胚胎型大腦后動脈伴發顱內動脈瘤的多層螺旋CT血管造影分析
何 珍,張繼揚,徐 勐,萬業達
(天津醫院放射一科,天津 300210)
胚胎型大腦后動脈伴發顱內動脈瘤的多層螺旋CT血管造影分析
何 珍,張繼揚,徐 勐,萬業達
(天津醫院放射一科,天津 300210)
目的:采用多層螺旋CT血管造影(CTA)分析胚胎型大腦后動脈(FTP)伴發顱內動脈瘤情況,探討FTP是否為顱內動脈瘤危險因素。同時對比分析FTP伴發顱內動脈瘤與FTP未伴發顱內動脈瘤的相關臨床資料。方法:3名醫師復習155例頭顱CTA的橫斷面、多平面重組(MPR)、容積再現(VR)圖像,觀察FTP是否存在及其分型,同時分析FTP患者與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的部位、大小,是否存在蛛網膜下腔出血。電話回訪FTP患者是否存在吸煙、高血壓、冠心病和糖尿病病史。總結FTP發生率,采用χ2檢驗分析是否存在性別差異。分別總結FTP與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率。采用Fisher確切概率法比較FTP與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率,以及伴發顱內動脈瘤的FTP與未伴發顱內動脈瘤的FTP患者在年齡、性別、吸煙史、高血壓、冠心病和糖尿病方面是否存在統計學差異。采用二項Logistic回歸分析FTP是否為顱內動脈瘤危險因素。結果:FTP總體發生率為16.13%(25/155),男性為12.12%(12/99),女性為23.21%(13/56),其發生率無性別差異(P=0.071)。FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率為20%(5/25),全部為女性,非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率為6.15%(8/135),FTP與非FTP在伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率上存在統計學差異(P=0.038)。FTP是顱內動脈瘤發生的危險因素(P=0.031)。伴發顱內動脈瘤FTP患者與未伴發顱內動脈瘤FTP患者在性別、高血壓、冠心病及糖尿病方面存在統計學差異(P<0.05),在年齡和吸煙史上不存在統計學差異(P>0.05)。結論:女性FTP患者在同時存在高血壓、冠心病或糖尿病病史時,其伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率明顯增高。
顱內動脈瘤;大腦后動脈;體層攝影術,螺旋計算機;血管造影術
胚胎型大腦后動脈 (Fetal origin of posterior cerebral artery,FTP)是Willis環常見的一種先天性變異,即大腦后動脈(Posterior cerebral artery,PCA)血供通過后交通動脈(Posterior communicatingartery,PComA)來自于頸內動脈系,而并非是椎基底動脈系[1]。大量文獻對這一變異進行了詳細報道[2-6]。國內外也有一些文獻對顱內動脈瘤伴發FTP的情況進行了報道。本文復習155例頭顱多層螺旋CT血管造影(CT angiograpy,CTA)的資料,從另一個角度總結FTP伴發顱內動脈瘤的情況,分析FTP是否為顱內動脈瘤危險因素。此外,對伴發顱內動脈瘤與未伴發顱內動脈瘤的FTP患者的臨床資料進行了對照分析。
1 資料與方法
1.1 資料
復習2008年1月—2009年1月連續的155例中國人頭顱CTA資料。男99例,女56例,年齡(60.23±13.24)歲。本研究經醫院倫理委員會同意。在行CTA檢查前,患者均簽署知情同意書。
1.2 臨床癥狀
155例中頭暈、頭痛98例,一側肢體麻木或活動不利125例,飲水嗆咳30例,走路不穩35例,復視24例。
1.3 檢查方法及圖像處理
采用GE Lightspeed 16層螺旋CT,美國 LF 9000高壓注射器。經肘靜脈或手背靜脈以4 mL/s的流率注入歐乃派克350 mgI/mL 100 mL。掃描層厚為5 mm,螺距為1.375∶1。延遲時間25 s。管電壓140 kV,管電流230 mA。
采用AW 4.5工作站進行圖像重組,完成顱內動脈容積再現(Volume rendering,VR)、多平面重組(Multiple planner reconstruction,MPR)圖像。重建層厚為0.625 mm。DFOV為6.5 cm。觀察窗位500 HU、窗寬1 500 HU。
1.4 FTP分型及伴發顱內動脈瘤觀察內容
當后交通動脈管徑大于PCA-P1段管徑時,稱為部分型。當PCA-P1段缺如時,稱為完全型[7]。復習顱內動脈CTA資料,明確是否存在FTP、FTP位于哪側、FTP分型。觀察FTP與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤部位,是否伴發蛛網膜下腔出血。在顯示動脈瘤瘤徑最佳的MPR層面,測量瘤徑寬度。在顯示動脈瘤最大徑線層面測量其長徑、短徑,記錄平均直徑(長徑與短徑平均值)。
1.5 FTP患者病史隨訪
對經CTA確定為FTP的患者,從原始檢查登記記錄中獲取聯系電話,對患者本人或家屬進行電話回訪。回訪內容包括吸煙史(曾經有1年連續吸煙歷史即確定為存在吸煙史)及臨床是否確診為高血壓、冠心病或糖尿病。
1.6 統計分析
計算FTP的發生率,采用χ2檢驗分析其發生率是否存在性別差異。分別計算FTP與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率,采用Fisher確切概率法分析二者間是否存在統計學差異。采用二項Logistic回歸分析FTP是否為顱內動脈瘤危險因素。總結FTP患者年齡、性別、吸煙史、高血壓、冠心病及糖尿病情況,采用Fisher確切概率法分析伴發顱內動脈瘤與未伴發顱內動脈瘤在上述因素中是否存在統計學差異。
2 結果
2.1 FTP發生率
155例顱內動脈CTA檢查中,明確存在FTP者25例,男12例,女13例,平均年齡(71.40±6.02)歲。
25例出現29條FTP,13條為部分型,16條為完全型。其中1例右側出現2條FTP(圖1),3例雙側出現FTP(圖2,3)。FTP總體發生率為16.13%(25/155),男性發生率為12.12%(12/99),女性發生率為 23.21%(13/56)。采用 χ2檢驗,χ2=3.254,P= 0.071>0.05,因此FTP發生率無明顯性別差異。雙側FTP發生率在總體及FTP人群中分別為1.94%(3/ 155)、12.00%(3/25)。
2.2 FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤情況
FTP患者中20%(5/25)伴發顱內動脈瘤,全部為女性。大腦中動脈-后交通動脈移行部動脈瘤1例(圖2);頸內動脈(Internal carotid artery,ICA)顱內段動脈瘤2例(圖3,4),其中1例(圖3)有蛛網膜下腔出血史,此次伴發左側基底節區血腫;PcomAPCA移行部動脈瘤1例(圖5);基底動脈遠端動脈瘤1例(圖6)。
FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤瘤頸平均值為 (3.3± 1.6)mm,瘤體平均直徑為(5.5±2.9)mm。
2.3 非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤情況
非FTP患者中6.15%(8/130)伴發顱內動脈瘤,男5例,女3例。大腦前動脈-前交通動脈移行部動脈瘤2例,ICA顱內段動脈瘤3例,大腦中動脈M1段動脈瘤1例,PCA-PcomA移行部動脈瘤2例,未見伴發蛛網膜下腔出血。
非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤平均瘤頸為 (2.8± 1.8)mm,瘤體平均直徑為(6.5±2.4)mm。
2.4 FTP與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤發生率分析
由于病例數不足40例,采用Fisher確切概率法比較FTP與非FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率,P=0.038<0.05,二者發生率存在統計學差異。FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤的發生率明顯高于非FTP患者。
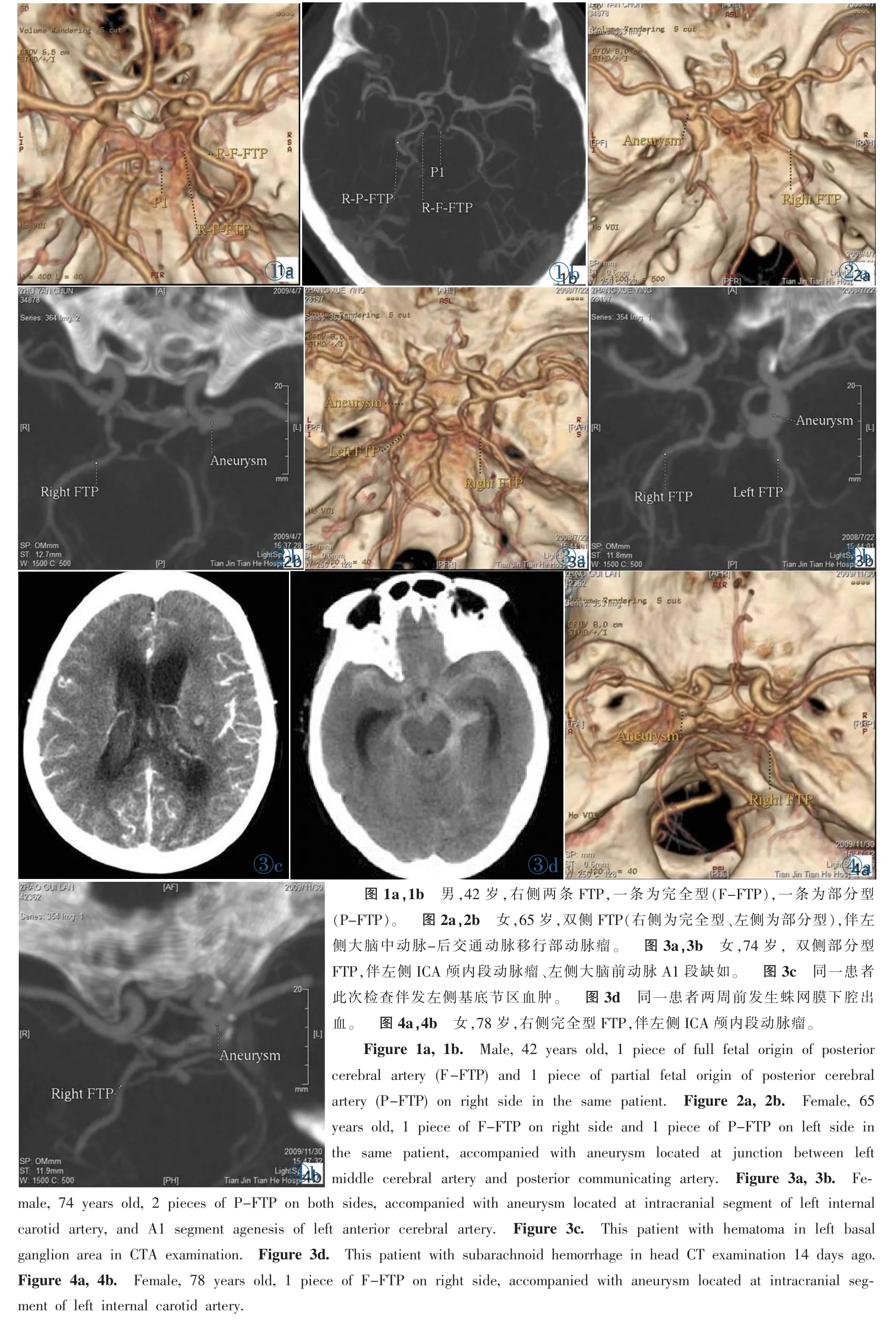
圖1a,1b 男,42歲,右側兩條FTP,一條為完全型(F-FTP),一條為部分型(P-FTP)。 圖2a,2b 女,65歲,雙側FTP(右側為完全型、左側為部分型),伴左側大腦中動脈-后交通動脈移行部動脈瘤。 圖3a,3b 女,74歲,雙側部分型FTP,伴左側ICA顱內段動脈瘤、左側大腦前動脈A1段缺如。 圖3c 同一患者此次檢查伴發左側基底節區血腫。 圖3d 同一患者兩周前發生蛛網膜下腔出血。 圖4a,4b 女,78歲,右側完全型FTP,伴左側ICA顱內段動脈瘤。Figure 1a,1b. Male,42 years old,1 piece of full fetal origin of posterior cerebral artery(F-FTP)and 1 piece of partial fetal origin of posterior cerebral artery(P-FTP)on right side in the same patient. Figure 2a,2b. Female,65 years old,1 piece of F-FTP on right side and 1 piece of P-FTP on left side in the same patient,accompanied with aneurysm located at junction between left middle cerebral artery and posterior communicating artery. Figure 3a,3b. Female,74 years old,2 pieces of P-FTP on both sides,accompanied with aneurysm located at intracranial segment of left internal carotid artery,and A1 segment agenesis of left anterior cerebral artery. Figure 3c. This patient with hematoma in left basal ganglion area in CTA examination. Figure 3d.This patient with subarachnoid hemorrhage in head CT examination 14 days ago. Figure 4a,4b. Female,78 years old,1 piece of F-FTP on right side,accompanied with aneurysm located at intracranial segment of left internal carotid artery.
2.5 二項Logistic回歸分析FTP是否為顱內動脈瘤危險因素
統計分析FTP是顱內動脈瘤危險因素,見表1。
2.6 伴發顱內動脈瘤與未伴發顱內動脈瘤的FTP患者臨床資料對照分析
由于病例數不足40例,采用Fisher確切概率法分析伴發顱內動脈瘤與未伴發顱內動脈瘤的FTP患者的臨床資料,見表2。
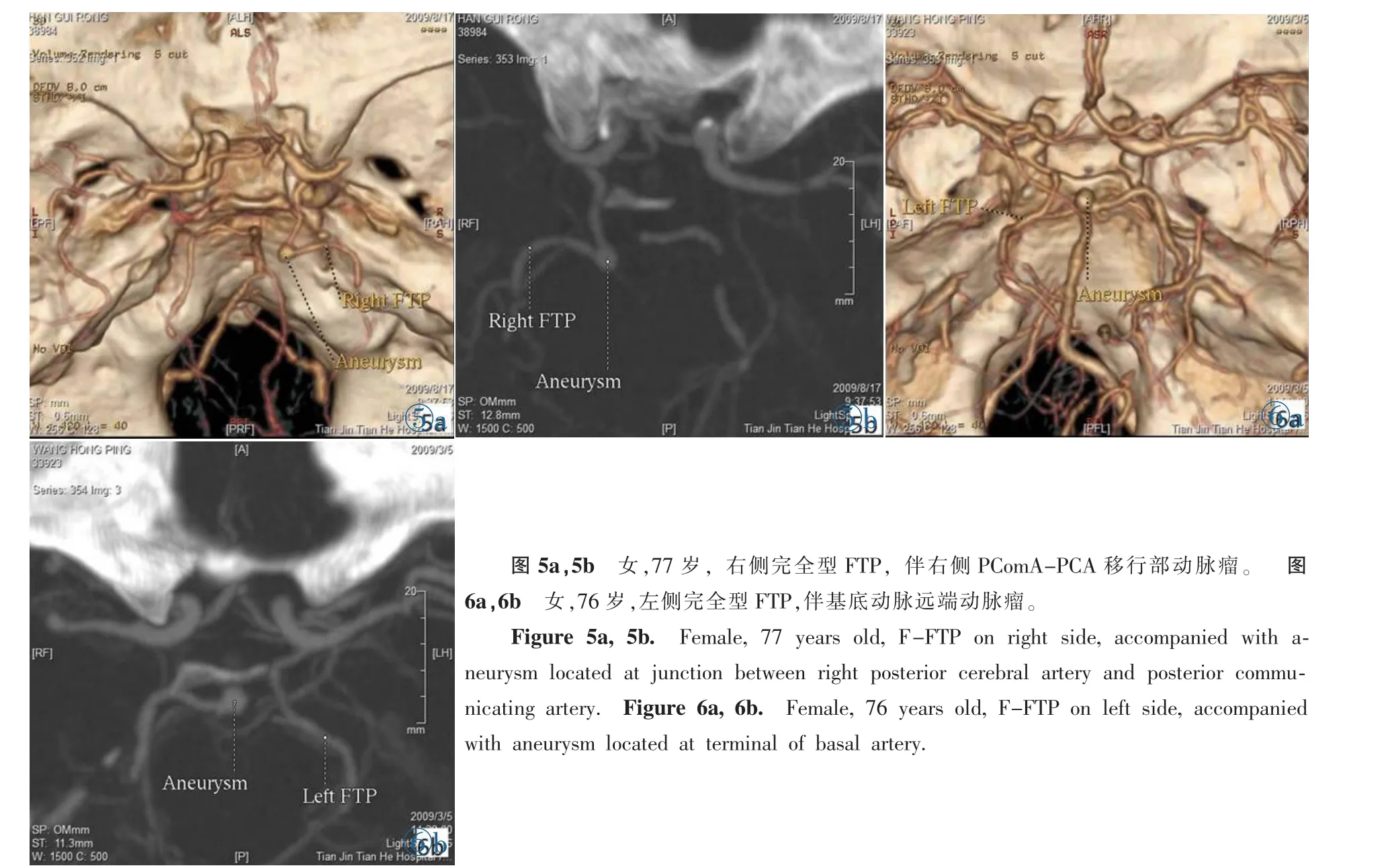
圖5a,5b 女,77歲,右側完全型FTP,伴右側PComA-PCA移行部動脈瘤。 圖6a,6b 女,76歲,左側完全型FTP,伴基底動脈遠端動脈瘤。Figure 5a,5b. Female,77 years old,F-FTP on right side,accompanied with aneurysm located at junction between right posterior cerebral artery and posterior communicating artery.Figure 6a,6b.Female,76 years old,F-FTP on left side,accompanied with aneurysm located at terminal of basal artery.
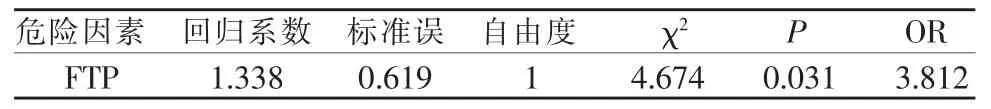
表1 FTP是否為顱內動脈瘤危險因素二項Logistic回歸分析

表2 伴發顱內動脈瘤與未伴發顱內動脈瘤的FTP患者臨床資料對照分析
3 討論
3.1 FTP胚胎發育
在胚胎28~30 d(4.0~5.7 mm),從成對的背主動脈向頭側延伸,形成ICA[4]。在胚胎5~8 mm階段,成對的縱行的神經動脈沿著菱腦出現,并合并形成基底動脈。ICA和神經動脈吻合支的尾側部分形成PComA。在40 mm階段 (8周)PCA是PComA的延伸,椎基底系形成,并通過P1段參與PCA的供血。在這期間,Willis環各組成部分管徑相同[8]。在發育過程中,PCA-P1段管徑逐漸增寬,PComA管徑逐漸變細,至出生時,PCA-P1段管徑大于PComA管徑。這是我們最常見到的類型,稱為成人型PCA。如果在胚胎發育過程中,出現停滯,就會出現以下兩種情況。其一,P1段管徑與PComA一致,稱為中間型PCA。其二,P1段缺如或P1段管徑小于PComA,即本文分析的FTP。當P1段缺如時,稱為完全型FTP。當P1段管徑小于PComA時,稱為部分型FTP[5,7,9]。
3.2 FTP伴發顱內動脈瘤
FTP是Willis環后循環變異的一種。FTP側PCA血供經PComA完全來自同側ICA,或者由同側ICA與基底動脈共同供血,但是以ICA為主。這種變異導致顱內血流灌注的不對稱[10],ICA、PComA發生一系列血流動力學變化。首先血流壓力增高,尤其在動脈分叉處。同時動脈分叉處血管壁中膜缺乏肌肉層,血管壁明顯變薄[11-12]。而且,FTP患者更易伴發大腦前動脈A1段、PCA-P1段和椎動脈的變異[13]。因此,在上述多因素共同作用下導致動脈瘤的發生率增加。
部分國內外文獻,對顱內動脈瘤伴發FTP情況進行了研究報道。Horikoshi等[11]報道47%的ICA動脈瘤病人伴有FTP,且女性多見。Zada等[2]也報道ICA-PComA瘤中11%發生在PComA起始部,且伴有FTP,其中女性常見。值得注意的是,由于處理方式不同,ICA-PComA瘤需要與PComA漏斗相鑒別,后者僅是變異,不需手術處理。PComA漏斗是指PComA起自ICA處呈漏斗狀擴張,呈圓形或圓錐形,直徑<2 mm。它以ICA為基底,PComA起自其頂端[14]。國內王洪生等[15]報道的PComA瘤中,伴發FTP達56.1%。石建成等[16]也報道ICA-PComA瘤發生率在前循環優勢型(即存在FTP)中明顯高于標準均衡型。
本研究從另一個角度對FTP患者并發顱內動脈瘤的情況進行了詳細分析。本研究發現20%的FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤,且都發生在女性。2例發生在PComA與大腦中動脈、PCA移行部,2例發生在ICA顱內段,1例發生在基底動脈遠端。此外,本研究發現1例雙側FTP伴發ICA瘤患者,在此次檢查前2周發生蛛網膜下腔出血,本次檢查發生左側基底節區血腫。這證實了陳仁智等[17]的觀點,即雙側FTP患者由于血流動力學異常,導致后循環缺血、動脈瘤、高血壓等疾病的發生率明顯升高。與非FTP患者發生顱內動脈瘤比較 (本研究發生率為6.15%),FTP患者伴發顱內動脈瘤幾率明顯增高。這與葉瑩瑩等[13]報道差距較大。葉瑩瑩等發現201例FTP患者中僅2例伴發對側PComA瘤,而對照組201例非FTP患者伴發PComA瘤僅1例。分析原因為2個研究的樣本構成差異所致。葉瑩瑩等研究中有大部分(76例)為健康查體者,且平均年齡為56.2歲。本研究中全部為臨床疑診腦血管病患者,平均年齡為60.2歲。
文獻報道年齡、性別、吸煙、飲酒、高血壓、冠心病、糖尿病等都是顱內動脈瘤發生的危險因素[18-20]。本研究發現FTP也是顱內動脈瘤發生的危險因素。而且本研究也對FTP病例中伴發顱內動脈瘤與未伴發顱內動脈瘤患者的年齡、性別、吸煙史、高血壓、冠心病及糖尿病情況進行了對照分析。結果顯示60歲以上的FTP患者,在伴有高血壓、冠心病或糖尿病病史時,顱內動脈瘤發生率增高。因此,臨床醫生應該提高對這部分患者的關注。
[1]Fawcett E,Blachford JV.The Circle of Willis:an Examination of 700 Specimens[J].J Anat Physiol,1905,40(Pt 1):63-70.
[2]Zada G,Breault J,Liu CY,et al.Internal carotid artery aneurysms occurring at the origin of fetal variant posterior cerebral arteries:surgical and endovascular experience[J].Neurosurgery, 2008,63(1 Suppl 1):ONS55-61.
[3]Dimmick SJ,Faulder KC.Normal variants of the cerebral circulation at multidetector CT angiography[J].Radiographics,2009,29 (4):1027-1043.
[4]Okahara M,Kiyosue H,Mori H,et al.Anatomic variations of the cerebral arteries and their embryology:a pictorial review[J].Eur Radiol,2002,12(10):2548-2561.
[5]Krabbe-Hartkamp MJ,van der Grond J,de Leeuw FE,et al.Circle of Willis:morphologic variation on three-dimensional timeof-flight MR angiograms[J].Radiology,1998,207(1):103-111.
[6]Kovac JD,Stankovic A,Stankovic D,et al.Intracranial arterial variations:a comprehensive evaluation using CT angiography[J].Med Sci Monit,2014,20:420-427.
[7]van Raamt AF,Mali WP,van Laar PJ,et al.The fetal variant of the circle of Willis and its influence on the cerebral collateral circulation[J].Cerebrovasc Dis,2006,22(4):217-224.
[8]Padget DH.The development of the cranial arteries in the human embryo[J].Contrib Embryol,1948,32:205-261.
[9]van der Lugt A,Buter TC,Govaere F,et al.Accuracy of CT angiography in the assessment of a fetal origin of the posterior cerebral artery[J].Eur Radiol,2004,14(9):1627-1633.
[10]Wentland AL,Rowley HA,Vigen KK,et al.Fetal origin of the posterior cerebral artery produces left-right asymmetry on perfusion imaging[J].Am J Neuroradiol,2010,31(3):448-453.
[11]Horikoshi T,Akiyama I,Yamagata Z,et al.Magnetic resonance angiographic evidence of sex-linked variations in the circle of Willis and occurrence of cerebral aneurysms[J].J Neurosurg, 2002,96(4):697-703.
[12]Hillen B,Hoogstraten HW,Van Overbeeke JJ,et al.Functional anatomy of the circulus arteriosus cerebri(WillisⅡ)[J].Bull Assoc Anat(Nancy),1991,75(229):123-126.
[13]葉瑩瑩,張偉國,陳蓉,等.64層螺旋CTA顯示胚胎型大腦后動脈伴發Willis環多血管段變異的價值 [J].中國醫學影像技術,2007,23(12):1773-1776.
[14]Osborn AG.Diagnostic cerebralangiography [M].2nd ed.Philadeiphia:Lippincott Williams&Wilkins,1999:111.
[15]王洪生,徐新文,王輝,等.CT血管成像評價顱內Willis環變異與前后交通動脈動脈瘤發生的關系 [J].中國腦血管病雜志,2011,8(12):641-644.
[16]石建成,劉懷軍,趙林,等.腦血管形態學類型與腦動脈瘤形成相關性研究[J].實用放射學雜志,2010,26(10):1401-1404.
[17]陳仁智,閆宏亮,薄曉霞,等.雙側胚胎型大腦后動脈38例臨床分析[J].中國醫師進修雜志,2012,35(13):43-45.
[18]Brinjikji W,Zhu YQ,Lanzino G,et al.Risk Factors for Growth of Intracranial Aneurysms:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J].AJNR,2016,37(4):615-620.
[19]Kang HG,Kim BJ,Lee J,et al.Risk Factors Associated With the Presence of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms[J].Stroke, 2015,46(11):3093-3098.
[20]JangEW,Kim YB,ChungJ,etal.ClinicalRisk Factors Affecting Procedure-Related Major Neurological Complications in Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms[J].Yonsei Med J,2015,56 (4):987-992.
Evaluate fetal origin of posterior cerebral artery accompanied with intracranial aneurysm by CT angiography
HE Zhen,ZHANG Ji-yang,XU Meng,WAN Ye-da
(Department of Radiology,Tianjin Hospital,Tianjin 300210,China)
Objective:To observe fetal origin of posterior cerebral artery(FTP)accompanied with intracranial aneurysm by CT angiography(CTA).To investigate whether FTP is the risk factor of intracranial aneurysm.To analyze clinical datas(including age,gender,smoking history,hypertension,coronary heart disease and diabetes)of FTP patients whether accompanied with intracranial aneurysm.Methods:Three doctors reviewed intracranial CTA of 155 consecutive patients.Whether the FTP existed or not was observed firstly.Then,FTP type and intracranial aneurysms accompanied with FTP were observed carefully,including aneurysms’location,size,and subarachnoid hemorrhage.The clinical data including smoking history,hypertension, coronary heart disease and diabetes of patients with FTP were interviewed by telephone.The incidence of FTP,intracranial aneurysms accompanied with FTP and non-FTP were calculated respectively.Gender difference about FTP was analyzed by χ2test.The incidence of intracranial aneurysms(including accompanied with FTP and non-FTP)and their clinical data were analyzed by Fisher’s exact test.Binary logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate weather FTP is the risk factor of intracranial aneurysm.Results:The FTP incidence was 16.13%(25/155)in overall,12.12%(12/99)in male,23.21%(13/56)in female.There was no gender difference in FTP incidence(P=0.071).The incidence of intracranial aneurysms accompanied with FTP and non-FTP was 20%(5/25),6.15%(8/135),respectively.There was statistical difference in the incidence of intracranial aneurysms between FTP and non-FTP(P=0.038).FTP is the risk factor of intracranial aneurysm(P=0.031).There were statistical differences between intracranial aneurysms accompanied with FTP and non-FTP on gender,hypertension,coronary heart disease and diabetes(P<0.05).On the contrary,there were no statistical difference between above on age and smoking(P>0.05).Conclusions:The incidence of intracranial aneurysms about female patients with FTP is significantly higher when they suffered hypertension,coronary heart disease or diabetes.
Intracranial aneurysm;Posterior cerebral artery;Tomography,spiral computed;Angiography
R739.41;R814.42;R814.43
A
1008-1062(2016)08-0538-05
2015-11-26;
2015-12-29
何珍(1975-),女,河北安平人,副主任醫師。E-mail:hzok@163.com
萬業達,天津醫院放射科,300210。E-mail:yd_wan@sina.com

