Efficacy observation of combining tuina and Chinese herbal fumigation for chronic ankle sprain
Chen Bin (陳斌), Zhang Jun-feng (張峻峰), Li Yan (李艷), Wu Yao-chi (吳耀持)
1 Fenghua Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang 315500, China
2 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai 200233, China
Efficacy observation of combining tuina and Chinese herbal fumigation for chronic ankle sprain
Chen Bin (陳斌)1, Zhang Jun-feng (張峻峰)2, Li Yan (李艷)2, Wu Yao-chi (吳耀持)2
1 Fenghua Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang 315500, China
2 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai 200233, China
Objective:To observe the clinical efficacy of combining tuina and Chinese herbal fumigation for chronic ankle sprain.
Ankle sprain is a common sports injury. Chronic ankle sprain may occur as a result of delayed or inappropriate treatment of acute ankle sprain. Patients may experience long-term ankle swelling, pain and limited motion. Due to its anatomical feature, ankle joint is susceptible to injury, especially its lateral collateral ligament. Over time, chronic ankle sprain may progress into traumatic arthritis with dysfunctions of the ankle joint. Unstable ankle joint may in turn cause recurrent sprain. We’ve treated this condition with tuina combining with Chinese herbal fumigation. The results are now summarized as follow.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
This was based on the diagnosis for sprained ankle in theCriteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[1]: a history of ankle sprain; duration
≥1 month; inability to walk for long period of time, ankle pain and weakness that affect life, work and physical activity; swelling, tenderness or painful nodule in medial or lateral aspect of the ankle; no fracture or dislocation in radiographic films.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Having a history of ankle sprain; duration ≥1 month; inability to walk for long period of time, ankle pain and weakness that affect life, work and physical activity; swelling, tenderness or painful nodule in medial or lateral aspect of the ankle; those who agreed to participate in the trial and signed the informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Rheumatic arthritis and gout by blood sedimentation, rheumatic factor and serum uric acid measurement; and tuberculosis or tumor by anterior-posterior and lateral film of the ankle joint.
1.4 Statistical methods
The SPSS 17.0 version software was used for statistical analysis. The group t-test was used for measurement data [expressed as. The Chisquare test was used for enumeration data and rank sum test for ranked data. A P value of less than 0.05 indicated a statistical significance.
1.5 General materials
A total of 93 eligible outpatients in our hospital were randomly allocated into an observation group (n=47) and a treatment group (n=46). Cases in the observation group were aged between 18 and 46 years and their duration lasted from 3 months to 4 years. Cases in the control group were aged between 23 and 50 years and their duration lasted from 4 months to 2.5 years. There were no significant between-group differences in age, gender, duration and sprain (P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).
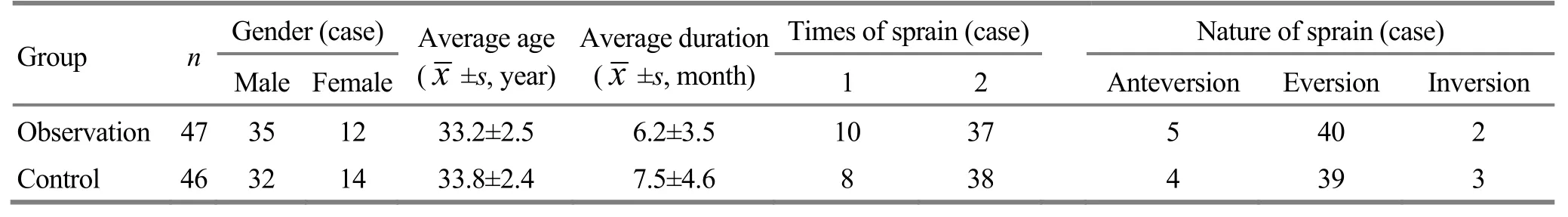
Table 1. Between-group comparison in baseline data
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Observation group
Patients received Chinese herbal fumigation combining with tuina based on the muscle region theory.
2.1.1 Tuina treatment
Point pressure: Apply An-pressing to Jiexi (ST 41), Qiuxu (GB 40), Yanglingquan (GB 34), Zusanli (ST 36), Chengshan (BL 57), Kunlun (BL 60) and Xuanzhong (GB 39), 30 s for each point until the patient feels soreness and distension (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Regulation of muscle regions: Muscle regions of corresponding meridians are regulated based on sprained site and clinical symptoms. Specifically, regulate muscle regions of the Bladder Meridian and the Gallbladder Meridian for lateral aspect of the ankle; regulate muscle regions of the Gallbladder Meridian and the Stomach Meridian for anterior aspect of the ankle; and regulate muscle regions of the Spleen Meridian, the Kidney Meridian and the Liver Meridian for medial aspect of the ankle. Take the Bladder Meridian for example, with a side lying position towards the healthy side, grasp the middle part of the patient’s lower leg, i.e., the cross section of Chengshan (BL 57), immobilize the affected limb. Then the practitioner grasp and stretch the small toe with one hand and apply a 3-min An-pressing and Rou-kneading to the pathway (against the direction of bladder meridian) from the small toe to the heel, Achilles tendon and Chengshan (BL 57) along the lateral aspect (Figure 3).
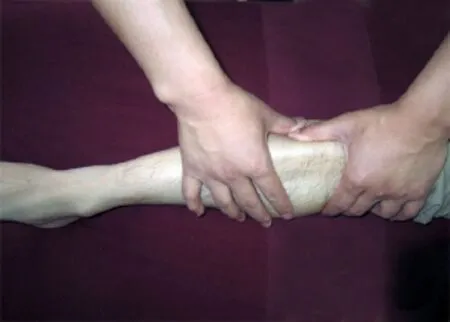
Figure 1. An-pressing Zusanli (ST 36)
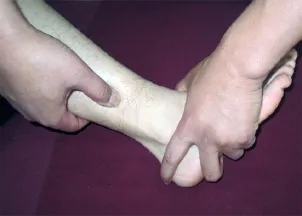
Figure 2. An-pressing Xuanzhong (GB 39)
Tanbo-plucking: Different areas are Tanbo-plucked 3 min based on sprained site and clinical symptoms. Specifically, Tanbo-pluck the lateral aspect of the achilles tendon and calcaneofibular ligament for lateral aspect of the ankle; Tanbo-pluck the extensor pollicis longus, extensor digitorum longus and tibialis anterior for anterior aspect of the ankle; and Tanbo-pluck the medial aspect of the Achilles tendon and triangular ligament for the medial aspect of the ankle (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
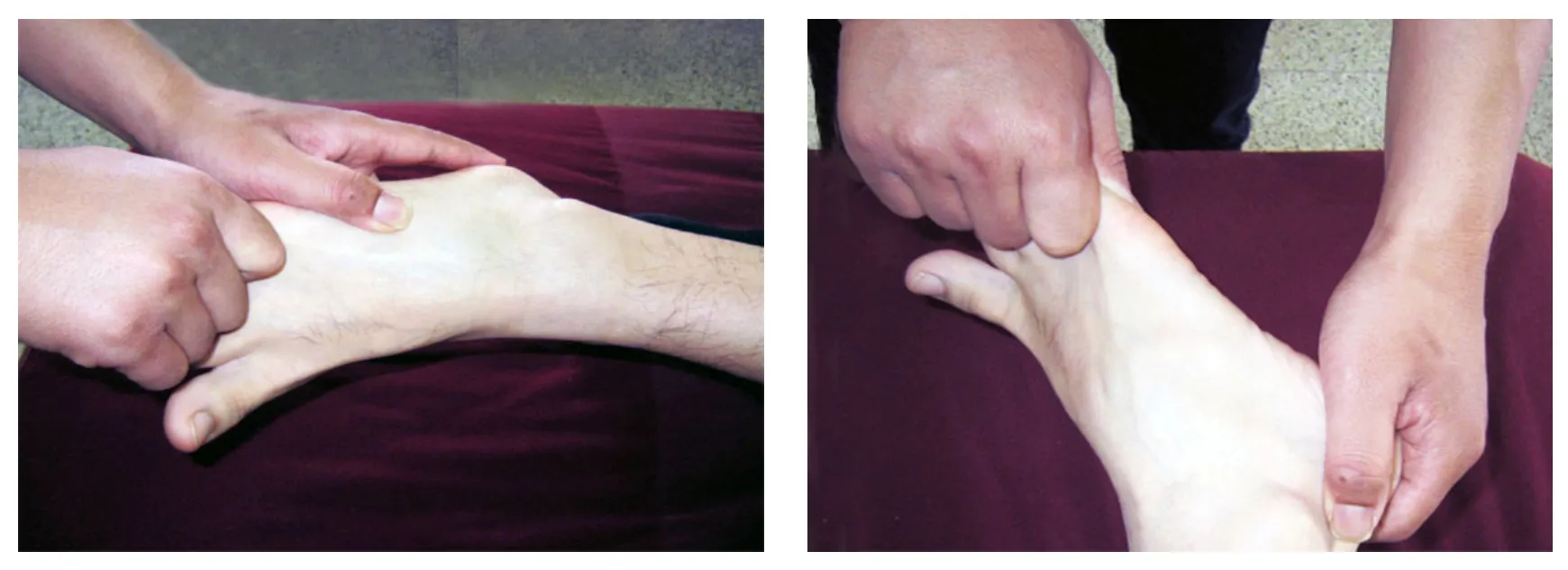
Figure 3. Regulating muscle regions of the Bladder Meridian
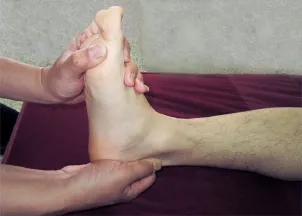
Figure 4. Tanbo-plucking the achilles tendon
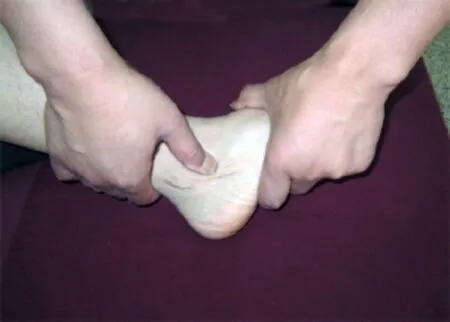
Figure 5. Tanbo-plucking the calcaneofibular ligament
An-pressing and Rou-kneading Ashi points and area upon palpation and apply Dian-digital pressing, An-pressing, Rou-kneading and Bashen-stretching to palpable ropy, linear or patchy nodules for 3 min (Figure 6).
It’s essential to apply soft and penetrating tuina manipulation to treatment area until the presence of soreness and distending sensation, especially to the origin and insertion of Achilles tendon (junction of the triceps muscle and heel bone) and extensor retinaculum of the extensor pollicis longus and extensor digitorum longus.

Figure 6. An-pressing and Rou-kneading ropy nodules
The above tuina treatment was done once every other day and 10 times made up a course of treatment. The efficacy was observed after 1 course of treatment.
2.1.2 Chinese herbal fumigation
The self-made tendon-relaxing and blood-circulating formula was used for herbal fumigation.
Ingredients: Hong Hua (Flos Carthami) 9 g, Dang Gui (Radix Angelicae Sinensis) 15 g, Ai Ye (Folium Artemisiae Argyi) 18 g, Lu Lu Tong (Fructus Liquidambaris) 18 g, Shen Jin Cao (Caulis Tinosporae Sinensis) 30 g, Chuan Lian Zi (Fructus Toosendan) 10 g, Dan Shen (Radix etRhizoma Salviae Miltiorrhizae) 30 g,Sang Zhi(Ramulus Mori) 30 g,Hai Tong Pi(Cortex Erythrinae) 30 g,Tou Gu Cao(Caulis Impatientis) 30 g,Hu Lu(Fructus Lagenariae) 20 g,Bie Jia(Carapax Trionycis) 24 g andGan Cao(Radix et Rhizoma Glycyrrhizae) 6 g.
Method: The above formula was decocted using the decocting machine into medicinal liquid of 200 mL. Then the XJZE-1 automatic Chinese herbal fumigation device (manufactured by Huzhou Sanzhou Electronic Device Factory, China) was used to fumigate the affected area using 200 mL of medicinal liquid and 600 mL water (Figure 7). The fumigation was done once every other day, 30 min for each treatment and 10 times made up a course of treatment. The efficacy was observed after 1 course of treatment.
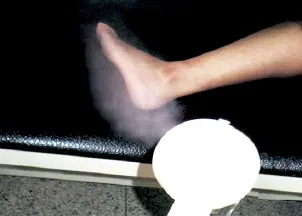
Figure 7. Fumigation with Chinese herbs
2.2 Control group
Cases in the control group received the same fumigation as those in the observation group coupled with oral blood-circulating and pain-alleviating capsules (manufactured by Jiangxi Changnuo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China, China Food and Drug Administration approval number: 20053669, batch No: 14120177), 4 capsules (0.25 g/capsule) for each dose, 3 doses a day, for a total of 20 d.
3 Efficacy Observation
3.1 Observation items and criteria
The Baird-Jackson ankle scoring system[2]was used to evaluate pain (15 points), ankle stability (15 points), walking ability (15 points), running ability (10 points), ankle joint range of motion (ROM, 10 points) and radiographic findings (talar shift, talar tilt and gap between medial and superior aspects of the ankle) (25 points). The total score ranges from 0 to 100. A higher score indicates a better ankle joint function.
The efficacy was evaluated according to the Baird-Jackson scoring system.
Excellence: Baird-Jackson ankle score ≥96 points.
Good: Baird-Jackson ankle score ≥91 points but<96 points.
Fair: Baird-Jackson ankle score ≥81 points but<91 points.
Poor: Baird-Jackson ankle score <81 points.
3.2 Treatment results
3.2.1 Comparison in Baird-Jackson ankle score
Before treatment, there were no significant betweengroup differences in individual item scores and total score (P> 0.05). After treatment, except for radiographic findings, there were significant intra-group differences in individual item scores (P<0.05,P<0.01), there were significant between-group differences in individual item scores and total scores (P<0.05,P<0.01), indicating that both treatment protocols can effectively improve the ankle joint function, combining Chinese herbal fumigation and tuina based on the muscle region theory can obtain better effect than combining Chinese herbal fumigation and oral capsules to circulate blood and alleviate pain (Table 2).
3.2.2 Between-group comparison in efficacy
The excellence and good rate was 76.6% in the observation group, versus 54.4% in the control group, showing a statistical difference (P<0.05) and indicating a better effect in the observation group than that in the control group (Table 3).
Table 2. Between-group comparison in ankle joint function before and after treatment

Table 2. Between-group comparison in ankle joint function before and after treatment
Note: Intra-group comparison, 1) P<0.01, 2) P<0.05; compared with the control group after treatment, 3) P<0.01
Group n Time Pain Stability Walking Running Work ROM X-ray finding Total score Observation 47 BT 7.25±1.83 5.87±3.62 8.87±2.17 4.87±1.25 5.26±1.32 5.67±1.88 25.00±0.00 72.85±5.32 AT 14.57±2.351)3)11.85±4.651)3)13.56±2.781)3)9.62±1.631)3)9.54±1.721)3)9.31±2.421) 25.00±0.00 93.45±4.861)3)Control 46 BT 7.84±3.62 5.52±3.78 7.75±2.33 4.25±1.47 4.99±1.26 5.89±1.78 25.00±0.00 73.46±5.28 AT 12.53±2.652) 9.19±4.872)11.68±3.012)8.49±1.892)7.68±1.632)8.36±2.342) 25.00±0.00 86.53±5.321)

Table 3. Between-group comparison in treatment effect (case)
4 Discussion
Ankle joint is the most vulnerable joint to be injured. Sprained ankle is the most common sports injury. Stability of the ankle joint is maintained by the articular fossa formed by the inferior articular surface of the tibia and medial and lateral articular surfaces of the ankle as well as the medial and lateral ligaments. Ankle joint remains stable during normal standing or walking. However, stability of the ankle joint relies only on the medial and lateral ligaments when the feet bend downward. Since the triangular ligaments on the medial side of the ankle are strong, whereas three independent ligaments are weak, sprained ankle often manifests as eversion (medial)[3]. Weight-bearing activities without immediate treatment or adequate rest may cause local aseptic inflammation, soft tissue adhesion and forming of scar. As a result, unstable ankle joint and accidental twisting may cause repeated ankle sprain, leading to local swelling and pain that alleviate upon rest. Over time, chronic ankle sprain may occur. Factors including delayed, improper treatment and unstable ankle due to lacking or inadequate immobilization, premature weight-bearing activities and recurrent injuries can contribute to chronic ankle sprain[4].
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), many problems are associated with obstructed circulation of qi and blood. Four limbs, muscles, bones and five-zang and six-fu organs are all nourished by qi and blood. Stagnation of qi and blood can block meridians and result in swelling and pain, known as ‘obstruction causes pain’. The twelve muscle regions meet in joints throughout the body and connect the skeletons. They bind the skeleton, mobilize the joints and maintain normal motion and physiological functions[5]. Tuina manipulation can regulate the twelve muscle regions and circulate qi and blood within the body.
Attached to the twelve regular meridians, the twelve muscle regions are the system to gather meridian qi at muscles, tendons and joints. They act to connect muscles, tendons and bones and maintain normal human motion. Trauma or chronic strain may cause local swelling, deformation, contracture and adhesion, which may further result in qi stagnation, blood stasis and subsequently, pain. Based on the muscle region theory, apply Rou-kneading, An-pressing, Tui-pushing and Na-grasping to certain body parts can accelerate blood circulation, resolve stagnant blood and water retention, relieve muscle spasm and alleviate pain. In human body, mechanical force results from muscle contraction and then conducts along the muscle regions. Through tendons, the mechanical force acts on bones and eventually on joints, generating coordinated body movement[6]. Muscle regions are essential to maintain the stability of ankle. The muscle region theory provides a new perspective for management of chronic soft tissue injury[7].
In TCM, ankle sprain falls under the category of‘tendonBi-impediment’ or ‘tendon injury’. It often results from trauma-related blood stasis coupled with external contraction of cold-dampness[8]. Consequently, the treatment strategies are to relax tendons, unblock meridians, circulate blood and resolve stasis. Of the Chinese herbal formula in this study,Dang Gui(Radix Angelicae Sinensis) tonifies blood, unblocks meridians, circulates blood and alleviates pain;Ai Ye(Folium Artemisiae Argyiwarms meridians, circulates blood, unblocks meridians and alleviates pain;Shen Jin Cao(Caulis Tinosporae Sinensis) relaxes tendons, unblocks meridians, circulates blood and alleviates pain;Hong Hua(Flos Carthami) andDan Shen(Radix et Rhizoma Salviae Miltiorrhizae) circulate blood, unblock meridians, resolve stasis and alleviate pain;Sang Zhi(Ramulus Mori),Hai Tong Pi(Cortex Erythrinae) andLu Lu Tong(Fructus Liquidambaris) remove wind and unblock meridians.Chuan Lian Zi(Fructus Toosendan) circulates qi and alleviates pain.Tou Gu Cao(Caulis Impatientis) circulates blood, resolves stasis, and unblocks meridians.Hu Lu(Fructus Lagenariae) resolves edema.Bie Jia(Carapax Trionycis) softens masses.Gan Cao(Radix et Rhizoma Glycyrrhizae) coordinates other herbs. Local fumigation can directly circulate blood in the ankle area and open the striae to allow the medicinal effect to the affected layer[9-10].
Tuina manipulation based on the muscle region theory in this study can unblock meridians, circulate qi and blood, stimulate peripheral nerve, promote lymph circulation, resolve edema, soften masses and relax muscle spasm[11-13]. The study results have suggested that combining tuina and Chinese herbal fumigation can dilate capillaries, accelerate blood circulation[14-15]and obtain better effect than combining oral capsules and Chinese herbal fumigation.
Conflict of Interest
There was no conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shanghai Key Clinical Support Program for Chinse Medicine and Integrated Chinse and Western Medicine (上海市中醫、中西醫結合臨床 重 點 扶 持 項 目 , No. ZY3-JSFC-1-1008); Lu’s Acupuncture Inheritance Study of Shanghai Schools of Traditional Chinese Medicine (海派中醫流派陸氏針灸傳承研究, No. ZYSNXD-CC-HPGC-JD-004).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Received: 5 June 2015/Accepted: 28 June 2015
[1] State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994: 201-202.
[2] Baird RA, Jackson ST. Fractures of the distal part of the fibula with associated disruption of the deltoid ligament. Treatment without repair of the deltoid ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1987, 69(9): 1346-1352.
[3] Yan ZG. Normal Human Anatomy. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1995: 47-48.
[4] Qiao XJ. Manipulation for 52 cases with chronic ankle sprain. Zhongyi Zhenggu, 1999, 11(1): 26.
[5] Huang FY, Yuan JM, Dong BQ. Muscle region theory and low back and knee pain. Tianjin Zhongyiyao, 2010, 27(5): 394-396.
[6] Zhang R, Li F, Wang CH, Li H, Song YH. Role of muscle region theory in pathogenesis and treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2007, 22(7): 644-645
[7] Xie J, You FG. Combining reinforcing tuina manipulation and Chinese herbal fumigation for 30 cases with chronic ankle sprain. Guoyi Luntan, 2013, 28(1): 25-26.
[8] Wu DL. Efficacy analysis on physical therapy combining with Chinese medicine for chronic ankle sprain. Qiuyi Wenyao, 2013, 11(4): 138.
[9] Chen XY. Therapeutic observation on electroacupuncture plus herbal fumigation for ankle sprain. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2012, 31 (4): 261-262.
[10] Zhao CF, Liu XA, Ding Y. Effect of Chinese herbal fumigation combining with tuina on vertigo and concentrations of endothelin and calcitonin gene-related peptide in patients with vertebral artery cervical spondylosis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2014, 12(6): 335-340.
[11] Feng Q, Liang HY, Luo HJ. Combining tuina and Chinese herbal fumigation for 81 cases with ankle sprain. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi, 2012, 20(9): 59-60.
[12] Shen ZF, Luo KT, Zhu GF, Jin YQ. Tuina plus ultrasonic therapy for infantile muscular torticollis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2012, 12(6): 389-392.
[13] Song HQ. Tuina therapy for 98 cases with ankle sprain. Zhejiang Linchuang Yixue, 2002, 4(10): 769.
[14] Shi Y, Wang X, Chen DY, Chen B, Gao NY, Zhan HS, Shi YY. Clinical observation on the treatment of acute ankle sprain by Shi’s manipulative therapy combining with compoundZijingplaster. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi, 2014, 22(5): 1-3.
[15] Shi ZX. Treating 134 cases of limbs soft tissue injuries withHonghua Huayudecoction fumigation plus point massage. CJCM, 2014, 6(8): 138-139.
Translator:Han Chou-ping (韓丑萍)
推拿配合中藥熏蒸治療陳舊性踝關節扭傷療效觀察
目的:觀察推拿配合中藥熏蒸治療陳舊性踝關節扭傷的臨床療效。方法:將納入的93例患者根據隨機數字表隨機分為2組, 觀察組47例, 給予經筋理論指導下推拿配合中藥熏蒸治療; 對照組46例, 予口服活血止痛藥物配合中藥熏蒸治療。推拿和中藥熏蒸均隔日1次, 10次為1個療程, 治療1個療程后觀察兩組踝關節功能評分(Baird-Jackson)及臨床療效。結果:治療后, 除放射線檢查結果外, 兩組治療前后Baird-Jackson各項評分均有統計學差異(P<0.05,P<0.01); 除踝關節活動度量(range of motion, ROM)外, 兩組間各項評分及總分差異亦有統計學意義(P<0.01)。觀察組優良率為76.6%, 對照組優良率為54.4%, 兩組優良率差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:經筋理論指導下推拿配合中藥熏蒸治療陳舊性踝關節扭傷的臨床效果優于口服活血止痛藥物配合中藥熏蒸治療。
推拿; 按摩; 扭傷與勞損; 十二經筋; 中草藥; 熏蒸
R244.1 【
】A
Tuina; Massage; Sprains and Strains; Musculature of 12 Meridians; Drugs, Chinese Herbal; Fumigation
Author: Chen Bin, attending physician
Wu Yao-chi, professor, chief physician, doctoral supervisor.
E-mail: chenbin998@qq.com
Methods:A total of 93 cases were randomly allocated into an observation group (n=47) and a control group (n=46) according to the table of random number. Cases in the observation group received tuina combining with Chinese herbal fumigation, whereas cases in the control group received oral blood-circulating and pain-alleviating capsules combining with Chinese herbal fumigation. Both tuina and Chinese herbal fumigation were done once every other day and 10 times made up a course of treatment. The Baird-Jackson ankle scoring system and clinical efficacy were observed after 1 course of treatment.
Results:After treatment, except for radiographic findings, there were significant intra-group differences in individual item scores of Baird-Jackson (P<0.05,P<0.01); except for ankle joint range of motion (ROM), there were significant betweengroup differences in individual item scores and total score (P<0.01). The excellence and good rate was 76.6% in the observation group, versus 54.4% in the control group, showing a statistical significance (P<0.05).
Conclusion:Combining Chinese herbal fumigation and tuina based on the muscle region theory can obtain better effect than combining oral blood-circulating and pain-alleviating capsules and Chinese herbal fumigation for chronic ankle sprain.
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2015年6期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2015年6期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical observation of Da Huang (Rheum Officinale) application at Shenque (CV 8) for constipation after operation for lumbar vertebral fracture
- Therapeutic efficacy observation on combining interaction and routine acupuncture for intractable facial palsy
- Therapeutic efficacy observation on needling Yangming method for facial palsy
- Effect of breathing and Daoyin exercises on the quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Observation on clinical effect of acupuncture for peripheral facial paralysis in acute period and facial nerve F-wave
- Review on studies of acupuncture treatment for luteinized unruptured follicle syndrome
