Lingual angioedema after alteplase treatment in a patient with acute ischemic stroke
Seyran Bozkurt, Engin Deniz Arslan, Ataman K?se, Cüneyt Ayr?k, Arda Y?lmaz, Güllü Akbaydo?an Dündar
1Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Mersin University, Mersin, Turkey
2Department of Emergency Medicine, Diskap? Y?ld?r?m Beyazit Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
3Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Mersin University, Mersin, Turkey
Case Report
Lingual angioedema after alteplase treatment in a patient with acute ischemic stroke
Seyran Bozkurt1, Engin Deniz Arslan2, Ataman K?se1, Cüneyt Ayr?k1, Arda Y?lmaz3, Güllü Akbaydo?an Dündar1
1Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Mersin University, Mersin, Turkey
2Department of Emergency Medicine, Diskap? Y?ld?r?m Beyazit Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
3Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Mersin University, Mersin, Turkey
BACKGROUND:In recent years, thrombolytic therapy has become the main treatment of ischemic stroke. But the increasing use of alteplase in ischemic stroke has made some complications more evident. Angioedema is a rare but potentially life-threatening complication of alteplase treatment. Only a few studies have examined the incidence of angioedema after treatment with alteplase for stroke.
METHODS:A 75-year-old man complaining of right hemiparesis was admitted to our emergency department. He was diagnosed as having acute ischemic stroke, and alteplase infusion was given two hours after the onset of stroke symptoms. Immediately after the completion of infusion he was noted to have a large swollen tongue.
RESULTS:His neurological symptoms resolved gradually within 4 hours, whereas his upper extremity strength improved to 4/5 and lower extremity 5/5. Lingual edema resolved within 16 hours without any complication. He died from presumed nosocomial infection 5 days later.
CONCLUSIONS:Lingual angioedema may appear as a possible complication in patients who were treated with alteplase. The management of these patients should be very careful.
Angioedema; Alteplase; Ischemic stroke
INTRODUCTION
Angioedema is a sudden, transient swelling of welldemarcated areas of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, mucosa, and submucosal tissues, which occurs with or without urticaria. Angioedema can progress rapidly, and cases that involve the mouth, tongue, larynx, lips, or face constitute a medical emergency.[1]It could be hereditary, acquired, idiopathic, and allergic because of the administration of drugs such as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or thrombolytics.[2,3]Angioedema can lead to imminent airway obstruction and a life-threatening emergency.[1]Maertins et al[3]have examined the incidence of angioedema after treatment with alteplase for stroke. A number of these patients were simultaneously treated with an ACE inhibitor.[4]Our patient was not treated with ACE inhibitor but he developed angioedema after administration of alteplase for ischemic stroke.
CASE REPORT
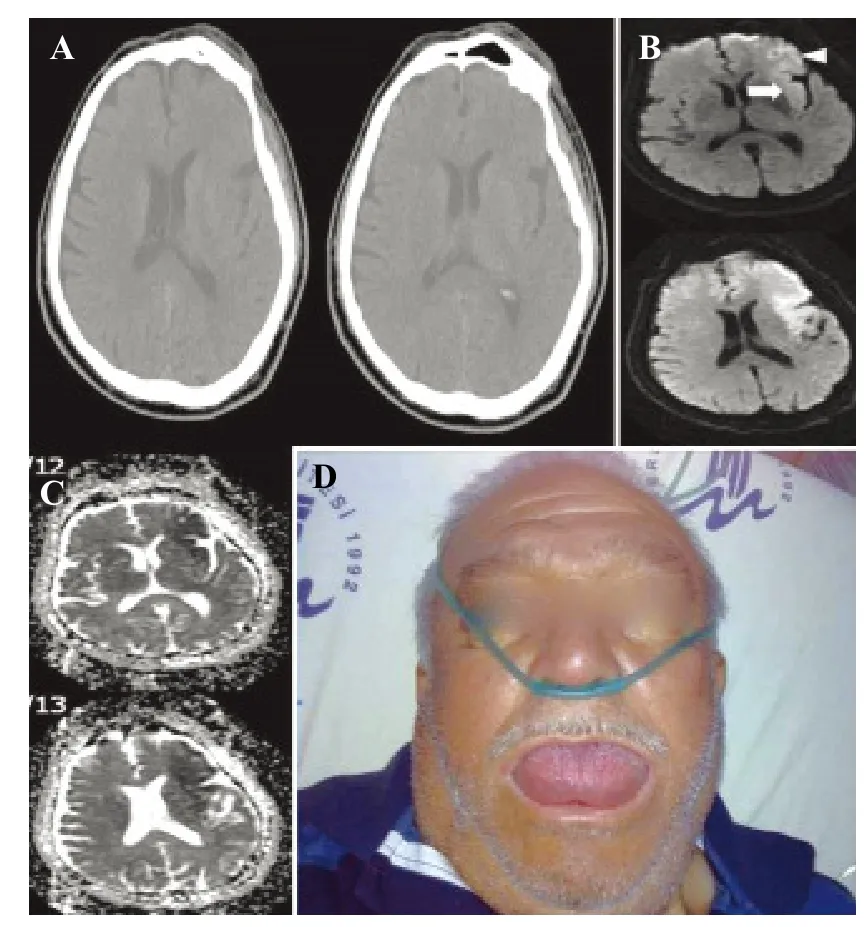
Figure 1. Non-contrast cranial CT on admission (90 minutes after stroke onset) revealed no early ischemic stroke changes (A). MRI revealed acute superior division infarction of the left middle cerebral artery at left insular (arrow) and frontal opercular (arrow head) regions. Diffusion-weighted MRI was performed 3 hours after onset of symptoms (B). MRI revealed acute superior division infarction of the left middle cerebral artery at left insular and frontal opercular regions (apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map obtained from the same patient at the same time) (C ). Lingual angioedema (D).
A 75-year-old man with a complaint of right hemiparesis was admitted to our emergency department. He had a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus but he did not use any antihypertensive agent. His vital findings were within normal limits. Physical examination was normal except neurologic examination that revealed right hemiplegia and global aphasia with positive Babinski sign on the right side. Cranial computed tomography (CT) was unremarkable for hemorrhage and early signs of ischemia (Figure 1A). Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed immediately after cranial CT that revealed acute superior division infarction of the left middle cerebral artery (Figure 1B, C). He was diagnosed as having acute ischemic stroke, and alteplase (Actilyse: Boehringer ingelheim pharma, Biberach, Germany) infusion was started two hours after the onset of stroke symptoms. Immediately after the infusion he was found to have a large swollen tongue (Figure 1D). He had no urticeria, hyperemia or respiratory distress. He was diagnosed with lingual angioedema and treated with histamine H1 receptor blockers (Avil; Sandoz pharma, Gebze, Kocaeli) and methylprednisolone (Prednol L: Mustafa Nevzat Pharma, Yenibosna, Istanbul). His neurological manifestations resolved gradually within 4 hours, but the strength of the upper and lower extremities improved to 4/5 and 5/5 respectively and lingual edema disappeared without any complication within 16 hours. He had a fever at the 5th day after admission, and blood and urine were cultured before the initiation of prophylactic antibiotic therapy. Methicillin-susceptible coagülase-negative Staphylococci and Klebsiella pneumonia were observed in blood and urine. The patient died from presumed nosocomial infection 5 days later.
DISCUSSION
Hill et al[4]reported that serious allergic reactions (anaphylactoid reactions or angioedema) have been observed during thrombolytic therapy with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) (alteplase) used for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, and deep vein thrombosis. Angioedema is a rare but potentially life-threatening complication induced by alteplase treatment.[5]The mechanisms underlying the development of angioedema are hydrolyzes of plasminogen to plasmin that activates the kinin system with occurrence of potent vasodilator bradykinin and activation of the complement system resulting in mast cell degranulation and histamine release.[1,6,7]The incidence of angioedema after alteplase treatment was up to 5%, and concurrent use of ACE inhibitors and signs of ischemia on initial CT were the major risk factors for the development of angioedema.[6,7]ACE inhibitors may have an additional effect on the development of angioedema by inhibiting plasma kininases which are responsible for bradykinin degradation. Our patient neither was on ACE inhibitor therapy nor had any sign of ischemia on initial CT. Thus the only factor for the development of lingual angioedema in our patient was the alteplase therapy. Hill and collegues[2]reported that in patients with ischemic stroke, infarction of the insular cortex might lead to autonomic dysregulation and changes in vasomotor tone, which should further interact with the angioedema cascade. Insular cortex involvement was present in our patient, as shown in Figure 1B compatible with a previous report. In acute myocardial infarction, lack of autonomic dysfunction seen in stroke patients may prevent patients from the development of angioedema. From this theory we may speculate that autonomic dysfunction is essential for developing angioedema in patients with ischemic stroke treated with alteplase. Papamitsakis and colleagues[5]reported that angioedema developed within 25 to 120 minutes after the start of thrombolytic therapy. Angioedema that occurs after alteplase treatment has a tendency to be mild, and most patients respond to antihistamines, steroids and epinephrine but they need to be intubated and require surgical airway management.[8]In our patient, lingual angioedema developed after alteplase infusion and he responded to antihistamine and steroid therapy but did not have any airway intervention.
In conclusion, angioedema is a rare but lifethreatening complication of alteplase treatment particularly in patients with ischemic stroke, which has to be promptly recognized and treated. Patients with ischemic stroke who are subjected to alteplase treatment should be closely monitored for neurologic status and hemorrhagic complications in addition to lingual angioedema.
Funding:This study did not receive any f nancial support.
Ethical approval:Not needed.
Conf icts of interest:The authors have no competing interests.
Contributors:Bozkurt S, Arslan ED and Kose A contributed to the writing of the manuscript. Bozkurt S, Y?lmaz A and Dündar GA treated the patient and, analyzed the data.
1 Bernstein JA, Moellman J. Emerging concepts in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with undifferentiated angioedema. Int J Emerg Med 2012; 5: 39.
2 Hill MD, Barber PA, Takahashi J, Demchuk AM, Feasby TE, Buchan AM. Anaphylactoid reactions and angioedema during alteplase treatment of acute ischemic stroke. CMAJ 2000; 162: 1281–1284.
3 Maertins M, Wold R, Swider M. Angioedema after administration of tPA for ischemic stroke: Case report. Air Medical Journal 2011; 30: 276–278.
4 Hill MD, Barber PA, Takahashi J, Demchuk AM, Feasby TE, Buchan AM. Anaphylactoid reactions and angioedema during alteplase treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Can Med Assoc J 2000; 162: 1281–1284.
5 Papamitsakis NI, Kuyl J, Lutsep HL, Clark WM. Benign angioedema after thrombolysis for acute stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2000; 9: 79–81.
6 Engelter ST, Fluri F, Buitrago-Tellez C, Marsch S, Steck AJ, Ruegg S, et al. Lifethreatening orolingual angioedema during thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol 2005; 252: 1167–1170.
7 Hill MD, Lye T, Moss H, Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Newcommon NJ, et al. Hemiorolingual angioedema and ACE inhibition after alteplase treatment of stroke. Neurology 2003; 60: 1525–1527.
8 Hill MD, Buchan AM. Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: results of the Canadian alteplase for stroke effectiveness study. Can Med Assoc J 2005; 172: 1307–1312.
Received May 20, 2014
Accepted after revision December 22, 2014
Seyran Bozkurt, Email: seyranbozkurt@yahoo.com
World J Emerg Med 2015;6(1):74–76
10.5847/wjem.j.1920–8642.2015.01.013
 World journal of emergency medicine2015年1期
World journal of emergency medicine2015年1期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- The role of regulatory T cells in immune dysfunction during sepsis
- Instructions for Authors
- Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulf de on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury
- Relationship between intubation rate and continuous positive airway pressure therapy in the prehospital setting
- Acute intoxication cases admitted to the emergency department of a university hospital
- Trauma patterns in patients attending the Emergency Department of Jazan General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
