前列腺特異性抗原比值在前列腺癌診斷灰區的臨床意義
劉亞巍 ,蔡小兵 ,王 飛 ,劉 明 ?,王建業
(1.總參警衛局 衛生保健處,北京 100017;2.北京醫院 泌尿外科,北京 100730)
前列腺特異性抗原比值在前列腺癌診斷灰區的臨床意義
劉亞巍1,蔡小兵1,王 飛2,劉 明2?,王建業2
(1.總參警衛局 衛生保健處,北京 100017;2.北京醫院 泌尿外科,北京 100730)
目的:探討游離前列腺特異性抗原(fPSA)與總前列腺特異性抗原(tPSA)比值(f/t)在tPSA為4~10ng/ml時對前列腺癌診斷的意義。方法:對83例血清tPSA為4~10ng/ml的前列腺增生和前列腺癌患者進行回顧行分析。均經由B超引導下行前列腺穿刺組織學驗證。酶免微粒子捕捉法測定血清中tPSA與fPSA。結果:本組中32例(38%)為前列腺癌,51例(62%)為前列腺增生。前列腺癌及前列腺增生組tPSA的平均值分別為6.63ng/ml和6.99ng/ml,兩者間無顯著性差異 (P>0.05);前列腺癌患者f/t值顯著低于前列腺增生患者 (0.16vs0.23,P<0.01)。以f/t比值0.16作為前列腺癌的診斷臨界值時,其敏感性及特異性分別為71%、78%。結論:f/t值對前列腺癌及前列腺增生的鑒別有重要意義,以0.16作為診斷臨界值準確率較高。
前列腺腫瘤;前列腺特異性抗原比值
Author’s addressDivision of Health,Bureau of Guard,General Advisor Office of Chinese PLA,Beijing 100017,China
從上世紀80年代開始,前列腺抗原(prostate antigen,PSA)作為前列腺癌的腫瘤標記物逐漸被廣泛應用于臨床前列腺癌的篩選檢查,也提高了早期前列腺癌的診斷率[1]。但PSA僅為腫瘤相關性抗原,并非腫瘤特異性抗原,受多種因素影響。前列腺炎、良性前列腺增生 (benign prostate hyperplasia,BPH)、泌尿系統感染以及一些物理因素刺激(如導尿、前列腺按摩等)都可導致患者血清PSA增高。為進一步準確預測前列腺癌,游離PSA和總 PSA的比值(free prostate antigen and total prostate antigen ratio,f/t)近年來得到人們的關注。本研究通過對于前列腺穿刺活檢資料的分析,評估f/t在前列腺癌診斷灰區中的作用。
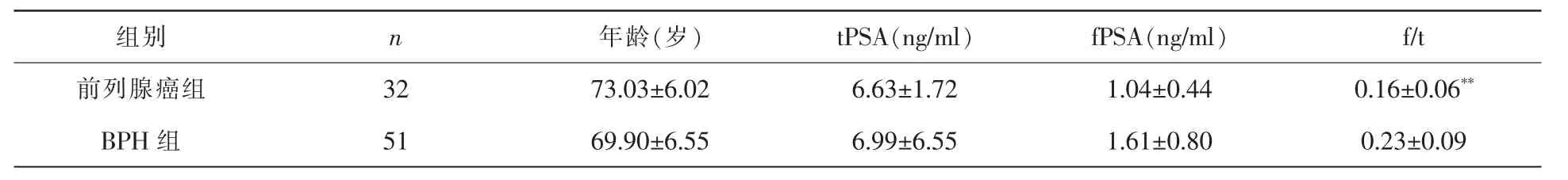
表1 前列腺癌和BPH組患者各項指標的檢測結果
1 資料與方法
1.1 臨床資料
83例前列腺穿刺活檢病例為2009年1月~2010年12月在北京醫院泌尿外科行前列腺穿刺的患者。穿刺活檢前檢測其tPSA值為4~10ng/ml。避免近期直腸指診、前列腺B超、前列腺按摩、膀胱鏡檢等外界刺激因素,患者均在穿刺前清晨空腹取外周靜脈血。
1.2 血清PSA檢測方法
于直腸指檢前或指檢后1周抽血,對采集的血液進行離心后,8h內檢測血清PSA。采用美國雅培公司生產Axsym的自動酶標儀,通過酶免微粒子捕捉法測定tPSA、fPSA。通過公式計算f/t。
1.3 統計學方法
組間比較采用t檢驗。
2 結果
本組83例中前列腺癌32例,占38%,年齡56~82歲,平均 73.03歲;BPH 51例,占 62%,年齡47~86歲,平均69.90歲。前列腺癌組與BPH組間各項指標檢測結果見表1。2組患者的年齡、tPSA、fPSA 均無顯著性差異 (均 P>0.05),f/t比值在前列腺癌患者顯著低于BPH患者(P<0.01)。
分別以f/t比值 0.1、0.16、0.23為診斷標準,對其診斷前列腺癌的敏感性及特異性進行分析,結果見表2。f/t比值0.16作為前列腺癌的診斷臨界值時,其敏感性及特異性分別為71%、78%。
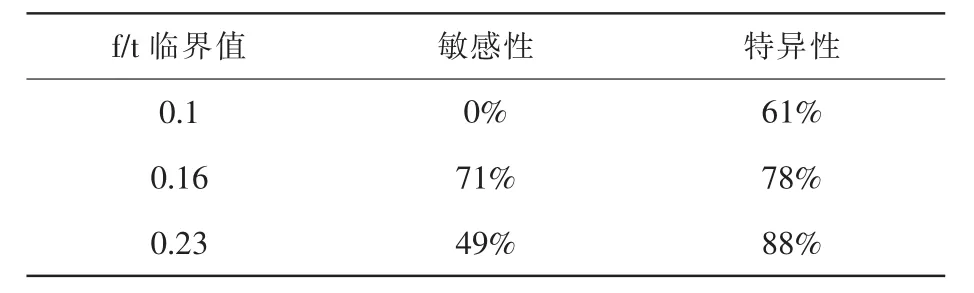
表2 對前列腺癌診斷的敏感性和特異性
3 討論
腫瘤標志物是在腫瘤發生和增殖過程中,由腫瘤細胞生物合成、釋放或者是宿主對癌類反應性的一類物質,易受各種因素的影響[2]。前列腺癌的臨床癥狀常在晚期才出現,有很多患者已發生骨轉移,失去了治愈的機會。PSA是檢測前列腺癌最具臨床價值的腫瘤標記物,但PSA對前列腺組織特異而非前列腺癌特異,在診斷灰區,前列腺癌和BPH的tPSA值存在相互重疊,原因在于PSA只是前列腺上皮細胞標記物,正常、增生及腺癌組織的上皮細胞均可產PSA,在此范圍內活檢陽性率僅為22%[3]。因此,當PSA值在診斷灰區時,僅憑tPSA不能直接鑒別前列腺癌和BPH。本研究也表明,在此區間內,前列腺癌和BPH的tPSA無顯著性差異(P>0.05)。
PSA在血清中以不同的形式存在。PSA主要與 ɑ1-抗糜蛋白(ɑ1-ACT)結合,稱為結合 PSA,約占tPSA的70%~90%。此外,微量PSA也可與ɑ2-巨球蛋白結合。由于ɑ2-巨球蛋白掩蓋PSA抗原決定簇,不能被檢測出來。另一部分PSA不與任何蛋白結合,稱之為游離PSA,約占tPSA的10%~30%。因此,可測定的tPSA僅包括結合PSA(PSA-ACT)和游離 PSA(fPSA)。
Bjork等[4]通過研究發現大多數前列腺癌患者的腫瘤細胞中存在抗糜蛋白酶(ACT)轉錄及表達的蛋白,而BPH患者其前列腺增生結節產生PSA的上皮細胞中,ACT轉錄及表達的蛋白稀少,僅為前列腺癌細胞轉錄及表達的1%。前列腺癌細胞產生的ACT很容易同PSA結合形成復合物進入血液循環。相比之下,BPH患者前列腺局部產生的ACT較少,PSA多以游離形式進入血液循環。這就是前列腺癌比BPH患者f/t低的原因。
Weckermann等[5]研究認為,應用f/t比值能有效地區別BPH和前列腺癌,特別是對于診斷灰區的患者,f/t<0.18能作為選擇是否穿刺或者重復穿刺的參考指標,而且該比值不受患者年齡、前列腺體積、尿路感染和腫瘤分級、分期的影響。本組資料對tPSA在4~10ng/ml之間的前列腺癌和BPH患者年齡、tPSA、fPSA、f/t進行分析,結果表明前列腺癌組和BPH組在年齡、tPSA、fPSA上均無顯著性差異(均P>0.05),而2組的f/t比值差異顯著(P<0.01),提示 f/t比值對 tPSA 在 4~10ng/ml患者的鑒別診斷具有重要的意義。
Christenssont等首先提出了游離PSA與總PSA之比f/t的概念。隨著前列腺癌血PSA增高,其fPSA增高不明顯,這使f/t比值成為鑒別前列腺癌和前列腺增生的重要依據,尤其對于血PSA處于4~10ng/ml的患者。以往的研究分別有學者以0.1、0.16、0.23為臨界值來預測前列腺癌檢出率[6~9]。從本研究的表2可以看出,以0.16為臨界標準值診斷前列腺癌,敏感性是71%、特異性是78%,準確率較高,可提高tPSA在診斷灰區時對前列腺癌的診出率,減少臨床不必要的穿刺活檢。
總之,應用f/t比值鑒別診斷前列腺癌和BPH,可顯著提高前列腺癌診斷的特異性和敏感性,當 PSA 在 4~10ng/ml時,以 f/t 0.16[10~12]作為臨界診斷值可以獲得較高的準確性。
[1]Gara S,Boussen H,Ghanem A,et al.Use of common seric tumor markers in patients with solid cancers[J].Tunis Med,2008,86(6):579-583.
[2]Sayre EC,Bunting PS,Kope JA.Reliability of self.Report versus chart-based prostate cancer,PSA,DRE and urinary symptoms[J].Can J Urol,2009,16(1):4463-4471.
[3]Okegawa T,Noda H,Nutahara K,et al.Comparison of two investigative assays for the complexed prostate-specific antigen in totalprostate-specific antigen between 4.1 and 10.0ng/ml[J].Urology,2000,55:700-704.
[4]Bjork T,Bjartell A,Abrahamsson PA,et al.Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin production in PSA-producing cell is common in prostate cancer but rare in benign prostatic hyperplasia[J].Urology,1994,43:427-434.
[5]WeckermannD,Maassen C,WawroschekF,etal.Improved discrimination of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia by means of the quotient of free and total PSA[J].Int Urol Nephrol,1999,31(3):351-359.
[6]Pepe P and Aragona F.Incidence of insignificant prostate cancer using free/total PSA[J].Urology Unit,2010,13:316-319.
[7]田連芳.血清fPSA及f-PSA/t-PSA比值診斷前列腺癌的臨床意義[J].放射免疫學雜志,2007,20(3):287-288.
[8]劉欣,唐杰,王知力,等.f-PSA/t-PSA比值在良性前列腺增生和前列腺癌鑒別診斷中的應用 [J].臨床泌尿外科雜志,2007,22(2):99-101.
[9]Greene KL,Albertsen PC,Babaian RJ,et al.PSA best practice statement 2009 update[J].J Urol,2009,182:2232-2241.
[10]顧煒,徐耀庭,謝敏,等.PSA、f-PSA/t-PSA和PSAD在前列腺癌診斷中的價值[J].老年醫學與保健,2010,16(2):117-119.
[11]梁濤,蔡明,李州利,等.f-PSA/t-PSA在前列腺疾病中的意義[J].醫學信息,2010,23(6):110.
[12]Azmi AH,Azmy SH,Ziad MA,et al.Utility of free prostate specific antigen serum level and its related parameters in the diagnosis of prostate cancer[J].Saudi Journal kidney diseases and Transplantation,2011,22(2):291-297.
Clinic significance of f/t prostate antigen ratio in the diagnosis of prostate cancer with prostate antigenin diagnosticgrayzone
LIU Ya-wei,CAIXiao-bing,WANG Fei,etal//JournalofChina-Japan Friendship Hospital,2011 Feb,26(1):12-14
Objective:To study significance of free prostate antigen(fPSA) and total prostate antigen(tPSA) ratio(f/t)in the diagnosis of prostate cancer with tPSA in diagnostic gray zone.Methods:We analysed retrospectively 83 prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH)patients whose serum tPSA levels between 4 and 10 ng/ml.All the results confirmed by histology of transrectal ultrasound guided biopsies.The tPSA and fPSA in serum were measured by micropartical enzyme immunoassay.Results:Of the 83 patients,32 were prostate cancer(38%)and 51 were BPH (62%).The mean values of tPSA were 6.63ng/ml and 6.99ng/ml in patients with prostate cancer and BPH,the f/t were 0.16 and 0.23,respectively.The mean values of tPSA,fPSA were no significant differentiation between two groups of prostate cancer and BPH(P>0.05).However,the mean value of f/t PSA of patients with prostate cancer was significantly lower than that of patients with BPH (P<0.01).When f/t PSA value was 0.16 as a critical value,the sensitivity and specificity were 71%and 78%.Conclusion:PSA ratio has a significant value in differential diagnosis between prostate cancer and BPH with serum tPSA level in diagnostic gray zone.The value of 0.16 is comparative accurate for differential diagnosis.
prostate cancer;free prostate antigen and total prostate antigen ratio
R697.+3
A
1001-0025(2012)01-0012-03
10.3969/j.issn.1001-0025.2012.01.004
2*本文通訊作者。
劉亞巍(1980-),男,主治醫師,碩士研究生。
2011-12-16
2012-01-06

