基于車輛關鍵部位特征的再識別算法
趙斌 董長元
[摘 要]圖像識別任務中,要想得到更具辨識度的特征的前提是精準定位到關鍵位置,汽車的車頂、車窗、前臉為車輛最關鍵的3個部位。將一種PCB-LS方法用于車輛再識別,基于提取局部特征的思想,使用ResNet50的主干網絡提取特征圖,然后將特征圖平均劃分為3個部分,對于3個部位分別訓練分類器;對于模型在訓練集中出現的過擬合現象,采用標簽平滑的正則化方法降低模型對訓練集樣本的信任度,提高模型在測試集上的準確率;使用VeRi776數據集進行訓練和測試,使用PCB-LS方法在測試集上能達到準確率Rank@1、Rank@5、Rank@10分別為93.62%、96.72%、97.74%,mAP為76.17%。PCB-LS方法不僅能獲得辨識度高的特征,還有很好的泛化能力。
[關鍵詞]車輛再識別;局部特征;特征提取;標簽平滑;泛化能力
[中圖分類號]TP391.4[文獻標識碼]A
車輛重識別就是在車輛數據中檢索特定的車輛,并給出和特定車輛最相近的檢索結果。隨著深度學習在圖像識別領域的發展,大量的基于深度學習的車輛再識別技術應運而生,識別車輛不僅僅是依靠車牌信息,還可以通過整體車身的有辨識度的特征。車輛的重識別技術可以應用在車輛行駛軌跡分析、高速公路ETC收費稽查系統、在逃車輛追蹤等方面。
基于傳感器或者人工設計特征的車輛再識別方法大致分為基于傳感器的方法[1-2]、基于人工設計特征的方法[3-4]以及基于深度學習的方法。自從卷積神經網絡被提出以后,深度學習在圖像識別和檢索領域逐漸流行起來,目前性能最好的圖像識別模型都是基于深度學習的方法提出的。Shen et al[5]提出了一種兩階段識別模型,并結合車輛空間實時信息來調整車輛重識別結果。He et al[6]提出了一種簡單高效的局部關鍵特征提取模型,該方法增強了模型對微小差別的區分能力,識別準確率獲得了較大提升。文獻[6-7]表明,車窗、車燈和汽車輪廓等特定位置包含更具分辨度的信息。由于車輛和行人重識別任務具有很高的相似性,部分文獻還將行人重識別方法應用在車輛重識別中。Luo et al[8]將ResNet50作為基礎模型,使用隨機擦除、分段學習率、將Last Stride改為1等技巧提高了行人重識別準確率,He et al[9]將文獻[8]的技巧用于車輛識別任務上,在AICITY2020中取得了96.9%Rank@1和82.0%mAP的成績。
Sun et al[10]提出的PCB方法是近年來非常優秀的行人重識別方法。PCB方法使用ResNet主干網絡提取特征圖,然后將特征圖平均劃分為6個部分,分別訓練分類器計算交叉熵損失訓練模型,使用訓練的模型提取測試集圖片的特征并計算之間的相似度,找出相似的車輛。車輛的局部特征也可以通過劃分關鍵部位提取,然后分別訓練網絡提取特征計算相似度對車輛進行重識別。在使用訓練集訓練PCB模型的過程中,采用one-hot標簽進行計算交叉熵損失時,只考慮訓練樣本中正確的標簽位置(one-hot標簽為1的位置)的損失,而忽略錯誤標簽位置(one-hot標簽為0的位置)的損失。這樣一來,模型可以在訓練集上擬合得很好,但由于其他錯誤標簽位置的損失沒有計算,導致預測時預測錯誤概率增大。Szegedy et al[11]提出使用label smoothing(LS)的方法修改p值以降低模型對訓練集標簽的敏感度,從而避免過擬合問題,通過將PCB方法和LS方法相結合,既可以有效提取到最具有辨識度的特征,又能提高模型的泛化能力,使得模型在測試集上也有很好的預測效果。
1 車輛重識別模型
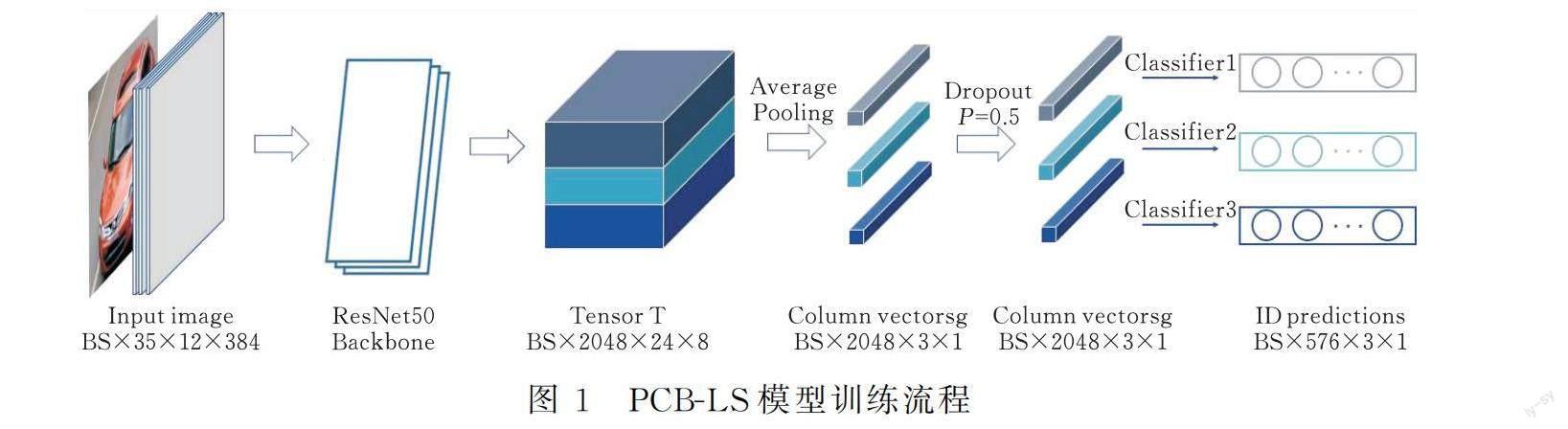
深度學習模型彌補了傳統手工特征表達能力不足的問題,可以通過設計深度學習模型提取到更具辨識度的特征,提高識別率。為了更好地提取辨識度更高的特征,可以先定位關鍵部位,對不同的部位分別訓練分類器,這正是PCB-LS模型的思想。使用ResNet50作為主干網絡,將輸出的tensor數據劃分為3個部分,分別訓練分類器并使用標簽平滑(Label Smoothing)損失函數作為目標函數反向訓練模型。學習率對模型的表現具有較大的影響,對于較大的批尺寸需要設定一個較大的初始值。為了避免在初始階段出現數值不穩定的情況,使用熱啟動啟發式學習,使學習率從0線性上升到初始學習率;為了加快模型的收斂速度,使用余弦衰減函數計算每個回合的學習率。
1.1 PCB-LS模型
PCB方法最初是在行人重識別任務中提出的,主要思想是通過提前定位關鍵部位來提取更具辨識度的特征。PCB方法采用ResNet50作為主干網絡,刪除ResNet50最后兩層,將輸出的特征圖劃分為6塊,對每一塊訓練出一個分類器,將分類結果與標簽計算交叉熵損失,用6塊的損失之和作為目標損失函數,通過最小化目標損失函數來優化模型。
ResNet是當前深度學習非常流行的網絡結構,殘差網絡通過重復使用殘差塊來提取特征。而在殘差塊中,通過對卷積相關參數的設置,控制殘差塊輸入與輸出的特征圖尺寸一致,從而進行相加處理,避免深層網絡的梯度消失和退化問題。ResNet50包含50層,主干網絡包含5個階段,第1個階段為對輸入的預處理,后面4個階段都由Bottleneck組成,結構較為相似。本文采用ResNet50的主干網絡初步提取輸入圖片特征,將圖片尺寸調整為512×384后作為輸入X,輸入尺寸為B×3×512×384,其中B為batch-size,通過ResNet50主干網絡后的特征圖設為T,大小為B×2048×32×24,車輛最具辨識度的位置為車頂、車窗、前臉等3個部分,可以將特征圖T劃分為3個位置,使用自適應池化方法將數據變為g,大小為B×2048×3×1,使用1×1卷積核,Dropout設為0.5,然后對3個部分分別訓練分類器進行訓練。大致的訓練流程如圖1所示。
[2] JENG S,CHU L.Vehicle re-identification with the inductive loop signature technology[J].Journal of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies,2013,12(10): 1896-1915.
[3] ZHANG Z,TAN T,HUANG K.Three-dimensional deformable-model-based localization and recognition of road vehicles[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2012,21(01):1-13.
[4] WOESLER R.Fast extraction of traffic parameters and re-identification of vehicles from video data[C].∥ The 2003 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems.Piscataway: IEEE Press,2003.774-778.
[5] SHEN Y T,XIAO T,LI H S,et al.Learning deep neural networks for vehicle re-id with visual-spatio-temporal path proposals[J].Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,2017,12(01): 1900-1909.
[6] BING H, JIA L,YIFAN Z,et al.Partregularized near-duplicate vehicle re-identification[J].Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2019,12(01): 3997-4005.
[7] SHANGZHI T, XIAOBIN L,SHILIANG Z, et al. Spatial and channel attention network for vehicle re-identification[J].Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia,2018,23(10): 350-361.
[8] HAO L, YOUZHI G,XINGYU L,et al.Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep personre-identification[J].Proceedings of the IEEE Conference onComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops,2019,3(10): 432-443.
[9] SHUTING H,HAO L,WEIHUA C,et al.Multi-domain learning and identity mining for vehicle re-identification[J].IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,2022(09):1-15.
[10]YIFAN S,LIANG Z,YI Y,et al.Beyond part model person retrieval with refined part pooling[J].Computer Vision-ECCV 2018,11208:510-518.
[11]SZEGEDY C,VANHOUCKE V,IOFFE S,et al.Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[J].Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2016:2818-2826.
[12]LIUHONGYE,TIAN YONGHONG,WANG YAOWEI,et al.Deep relative distance learning: Tell the difference between similar vehicles[J].Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2016,24(01): 2167-2175.
[13]SZEGEDY C,VANHOUCKE V,IOFFE,et al.Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[J].Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition,2016,12(01): 2818-2826.
[14]SMITH S L,KINDERMANS PGJ,YING C,e tal. Don't Decay the Learning Rate, Increase the Batch Size[A/OL].[2018-02-24].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1711.00489.
[15]GOYAL P, DOLLAR P, GIRSHICK R B, et al.Accurate, Large Minibatch SGD: Training ImageNet in 1 Hour[A/OL].[2018-01-30].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
[16]JIA X, SONG S, HE W, et al. Highly Scalable Deep Learning Training System with Mixed-Precision: Training ImageNet in Four Minutes[A/OL].[2018-07-30].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1807.11205.
[17]GOYAL P,DOLLAR P,GIRSHICK R B,et al.Noordhuis,′ L.Wesolowski,A.Kyrola,A.Tulloch,Y.Jia,and K.He.Accurate,large minibatch SGD: training imagenet in 1 hour[J].CoRR,abs/1706.02677,2017.
[18]HE K,ZHANG X,REN S,et al.Deep residual learning for image recognition[J].Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition,2016,24(01): 770-778.
[19] LOSHCHILOV I , HUTTER F. SGDR: Stochastic gradient descent with warm Restarts[A/OL].[2017-03-03].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/1608.03983v2.
[20]LIU X,ZHANG S,HUANG Q.Ram:a region aware deep model for vehicle re-identification[C].∥IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo(ICME),2018:1-6.
[21]ZHOU K,YANG Y,Cavallaro A,et al.Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification[C].∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,2019:3702-3712.
[22]JIN X, LAN C, ZENG W, et al. Uncertainty-aware multi-shot knowledge distillation for image-based object re-identification[A/OL].[2020-01-21].https:∥arxiv.org/abs/2001.05197.
Vehicle Re-identification Algorithm Based on Key Position Feature
ZHAO Bin, DONG Changyuan
(School of Sciences, Hubei Univ. of Tech., Wuhan 430068,China)
Abstract:In the image recognition task, the premise of getting more recognizable features is to accurately locate the key position. The roof, window and front face of the car are the three most critical parts of the vehicle. A PCB-LS method is proposed for vehicle re-identification. Based on the idea of extracting local features, the feature map is extracted by using the backbone network of Resnet50, and then the feature map is divided into three parts, and the classifier is trained for the three parts respectively. For the over-fitting phenomenon of the model in the training set, the label smoothing regularization method is used to reduce the trust of the model to the training set samples and improve the accuracy of the model in the test set. Using the Veri776 dataset for training and testing, the accuracy of the PCB-LSS method on the test set can reach Rank@1, 5, 10 are 93.62%, 96.72%, 97.74% respectively, and mAP is 76.17%. The PCB-LS method can not only obtain the features with high recognition, but also the excellent generalization ability.
Keywords:vehicle re-identification; PCB; feature extraction; label smoothing; generalization ability
[責任編校:張 眾]

