T-2毒素對小鼠胚胎干細胞線粒體功能的抑制作用
方海琴,李利忠,趙增明,何 俊,趙 君,楊 嶸,耿 雪,彭雙清
(1.軍事醫學科學院疾病預防控制研究所毒理學評價研究中心,北京 100071;2.國家食品安全風險評估中心衛生部食品安全風險評估重點實驗室,北京 100021)
T-2毒素對小鼠胚胎干細胞線粒體功能的抑制作用
方海琴1,2,李利忠1,趙增明1,何 俊1,趙 君1,楊 嶸1,耿 雪2,彭雙清1
(1.軍事醫學科學院疾病預防控制研究所毒理學評價研究中心,北京 100071;2.國家食品安全風險評估中心衛生部食品安全風險評估重點實驗室,北京 100021)
目的觀察T-2毒素對小鼠胚胎干細胞(m ESC)線粒體功能的毒性作用,探討其胚胎毒性的可能作用靶點與作用機制。方法處于分化過程中的m ESC加入T-2 0.5μg·L-1分別作用24,72及120 h,同時設Trolox 200μmol·L-1預處理后30 m in再加入T-2毒素0.5μg·L-1染毒72 h組。透射電子顯微鏡觀察線粒體內結構;羅丹明123熒光探針法流式細胞術檢測mESC內線粒體膜電位,氧電極法檢測線粒體呼吸速率,計算呼吸控制比,熒光素-熒光素酶發光法測定ATP合成酶活性。結果透射電鏡觀察可見,T-2 0.5μg·L-1作用72與120 h組m ESC內線粒體數量明顯減少,結構變形,線粒體中少見或缺少完整的嵴,與正常對照組相比,mESC內線粒體呼吸控制比分別下降49.5%和55.1%(P<0.05),ATP合成酶活性分別下降84.9%和89.3%(P<0.05),m ESC線粒體膜電位下降23.2%和35.2%(P<0.05)。Trolox預處理可以改善T-2毒素對上述線粒體功能指標的抑制作用。結論T-2毒素可降低m ESC的線粒體功能,進而抑制m ESC的分化能力,可能是其胚胎發育毒性的作用機制之一。
T-2毒素;毒性作用;胚胎干細胞;線粒體;細胞分化
DO l:10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2014.03.018
T-2毒素是一種由三線鐮刀菌產生的單端孢霉烯族毒素,廣泛分布于自然界,尤其對糧谷作物的污染范圍廣程度重。經食物連續攝入T-2毒素會對人類和動物的健康造成嚴重危害,表現出對生殖發育系統的母體毒性和胎仔毒性,可導致胚胎發育異常,甚至死亡[1-2]。
胚胎干細胞實驗(embryonic stem cell test,EST)作為歐洲替代方法驗證中心(European Centre for the Va lidation o f Alternative Methods,ECVAM)正式批準為體外發育毒性篩選的動物替代方法,EST可以從細胞毒性、分化抑制以及分子生物學水平反映發育毒性,其中受試物對ESC向心肌細胞分化的半數抑制濃度ID50可反映受試物對胚胎干細胞(em bryonic stem ce ll,ESC)分化過程的影響[3-5],本課題前期應用EST評價T-2毒素為強發育毒性化合物,并得出T-2毒素對ESC的半數抑制濃度為0.57μg·L-1[6]。
ESC在分化過程中,氧耗與供能方式發生改變,即從糖酵解向需氧代謝轉換,因此,線粒體的功能對于ESC的分化能力發揮重要作用。已有報道,在ESC自發分化為多種細胞的過程中,發現線粒體DNA的含量和分化的相關性,線粒體DNA數量隨著干細胞分化程度的增加而增加,線粒體數目和形態結構發生變化[7-9];以及過氧化物酶體增殖活化受體γ輔助活化因子1α和活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)對線粒體的調控在ESC向心肌細胞的分化,線粒體功能在多能干細胞和細胞重編程中皆發揮著重要的作用[10-11]。
本研究將通過建立ESC分化模型來作為胚胎毒性測試體外替代模型,從細胞和分子機制來探討T-2毒素發育毒性作用機制,重點關注T-2毒素在抑制分化作用濃度下對小鼠ESC線粒體功能的影響。
1 材料與方法
1.1 細胞、試劑和主要儀器
小鼠ESC-D3細胞(murine embryonic stem cell,mESC)購自中國科學院上海生物細胞研究所。T-2毒素由軍事醫學科學院疾病預控制研究所毒理學評價研究中心提供。knockout-DMEM培養基(Du lbecco′s modified Eagle medium)、高糖DMEM、胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum,FBS),β-巰基乙醇、非必需氨基酸(NEAA)、N-2-羥乙基哌嗪-N-2-乙磺酸(HEPES)、L-谷氨酰胺,青鏈霉素雙抗和Trizol均購自德國Invitrogen Gibco公司;四甲基偶氮唑藍(MTT)、二甲亞砜(DMSO)和明膠購自美國Sigma公司。小鼠白血病抑制因子(murine leukem ia inhibitory factor,m LIF)購自美國Chem icon公司。BCA法蛋白質定量試劑盒購自北京普利來生物公司。2′,7′-二氯熒光素〔2′,7′-dichlorofluorescineiacetate(H2-DCFDA)〕、羅丹明123、ADP、地高辛、蘋果酸、谷氨酸均購自美國Sigma公司,ATP合成酶活力試劑盒(PROMEGA ENLITEN?Total ATP Rapid Biocontamination Detection Kit)購自美國Promega公司。
1.2 細胞培養及處理
10 mg T-2毒素溶于1 m L DMSO,配成濃度10 g·L-1的母液,每管50μL分裝凍存,用時按需用培養基倍比稀釋。Tro lox溶解于10 m L超純水配制成濃度2 mmol·L-1儲液,過濾除菌后4℃保存,染毒時用無血清培養基稀釋至200μmo l·L-1。
m ESC培養與分化處理按文獻描述[6,12],懸滴3 d、轉懸浮2 d生成擬胚體(embroynic body,EB),分別在EB貼壁24,72和120 h后加入T-2毒素,作用濃度為0.5μg·L-1。按照處理時間分組為正常對照組、T-2毒素給藥24,72和120 h組。此外,按給藥30 m in前Trolox預處理分為單純Trolox預處理組、Trolox預處理后T-2毒素0.5μg·L-1染毒72 h組。
1.3 透射電子顯微鏡觀察分化m ESC內線粒體結構
收集細胞,鋨酸固定,乙醇梯度脫水,環氧丙烷置換,環氧樹脂包埋,切片,采用PhilipsEM208s型透射電子顯微鏡觀察,攝片。每組細胞采用3張切片,低倍鏡下進行全面細致的觀察后8000倍放大倍數下拍照,即在選定的每張切片上隨機拍攝細胞內照片各5張。
1.4 線粒體膜電位的測定
收集指數生長期細胞,重懸細胞后,加入羅丹明123染液10 m g·L-1;37℃,5%CO2細胞培養箱孵育30 m in;4℃下800×g離心10 m in,培養基洗細胞2次,PBS重懸;激發波長488~505 nm,發射波長530 nm。以相應熒光探針熒光讀數的對數為橫坐標,細胞數為縱坐標即可測定m ESC線粒體膜電位的相對強度。
1.5 極譜法[13]測定線粒體呼吸速率
收集細胞,細胞計數,細胞數量為1×105。反應體系3 m L,25℃恒溫,以90%速度攪拌。反應介質為(mmol·L-1):KCl130,HEPES 10,EDTA 1,KH2PO42.5,去脂牛血清蛋白1.5 mg,pH 7.4。加入蘋果酸0.1 mmol·L-1和谷氨酸1 mmol·L-1啟動態4(ST4)呼吸。平穩后加入200 nmol ADP啟ST3呼吸速率。ADP耗盡后重又回到ST4。記錄儀記錄耗氧曲線,通過曲線測定ST4和ST3呼吸,并計算出呼吸控制比(respiratory control rate,RCR)(ST3/ST4)。
1.6 線粒體ATP合成酶活性的測定
收集細胞,細胞數量為1×105,用線粒體呼吸介質重懸,反應溫度為25℃,在0.5 m L反應體系(mmol·L-1)中含有HEPES 10,EDTA 0.5,磷酸緩沖液5,蘋果酸6,MgCl22.5,反應溫度為25℃,在0.5 m L反應體系中含有(mm o l·L-1)HEPES 10,EDT 0.5,磷酸緩沖液5,蘋果酸6,MgCl22.5,記錄以上體系的發光強度為本底,加入4μL ADP啟動反應,記錄發光強度。在不加細胞和ADP的平行實驗中,加入ATP 1 nm o l·L-1,記錄發光強度,標定ATP合成量。
1.7 統計學分析
2 結果
2.1 T-2毒素對m ESC的線粒體結構的影響
透射電鏡顯示(圖1),正常對照組的m ESC分化后,細胞內線粒體豐富,形態正常,線粒體內可見結構完整的嵴(圖1A);T-2毒素0.5μg·L-1干預后,隨時間變化,線粒體數量與質量發生改變,T-2毒素0.5μg·L-1作用24 h線粒體數目未見減少(圖1B),而在72與120 h組,可見線粒體數目的明顯減少,同時可見線粒體變形,線粒體中少見或缺乏完整的嵴(圖1C,D),提示T-2毒素0.5μg·L-1的長期干預會抑制線粒體生成的數量與功能。
2.2 T-2毒素對m ESC線粒體膜電位的影響
結果如圖2所示,在T-2毒素作用下,m ESC線粒體膜電位呈時間依賴性下降,表現為膜電位曲線左移(圖2A1)。T-2毒素0.5μg·L-1分別作用72和120 h,m ESC線粒體膜電位分別下降23.2%和35.2%(圖2A2),差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。Trolox預處理后導致m ESC線粒體膜電位下降減小,膜電位曲線明顯右移(圖B1和B2),具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。
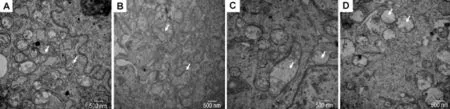
Fig.1 Effec t o f T-2 tox in on m itochond ria l u ltrastruc tu re o f m u rine em b ryonic stem cells(m ESCs)by transm ission elec trica lm ic roscope.A:norm al control group;B,C and D:ESCs were treated w ith T-2 0.5μg·L-1for 24,72 and 120 h,respectively.Arrows show m itochondria in differentiated m ESCs.
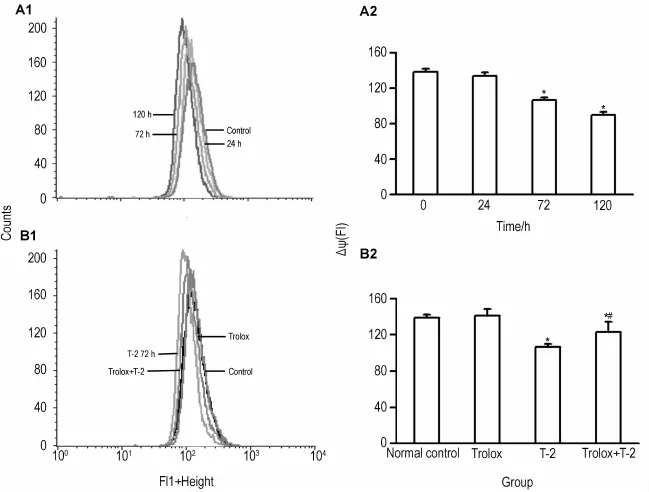
Fig.2 Effec t o f T-2 tox in on m itochond ria lm em b rane po ten tial(△Ψ)o f m ESCs.A1 and A2:ESCs were treated w ith T-2 0.5μg·L-1for 24,72 and 120 h;B1 and B2:ESCs were pretreated with Trolox 200μmol·L-1for30 m in,then exposed to T-2 toxin 0.5μg·L-1for 72 h.,n=3.*P<0.05,compared with normal controlgroup;#P<0.05,com pared w ith Trolox group
2.3 T-2毒素對m ESC線粒體呼吸速率的影響
結果如圖3所示,T-2毒素對m ESC的RCR有顯著影響(圖3A)。T-2毒素作用72與120 h,其RCR值分別下降49.5%與55.1%(P<0.05)(圖3B)。經Tro lox預處理后m ESC線粒體呼吸控制比仍明顯下降,但與單純T-2毒素作用比較,mESC中線粒體呼吸控制比顯著增加,約增加31%(圖3C),差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。
2.4 T-2毒素對mESC線粒體ATP合成酶活性的影響
結果如圖4所示,T-2毒素對mESC線粒體的ATP合成酶活性有顯著的抑制作用。與對照組相比,各實驗組都表現出顯著性差異,T-2毒素作用24,72和120 h ATP合成酶活性分別下降25.5%,84.9%和89.3%(圖4A)。經Trolox預處理后mESC線粒體合成酶活性仍明顯下降,但與單純T-2毒素作用比較,m ESC中線粒體合成酶活性顯著增加,約增加2倍(圖4B),差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。
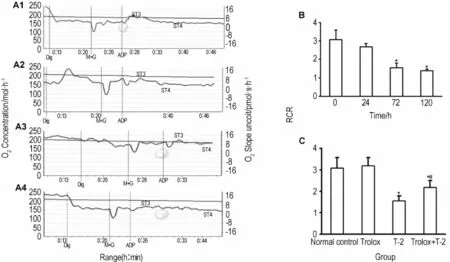
Fig.3 Effect o f T-2 toxin on respiratory contro l ratio(RCR)o fm itochond ria o fm ESCs.A,B:ESCs were treated w ith T-2 0.5μg·L-1for 24,72 and 120 h.C:ESCs were pretreated w ith Trolox 200μmol·L-1for 30 m in,then exposed to T-2 toxin 0.5μg·L-1for 72 h.Dig:digitonin;M+G:m alage+glutate.,n=3.*P<0.05,com pared w ith normal control group;#P<0.05,compared w ith Trolox group.
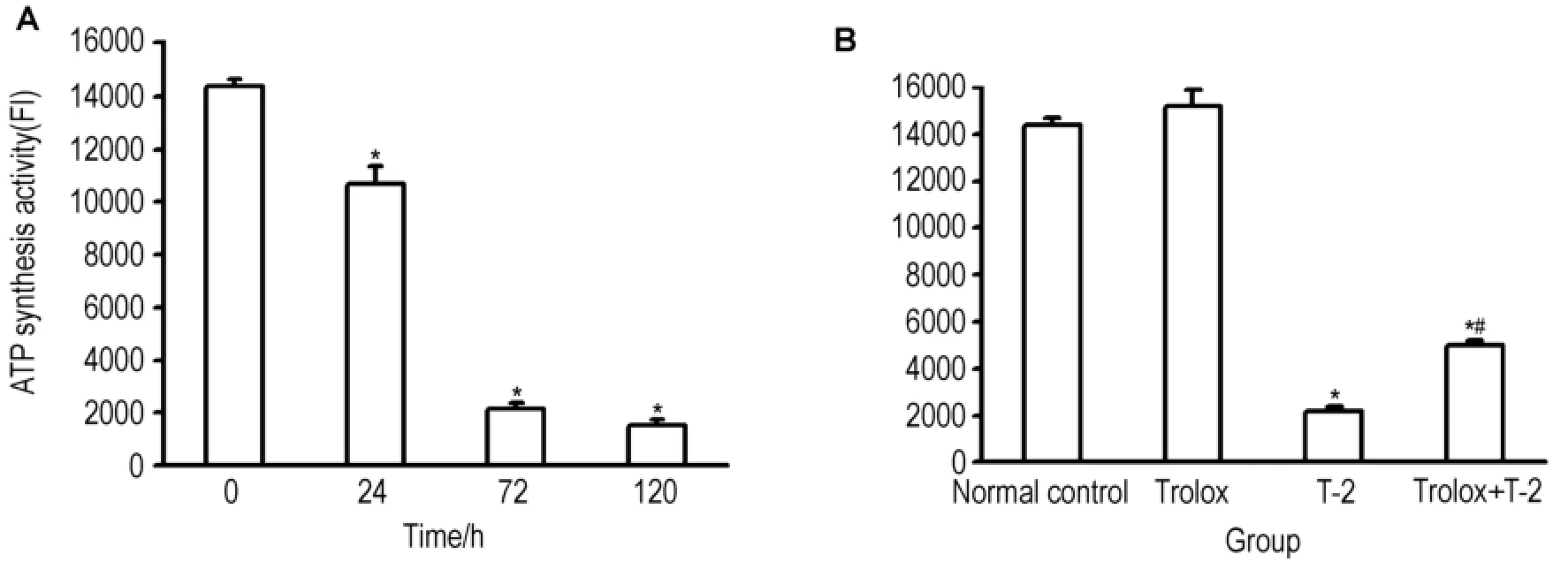
Fig.4 Effect o f T-2 toxin on ATP synthesis activity o fm ESCs.A:ESCs were treated with T-2 0.5μg·L-1for 24,72 and 120 h.B:ESCs were pretreated with Trolox 200μmol·L-1for30 min,then exposed to T-2 toxin 0.5μg·L-1for72 h.,n=3.*P<0.05,compared with normal controlgroup;#P<0.05,com pared w ith Trolox group.
3 討論
ESC分化時有較高的能量要求,分化過程中耗氧與供能方式發生轉變,即從糖酵解供能到有氧氧化的轉變,線粒體由一種相對較低的活動狀態向較高的呼吸功能轉化[14-15]。此變化類似于胚胎發育中的線粒體受到體內環境的影響,線粒體的活性和分布狀況會隨著胚胎發育時期的不同而改變[16-17]。本研究觀察到在未分化ESC中線粒體的數目以及嵴都較貧乏,而ESC分化時其發生急劇變化,表現為嵴豐富,數目增加,這與文獻報道一致,T-2毒素干預后,ESC內線粒體數目減少,且形態異常,線粒體嵴缺少,提示T-2毒素干預抑制分化的ESC線粒體功能。
Esteban等[18]報道,線粒體膜電位在誘導多能干細胞(induced p luripotent stem ce lls,iPSC)獲得多能性的重編程過程中發生了變化。ATP的合成要靠呼吸鏈不斷供給質子以維持一個強大的質子電化學梯度,并經線粒體ATP合成酶的作用將能量轉換用于合成ATP,ROS可導致線粒體內膜通透性增加,通透性增加將不能維持質子電化學梯度[13,17]。本研究發現,T-2毒素導致m ESC線粒體功能下降呈時間依賴效應關系,表現為線粒體呼吸速率比下降、膜電位下降及ATP合成酶活性下降。
m ESC分化時需要線粒體功能增加以適應其供能需求與氧耗方式的轉變,我們在前期研究中發現T-2毒素可以致分化m ESC內ROS生成增加[6],推測在長時間的ROS作用下,線粒體呼吸鏈復合體活力降低,電子傳遞鏈功能下降,電子傳遞受阻,使電子漏增加,電子漏的增加進一步導致自由基的增加,線粒體ROS的生成與清除進一步失衡;過量ROS引發線粒體的自身氧化,線粒體內膜的完整性被破壞,進而引起線粒體膜電位的改變,膜電位的下降又進一步使得ATP生成得到抑制,ATP生成的減少使ESC細胞能量供應降低,進而分化所需能量供給不足,最終表現出抑制ESC的分化,同時也造成線粒體功能降低與氧化損傷的惡性循環。為了進一步證實T-2毒素對m ESC線粒體功能影響的作用機制,本研究選擇自由基清除劑Trolox對m ESC進行預處理,結果發現ROS的下降導致線粒體功能在一定程度上得到恢復。由此可見,T-2毒素對線粒體功能的影響與T-2毒素導致ROS的生成有關,其對m ESC線粒體功能的抑制可能是產生發育毒性的作用機制之一。
[1] Doi K,Ishigam i N,Sehata S.T-2 toxin-induced toxicity in pregnant m ice and rats[J].Int J Mol Sci,2008,9(11):2146-2158.
[2] Sehata S,TeranishiM,Atsum i F,Uetsuka K,Nakayama H,Doi K.T-2 toxin-induced morphological changes in pregnant rats[J].JToxicolPathol,2003,16(1):59-65.
[3] Spielmann H,Seiler A,Bremer S,Hareng L,Hartung T,Ahr H,et al.The practical app lication of th ree validated in vitro embryotoxicity tests.The report and recommendations of an ECVAM/ZEBET workshop(ECVAM workshop 57)[J].Altern Lab Anim,2006.
[4] Riebeling C,Pirow R,Becker K,Buesen R,Eike l D,Kaltenh?use r J,et al.The embryonic stem cell test as tool to assess structure-dependent teratogenicity:the case of valproic acid[J].Toxicol Sci,2011,120(2):360-370.
[5] Rolletschek A,Blyszczuk P,Wobus AM.Embryonic stem ce ll-derived cardiac,neuronal and pancreatic cells as model system s to study toxicological effects[J].Toxicol Lett,2004,149(1-3):361-369.
[6] Fang H,Wu Y,Guo J,Rong J,Ma L,Zhao Z,e t al.T-2 toxin induces apoptosis in differentiated murine em bryonic stem cells th rough reactive oxygen species-mediated m itochondrial pathw ay[J].Apoptosis,2012,17(8):895-907.
[7] Prigione A,Adjaye J.Modulation ofm itochondrial biogenesis and bioenergetic metabolism upon in vitro and in vivo diffe rentiation of hum an ES and iPS cells[J].Int J Dev Biol,2010,54(11-12):1729-1741.
[8] Chung S,Dzeja PP,Faustino RS,Perez-Te rzic C,Behfar A,Terzic A.Mitochondrial oxida tive metabolism is required for the cardiac differentiation of stem ce lls[J].Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med,2007,4(Suppl1):S60-S67.
[9] St John JC,Ram alho-Santos J,G ray HL,Petrosko P,Rawe VY,Navara CS,et al.The expression ofm itochondrialDNA transcription factors during early ca rdiom yocyte in vitro d iffe rentiation from human embryonic stem cells[J].Cloning Stem Cells,2005,7(3):141-153.
[10] Birket MJ,Casini S,Kosm idis G,Elliott DA,Gerencse r AA,Baartscheer A,e t al.PGC-1αand reactive oxygen species regulate human embryonic stem ce ll-derived cardiom yocyte function[J].Stem Ce ll Reports,2013,1(6):560-574.
[11] Bukow iecki R,Ad jaye J,Prigione A Mitochondrial function in pluripotent stem cells and cellular reprogramm ing[J].Gerontology,2014,60(2):174-182.
[12] Fang HQ,Zhao J,Cui YX,Yuan HT,Yang R,Rong J,et al.Resveratrol promotes expression o f peroxisome proliferator activated receptorγcoactivator 1αduring cardiom yocyte differentiation o f murine embryonic stem cells in vitro[J].Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol(中國藥理學與毒理學雜志),2013,27(2):156-162.
[13] Liu SS,Wei YY.Kinetic properties of ATP synthase of rat liver m itochondria[J].Acta Biochim Biophys Sin(生物化學與生物物理學報),1987,19(3):241-250.
[14] Huang LY,Chen SY.Telomeres,m itochond ria and stem cellaging[J].JShanghai Jiaotong Univ(Med Sci)〔上海交通大學學報(醫學版)〕,2012,32(5):679-683.
[15] Mandal S,Lindgren AG,Srivastava AS,C larkAT,Banerjee U.M itochondrial function controls p roliferation and early differentiation potential of embryonic stem cells[J].Stem Cells,2011:29(3):486-495.
[16] Reynier P,May-Panloup P,Chrétien MF,Morgan CJ,Jean M,Savagner F,et al.Mitochondrial DNA content affects the fertilizability of hum an oocytes[J].Mol Hum Reprod,2001,7(5):425-429.
[17] Spikings EC,Alderson J,St John JC.Regulated m itochondrial DNA rep lication during oocyte maturation is essential for successful porcine embryonic development[J].BiolReprod,2007,76(2):327-335.
[18] Esteban MA,W ang T,Qin B,Yang J,Qin D,Cai J,et al.Vitam in C enhances the generation o f mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells[J].Cell Stem Cell,2010,6(1):71-79.
[19] Zhang H,Jiao XM,Liu SS,W ang XM.The effee t of ischem ia and reperfusion on energy tralsductional function o f ratheartm itochondria[J].Chin J Pathophysiol(中國病理生理雜志),1993,9(5):561-564.
T-2 toxin inhibits m itochond rial func tion o f d ifferen tiated m u rine em b ryonic stem cells
FANG Hai-qin1,2,LILi-zhong1,ZHAO Zeng-m ing1,HE Jun1,ZHAO Jun1,YANG Rong1,GENG Xue2,PENG Shuang-qing1
(1.Evaluation and Research Center for Toxicology,Institute of Disease Prevention and Control,Academy o f M ilitary Medica l Sciences,Beijing 100071,China;2.Key Laboratory o f Food Sa fety Risk Assessm ent o f Ministry of Hea lth,China Nationa l Center for Food Safety Risk Assessm ent,Beijing 100021,China)
OBJECTlVE To exp lore the possib le m echanism or action targets of T-2 toxin em bryo toxicity by observing the effect of T-2 toxin on m itochondrial function of differentiated murine embryonic stem cells(m ESCs).METHODS During differentiation at24,72 and 120 h,ESCs were exposed to T-2 toxin 0.5μg·L-1.Meanwhile,m ESCs were pre-treated with antioxidant Trolox(200μmol·L-1)for 30 m in and exposed to T-2 toxin(0.5μg·L-1)for 72 h.The m itochondrial ultrasture of differentiated m ESCs was observed under a transim ission electricalm icroscope(TEM).The differentiated ESC m itochond ria l function,inc luding respiratory contro l ratio(RCR),ATP synthase activity and m itochondria l m embrane potentia l(MMP),was measured at 144 h a fter differentiation.RESULTS Significant decrease of the m itochondria lnumber,de formation o fm itochond ria lstructure,and lack o f comp lete m itochod rial crestwere observed through TEM in the groups o f T-2 toxin exposed for 72 and 120 h,respectively.Compared with the normal control group,RCR declined by 49.5%and 55.1%,ATP synthase activity decreased by 84.9%and 89.3%,and MMP decreased by 23.2%and 35.2%in T-2 toxin 0.5μg·L-1exposure 72 and 120 h group,respectively.However,the inhibition ofm itochondrial function by T-2 toxin in differentiated m ESCs recovered significantly in the presence of the antioxidant Trolox.CONCLUSlON T-2 toxin induces oxidative stress and inhibitsm ESCsm itochondrial function in differentiated m ESCs,and ROS-induced m itochondria lm a lfunction p lays an im portant ro le in T-2 toxin em bryonic toxicity m echanism.
T-2 toxin;toxic actions;embryonic stem ce lls;m itochond ria l;ce ll differentiation
PENG Shuang-qing,E-mail:pengsq@hotmail.com,Tel:(010)66948462
R394.1
A
1000-3002(2014)03-0415-06
Foundation item:The project supported by International Cooperation Project from Ministry of Science and Technology of China(2011DFA32190);National Natural Science Founda tion of China(81172699);National Natural Science Foundation of China(81302462);and Natural Science Foundation of Beijing City(7142128)
2014-01-02 接受日期:2014-05-10)
(本文編輯:喬 虹)
國家科技部國際合作項目(2011DFA32190);國家自然科學基金項目(81172699);國家自然科學基金項目(81302462);北京市自然科學基金資助項目(7142128)
方海琴(1977-),女,博士,助理研究員,主要從事食品毒理學研究;彭雙清(1962-),男,博士,研究員,博士生導師,主要從事化學物安全性評價研究。
彭雙清,E-mail:pengsq@hotm ail.com,Tel:(010)66948462

