MATLAB軟件編寫了基于卷積模型的核信號仿真程序,通過該程序可以生成各種計數率下的核信號,為開展數字化核信號處理算法研究及能譜算法研究提供了便利性.
2 卷積模型
NaI(Tl)探測器是一個線性時不變系統,而線性時不變系統的最終響應可以轉換為各部分響應的卷積. NaI(Tl)探測器可視為由三個部分組成:閃爍體,光電倍增管(PMT)和探測器輸出電路,如圖1所示[5]. 因而NaI(Tl)探測器的輸出信號與這三個部分有關,可視為其響應的卷積[6,7]. 下面分別對各部分的響應進行介紹.
3.3.2 能譜對比 通過常用數字成形算法處理后的比較,可以看出仿真核信號與實測信號有很好的一致性. 還需要將通過實測信號獲取的能譜與通過仿真信號獲取的能譜相比較,以驗證仿真信號的可用性,見圖8. 通過示波器采集到137Cs源的實測信號得到能譜,計數率為60 kcps. 再通過仿真信號得到能譜,將兩種信號得到的能譜進行比較. 在100 kcps計數率下獲取的能譜與對應的仿真信號得到的能譜的結果見圖9.
在各種不同計數率實驗環境下,通過仿真信號得到的能譜,與實測信號得到的能譜相同,光電峰、康普頓坪和反散射峰等特征都能很好地表現出來. 說明仿真核信號與實測信號基本一致,驗證了仿真信號的可用性.
4 結 論
本文通過分析NaI(Tl)閃爍體探測器輸出信號的形成過程,推導出輸出信號的卷積模型;基于這種卷積模型,結合信號的幅度規律和相鄰核信號時間間隔規律,通過設置程序參數,就可以生成不同計數率下的NaI(Tl)閃爍體探測器輸出的核信號數據. 這些數據為科研人員獲取理想計數率下的核信號數據提供便利. 根據這種推導方式,我們可以結合其他類型探測器,得到不同探測器在不同計數率環境下獲取的核信號. 此方式應用更為廣泛,既避免了研究人員接觸放射源,提高輻射防護安全性,又為開展數字化核信號處理算法研究及能譜算法研究提供了極大的便利性.
參考文獻:
[1] 張軟玉. 數字化核能譜獲取系統的研究[D].成都:四川大學, 2006.
[2] Knoll G F. 輻射探測與測量[M]. 李旭, 張瑞增, 徐海珊, 等譯. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1988.
[3] 覃駿, 周偉, 杜洋, 等. 基于MATLAB的核信號仿真與成形研究[J]. 電子質量, 2017(1): 95.
[4] 洪旭, 倪師軍, 周建斌, 等. 數字高斯脈沖成形算法仿真研究[J]. 核技術, 2016, 39: 53.
[5] 王經瑾, 范天民, 錢永庚, 等. 核電子學[M]. 北京:原子能出版社, 1983.
[6] Xiao W, Farsoni A T, Yang H, et al. A new pulse model for NaI (Tl) detection systems [J]. Nucl Instrum Meth A, 2014, 763: 170.
[7] Xiao W, Farsoni A T, Yang H, et al. Model-based pulse deconvolution method for NaI(Tl) detectors [J]. Nucl Instrum Meth A, 2015, 769: 5.
[8] 日本濱松光子學株式會社. 光電倍增管的基礎及應用[M/OL].北京濱松光子技術股份有限公司, 譯. 3版. [S.l.:s.n.], 2010 [2022-06-12]. http://share.hamamatsu.com.cn/07ccc55cf70b4ab0b 9a3561f0e82e40e/download.html.
[9] Ingle V K, Proakis J G. 數字信號處理: 使用MATLAB[M]. 劉樹棠, 譯. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大學出版社, 2002.
[10] 復旦大學, 清華大學, 北京大學. 原子核物理實驗方法[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1981.
[11] 周清華. 核能譜獲取系統仿真模塊庫的設計與實現[D]. 成都: 四川大學, 2007.
[12] 肖無云, 魏義祥, 艾憲蕓, 等. 數字化多道脈沖幅度分析技術研究[J]. 核技術, 2005, 28: 4.
[13] 李京倫, 肖無云, 艾憲蕓, 等. 新型數字多道脈沖幅度分析器設計[J]. 核電子學與探測技術, 2018, 38: 387.
[14] 周偉, 周建斌, 方方, 等. 核脈沖信號數字高斯成形模型的建立與仿真[J]. 物探與化探, 2012, 36: 3.
[15] Jordanov V T, Knoll G F, Huber A C, et al. Digital techniques for real-time pulse shaping in radiation measurements [J]. Nucl Instrum Meth A, 1994, 353: 261.

