華夏陸塊古元古代A型流紋斑巖的發現及其地質意義
陳志洪,邢光福,姜 楊,匡福祥
(南京地質礦產研究所,江蘇 南京 210016)
華夏陸塊是中國東部大陸重要的組成部分之一,了解其早期的形成與演化對充分認識中國大陸地殼的形成、構造格局的演變乃至全球構造事件均具有重要意義(舒良樹,2006;于津海等,2007;鄭永飛和張少兵,2007)。經過長期的研究積累,特別是近十年來,隨著同位素測年技術(SHRIMP和LA-ICP-MS)迅猛發展,對華夏陸塊變質基底的地層、構造、巖石、同位素年代學及陸殼深部結構等研究取得了很大的進展,提供了更多可靠“古陸塊”存在的證據(Li et al.,2000,2005;Wan et al.,2007;Xu et al.,2007;Xia et al.,2012;Yu et al.,2008,2009,2012;Chen and Xing,in press)。但是,由于區域前寒武紀地質構造的復雜性,以及顯生宙以來歷次構造事件的疊加改造,制約了對早期構造巖漿熱事件性質的深入理解。因此,尋找相關事件記錄的地質體就是破解這一難題的關鍵。筆者最近在對出露于北武夷淡竹地區前寒武紀基底巖石進行的專題研究中,首次識別出了古元古代 A型流紋斑巖,這為深入研究華夏陸塊基底物質組成和早期構造演化提供了新的資料。
1 區域地質概況與樣品特征
研究區地處武夷地塊北部的浙西南地區(圖1)。區域上出露的前寒武紀變質巖系大致可以劃分為上、下兩套巖石地層單元:下部為古元古代的八都群,主要巖性為黑云斜長片麻巖、變粒巖、黑云片巖和斜長角閃巖,經歷了角閃巖相的中高溫區域變質作用和較強烈的混合巖化作用(胡雄健等,1992;甘曉春等,1995;Yu et al.,2012);上部為新元古代的龍泉群,主要巖性為變粒巖、云母片巖、綠簾斜長角閃巖、含鐵石英巖和大理巖等,經歷了高綠片巖相到低角閃巖相的區域變質作用(金文山等,1992;陳正宏等,2008;Li et al.,2010)。
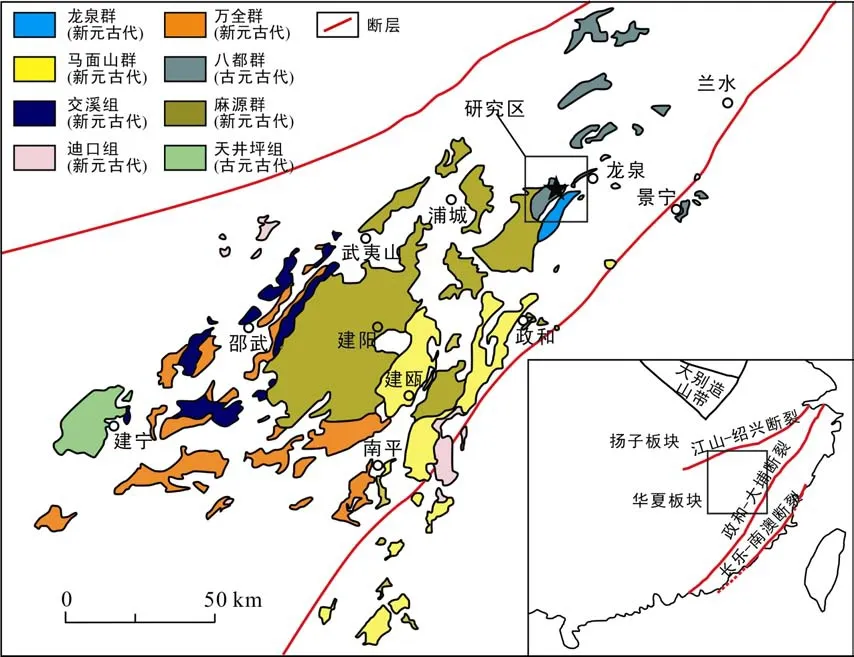
圖1 浙西南-閩西北地質簡圖(底圖據Li et al.,2005;Wan et al.,2007)Fig.1 Geological sketch map of SW Zhejiang and NW Fujian provinces (modified from Li et al.,2005;Wan et al.,2007)
本次研究新發現的流紋斑巖位于浙江省仙居縣淡竹鄉龍竹村,與八都群變質巖呈侵入接觸關系(圖2a);流紋斑巖主要零星(小于 0.01 km2)出露于龍竹村旁的一條河溝內,呈肉紅色,斑狀結構,具片狀-片麻狀的變形特征。斑晶總量約10%~15%,主要為熔蝕的高溫石英,普遍有較寬的反應邊且波狀消光(圖2b,d);另有少量斜長石斑晶(碳酸鹽化和絹云母化)和褐簾石化的黑云母(圖2c)。基質具有霏細結構,未能辨析其礦物組成(圖2d)。
2 分析方法
鋯石用人工重砂方法選出,然后在雙目鏡下挑純,選出晶形較好、具代表性的鋯石粘貼在環氧樹脂表面,拋光后將待測鋯石進行陰極發光(CL)圖像分析。CL照相在中國科學院地質與地球物理研究所電子探針實驗室完成。鋯石U-Pb測年和微量元素分析在合肥工業大學資源與環境工程學院完成,采用的儀器型號為 Agilent 7500a,激光剝蝕系統為Coherent Inc公司生產的ComPex102 ArF準分子激光剝蝕系統。分析時激光束斑直徑為32 μm,激光脈沖重復頻率為6 Hz。應用Nist610玻璃作為微量元素外標,鋯石標樣 91500進行同位素分餾校正,鋯石標樣Mud Tank作為同位素監控樣,實驗原理和詳細的測試方法見閆峻等(2012)。ICP-MS的分析數據通過 ICPMSDataCal程序計算獲得同位素比值、年齡和誤差(Liu et al.,2008,2010)。普通鉛校正采用Andersen (2002)的方法進行,校正后的結果用ISOPLOT程序(ver 2.49)完成年齡計算和諧和圖的繪制(Ludwig,2001)。
鋯石Hf同位素分析在中國地質科學院礦產資源研究所實驗室Thermo Fisher Neptune多接收電感耦合等離子質譜和New Wave UP213激光剝蝕系統上進行。激光剝蝕直徑為 44 μm,激光脈沖重復頻率為 8 Hz。測定時采用鋯石國際標樣GJ-1作為參考物質,儀器的運行條件及詳細的分析流程見Wu et al.(2006)和候可軍和袁順達(2010)。分析過程中GJ-1的176Hf/177Hf加權平均值為(0.282012±12)(2SD,n=15),與推薦值(候可軍和袁順達,2010)在誤差范圍內完全一致。εHf(t)的計算利用176Lu的衰變常數為1.865×10-11/a(Scherer et al.,2001),球粒隕石現今值176Hf/177Hf=0.282772和176Lu/177Hf=0.0332(Blichert-Toft and Albarede,1997);虧損地幔 Hf模式年齡計算采用當前虧損地幔值176Hf/177Hf=0.28325和176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Griffin et al.,2000);二階段 Hf模式年齡采用上地殼平均值176Lu/177Hf=0.015(Griffin et al.,2002)。

圖2 淡竹流紋斑巖的野外地質及鏡下特征Fig.2 Photos and microphotographs for the rhyolitic porphyries in the Danzhu region
全巖主量元素在南京地質礦產研究所實驗測試中心采用荷蘭Panalytical公司生產的Axios型波長色散X射線熒光光譜儀測定,分析精度優于5%。微量元素在南京地質礦產研究所實驗測試中心采用 Finnigan ELEMENT2型電感耦合等離子質譜(ICP-MS)測定,分析精度優于5% (Rudnick et al.,2004)。
3 結 果
3.1 鋯石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年齡和稀土元素
對淡竹流紋斑巖(樣品ZJ-11-1)中的25顆鋯石共計完成了25個測點的LA-ICP-MS分析,U-Pb同位素組成列于表1。標定的測年鋯石大部分為長柱狀,長/寬比為 2∶1~3∶1,顆粒大小約100~300 μm。樣品鋯石普遍受到了后期變質作用改造而發生重結晶,發育一定的核邊結構,具核部較黑且環帶結構不清晰(圖3a)。測年結果顯示,23顆鋯石分析點的Th(77×10-6~ 433×10-6)和U(108×10-6~2024×10-6)含量相對較高,相應的Th/U比值范圍為0.25~1.62,屬于典型的巖漿鋯石(吳元保和鄭永飛,2004),給出的207Pb/206Pb的年齡范圍為1902~1776 Ma。在諧和圖上,23個分析點構成一條很好的不一致線,上下交點的年齡分別為 1844±26 Ma和157±650 Ma(MSWD=0.91)。23個分析點給出的207Pb/206Pb年齡加權平均值為(1819±16 Ma)(MSWD=0.91),代表了流紋斑巖的成巖年齡(圖3b)。另外 2顆鋯石的 Th(12×10-6~15×10-6)和U(134× 10-6~186×10-6)的含量較低,Th/U比值變化于 0.08~0.09,可能代表變質成因(吳元保和鄭永飛,2004),給出的206Pb/238U年齡分別為240±6 Ma(5號分析點)和238±6 Ma(6號分析點)。
23個巖漿型鋯石測點在進行U-Pb同位素分析時,同步原位測定了鋯石稀土元素的含量(表2)。結果顯示,該類鋯石具有較高的 REE總量(∑REE=309×10-6~1112×10-6),在鋯石稀土元素球粒隕石標準化配分圖解上(圖3c),該類鋯石極度富集 HREE,呈左傾型,并具明顯的正Ce異常(Ce/Ce*=6.8~90.6)和負 Eu異常(Eu/Eu*=0.02~0.24),符合一般巖漿鋯石的稀土元素特征(Belousova et al.,2002)。另外2個變質鋯石的測點,由于當時儀器運行狀態不佳,未能獲得其理想數據。
3.2 全巖元素地球化學特征
4組流紋斑巖樣品的全巖主量、微量與稀土元素的成分見表3。它們與典型的A型花崗巖在地球化學組成上非常類似(Whalen et al.,1987),具高 Si(SiO2=67.0%~72.1%),富堿(Na2O+K2O=8.1%~9.0%),富 Fe(FeOT=2.9%~5.8%),顯著貧 Mg(MgO=0.19%~0.42%)和鈣(CaO=0.97%~1.7%)的特征。在 K2O-SiO2圖解中,全部樣品落入鉀玄巖系列中(圖略)。它們的Al2O3含量為13.2%~14.0%,A/CNK值為0.99~1.08,顯示出準鋁質-弱過鋁的特征。流紋斑巖的稀土元素總量較高,∑REE =626×10-6~765×10-6,輕重稀土之間分異明顯(圖4a),(La/Yb)N=14.3~28.1,Eu虧損強烈,Eu/Eu*為0.29~0.42。微量元素方面,流紋斑巖的 Ga含量較高(22.1×10-6~28.9×10-6),10000Ga/Al值為 3.0~4.1;HFSE元素組合(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)的值也很高,為 880×10-6~999×10-6。在原始地幔標準化蛛網圖上(圖4b),所有樣品均表現為明顯的Rb、Th、U和Pb峰以及Ba、Sr、Nb、Ta和(Ti+Eu)谷的分布特征。
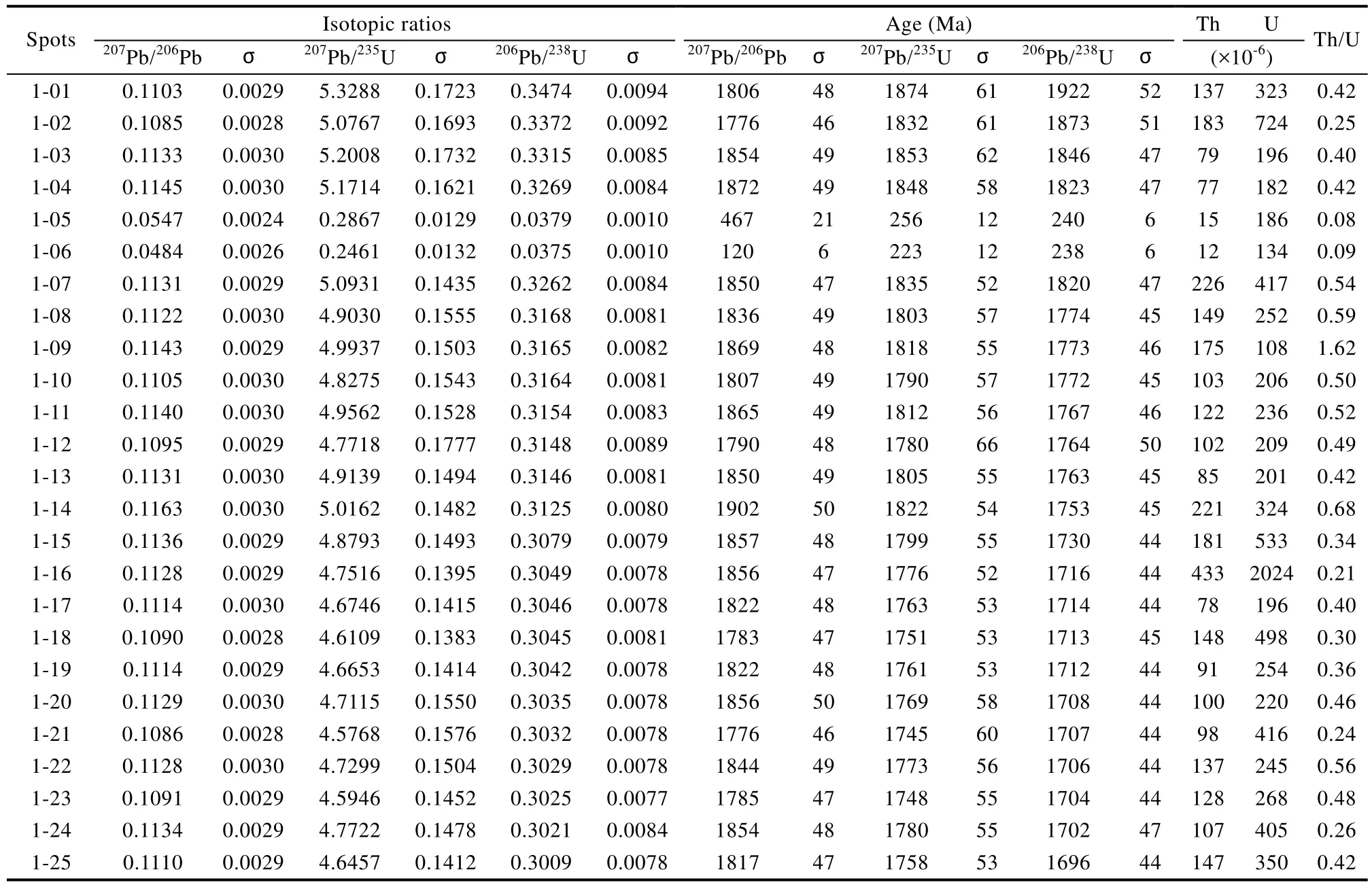
表1 淡竹流紋斑巖的鋯石U-Pb同位素分析數據Table1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb results for the rhyolitic porphyry in the Danzhu region
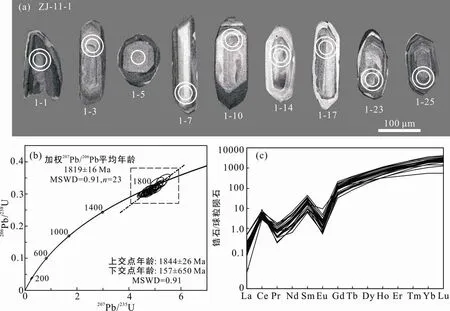
圖3 淡竹流紋斑巖的鋯石CL圖像(a),鋯石U-Pb年齡諧和圖(b)和稀土元素球粒隕石配分曲線圖(c)(內圈(小)為LA-ICP-MS靶位,外圈(大)為Hf同位素激光剝蝕靶位;球粒隕石值取自Sun and McDonough,1989)Fig.3 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of the representative zircons from the Danzhu rhyolitic porphyry(a) (with small and large white circles showing areas for U–Pb and Lu–Hf isotope analysis,respectively),U-Pb concordia diagram for zircons from the Danzhu rhyolitic porphyry(b) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns for zircons from the Danzhu rhyolitic porphyry(c) (chondrite and primitive mantle values are from Sun and McDonough (1989))
3.3 鋯石Hf同位素組成
在U-Pb年齡的基礎上,選擇15個巖漿鋯石分析點進行了 Hf同位素測定,結果列于表4。鋯石176Lu/177Hf比值介于 0.000345~0.000817之間,176Hf/177Hf比值介于 0.281405~0.281588,單階段鋯石Hf模式年齡tDM為2.31~2.55 Ga,兩階段鋯石Hf模式年齡t2DM為2.46~2.76 Ga。鋯石Hf同位素初始比值εHf(t)為-8.4~-2.2。
4 討 論
4.1 巖石類型與成因
最早Loiselle and Wones(1979)將A型花崗巖定義為堿性(alkaline)、貧水(anhydrous)和非造山(anorogenic)的花崗巖,它一般是堿過飽和而鋁不飽和。但近年來的研究表明,A型花崗巖不僅包括堿性巖類,還擴大到鈣堿性、弱堿、準鋁、弱過鋁甚至強過鋁質巖石(吳福元等,2007)。同時,一些流紋巖也顯示出A型花崗巖的特征,通常認為它們是A型花崗巖噴出相的產物(Li et al.,2005)。淡竹流紋斑巖具有A型花崗巖的地球化學特征:(1)高Si富堿,高K貧Al、Ca和Mg,巖石的FeOT/MgO值(13.8~15.1)明顯高于I、S和M型花崗巖的平均值,與典型的A型花崗巖一致(~13.4) (Whalen et al.,1987);(2)富集大離子親石元素(Rb、Th、U)和高場強元素Zr和Hf,虧損 Ba、Sr、Eu和Ti(圖4b),富 Ga,10000Ga/Al值為3.0~4.1,接近全球A型花崗巖的平均值(~3.75)(Whalen et al.,1987),在 10000Ga/Al和(Na2O+K2O)/CaO 對(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)的判別圖解里(圖5),淡竹流紋斑巖均落入 A型花崗巖區域,而與分異的 I或 S型花崗巖相區別。根據Watson and Harrison(1983)的公式,用巖石主量元素及其Zr含量計算得到流紋斑巖的鋯石飽和溫度在881~912 °C之間,顯示其接近于A型而明顯高于I和S型花崗巖的原始巖漿溫度。綜上所述,巖石學、地球化學特征及巖漿形成溫度都表明淡竹流紋斑巖屬于典型的A型流紋斑巖。
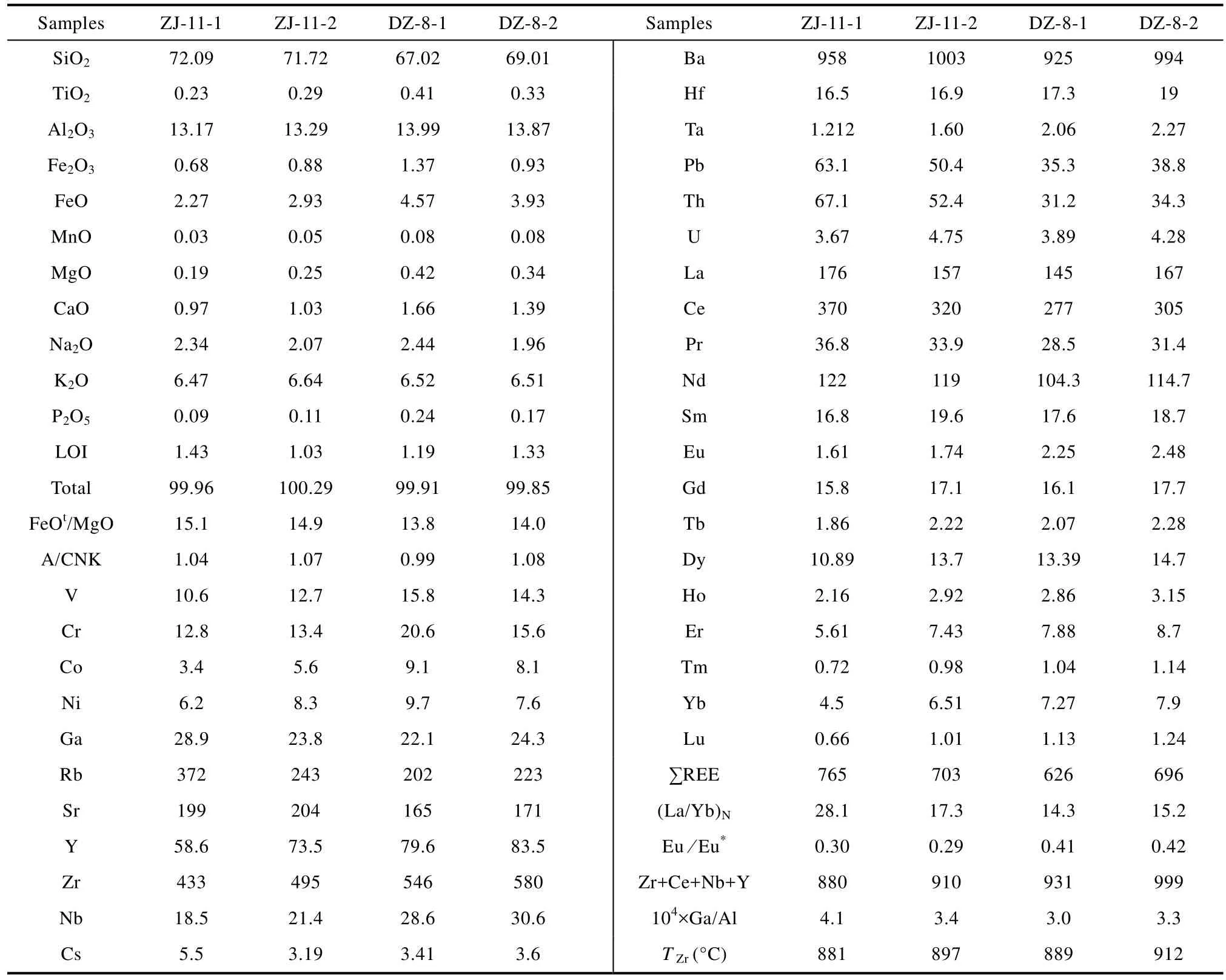
表3 淡竹流紋斑巖的主量元素(%)和微量元素組成(×10-6)Table3 Major (%) and trace element (×10-6) concentrations of the rhyolitic porphyries in the Danzhu region
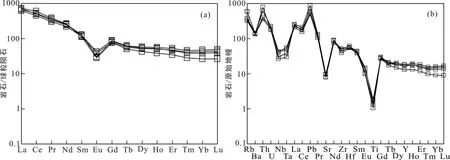
圖4 淡竹流紋斑巖的稀土元素球粒隕石標準化配分圖解(a)和原始地幔標準化的微量元素圖解(b)(球粒隕石與原始地幔值取自Sun and McDonough,1989)Fig.4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized spidergrams(b) of the Danzhu rhyolite porphyries(chondrite and primitive mantle values are from Sun and McDonough (1989))
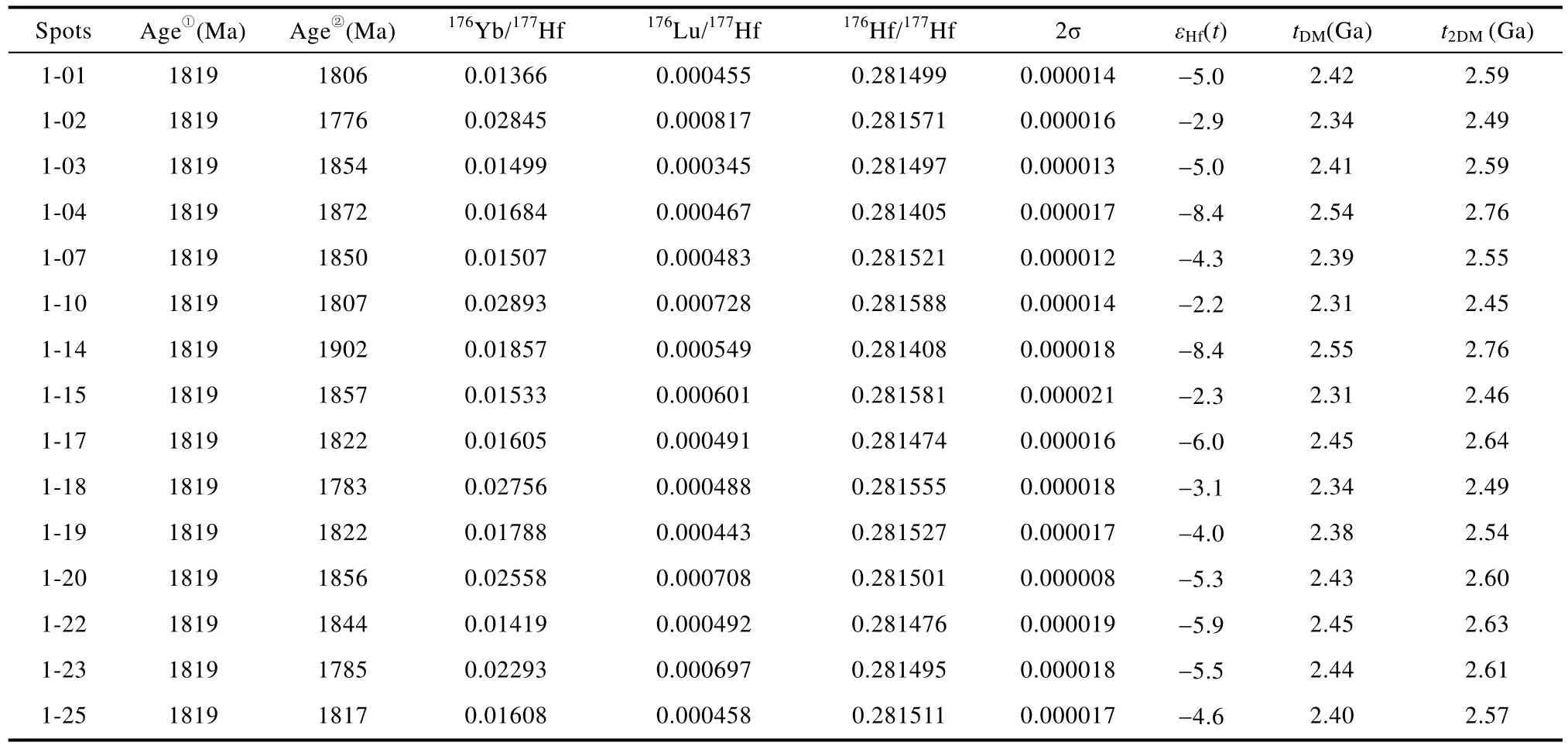
表4 淡竹流紋斑巖的鋯石Hf同位素組成Table4 LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon Lu-Hf isotope results for the rhyolitic porphyries in the Danzhu region
已有研究表明,A型花崗巖(流紋巖)的成因有如下幾種可能:(1)幔源玄武質巖漿的結晶分異作用(Mushkin et al.,2003);(2)深部地殼巖石的部分熔融(Clemens et al.,1986;Whalen et al.,1987;King et al.,1997;Wu et al.,2002);(3)殼幔巖漿混合(Yang et al.,2006)。首先,研究區和相鄰地區缺乏同時代的大規模基性火成巖這一事實,可以排除本區流紋斑巖由基性巖漿分離結晶作用所成的可能性。此外,A型花崗巖(流紋巖)具有富堿、貧水的晶體粥特性,說明它們也不可能通過較大規模的分離結晶作用所形成(吳福元等,2007)。另外,淡竹流紋斑巖中尚未發現有中基性的暗色包體,也可以排除巖漿混合的成因模式。那么,深部陸殼巖石部分熔融可能是形成淡竹流紋斑巖較理想的成巖模式。流紋斑巖具有明顯的Pb的正異常和Nb的負異常,也表明巖石熔融的源巖可能以陸殼物質為主。顯著的Sr及Eu的負異常,則進一步說明長英質巖石在其源區可能占主導(吳福元等,2007)。此外,流紋斑巖的兩階段Hf模式年齡t2DM(2.46~2.76 Ga)為新太古代,在εHf(t)-t圖解上,其落入華夏陸塊古老基底(八都群)演化域內(圖6)。因此,華夏陸塊深部古老基底巖石(類似八都群)的部分熔融可能是淡竹流紋斑巖的巖漿物質的主要來源。
4.2 構造意義
眾所周知,一系列重要的地質事件發生于古元古代已經成為共識,如全球性的碰撞造山事件和Columbia超級大陸的形成(Rogers and Santosh,2002;Zhao et al.,2002,2004,2009)、大陸地殼的快速生長(Condie,1998,2000)、超級地幔柱活動(Condie et al.,2001)等。中國東部的華北陸塊(Zhao et al.,2002,2004,2009;Wang et al.,2007;Hou et al.,2008;Peng et al.,2008;He et al.,2009)和揚子陸塊(Zhang et al.,2006;Sun et al.,2008;Wu et al.,2008;Zhao et al.,2010)同樣有著與 Columbia超大陸聚合和裂解有關的古元古代大規模構造-巖漿作用的響應。在華夏陸塊,越來越多古元古代構造-熱事件近年來陸續被發現(Li,1997;Li et al.,2000;Xiang et al.,2008;Liu et al.,2009;Xia et al.,2012;Yu et al.,2009,2012;Chen and Xing,in press),但目前對這些地質事件性質還存在認識上的分歧。如,基于對武夷地塊古元古代的S型(1888~1875 Ma)和A型(1867~1855 Ma)花崗巖及裂谷型基性巖(天井坪組)(1760 Ma)的研究(Li,1997;Li et al.,2000),Yu et al.(2009)提出華夏陸塊可能存在一個與Columbia超大陸匯聚有關的造山旋回:同造山-后造山期(1.89~1.83 Ga)和非造山(裂谷)期(1.80~1.76 Ga);然而,Xiang et al.(2008)強調板內基性-超基性的巖漿活動早在~1.85 Ga就已開始;Xia et al.(2012)則認為武夷地塊北部古元古代A和S型花崗巖(1.89~1.85 Ga)同樣形成于板內裂谷環境;最近,在武夷地塊中部還發現有~1.84 Ga過鋁質 S型花崗巖,其成因機制也與板內伸展環境有關(Chen and Xing,in press)。我們注意到,武夷地塊出露的古元古代 S和A型花崗巖(流紋斑巖),其實是在相隔很短的時間內(1.89~1.83 Ga)形成,暗示它們可能是同一構造-熱事件背景下的產物。
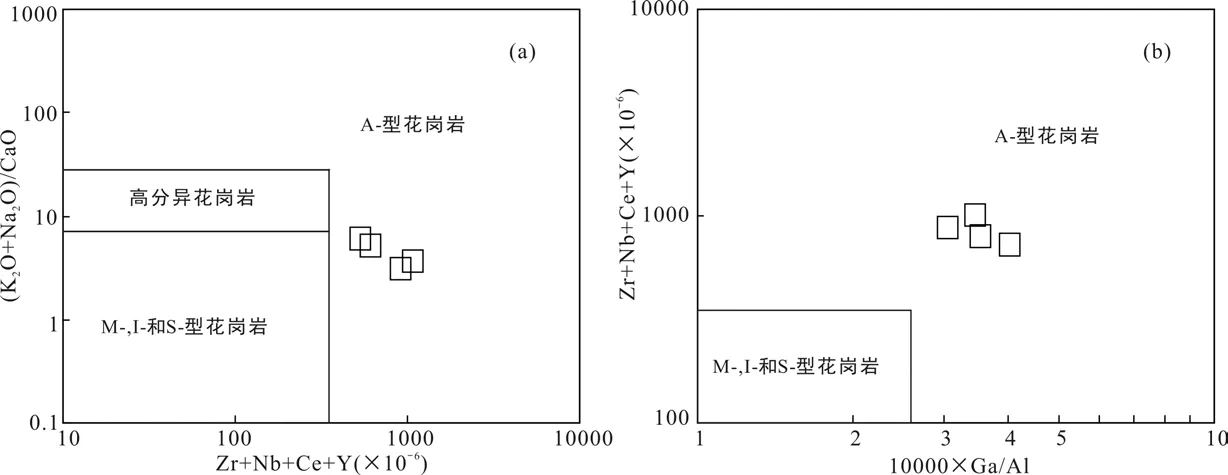
圖5 淡竹流紋斑巖的(Na2O+K2O)/CaO-(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)圖解(a)和(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-10000×Ga/Al圖解(b) (底圖據Whalen et al.,1987)Fig.5 (Na2O+K2O)/CaO vs (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) (a) and (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) vs 10000×Ga/Al (b) plots for the Danzhu rhyolitic porphyries (after Whalen et al.,1987)
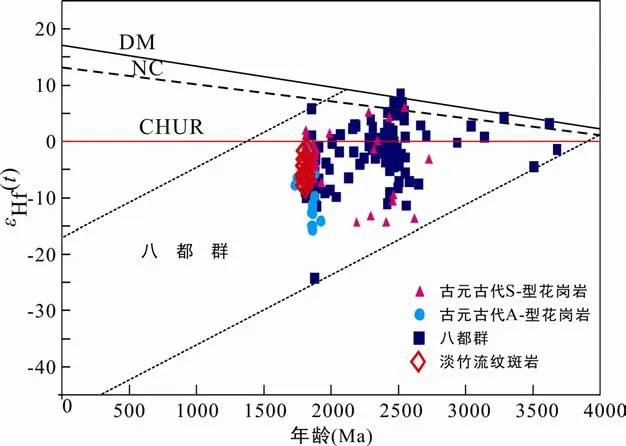
圖6 淡竹流紋斑巖的鋯石εHf(t)-t圖解(八都群、古元古代S和A型花崗巖的鋯石Hf同位素數據來自Liu et al.(2009),Yu et al.(2009,2012)和Xia et al.(2012))Fig.6 εHf(t) vs 207Pb/206Pb age plot for the Danzhu rhyolitic porphyries(The zircon Hf-isotope data of the Badu Group and Paleoproterozoic S- and A-type granites are from Liu et al.,(2009);Yu et al.,(2009,2012);Xia et al.,(2012))
武夷地塊~1.82 Ga的A型流紋斑巖的發現和確證,為深入理解華夏陸塊的基底性質和早期構造格局的演化提供了新的地質內容,同時表明武夷地塊的S和A型花崗巖(流紋斑巖)的成巖年齡并無明顯的規律性。另外,武夷地塊的A型花崗巖(流紋斑巖)形成于1.87~1.82 Ga,至少還說明~1.87 Ga之后區域上一直處于板內伸展環境。一般認為,花崗巖(流紋巖)的地球化學成分取決于其源巖的礦物組成和化學成分、熔融時的物理化學條件(包括溫度、壓力和揮發份)和其后巖漿的演化(如分離結晶作用、巖漿混合作用、同化混染作用等),因此大部分花崗巖(流紋巖)的地球化學組成與構造背景可能無直接的對應關系(吳福元等,2007)。但是需要指出的是,學術界對A型花崗巖(流紋巖)的構造指示意義還是有較統一的認識,認為它們的產出通常與伸展構造環境有關(Whalen et al.,1987;Clemens et al.,1986;Barbarin,1999)。因此,結合區域地質資料,我們傾向于認為北武夷淡竹A型流紋斑巖可能是板內伸展背景下巖漿活動的產物,也正是由于這種拉張作用的機制,促使了軟流圈地幔上涌、巖石圈地幔減壓熔融生成基性巖漿底侵,導致地殼深熔作用形成了中-北武夷地區的古元古代花崗巖(流紋斑巖)。如前所述,流紋斑巖具有較高的形成溫度和負的εHf(t)值,表明淡竹流紋斑巖的成巖過程中幔源巖漿可能僅提供了熱量而缺乏物質的輸入。另外,區域上未發現有大規模同期的雙峰式火山巖,也暗示這種伸展環境可能僅處于板內拉張作用的初級階段,尚未進入板內裂谷期。
淡竹流紋斑巖中印支期變質年齡信息的發現和厘定,還說明它與區域上出露的其它古元古代 S和A型花崗巖一樣,共同經歷了一次變質事件的改造(Xiang et al.,2008;Yu et al.,2009;Xia et al.,2012)。事實上,華南及其鄰區在二疊紀-三疊紀時處于地質構造的活躍期,如 Sibumasu(中緬馬蘇)地塊向印支-華南板塊增生(Carter et al.,2001)、印支板塊與華南板塊開始碰撞(Lepvrier et al.,2004)以及華南板塊與華北板塊的碰撞等(Ames et al.,1993;Li et al.,1993;Jahn,1998;Zheng et al.,2006)。最近,Li and Li(2007)提出華夏陸塊晚二疊世-三疊紀(251~233 Ma)強烈的板內造山作用,可能還與中生代太平洋板塊平俯沖到華南板塊有關。盡管,目前對華南印支造山事件的認識還存在分歧,但是都認同這期重要的造山作用直接導致了中-北武夷地區基底巖石發生了強烈的變質變形作用(達角閃巖相)。同時,也造成包括淡竹流紋斑巖在內的大部分古元古代花崗巖中的鋯石發生了不同程度的Pb丟失,并促使這些鋯石發生不同程度的重結晶作用或形成新生的變質鋯石(或增生邊)(Yu et al.,2009,2012;Xia et al.,2012)。
5 結 論
(1) 獲得華夏陸塊北武夷淡竹流紋斑巖的LA-ICP-MS 鋯石U-Pb年齡為1819±16 Ma,為古元古代巖漿活動的產物,并受到印支期一定的變質改造作用影響。
(2) 元素地球化學組成和鋯石Hf同位素特征表明,~1.82 Ga的淡竹流紋斑巖具有典型的A型花崗巖(流紋巖)的特征,來自華夏陸塊基底新太古代陸殼物質的再造重熔,形成于板內伸展環境。
致謝:研究工作得到了包志偉研究員、王孝磊博士、余明剛、趙希林和李亮等工程師的指導和幫助,論文初稿承蒙李武顯研究員的審閱并提出寶貴意見,在此一并向他們表示感謝。
陳正宏,李寄嵎,謝佩珊,曾雯,周漢文.2008.利用EMP獨居石定年法探討浙閩武夷山地區變質基底巖石與花崗巖的年齡.高校地質學報,14(1):1–15.
甘曉春,李惠民,孫大中,金文山,趙風清.1995.浙西南古元古代花崗質巖石的年代.礦物巖石學雜志,14(1):1–8.
侯可軍,袁順達.2010.寧蕪盆地火山-次火山巖的鋯石U-Pb年齡、Hf同位素組成及其地質意義.巖石學報,26(3):888–1002.
胡雄健,許金坤,童朝旭.1992.浙西南前寒武紀地質.北京:地質出版社:1–278.
金文山,莊建民,楊傳夏.1992.福建前加里東區域變質巖系的巖石學、地球化學和變質作用特征.福建地質,11:241–251.
舒良樹.2006.華南前泥盆紀構造演化:從華夏地塊到加里東期造山帶.高校地質學報,12(4):418–431.
吳福元,李獻華,楊進輝,鄭永飛.2007.花崗巖成因研究的若干問題.巖石學報,23(6):1217–1238.
吳元保,鄭永飛.2004.鋯石成因礦物學研究及其對U-Pb年齡解釋的制約.科學通報,49(16):1589–1604.
閆峻,彭戈,劉建敏,李全忠,陳志洪,史磊,劉曉強,姜子朝.2012.下揚子繁昌地區花崗巖成因:鋯石年代學和Hf-O 同位素制約.巖石學報,28(10):3209–3227.
于津海,O’Reilly S Y,王麗娟,Griffin W L,蔣少涌,王汝成,徐夕生.2007.華夏地塊古老物質的發現和前寒武紀地殼的形成.科學通報,52(1):11–18.
鄭永飛,張少兵.2007.華南前寒武紀大陸地殼的形成和演化.科學通報,52(1):1–10.
Ames L,Tilton G R and Zhou G.1993.Timing of collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtse cratons:U-Pb zircon dating of coesite-bearing eclogites.Geology,21:339–342.
Andersen T.2002.Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report204Pb.Chemical Geology,192:59–79.
Barbarin B.1999.A review of the relationships between granitoid types,their origins and their geodynamic environments.Lithos,46:605–626.
Belousova E A,Griffin W L,O’Reilly S Y and Fisher N I.2002.Igneous zircon:Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,143:602–622.
Blichert–Toft J and Albarède F.1997.The Lu-Hf geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,148:243–258.
Carter A,Roques D,Bristow C and Kinny P.2001.Understanding Mesozoic accretion in Southeast Asia:Significance of Triassic thermotectonism (Indosinian orogeny) in Vietnam.Geology,29(3):211–214.
Chen Z H and Xing G F.Petrogenesis of a Paleoproterozoic S-type granite,central Wuyishan terrane,SE China:Implications for crustal evolution of the Cathaysia Block.International Geology Review,doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2013.779065,in press.
Clemens J D,Holloway J R and White A J R.1986.Origin of an A-type granite:Experimental constraints.American Mineralogist,71:317–324.
Condie K C.1998.Episodic continental growth and supercontinents:A mantle avalanche connection?Earth Planet Sci Let,163:97–108.
Condie K C.2000.Episodic continental growth models:Afterthoughts and extensions.Tectonophysics,322:153–162.
Condie K C,Des Marais D J and Abbott D.2001.Precambrian superplumes and supercontinents:A record in black shales,carbon isotopes,and paleoclimates?Precambrian Res,106:239–260.
Griffin W L,Pearson N J,Elusive E,Jackson S E,Van A E,O’Reilly,S Y and She S R.2000.The Hf isotope composition of carbonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,64:133–147.
Griffin W L,Wang X,Jackson S E,Pearson N J,O’Reilly S Y,Xu X S and Zhou X M.2002.Zircon chemistry and magma mixing,SE China:In-situanalysis of Hf isotopes,Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes.Lithos,61(3-4):237–269.
He Y H,Zhao G C,Sun M,and Xia X P.2009.SHRIMP and LA-ICP-MS zircon geochronology of the Xiong’er volcanic rocks:Implications for the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic evolution of the southern margin of the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,168:213–222.
Hou G,Santosh M,Qian X,Lister G S and Li J.2008.Configuration of the Late Paleoproterozoic supercontinent Columbia:insights from radiating mafic dyke swarms.Gondwana Research,14:395–409.
Jahn B M.1998.Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of UHP eclogites and ultramafic rocks of the Dabie orogen:Implications for continental subduction and collisional tectonics // Hacker B R and Liou J G.When Continental Collide:Geodynamics and Geochemistry of Ultrahigh-Pressure Rocks,Kluwer Academic Publishers,Netherlands:203–239.
King P L,White A J R,Chappell B W and Allen C M.1997.Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt,Southeastern Australia.Journal of Petrology,38:371–391.
Lepvrier C,Maluski H,Van T V,Leyreloup A,Phan T T and Nguyen V V.2004.The Early Triassic Indosinian Orogeny in Vietnam (Truong Son Belt and Kontum Massif):Implications for the geodynamic evolution of Indochina.Tectonophysics,393(1–4):87–118.
Li S G,Xiao Y L,Liou D L,Chen Y Z,Ge N J,Zhang Z Q,Sun S S,Cong B,Zhang R Y,Hart S R and Wang S S.1993.Collision of the North China and Yangtse blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites:Timing and processes.Chem Geol,109(1–4):89–111.
Li W X,Li X H and Li Z X.2005.Neoproterozoic bimodal magmatismin the Cathaysia Block of South China and its tectonic significance.Precambrian Research,136:51–66.
Li X H.1997.Timing of the Cathaysia Block formation:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology.Episodes,20:188–192.
Li X H,Sun M,Wei G J,Liu Y,Lee C Y and Malpas J.2000.Geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic study of amphibolites in the Cathaysia Block,southeastern China:Evidence for an extremely depleted mantle in the Paleoproterozoic.Precambrian Research,102:251–262.
Li Z X and Li X H.2007.Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A fiat-slab subduction model.Geology,35(2):179–182.
Li Z X,Li X H,Wartho J A,Clark C,Li W X,Zhang C L and Bao C.2010.Magmatic and metamorphic events during the early Paleozoic Wuyi-Yunkai orogeny,southeastern South China:New age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions.Geological Society of America Bulletin,122:772–793.
Liu R,Zhou H,Zhang L,Zhong Z,Zeng W,Xiang H,Jin S,Lu X and Li C.2009.Paleoproterozoic reworking of ancient crust in the Cathaysia Block,South China:Evidence from zircon trace elements,U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes.Chinese Science Bulletin,54:1543–1554.
Liu Y,Gao S,Hu Z,Gao C,Zong K and Wang D.2010.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced meltperidotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating,Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths.Journal of Petrology,51:537–571.
Liu Y S,Hu Z C,Gao S,Günther D,Xu J,Gao C G and Chen H H.2008.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard.Chemical Geology,257:34–43.
Loiselle M C and Wones D R.1979.Characteristics of anorogenic granites.Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs,11:468.
Ludwig K R.2001.ISOPLOT 2.49:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel.Berkeley Geochronology Centre,Special Publication,1:1–58.
Mushkin A,Navon O,Halicz L,Hartmann G and Stein M.2003.The petrogenesis of A-type magmas from the Amram Massif,Southern Israel.Journal of Petrology,44(5):815-832.
Peng P,Zhai M G,Richard E E,Guo J H,Liu F and Hu B.2008.A 1.78 Ga large igneous province in the North China craton:The Xiong’er Volcanic Province and the North China dyke swarm.Lithos,101:260–280.
Rogers J J W and Santosh M.2002.Configuration of Columbia,a Mesoproterozoic supercontinent.Gondwana Research,5:5–22.
Rudnick R L,Gao S,Ling W L,Liu Y S and McDonough W F.2004.Petrology and geochemistry of spinel peridotite xenoliths from Hannuoba and Qixia,North China craton.Lithos,77:609–637.
Scherer E,Munker C and Mezger K.2001.Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock.Science,293:683–687.
Sun M,Chen N,Zhao G,Wilde S A,Ye K,Guo J,Chen Y and Yuan C.2008.U-Pb Zircon and Sm-Nd isotopic study of the Huangtuling granulite,Dabie-Sulu belt,China:Implication for the Paleoproterozoic tectonic history of the Yangtze Craton.American Journal of Science,308:69–483.
Sun S S and McDonough W F.1989.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes //Saunder A D and Norry M J.Magmatism in the ocean basins.Geological Society Special Publications,42:313–345.
Wan Y S,Liu D Y,Xu M H,Zhuang J,Song B,Shi Y and Du L.2007.SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks in Northwestern Fujian,Cathaysia Block,China:Tectonic implications and the need to redefine lithostratigraphic units.Gondwana Research,12:166–183.
Wang Y J,Zhao G C,Fan W M,Peng T P,Sun L H and Xia X P.2007.LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Paleoproterozoic mafic dykes from western Shandong Province:Implications for back-arc basin magmatism in the Eastern Block,North China Craton.Precambrian Research,154:107–124.
Watson E B and Harrison T M.1983.Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,64:295–304.
Whalen J B,Currie K L and Chappell B W.1987.A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics,discrimination and petrogenesis.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,95:407–419.
Wu F Y,Sun D Y,Li H M,Jahn B M and Wilde S.2002.A-type granites in northeastern China:Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis.Chemical Geology,187:143–173.
Wu F Y,Yang Y H and Xie L W.2006.Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology.Chemical Geology,234:105–126.
Wu Y B,Zheng Y F,Gao S,Jiao W F and Liu Y S.2008.Zircon U-Pb age and trace element evidence for Paleoproterozoic granulite-facies metamorphism and Archean crustal rocks in the Dabie Orogen.Lithos,101:308–322.
Xia Y,Xu X S and Zhu K Y.2012.Paleoproterozoic S- and A-type granites in southwestern Zhejiang:Magmatism metamorphism and implications for the crustal evolution of the Cathaysia basement.Precambrian Research,216-219:177–207.
Xiang H,Zhang L,Zhou H W,Zhong Z Q and Zeng W.2008.Geochronology and Hf isotopes of zircon from mafic-ultramafic basement rocks of southwestern Zhejiang:Response to the Indosinian orogeny of the metamorphic basement of the Cathaysia Block.Science in China(Series D–Earth Sciences),51:788–800.
Xu X S,O’Reilly S Y,Griffin W L,Wang X L,Pearson N J and He Z Y.2007.The crust of Cathaysia:Age,assembly and reworking of two terranes.Precambrian Research,158:51–78.
Yang J H,Wu F Y,Chung S L,Wilde S A and Chu M F.2006.A hybrid origin for Qianshan A-type granite,Northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence.Lithos,89:89–106.
Yu J H,O’Reilly S Y,Griffin W L,Zhou M F and Wang L J.2012.U-Pb geochronology and Hf-Nd isotopic geochemistry of the Badu Complex,Southeastern China:Implications for the Precambrian crustal evolution and paleogeography of the Cathaysia Block.Precambrian Research,222-223:424–449.
Yu J H,O’Reilly S Y,Wang L J,Griffin W L,Zhang M,Wang R C,Jiang S Y and Shu L S.2008.Where was South China in the Rodinia supercontinent? Evidence from U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons.Precambrian Research,164:1–15.
Yu J H,Wang L J,Griffin W L,O’Reilly S Y,Zhang M,Li C Z and Shu L S.2009.A Paleoproterozoic orogeny recorded in a long-lived cratonic remnant (Wuyishan terrane),eastern Cathaysia Block,China.Precambrian Research,174:347–363.
Zhang S B,Zheng Y F,Wu Y B,Zhao Z F,Gao S and Wu F Y.2006.Zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotope evidence for Paleoproterozoic metamorphic event in South China.Precambrian Research,151:265–288.
Zhao G C,Cawood P A,Wilde S A and Sun M.2002.A review of the global 2.1–1.8 Ga orogens:Implications for a pre-Rodinian supercontinent.Earth Science Reviews,59:125–162.
Zhao G C,He Y H and Sun M.2009.The Xiong’er volcanic belt at the southern margin of the North China Craton:Petrographic and geochemical evidence for its outboard position in the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia Supercontinent.Gondwana Research,16:170–181.
Zhao G C,Sun M,Wilde S A and Li S Z.2004.A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic supercontinent:Assembly,growth and breakup.Earth Science Reviews,67:91–123.
Zhao X F,Zhou M F,Li J W,Sun M,Gao J F,Sun W H and Yang J H.2010.Late Paleoproterozoic to early Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group in Yunnan,SW China:Implications for tectonic evolution of the Yangtze Block.Precambrian Research,182:57–69.
Zheng J P,Griffin W L,O’Reilly S Y,Zhang M and Pearson N.2006.Zircons in mantle xenoliths record the Triassic Yangtze-North China continental collision.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,247 (1–2):130–142.

