雅庫茨克舊城區多年凍土溫度狀況分析
Igor Syromyatnikov
(俄羅斯科學院西伯利亞分院麥爾尼科夫凍土研究所,雅庫茨克677010,俄羅斯)
0 Introduction
The main part of infrastructure in Yakutsk is located on the first two terraces of the Lena River.The soils consist of lacustrine-alluvial deposits with a thickness of 20~22 m dominated by channel facies deposits-fine sands locally overlain by floodplain and lacustrine sediments.
For a long period the area of Yakutsk was being built by wooden,mostly single-storey buildings.From the mid-1970s,stone structures have become the main type of buildings.
Geotechnical conditions at Yakutsk are characterized by the presence of a cultural layer,2.5 to 4.0 m in thickness,in the upper part of the section.This layer generally consists of borrow sands and silts“contam-inated”with construction and domestic waste.Although these soils within the old part of the city form an almost continuous cover,their thickness varies considerably.
Since the late 1930s,regular temperature measurements have been taken in boreholes of the city and in adjacent areas.They showed that permafrost temperature in the city is significantly lower than in undisturbed areas.Soil temperature was as low as-8.1℃in some old part of the city,whereas in natural settings outside the city soil temperature was-2 to-3℃[1].Low soil temperatures within the limits of the city were attributed by most researches to the effect of a“territory development”factor.They considered the“cultural layer”,a mass of clayey silt mixed and interbedded with waste materials of various types,to be the main cooling factor.This layer has low thermal conductivity and prevents soil heating in summer.
Based on measurement data,P.I.Melnikov and P.A.Soloviev concluded that there was a variable mosaic of permafrost temperature distribution in the central part of Yakutsk.At the same time,Melnikov[2]was convinced that such situation of temperature conditions was predetermined by the geological history of the area,while Soloviev[5]believed that the surface layer was cooled to a considerable degree due to wooden type of buildings,which had been built for about three centuries,and the way of life of that time.Furthermore,he also wrote about temperature increase on the city territory in the future due to“the increase in building density and development of public utilities”.
1 Results and Discussion
Great problems of geocryological conditions of Yakutsk occurred in the second half of the 20th century when wooden buildings type was substituted by stone ones.This problem is primarily associated with the transition to centralized heat and water supply municipal economy and construction of public sewer.While heat pipelines were commonly placed on or above the ground surface,other utilities,including telecommunication and power supply cables,were buried.The situation was complicated by the absence of natural slopes and frequent utility failures.All these factors caused various deformations of buildings and required constant monitoring of the permafrost temperature regime in Yakutsk.In 2009,Melnikov Permafrost Institute started the development of a system for geothermal monitoring of Yakutsk.
Presently,temperature monitoring observations are conducted in 65 boreholes in different parts of the city.The boreholes are 10 to 30 m in depth,with about 80%varying in depth from 10 to 12 m.Measurements are taken once monthly using thermistor cables with sensor spacing of 1 m.Thermistors used are CMT-1(copper-manganic thermistor)and CMT-4 calibrated at the Permafrost Institute.In addition,eighteen boreholes are instrumented with temperature loggers.
Using the results of this monitoring,we tried to consider the nature of the soil temperature regime formation on the corner of Kulakovsky and Yaroslavsky Streets where we drilled a borehole(B-60)near the Shergin shaft.
Temperature observations were conducted in this shaft in different years by Erman,Shergin,Middendorff,and later,in the Soviet period,by Zatsepins,Belokrylov and other researchers(Table 1).
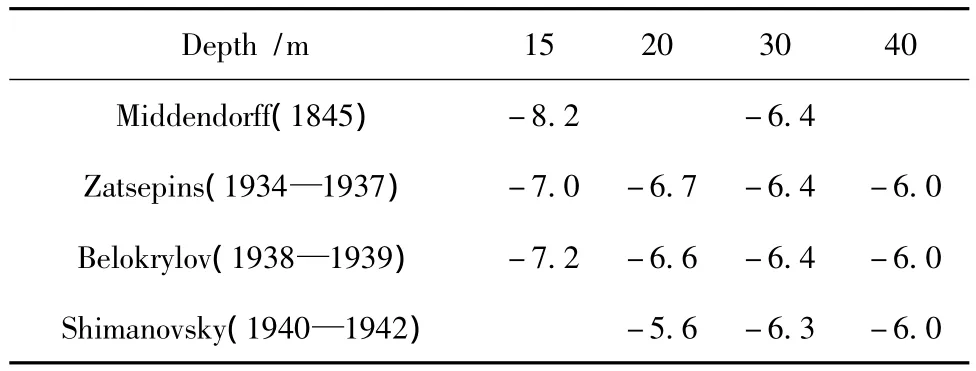
Table 1 Some results of temperature observations in the Shergin shaft in different years[5]
According to Middendorf,permafrost temperature in 1845 at a depth of 15 m was-8.2℃.In the early 1940s according to Zatsepins it was-7.0℃.Later,Belokrylov obtained on the same level a similar soil temperature negative values.
In 1937,a new borehole(B-2,see Fig.1)was drilled 50 m north from the Shergin shaft.The depth of this borehole was 6 m and it penetrated the following section[3]:

Fig.1 Cryolithology,moisture content and ground temperature in borehole B-60 near the Shergin shaft and the location of boreholes.Legend:1-cultural layer;2-fine-grained sand;3-active layer;4-frozen ground with a thin lens-type cryostructure; 5-frozen ground with a massive cryostructure
0.0 –0.4—construction waste;
0.4 –0.8—gray sandy silt with an admixture of construction waste and bricks;
0.8 –1.0—brown-yellow peat with inclusions of wood;
1.0 –1.5—muddy,fine,gray sandy silt with an admixture of remains of wood,charcoal pieces,bones and gravel,reacts with HCl;
1.5 – 3.0—gray clayey silt,below 2.5 m is yellow up to 2.5 m is with the inclusions of bones and wood,reacts with HCl;
3.0 –6.0—gray,fine,sand-rich silt,with inclusions of plant remains or ferruginized,does not react with HCl.
I.D.Belokrylov,who described the cross section structure of this borehole,qualified the soils to a depth of 3.0 m as the cultural layer.From October 1937 to January 1939,monthly temperature measurements were taken in this borehole.The measured permafrost temperatures were much higher than the temperature at the same depth in the Shergin shaft.On this basis,it was concluded that permafrost temperature increased on the territory of Yakutsk.
P.I.Melnikov,in his article on permafrost in Yakutsk(1962),analyzed in detail the data collected during different years and concluded that the process of ground temperature recovery in the lower parts of permafrost cross section takes a considerable period.Moreover,he considers that soils in the Shergin shaft could be cooled due to short-and long-period climate changes.
Borehole B-60(Fig.1)was drilled 45 m south from the Shergin shaft.The thickness of the cultural layer in the cross section of the borehole is 4.3 m.It is underlain with a layer of ice-rich alluvial sand.The base of the layer is presented by light-brown sand and inclusions of rusty sand with massive cryogenic structure.Frozen sandy silts with sand lenses and pockets are located above.The gravimetric moisture content of these soils is not less than 30%.The gravimetric moisture content of the cultural layer at a depth of 1.5 m reaches almost 60%.Ice-rich sand is covered with frozen sandy silts and sand deposits with inclusions of plant roots and fragments of red brick.
The cultural layer is complex due to dissimilar material,which consists of plant remains,brick fragments and sandy silts with sand lenses and pockets.The abundance of pockets of fine material with differing texture is a characteristic feature of the cultural layer.Furthermore,a great amount of household organics can be found in these sediments,that is why the soils of cultural layer accumulate soil moisture and solutes.
The data comparison of temperature observations during the 1940s in B-2[3],with our measurements obtained in B-60 at the same depth showed that the temperature regime at a depth of 6 m is very similar (Fig.2).While an increase in soil temperature can be registered under natural conditions everywhere,in this case,perhaps,we observe a cooling effect of the cultural layer.Some differences observed in the second half of winter can be explained by cold air drainage into shallow borehole B-2.
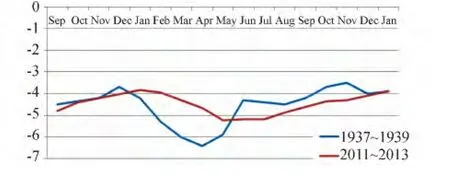
Fig.2 Permafrost temperature regime at 6 m depth in 1937-1939 in B-2 and in B-60 in 2011-2013
3 Conclusions
The analysis of temperature observations in the Yakutsk area conducted during different years shows that there is no considerable change in the temperature regime.Monitoringobservations showed a cooling effect of the cultural layer,which protects the soils from short-period climate changes.
The obtained data confirm the fact that the temperature data in the Shergin shaft according to Middendorff were,probably,lower than actual ones.That is why the author agreed with Melnikov[4]that frozen soils of the shaft could be cooled due to climate changes during short-and long-term periods.
[1] Soloiev P A.About impact of Yakutsk development on permafrost temperature[J].Yakutsk:North-East Branch of the Permafrost Institute,1958,179-191.
[2] Melnikov P I.Permafrost in Yakutsk region//Permafrost research in the Sakha(Yakutia)Republic[J].Moscow:Academy of Sciences of the USSR Press:1950,(2):53-70.
[3] Grave N A,Kunitsky V V,Soloviev P A,et al.The cadastre of exploring working in the city of Yakutsk conducted before 1965[R].–The result report(2000-2003)“Regional permafrost research”– Collection of Melnikov Permafrost Institute SB RAS,Yakutsk,2003,2:1 020-1 022.
[4] Melnikov P I.About temperature changes of rocks during a century in the Shergin shaft in Yakutsk and duration of thermal processes during temperature recovery of frozen rocks[J].Permafrost and accompanying phenomena on the territory of Yakut Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic.Moscow:The Academy of Sciences Publishing House,1962,54-67.
[5] Soloviev P A.The Shergin shaft[M].Yakutsk:Melnikov Permafrost Institute SB RAS Press,2003.
- 黑龍江大學工程學報的其它文章
- The harm of perennial frozen soil to the pipeline exporting the crude oil from Mohe county to Daqing city
- Overview of research methods of frozen soil hydrology in Heilongjiang Province
- Environmental geochemistry of urban areas in Yakutia
- A permafrost factor in the development of deformations on the Amur Highway
- The problem of project statement of construction principles of buildings and facilities in permafrost
- The forecast of a temperature regime of soils containing the pile foundation of a pithead on diamond-mining mines of cryolithic zone

