A Payne-Rayner Type Inequality for Semilinear Elliptic Equations with Mixed Boundary Condition
SHI Fei-lin
(School of Mathematics and Computer Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China)
?
A Payne-Rayner Type Inequality for Semilinear Elliptic Equations with Mixed Boundary Condition
SHI Fei-lin
(School of Mathematics and Computer Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China)
AbstractIn this paper, a Payne-Rayner type inequality for semilinear elliptic equations with mixed boundary condition is obtained byα-symmetrization method. Moreover, some estimates for the positive solution of a class of the related semilinear elliptic problem are given.
Key wordsPayne-Rayner type inequality; semilinear elliptic equations; mixed boundary problem; Chiti comparison principle;α-symmetrization
The present paper deals with the following semilinear elliptic problem with mixed boundary value condition
(1)
where Ω?RnisaboundeddomainhavingLipschitzboundary?Ω=Γ0∪Γ1,0
The study of Payne-Rayner inequality originates from [1]. Letλ1(Ω) andψ1(x) denote the first eigenvalue and the first eigenfunction respectively of the following eigenvalue problem

(2)
In1972,PayneandRaynerprovedthefollowinginequality

(3)
withequalityifandonlyifΩisaball. (3)isalsoshortforthePayne-Raynerinequality,whichmeansthatthefirsteigenfunctionsatisfiesareverseH?ldertypeinequality.Theliteraturefollowedthispioneeringworkissowidethatitisimpossibletoreportitexhaustively.AslightlydifferentapproachhasbeensuggestedbyJobin[2]andChiti[3]whosucceededinextendingthePayne-RaynerinequalitytoanarbitrarydimensionnbymeansofSchwarzsymmetrizationmethod.WangandXia[4]provedthatthePayne-Raynerinequalityholdsincompactmini-curvedsurfacecontainedinRn.In2011,FutoshiandAkinobu[5]establishedaPayne-RaynertypeinequalityfortheRobinLaplacianproblemonarbitraryminimalsurfacesinRn. Furthermore, many extensions have been given, concerning nonlinear differential operators (for the p-Laplace operator with Dirichlet boundary conditions[6], or for Monge-Ampere operator in the plane[7]) as well as different type of boundary conditions(for the Laplace operator with Neumann boundary conditions[8]).
However, much less has been done concerning mixed boundary problem since Schwarz symmetrization method is not suitable for mixed boundary problem any longer. For Dirichlet Laplacian (2) Schwarz symmetrization method requires an application of the classical isoperimetric inequality to the level set of the first eigenfunctionψ1(x). Unfortunately, classical isoperimetric inequality only applies to closed domains but the lever set for the solution of problem (1) is not closed. These considerations suggest that one should not expect the Payne-Rayner inequality for problem (1) using Schwarz symmetrization method. It is worth pointing out that Ashbaugh and Chiacchio[9]proved the Payne-Rayner type inequality for the following linear eigenvalue problem with mixed boundary condition
bymakinguseofsymmetrizationmethod.NaturallywewouldliketogeneralizethePayne-Raynerinequalitytosemilinearellipticproblemwithmixedboundarycondition.Inthispaper,weprovedaPayne-Raynertypeinequalityforproblem(1)byadoptingαsymmetrizationmethod.
α-symmetrizationisamethodthattransformsdomainsΩhavingfinite“isoperimetricconstantrelativetoΓ1”(denotethroughoutbyQ(Γ1,Ω)intocircularconesC(α,R*)suchthat|Ω|=|C(α,R*)|.ConicalsectorplaysthesameroleastheballinSchwarzsymmetrization.
Throughoutthispaperweassumethefollowingtwoconditionshold,
(H1) Hn-1(Γ0)>0, H(n-1)(Γ1)>0, ?ΩisLipschitz,

AssumeV2(Ω) is the Hilbert space naturally i.e.
V2(Ω)={u∈H1(Ω):u=0 onΓ0},
where the scalar product is given by
〈u,v〉=∫ΩDuDvdx.
We denote by

It is well known thatμ1(Ω) can be achieved by a unique positive functionu1(x). What is more,u1(x) is a solution of problem (1) forμ=μ1(Ω).
We chooseS=C(α,r) in such a way such thatμ1(Ω)=μ1(S). Then our main result can be stated as
Theroem1Letu1(x)betheminimizerofμ1(Ω)andz1(x)betheminimizerofμ1(S).Foranyp≥q+1,thenusatisfies


AsapplicationsofTheorem1,wecandeducetheestimatesforthepositivesolutionoftherelatedsemilinearellipticproblem
(4)
Leth(x) be the positive solution of the following problem
(5)
By similar arguments in [10], the first application of Theorem 1 can be read as
Corollary 2Letw(x) be the unique solution of problem (4),h(x) be the unique solution of problem (5). Then for anyp≥q+1, we have


AnotherapplicationofTheorem1canbeestablishedas
Corollary3Letw(x)betheuniquesolutionofproblem(4)andh(x)betheuniquesolutionofproblem(5).Thenforanyp≥q+1,wehave
∫Ωwp(x)dx≤∫C(α,R*)hp(x)dx,
and

1Notation and preliminary results
WewilldenotebyAαanopensetofSn-1suchthatHn-1(Aα)=α,by∑α={tx∈Rn,x∈Aαandt>0}andby∑(α,R)thefollowing
∑(α,R)=BR∩∑α.

LetΩbeaboundeddomaininRnwithboundaryincludingtwomanifoldsΓ0andΓ1.Wedenoteby|D|theLebesguemeasureofasetDinRnanddefine(see[11, 12, 13])
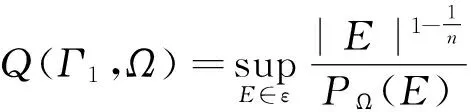
whereεdenotesthesetofallmeasurablesubsetsEofΩsuchthat?E∩Γ0doesnotcontainanysetofpositiven-1dimensionalHausdorffmeasure.IntheabovedefinitionPΩ(E)istheDeGiorgiPerameterofErelativetoΩ.Youcanseemanyexamplesin[13],whichisthen-1dimensionalHausdorffmeasureof?EΓ1intheregularcase.Generally, PΩ(E)isrepresentedby

WedenotebyC(α,R)anysphericalsectorofRnwithradiusRandsolidangleα.Moreprecisely,
C(α,R)={tx∈Rn,x∈Aαandt>0}∩B(0,R),
whereAαisasphericalcapofSn-1withHn-1(Aα)=α.
Subsequently,werecallsomenotationsandbasicfactsabouttherearrangementoffunction.LetubeameasurablefunctiondefinedinaboundeddomainofRn.
Letf:Ω→Rbeanonnegativemeasurablefunction.Thedistributionfunctionoffisdefinedas
μf(t)=|Ωt|=meas{x∈Ω:f(x)>t},t≥0.
Thedecreasingrearrangementf*offisafunctiondefinedon[0,∞)by
The increasing rearrangementf*offis a function defined on by
f*(s)=f*(|Ω|-s), fors∈(0,∞).
Finally,u#,αandu#,αrepresent the radially decreasing and increasingα-symmetrization ofurespectively and
u#,α=u*(αn|x|n),x∈Cα(Ω),
u#,α=u*(αn|x|n),x∈Cα(Ω),
whereCα(Ω)=∑(α,R*) withR*chosen such that |∑(α,R*)|=|Ω|.
There are many properties of rearrangement. Here, we only give two important properties needed in this paper.
Proposition 1[9,11]Let Ω be a bounded domain satisfying (H1) and (H2) . Then for anyubelong toV2(Ω), we have
∫Ω|Du|2dx≥∫Ca(Ω)|Du#,α|2dx.
Proposition 2[14]LetM,α,βbe real numbers such that 0<α≤βandM>0, Letf,gsatisfy the inequality

Then

3The proof of Theorem 1
In this section, we prove the Theorem 1 by symmetrization method. In order to obtain our results, we introduce the following auxiliary problem
(6)

Similarlyargumentin[16],ityieldsthefollowinglemmas.
Lemma1Letu1(x)betheminimizerofμ1(Ω).Thenthefollowinginequalityholds

(7)

InthesubsequentTheorem2,weproveaChititypecomparisonresultinthespiritofChiti’sapproach,whichconstitutesthemostimportantstepofourtheorem.
Theorem2Letu1(x)betheminimizerofμ1(Ω)andz1(x)betheminimizerofμ1(S).Thenthereexistss0∈2(0,|S|)suchthat
ProofWedefines0tobe


Ifs0=0,weset
Ifs0>0,weset
Finally,wehave
∫S|,
whichisacontradiction,asintheconclusionoftheproofofLemma2.
FromtheLemmasabove,itfollowstheproofofTheorem1.
ProofofTheorem1Since

(8)
Lets0bethepointasdefinedbefore.Fors∈[0,s0]byTheorem2wealsohave



Infact,fromTheorem2wehave

(9)
By(11)and(12)ityieldsthat

(10)
sowehave

By(13)andProposition2,wehave

i.e.
∫Ω(u1)pdx≤∫S(z1)pdxforanyp≥q+1.
Therefore

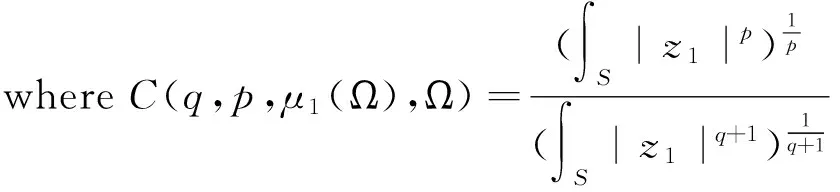
ItcompletestheproofTheorem1.
FromtheproofofTheorem1weobtain
∫Ω(u1)pdx≤∫S(z1)pdxforanyp≥q+1.
(11)
AcknowledgementsHeartfeltthanksaregiventoProfessorQiuyiDaiformanyinvaluablesuggestions.
References:
[1]PAYNELE,RAYNERME.Anisoperimetricinequalityforthefirsteigenfunctioninthefixedmembraneproblem[J].ZAngewMathPhys, 1972,23:13-15.
[2]THéRSEM,JOBINK.IsoperimetricmonotonicityandisoperimetricinequalitiesofPayne-RaynertypeforthefirsteigenfunctionoftheHelmholtzproblem[J].ZAngewMathPhys, 1981,32:25-646.
[3]CHITIG.AreverseH?derinequalityfortheeigenfunctionsoflinearsecondorderellipticoperators[J].ZAngewMathPhys, 1982,33:143-148.
[4]WANGQL,XIACY.IsoperimetricboundsforthefirsteigenvalueoftheLaplacian[J].ZAngewMathPhys, 2010,61:171-175.
[5]TAKAHASHIF,UEGAKIA.APayne-RaynertypeinequalityfortherobinproblemonarbitraryminimalsurfacesinRn[J].ResultsinMath, 2011,59:107-114.
[6]ALVINOA,FERONEV,TROMBETTIG.Onthepropertiesofsomenonlineareigenvalues[J].SIAMJMathAnal, 1998,29(2):437-445.
[7]BRANDOLINIB,TROMBETTIC.ComparisonresultsforHessianequationsviasymmetrization[J].JEurMathSoc, 2007,9(3):561-575.
[8]BRANDOLINIB,CHIACCHIOF,TROMBETTIC.SharpestimatesforeigenfunctionsofaNeumannproblem[J].CommPartialDifferEqu, 2009,34(10-12):1317-1337.
[9]ASHBAUGHMS,CHIACCHIOF.OnloweigenvaluesoftheLaplacianwithmixedboundaryconditions[J].JDifferEqu, 2011,250:2544-2566.
[10]胡華香,戴求億,賀仁初.半線性橢圓方程正解的等周不等式[J].數學年刊, 2013,34A(1):87-100.
[11]LIONS P L, PACELLA F, TRICARICO M. Best constants in Sobolev inequalities for functions vanishing on some part of the boundary and related questions[J]. Indiana Univ Math J, 1988,37:301-324.
[12]LIONS P L, PACELLA F. Isoperimetric inequalities for convex cones[J]. Proc Amer Math Soc, 1990,109:477-485.
[13]PACELLA F, TRICARICO M. Symmetrzation for a class of elliptic equations with mixed boundary conditions[J]. Atti Sem Mat Fis Univ Modena,1985-1986,XXXIV:75-94.
[14]HARDY G H, LITTLEWOOD J E, PLYA G. Some simple inequalities satised by convex functions[J]. Mess Math, 1929,58:152.
[15]BREZIS KH, KAMIN S. Sublinear elliptic equations in Rn[J]. Manage Math, 1992, 74:87-106.
[16]TALENTI G. Elliptic equations and rearrangements[J]. Ann Scuola Norm Sup Pisa, 1976,3:697-718.
[17]FLEMING H, RISHEL R. An integral formula for local gradient variation[J]. Arch Math, 1960,2:218-222.
(編輯HWJ)
DOI:10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2016.04.012
收稿日期:2015-04-17
基金項目:國家自然科學 項目(11271120);湖南省研究生創新 項目(CX2011B198)
*通訊作者,E-mail:shifeilin1116@163.com
中圖分類號O175.25
文獻標識碼A
文章編號1000-2537(2016)04-0072-06
帶混合邊值條件的半線性橢圓方程的Payne-Rayner型不等式
石飛林*
(湖南師范大學數學與計算機科學學院,中國 長沙410081 )
摘要利用α-對稱化方法證明了帶混合邊界條件的半線性橢圓方程的Raye-Rayner型不等式,并推出了相關線性橢圓方程混合邊界條件正解的一些重要估計.
關鍵詞Payne-Rayner型不等式;半線性橢圓方程;混合邊值問題;Chiti比較原理;α對稱

