Catalytic Decomposition of Cellulose in Cooperative Ionic Liquids
LONG Jin-Xing GUO Bin LI Xue-Hui WANG Fu-Rong WANG Le-Fu
(School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Pulp&Paper Engineering State Key Laboratory of China,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,P.R.China)
Catalytic Decomposition of Cellulose in Cooperative Ionic Liquids
LONG Jin-Xing GUO Bin LI Xue-Hui*WANG Fu-Rong WANG Le-Fu
(School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Pulp&Paper Engineering State Key Laboratory of China,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,P.R.China)
Abstract: Cellulose,the abundant and cost-ineffective resource,is considered to be a perfect alternative for the alleviation of energy crisis and environmental pollution.However,most processes for the treatment of cellulose are rigor currently as it is insoluble in water and conventional organic solvents due to its strong intra and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds,where the phase problem hampers its utilization widely.Here,we built a novel and efficient cooperative ionic liquid pairs system for the low temperature catalytic conversion of cellulose,which was constructed through the combination of an acidic ionic liquid catalyst and a cellulose soluble ionic liquid solvent.The catalytic decomposition behavior of microcrystal cellulose in this vigorous catalytic system was studied intensively by thermogravimetry(TG).Results show that the decomposition temperature of cellulose decreases greatly in all cooperative ionic liquid pairs,cellulose dissolved in ionic liquid solvents can bein situcatalytic decomposed by acidic ionic liquids.Furthermore,the decomposition temperature is dependent on the acidic strength of the ionic liquid catalysts,stronger acidity results in a lower decomposition temperature of the cellulose.Moreover,we found that cellulose can be decomposed at lower temperature when the ionic liquid with higher solubility of cellulose is used.
Key Words:Cooperative ionic liquid;Cellulose;Catalytic decomposition;Thermogravimetry;Acidic strength
1 Introduction
The rapidly growing demand for energy,a dwindling and unstable supply of petroleum,coal and natural gas,and the emergence of global warming by excess-combustion of fossil fuels have rekindled a strong interesting in pursuing alternative and renewable energy and resources.1-3Widely available bio-mass comes from directly photosynthesis of plants with CO2and water and it is mainly composed by C,H,and O elements,which are the dominating elements for modern organic chemistry and petrochemical engineering.Therefore it is regarded as renewable,carbon neutral and prefect substituted resource and energy.Gasification,hydrolysis,pyrolysis,and liquefaction are the primary ways for the conversion of biomass into basic chemical and energy carrier.4-6In order to achieve basic chemicals,a series of rigid transform processes,such as Fischer-Tropsch(F-T)synthesis,should be proceeded after the gasification process;platform chemical from hydrolysis is hard to utilize directly.And degradation followed by pyrolysis required extremely high processing temperature and pressure,so high cost and beyond controlled selectivity is inevitable.Hence,catalytic liquefaction attracts increasing attentions because it is fast,genial and relatively high products concentrated.7,8Unfortunately,cellulose is highly recalcitrant to transformation because it is not dissolved in water and traditional organic solvents due to the existence of strong intra-and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds.And thus,the catalytic degradation of cellulose is usually heterogeneous currently,which limits its use and prevents economically viable conversion largely.9,10In 2002,Rogers research group found that ionic liquid bmimCl(1-butyl-3-methylimidazole chloride)can dissolve cellulose efficiently with 10%solubility at 100°C,11which successfully bridges between biomass and biofuel/biochemical,and breaks the major vallum for the process development and utilization of biomass.
As an important analysis method,thermogravimetry(TG)is widely used on the characterization of substances,such as their thermochemical property and kinetics of thermo degradation.12-16Many prominent virtues are demonstrated,for example,a little sample is need,the results are more directly,and the effect of catalysts at various temperatures is more naked.12,17-19Herein,we report a novel method for catalytic liquefaction/decomposition of cellulose in cooperative ionic liquid pairs by TG.The cooperative ionic liquid pairs are composed of two ionic liquids:one plays the role for the dissolution of cellulose to form cellulose/ionic liquid homogenous solution,and the other acts as an acidic catalyst for the homogeneous catalytic degradation of cellulose in situ.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Cellulose was provided by Alfa Aesar and dried under vacuum at 70°C for 12 h before use.N-methyl imidazole,1-chlorine butane,1-bromine butane,1,4-sultone,and 1-chlorine methyl propionate were supplied by Acros.Other reagents were purchased from Guanghua Co.Ltd.All reagents are analytic grade and refreshed prior to use.Ionic liquids,bmimCl,bmimBr(1-butyl-3-methylimidazole bromate),bmimAc(1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate),C4H8SO3HmimHSO4(1-(4-sulfobutyl)-3-methyl imidazole hydrosulfate),bmimHSO4(1-butyl-3-methylimidazole hydrosulfate),and C2H4COOHmimCl(1-(2-carboxyethyl)-3-methylimidazole chloride),were synthesized according to reported literature20-28and characterized by1H-NMR,13C-NMR,and thermogravimetry-differential scanning calorimetry(TG-DSC),respectively.Element analysis and ion chromatogram analysis exhibited that their purities were all more than 99%.29
2.2 TG experiment
The TG experiment was carried out on a NETZSCH STA449C apparatus,3 mg cellulose,2 μmol acidic ionic liquid and 10 mg ionic liquid solvent were added in all the cases.The samples were heated from 40 to 600°C with a heating rate of 10 °C·min-1where 30 mL·min-1nitrogen was used as eluant gas.
2.3 UV-Vis acidity determination
The acidic strengths of ionic liquids were evaluated by UVVis spectra with 2,4-dinitroanline as indicator by a Shimadzu UV-2450 spectrophotometer according to literature:300.01 mol·L-1acidic ionic liquid is confected using dried CH3OH as solvent,then it is mixed with 0.1 mmol·L-1of 2,4-dinitroanline(dissolved in dried CH3OH)and followed by laid overnight for acidic strength measurement.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of ionic liquid solvent
In this paper,bmimBr,bmimCl,and bmimAc ionic liquids are selected as solvents for the dissolving of cellulose with the solubility of 5%,10%,and 13.2%(mass fraction),respectively.31,32Fig.1 shows that the onset decomposed temperature of cellulose,bmimBr,bmimCl,and bmimAc is 305,268,277,and 228°C,respectively,which is well agreement with corresponding literature.33-35In cooperative ionic liquid pairs system,the decomposed temperature of cellulose decreases sharply(Fig.1),which attributes to the breakage of inter-and intra-molecular hydrogen bonds by ionic liquid solvent and the formation of cellulose/ionic liquid homogeneous solution.At the same time,this homogeneous solution is miscible with acidic ionic liquid well,thus the degradation of cellulose is catalyzed in situ by acidic ionic liquid,which also pushes the dissolution equilibrium of cellulose forward.Fig.1 also demonstrates the relationship between the solubility of cellulose in ionic liquids and the decomposed temperature of cellulose clearly.
The decomposed temperature of cellulose decreases sharply with the increasing of its solubility in ionic liquids.For example,bmimBr shows the lowest soluble capability of cellulose among the three ionic liquids,the onset decomposed temperature(Tonset)of cellulose in bmimBr is as high as 178°C(Fig.1(a)).Conversely,bmimAc is regarded as the most efficient solvent for cellulose,and the onset decomposed temperature of dissolved cellulose is the lowest,accounted for 115°C(Fig.1(c)).Furthermore,almost all ionic liquid solvents are decomposed thoroughly upon 300°C while 90%mass loss is ob-served for acidic ionic liquid C4H8SO3HmimHSO4even the temperature reached 400°C,and the degradation is neglectable with continue increase of temperature(Fig.1),where carbon deposition from self-catalysis is considered to be the main cause.It also can be seen from Fig.1 that some indecomposable residues exist at 400°C in cooperative ionic liquid system and their mass losses are much less than that of acidic ionic liquid at the same condition(Fig.1(a,b)),this indicates that ionic liquid solvent can not dissolve all doped cellulose thoroughly before the thermal degradation of itself,so char from the pyrolysis of cellulose is also existed.However,one of the most quite interesting facts is that the mass loss of cooperative ionic liquid pairs containing the most robust ionic liquids solvent bmimAc is nearly the same as that of the acidic ionic liquids before 400°C(Fig.1(c)),this also certifies that the solvency of ionic liquid solvent plays a crucial role in the catalytic degradation process.

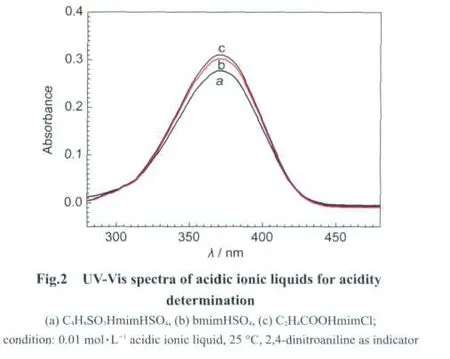
3.2 Acidic strength of acidic ionic liquid catalyst
In order to keep an deep eye on the effects of different acidic ionic liquids and their acidic strengths on the decomposition ofcellulose,threekindsoftypicalionic liquid acids,C4H8SO3HmimHSO4,bmimHSO4,and C2H4COOHmimCl,were adopted and their acidities were determined by UV-Vis spectra with 2,4-dintroaniline as indicator(Fig.2),the strong acidity for acidic ionic liquid is inversely proportional to its UV-Vis spectra absorbance,hence,the acidic strength of these acidic ionic liquids increases according to the order of C2H4COOH-mimCl<bmimHSO4<C4H8SO3HmimHSO4,which is accorded well with their structures.For instance,the reason that C4H8SO3H-mimHSO4demonstrates the strongest acidity is mainly attributed to both its cation and anion endowed one acidic functional group;carboxyl acid is a kind of weak acid,hence,carboxyl grafted ionic liquid,such as C2H4COOHmimCl,exhibits lower acidity reasonably.
3.3 Relationship between catalytic performances of ionic liquid catalysts and their acidic strengths
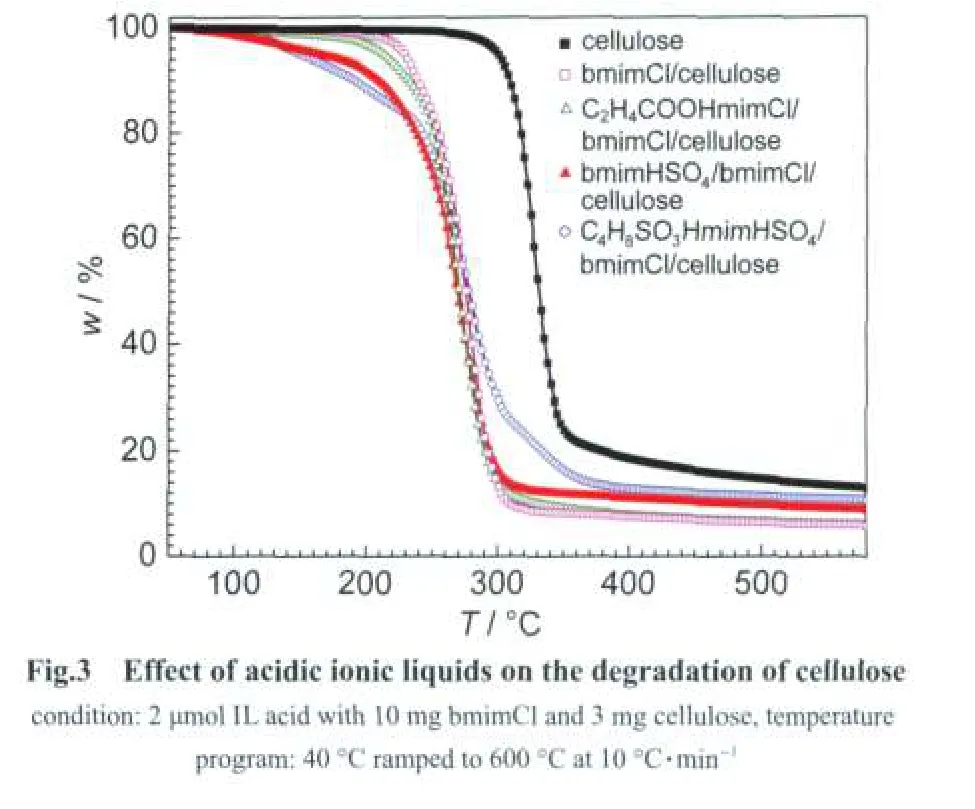
Decomposition experiments show that there are three kinds of mass losses in the TG curves(Fig.3).Mass loss from 60 to 120°C is regarded as the elimination of dissociative water andcrystal water.Catalytic decomposition of cellulose occurred from 120 to 260°C,which is much lower than that without ionic liquid.We think the dissolution of cellulose by bmimCl and its following in situ catalysis is responding to this.And the mass loss from 260 to 415°C is vested to the decomposition of ionic liquids and the pyrolysis of cellulose.Nearly 10%(w,mass fraction)of residues can be attributed to the char and tar from the decomposition of cellulose and cooperative ionic liquids.It is clear that the decomposition process of cellulose is accelerated when ionic liquids are added.For example,cellulose begins to decompose at 255°C in the presence of ionic liquid bmimCl without addition of any acidic catalyst,which is about 100°C lower than that of pure cellulose,it is because that the hydrogen bonds and rigid structure of cellulose are destroyed while it is dissolved in ionic liquids resulting in lower temperature decomposition behalf.The TG curve also indicates that the acidity strength affects significantly on the decomposition of cellulose.Stronger acidity means that stronger action between the acid and the cellulose,hence,the onset decomposed temperature decreases significantly with the increasing of the acidity strength.Take the strongest acidic ionic liquids C4H8SO3HmimHSO4for instance,cellulose decomposes at much more mild temperature(145°C)with comparison to that of C2H4COOHmimCl,where cellulose begins to decompose at 198°C.Further investigation shows that 100%of cellulose can be decomposed at 200°C in C4H8SO3HmimHSO4/bmimCl cooperative ionic liquid pairs system based on the above knowledgement about in situ dissolution-catalysis conversion process,which will be reported later.
4 Conclusions
In summary,catalytic decomposition of cellulose in cooperative ionic liquid pairs by thermo-gravimeter is investigated.Results show that the catalytic system is efficient and vigor.Cellulose dissolved in ionic liquid solvent can be catalytic decomposed in situ.Dissolved cellulose in ionic liquids is easier to be decomposed due to the destroy of the inter-and intramolecular hydrogen bonds and rigid structure of cellulose,the higher the solubility of ionic liquid for the cellulose,the more mild decomposition temperature of cellulose occurs.Furthermore,the acidity of acidic ionic liquid has a good impact on the decomposition of cellulose.Onset decomposed temperature is reversely proportion to the acidic strength,which proves that the decomposition of cellulose in cooperative ionic liquids pairs follows the catalytic process.
(1) Christensen,C.H.;Rass-Hansen,J.;Marsden,C.C.;Taarning,E.;Egeblad,K.Chemsuschem 2008,1,283.
(2)Himmel,M.E.;Ding,S.Y.;Johnson,D.K.;Adney,W.S.;Nimlos,M.R.;Brady,J.W.;Foust,T.D.Science 2007,315,804.
(3) Hoffert,M.I.;Caldeira,K.;Benford,G.;Criswell,D.R.;Green,C.;Herzog,H.;Jain,A.K.;Kheshgi,H.S.;Lackner,K.S.;Lewis,J.S.;Lightfoot,H.D.;Manheimer,W.;Mankins,J.C.;Mauel,M.E.;Perkins,L.J.;Schlesinger,M.E.;Volk,T.;Wigley,T.M.L.Science 2002,298,981.
(4) Corma,A.;Iborra,S.;Velty,A.Chem.Rev.2007,107,2411.
(5) Huber,G.W.;Iborra,S.;Corma,A.Chem.Rev.2006,106,4044.
(6)Alonso,D.M.;Bond,J.Q.;Dumesic,J.A.Green Chem.2010,12,1493.
(7)Zou,S.P.;Wu,Y.L.;Yang,M.D.;Li,C.;Tong,J.M.Energy Fuels 2009,23,3753.
(8) Balat,M.Energy Sources Part A 2008,30,649.
(9)Klemm,D.;Heublein,B.;Fink,H.P.;Bohn,A.Angew.Chem.Int.Edit.2005,44,3358.
(10) Lee,S.H.;Doherty,T.V.;Linhardt,R.J.;Dordick,J.S.Biotechnol.Bioeng.2009,102,1368.
(11) Swatloski,R.P.;Spear,S.K.;Holbrey,J.D.;Rogers,R.D.J.Am.Chem.Soc.2002,124,4974.
(12)Li,X.H.;Zhang,L.;Li,Q.;Geng,W.G.;Ye,Y.J.;Wang,L.F.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2004,20,1465.[李雪輝,張 磊,李瓊,耿衛國,葉玉嘉,王樂夫.物理化學學報,2004,20,1465.]
(13) Zhao,W.T.;Chen,H.X.;Zhou,J.J.;Liu,N.A.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2009,25,1756.[趙偉濤,陳海翔,周建軍,劉乃安.物理化學學報,2009,25,1756.]
(14) Feng,J.L.;Zhang,J.G.;Zhang,T.L.;Cui,Y.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2010,26,2410.[馮金玲,張建國,張同來,崔 燕.物理化學學報,2010,26,2410.]
(15)Meng,G.;Kong,D.J.;Qi,X.L.;Xu,Z.Q.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2010,26,3017.[蒙 根,孔德金,祁曉嵐,許中強.物理化學學報,2010,26,3017.]
(16)Lin,Y.C.;Cho,J.;Tompsett,G.A.;Westmoreland,P.R.;Huber,G.W.J.Phy.Chem.C 2009,113,20097.
(17)Zhang,H.;Zhao,F.Q.;Yi,J.H.;Zhang,X.H.;Hu,R.Z.;Xu,S.Y.;Ren,X.N.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2008,24,2263.[張 衡,趙鳳起,儀建華,張曉宏,胡榮祖,徐司雨,任曉寧.物理化學學報,2008,24,2263.]
(18) Chattopadhyay,J.;Kim,C.;Kim,R.;Pak,D.J.Ind.Eng.Chem.2009,15,72.
(19)Yu,Z.S.;Ma,X.Q.;Liu,A.Energy Convers.Manage.2009,50,561.
(20)Gui,J.Z.;Cong,X.H.;Liu,D.;Zhang,X.T.;Hu,Z.D.;Sun,Z.L.Catal.Commun.2004,5,473.
(21)Wang,W.;Shao,L.;Cheng,W.;Yang,J.;He,M.Catal.Commun.2008,9,337.
(22) Fei,Z.F.;Zhao,D.B.;Geldbach,T.J.;Scopelliti,R.;Dyson,P.J.Chem.Eur.J.2004,10,4886.
(23)Wasserscheid,P.;Sesing,M.;Korth,W.Green Chem.2002,4,134.
(24) Bonhote,P.;Dias,A.P.;Papageorgiou,N.;Kalyanasundaram,K.;Gr?tzel,M.Inorg.Chem.1996,35,1168.
(25) Cole,A.C.;Jensen,J.L.;Ntai,I.;Tran,K.L.T.;Weaver,K.J.;Forbes,D.C.;Davis,J.H.J.Am.Chem.Soc.2002,124,5962.
(26)Adamovsky,O.;Kopp,R.;Hilscherova,K.;Babica,P.;Palikova,M.;Paskova,V.;Navratil,S.;Marsalek,B.;Blaha,L.Environ.Toxicol.Chem.2007,26,2687.
(27) Handy,S.T.;Okello,M.;Dickenson,G.Org.Lett.2003,5,2513.
(28)Yoshizawa-Fujita,M.;Johansson,K.;Newman,P.;MacFarlane,D.R.;Forsyth,M.Tetrahedron Lett.2006,47,2755.
(29) Li,X.H.;Duan,H.L.;Pan,J.T.;Wang,L.F.Chin.J.Anal.Chem.2006,34(Suppl.1),192.[李雪輝,段紅麗,潘錦添,王樂夫.分析化學,2006,34(Suppl.1),192.]
(30) Thornazeau,C.;Olivier-Bourbigou,H.;Magna,L.;Luts,S.;Gilbert,B.J.Am.Chem.Soc.2003,125,5264.
(31) Kosan,B.;Michels,C.;Meister,F.Cellulose 2008,15,59.
(32) Pinkert,A.;Marsh,K.N.;Pang,S.S.;Staiger,M.P.Chem.Rev.2009,109,6712.
(33) Ciolacu,D.;Popa,V.I.Cellul.Chem.Technol.2006,40,445.
(34) Fredlake,C.P.;Crosthwaite,J.M.;Hert,D.G.;Aki,S.N.V.K.;Brennecke,J.F.J.Chem.Eng.Data 2004,49,954.
(35) Vitz,J.;Erdmenger,T.;Haensch,C.;Schubert,U.S.Green Chem.2009,11,417.
復合離子液體中纖維素的催化分解
龍金星 郭 斌 李雪輝*王芙蓉 王樂夫
(華南理工大學化學與化工學院,制漿造紙國家重點實驗室,廣州510640)
通過將酸性功能化離子液體與對纖維素具有溶解作用的離子液體進行復合,構建了一類新型的高效催化纖維素分解的體系,并采用熱重(TG)分析方法,研究了復合離子液體中纖維素的分解行為.結果表明:復合離子液體中纖維素的分解溫度明顯降低,溶于離子液體中的纖維素可被酸性離子液體原位催化分解.纖維素的分解溫度受離子液體催化劑的酸性及纖維素在復合離子液體中的溶解度影響明顯:酸性越強,溶解度越大,纖維素的分解溫度越低.
復合離子液體;纖維素;催化分解;熱重;酸強度
O642
Received:January 12,2011;Revised:March 15,2011;Published on Web:March 25,2011.
?Corresponding author.Email:cexhli@scut.edu.cn;Tel:+86-20-87114707.
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(20876055,21076085)and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities,SCUT,China.
國家自然科學基金(20876055,21076085)及華南理工大學高校業務基金資助項目

