姜黃素抑制哮喘大鼠氣道平滑肌細胞TGFβ1表達的研究
楊能力 梁亞峰 李昌崇 張維溪▲ 潘國權.溫州醫科大學附屬第一醫院麻醉科,浙江溫州 5000;.溫州醫科大學附屬第二醫院育英兒童醫院兒童ICU,浙江溫州5000;.溫州醫科大學附屬育英兒童醫院兒童呼吸科,浙江溫州 5000
姜黃素抑制哮喘大鼠氣道平滑肌細胞TGFβ1表達的研究
楊能力1梁亞峰2李昌崇3張維溪3▲潘國權2
1.溫州醫科大學附屬第一醫院麻醉科,浙江溫州325000;2.溫州醫科大學附屬第二醫院育英兒童醫院兒童ICU,浙江溫州325000;3.溫州醫科大學附屬育英兒童醫院兒童呼吸科,浙江溫州325000
[摘要]目的 觀察姜黃素對哮喘大鼠氣道平滑肌細胞(ASMC)增殖及TGFβ1表達的影響。方法 將24只雄性SD大鼠分為對照組、哮喘組和姜黃素組。以卵清白蛋白(OVA)致敏激發建立哮喘大鼠氣道重塑模型,圖像分析技術測定支氣管壁厚度(Wat)和平滑肌厚度(Wam),免疫組織化學法(IHC)測定肺組織 TGFβ1蛋白表達。酶聯免疫吸附法(ELISA)測定細胞培養液中TGFβ1含量,實時定量 PCR(Real-time PCR)檢測ASMC中TGFβ1mRNA表達,CCK-8分析ASMC增殖程度。結果 姜黃素組與哮喘組相比,Wat及Wam厚度減少(P<0.01),仍高于對照組(P<0.01);IHC顯示:姜黃素組肺組織中 TGFβ1蛋白表達與哮喘組比較明顯減少(P<0.01),仍高于對照組(P<0.01)。姜黃素組大鼠ASMC中TGFβ1和TGFβ1mRNA表達均降低,與對照組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.01);姜黃素組ASMC增殖明顯受到抑制(P<0.01)。結論 姜黃素能抑制哮喘大鼠ASMC增殖,其機制與降低TGFβ1的表達有關。
[關鍵詞]轉化生長因子β1;大鼠;哮喘;氣道重塑;姜黃素
支氣管哮喘(簡稱哮喘)(bronchial asthma)的病理特征主要包括氣道炎癥和氣道重塑。氣道的結構細胞參與了氣道重塑,其中平滑肌細胞(airway smooth muscle cell,ASMC)發生表型改變[1],參與氣道炎癥的進程,對哮喘氣道重塑發揮重要的作用[2]。轉換生長因子(transforming growth factor,TGF)β是一類生物學功能復雜的細胞因子,其中TGFβ1具有促進平滑肌細胞的分化、生長與增殖,肺纖維化等[3]多種生物學效應。由于姜黃素在抗纖維化、抗炎等方面都發揮顯著作用,近年來引起了越來越多學者的關注,尤其在哮喘方面的研究。姜黃素既往的研究主要以體內干預為主,但其對特定氣道結構細胞培養水平如何發揮抗炎、抗纖維化的作用機制尚未闡明。本研究通過體外培養平滑肌細胞,探討姜黃素對哮喘大鼠ASMC增殖及TGFβ1表達的影響,揭示姜黃素抑制哮喘氣道重塑中ASMC增殖的機制,為其防治哮喘提供科學的實驗依據。
1 材料與方法
1.1實驗動物
4~6周齡SPF級雄性Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠24只,體質量(100~120 g),購自上海斯萊克實驗動物有限責任公司,動物許可證號:SCXK(滬)2008-003。1.2主要藥品與試劑
姜黃素、卵清蛋白(OVA)購自美國sigma公司。TGFβ1小鼠抗大鼠單克隆抗體采購于美國Abcam公司,檢測TGFβ1蛋白含量的ELISA試劑盒采購于美國R&D公司;所有內參及TGFβ1引物委托上海生物工程技術有限公司合成。CCK-8試劑盒購自日本同仁公司。
1.3大鼠哮喘模型的復制[4]及給藥
24只SD大鼠飼養于SPF級動物中心,按照數字表法分成對照組、哮喘組和姜黃素組,每組8只。實驗包括致敏與激發兩部分,共10周。哮喘組大鼠分別在第1天、第8天腹腔注射1.5 mL OVA/Al(OH)3混合液[內含OVA 1 mg和Al(OH)3100 mg]進行致敏,對照組使用生理鹽水替代。在第15天開始霧化吸入1% OVA,隔天1次,每次30 min進行激發。姜黃素組在激發前30 min用姜黃素(200 mg/kg)灌胃,連續8周。對照組、哮喘組使用0.5%的羧甲基纖維素鈉液代替姜黃素灌胃。
1.4動物處理及指標檢測
末次霧化吸入12 h內,10%水合氯醛(400 mg/kg)腹腔麻醉,剪開胸腔并分離肺組織,切取右肺相同部位肺組織(肺門上段),固定、包埋及切片,使用HE染色進行病理觀察。
1.4.1支氣管管壁厚度和平滑肌厚度測量選擇直徑1000~1500 μm支氣管用于檢測支氣管壁厚度及平滑肌厚度,每只大鼠選3只。通過彩色醫學圖像分析技術分別測定支氣管的總面積(total area of the bronchial,At)和管腔面積(area of tracheal cavity,Ac)、基底膜周徑(Perimeter of basement membrane,Pbm),分別測量支氣管平滑肌外緣(the external edge of airway smooth muscle,Ame)及內緣(the inner edge of airway smooth muscle,AMi)包含的氣管面積。
計算公式:支氣管壁厚度(Wat)=(At-Ac)/Pbm
平滑肌厚度(Wam)=(AMe-AMi)/Pbm
1.4.2肺組織中TGFβ1含量檢測免疫組織化學法檢測肺組織TGFβ1蛋白表達,按照鏈霉菌抗生物素蛋白-過氧化酶(SP)法說明書進行。Image-pro plus 6.0圖像分析軟件進行測定,陽性蛋白水平使用平均吸光度(mean optical density,MOD)值表示。
1.5藥物干預ASMC及指標檢測
腹腔注射10%水合氯醛(400 mg/kg)將大鼠麻醉后,分離肺部組織和氣管,去除結締組織、血管,將剩余氣管、支氣管剪成1 mm左右組織塊,采用I型膠原酶及胰蛋白酶消化。實驗使用第2~5代ASMC,待細胞融合至80%時使其同步化。加入姜黃素(20 μmol/L)作用12 h收集ASMC,24 h后收集培養液。對照組中使用等量DMEM培養液作參照。實驗重復3次。
1.5.1細胞培養液中TGFβ1含量的檢測采用ELISA法檢測細胞培養液中TGFβ1含量,所有標本按照試劑盒說明書操作步驟進行。使用Bio-Tek酶標儀(U.S.A)在450 nm處測量吸光度。
1.5.2ASMC中TGFβ1mRNA表達變化 ASMC中TGF β1mRNA表達變化用Real-time PCR法檢測。分別收集各組106細胞,Trizol提取總RNA后進行反轉錄。GAPDH擴增長度為206 bp,TGFβ1為152 bp。GAPDH上游引物:AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGC,下游引物CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT;TGFβ1上游引物:ATACGCCTGAGTGGCTGTCT,下游引物TGGGACTGATCCCATTGATT。PCR主要反應條件如下:預變性溫度為95℃,90 s;變性溫度95℃,5 s;退火溫度60℃,30 s;共進行40次循環。
1.5.3ASMC的增殖檢測細胞按2.5×104/cm2的密度接種于96孔板,待細胞生長融合至80%時使其同步化于G0期。然后加入姜黃素(20 μmol/L)之后培養24 h。將預熱后的CCK-8溶液100 μL加入各個孔中,37℃孵育1 h。酶標儀450 nm處測定OD值,參比波長630 nm。以上步驟獨立實驗并重復3次。
1.6統計學方法
使用SPSS17.0統計學軟件,計量資料用均數±標準差(±s)表示。采用成組設計t檢驗進行兩組樣本均數比較;多組樣本均數比較采用單因素方差分析,采用LSD或q檢驗進行均數間兩兩比較,以P<0.05表示差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1大鼠Wat、Wam及肺組織中TGFβ1含量的變化
姜黃素組Wat及Wam與哮喘組相比明顯減少,仍高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。同樣,姜黃素組中TGFβ1含量較哮喘組明顯降低,但與對照組相比仍有升高,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01),見圖1、表1。
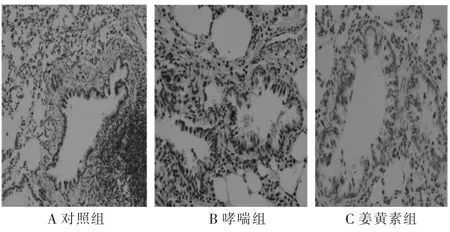
圖1 免疫組化法檢測大鼠肺組織中TGFβ1的表達(×400)
表1 大鼠Wat、Wam及肺組織TGFβ1含量的變化(±s)
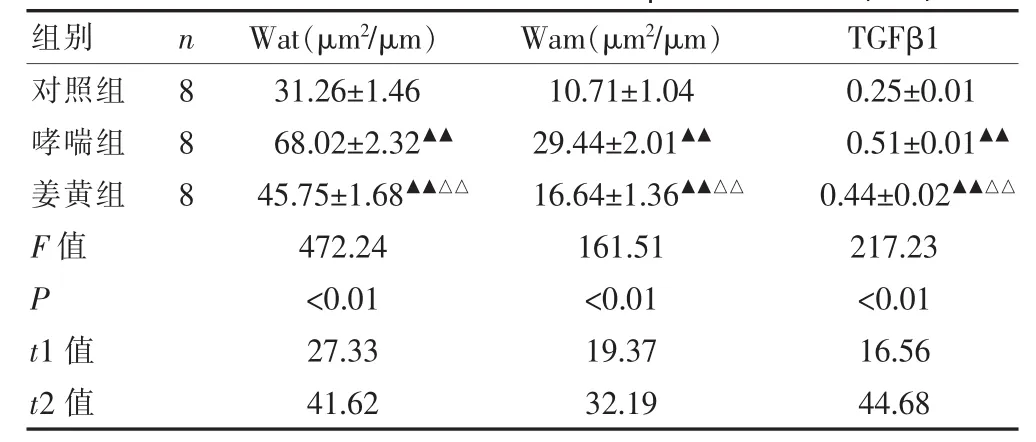
表1 大鼠Wat、Wam及肺組織TGFβ1含量的變化(±s)
注:哮喘組、姜黃素組與對照組比較,▲▲P<0.01;姜黃素組與哮喘組比較,△△P<0.01。t1表示哮喘組與對照組比較,t2表示姜黃素組與哮喘組比較
組別 n W a t (μ m2/ μ m) W a m (μ m2/ μ m) T G F β 1對照組哮喘組姜黃組F 值P t 1 值t 2 值8 8 8 3 1 . 2 6 ± 1 . 4 6 6 8 . 0 2 ± 2 . 3 2▲▲4 5 . 7 5 ± 1 . 6 8▲▲△△4 7 2 . 2 4 <0 . 0 1 2 7 . 3 3 4 1 . 6 2 1 0 . 7 1 ± 1 . 0 4 2 9 . 4 4 ± 2 . 0 1▲▲1 6 . 6 4 ± 1 . 3 6▲▲△△1 6 1 . 5 1 <0 . 0 1 1 9 . 3 7 3 2 . 1 9 0 . 2 5 ± 0 . 0 1 0 . 5 1 ± 0 . 0 1▲▲0 . 4 4 ± 0 . 0 2▲▲△△2 1 7 . 2 3 <0 . 0 1 1 6 . 5 6 4 4 . 6 8
2.2姜黃素對哮喘大鼠ASMC的TGFβ1表達影響及增殖調控
與對照組比較,姜黃素組ASMC中TGFβ1mRNA表達及ASMC培養上清液中TGFβ1蛋白含量均明顯減少,差異存在高度統計學意義(P<0.01)。在細胞增殖檢測中,姜黃素組ASMC增殖度較對照組明顯受到抑制(P<0.01)。見表2。
3 討論
氣道重塑是哮喘防治中最棘手的問題之一,其特征包括氣道壁增厚、平滑肌增生、上皮下纖維化等[5,6]。TGFβ1具有調節多種細胞生長和分化等功能,在調控哮喘氣道重塑中發揮重要作用,對氣道壁增厚及纖維化的形成有直接影響[7,8]。
表2 姜黃素對ASMC中TGFβ1mRNA和蛋白表達的影響(±s)
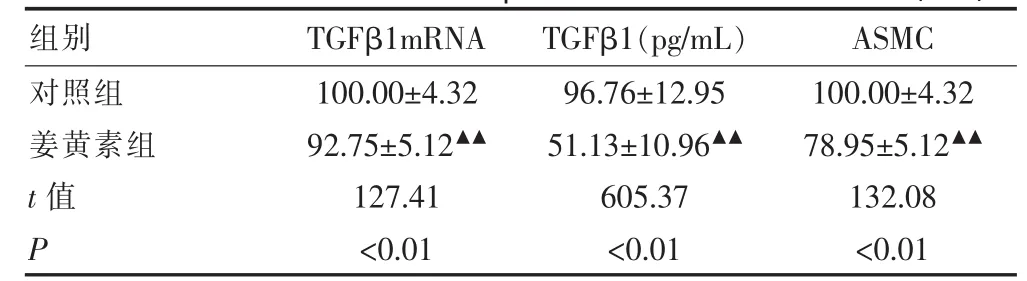
表2 姜黃素對ASMC中TGFβ1mRNA和蛋白表達的影響(±s)
注:與對照組比較,▲▲P<0.01
組別 T G F β 1 m R N A T G F β 1 (p g / m L) A S M C對照組姜黃素組t值 P 1 0 0 . 0 0 ± 4 . 3 2 9 2 . 7 5 ± 5 . 1 2▲▲1 2 7 . 4 1 <0 . 0 1 9 6 . 7 6 ± 1 2 . 9 5 5 1 . 1 3 ± 1 0 . 9 6▲▲6 0 5 . 3 7 <0 . 0 1 1 0 0 . 0 0 ± 4 . 3 2 7 8 . 9 5 ± 5 . 1 2▲▲1 3 2 . 0 8 <0 . 0 1
TGFβ1是由112個氨基酸組成的雙鏈多肽,其來源廣泛。哮喘時氣道炎癥細胞(肺泡巨噬細胞、嗜酸性粒細胞)及氣道結構細胞(上皮細胞、成纖維細胞及平滑肌細胞)均可表達TGFβ1。TGFβ1的遺傳多態性與哮喘有關,嚴重的哮喘患者有更高的血清TGFβ1水平[9]。TGFβ1可以促進ASMC、成纖維細胞的增殖[10],引起支氣管下層增厚與膠原沉積,最終導致哮喘患者支氣管狹窄。TGFβ1/Smad信號通路是哮喘氣道重塑形成的一條重要信號通路,它參與調控細胞的增殖[11]、轉化、合成、分泌和凋亡。在哮喘大鼠氣道重塑中,TGFβ1、Smad2、Smad3表達增多,Smad6、Smad7表達減少,提示TGFβ1通過Smad通路參與哮喘氣道重塑過程[12]。將TGFβ1加入大鼠氣道平滑肌細胞培養液中,可以刺激平滑肌細胞增殖,其增殖作用通過阻斷鈣離子通道被部分抑制[13]。Lee等[14]證實,TGFβ1信號通路在哮喘大鼠氣道重塑中發揮重要作用,通過調控TGFβ1的表達,可以改善氣道重塑,尤其減少平滑肌厚度。
姜黃素是從姜黃屬植物根莖中提取的一種植物多酚,也是姜黃發揮藥理作用主要活性成分。姜黃素除了傳統的作用外,還在抗炎、抗氧化、抗纖維化等方面均有顯著作用[15,16]。因此,姜黃素成為防治許多炎癥性疾病,尤其在呼吸系統疾病中作用的研究熱點[17]。姜黃素降低哮喘小鼠BALF中炎癥細胞百分比,減少嗜酸細胞浸潤,改善小鼠氣道炎癥,減少黏液產生。姜黃素通過抑制α-平滑肌肌動蛋白或增強IFN-γ的表達,減輕哮喘炎癥、延緩氣道重塑。除抗炎作用外,姜黃素對細胞因子的調控作用也可以抑制細胞增殖、細胞間質的合成等作用。姜黃素抑制上皮增生、平滑肌層增厚,減少氣道周圍膠原纖維沉積,下調TGFβ1的表達。Gaedeke等[18]研究發現,姜黃素能抑制腎成纖維細胞TGFβ1及受體信號通路的表達,實現其抗纖維化作用。在博來霉素誘導的肺纖維化實驗中,姜黃素可以減少TGFβ1的表達,抑制肺纖維化進展,且與糖皮質激素有相似的作用[19]。Hu Y等[20]研究發現,TGFβ1刺激HK-2細胞增殖的作用可以被姜黃素所抑制,其機制與下調TGFβ/Smad信號通路有關。然而,目前姜黃素對哮喘的研究主要停留在動物模型基礎上。本實驗通過姜黃素體內干預哮喘大鼠,發現大鼠Wat及Wam得到明顯緩解,同時肺組織中TGFβ1含量降低,但未降至正常水平。課題組進一步通過體外培養ASMCs,發現姜黃素可以減少ASMC合成分泌TGFβ1,抑制ASMC的增殖程度。
綜上所述,姜黃素可以減輕氣道重塑,可能通過減少TGFβ1合成分泌以及抑制ASMC的增殖發揮作用,但其更深層次的調控機制尚有待進一步研究。
[參考文獻]
[1]Liu F,Fang H,Tang BQ,et al.Phenotype change of airway smooth musle cell in brochial asthma rats and the intervention of zhichuan capsule on it[J].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi,2010,30(9):982-985.
[2]Solway J,Irvin CG.Airway smooth muscle as a target for asthma therapy[J].N Engl J Med,2007,356(13):1367-1369.
[3]Mirzamani MS,Nourani MR,Imani Fooladi AA,et al.Increased expression of transforming growth factor-β and receptors in primary human airway fibroblast-ts from chemical inhalation patients[J].Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol,2013,12(2):144-152.
[4]Guan XJ,Zhang WX,Li CC,et al.The role of external signal regulated kinase and transforming growth factor β1 in asthma airway remodeling and regulation of glucocorticoids[J].Natl Med J China,2007,87(25):1767-1772.
[5]Chiappara G,Gagliardo R,Siena A,et al.Airway remodelling in the pathogenesis of asthma[J].Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunl,2005,1(1):85-93.
[6]Fedorov IA,Wilson SJ,Davies DE,et al.Epithelial stress and structural remodelling in childhood asthma[J].Thorax,2005,60(5):389-394.
[7]Mabalirajan U,Aich J,Agrawal A,et al.Mepacrine inhibits subepithelial fibrosis by reducing the expression of arginase and TGF-beta1 in an extended subacute mouse model of allergic asthma[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2009,297(3):411-419.
[8]Halwani R,Al-Muhsen S,Al-Jahdali H,et al.Role of transforming growth factor-beta in airway remodeling in asthma[J].Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol,2011,44(2):127-133.
[9]Chiang CH,Chuang CH,Liu SL,et al.Genetic polymorphism of transforming growth factor β1 and tumor necrosis factor α is associated with asthma and modulates the severity of asthma[J].Respir Care,2013,58(8):1343-1350.
[10]Gao Y,Xu X,Ding K,et al.Rapamycin inhibits transforming growth factor β1-induced fibrogenesis in primary human lung fibroblasts[J].Yonsei Med J,2013,54(2):437-444.
[11]Zhang WX,Liang YF,Wang XM,et al.Urotensin upregulates transforming growth factor-β1 expression of asthma airway through ERK-dependent pathway[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2012,364(1-2):291-298.
[12]張維溪,戴歡,賀孝良,等.糖皮質激素調控哮喘大鼠氣道重塑中TGFβ/Smad信號通路的研究[J].中國藥理學通報,2009,25(9):1142-1146.
[13]Gao YD,Zheng JW,Li P,et al.Store-operated Ca2+entry is involved in transforming growth factor-β1 facilitated proliferation of rat airway smooth muscle cells[J].J Asthma,2013,50(5):439-448.
[14]Lee SY,Kim JS,Lee JM,et al.Inhaled corticosteroid prevents the thickening of airway smooth muscle in murine model of chronic asthma[J].Pulm Pharmacol Ther,2008,21(1):14-19.
[15]Kumari A1,Tyagi N,Dash D,et al.Intranasal curcumin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice[J].Inflammation,2015,38(3):1103-1112.
[16]Xu F,Lin SH,Yang YZ,et al.The effect of curcumin on sepsis-induced acute lung injury in a rat model through the inhibition of the TGF-β1/SMAD3 pathway[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2013,16(1):1-6.
[17]Hassani S,Sepand MR,Jafari A,et al.Protective effects of curcumin and vitamin E against chlorpyrifos-induced lung oxidative damage[J].Hum ExpToxicol,2015,34(6):668-676.
[18]Gaedeke J,Noble NA,Border WA.Curcumin blocks multiple sites of the TGF-beta signaling cascade inrenal cells[J].Kidney Int,2004,66(1):112-120.
[19]Min Xu,Bin Deng,Yeuk-lung Chow,et al.Effects of curcumin in treatment of Experimental pulmonary fibrosis:Acomparison with hydrocortisone[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2007,112(2):292-299.
[20]Hu Y,Liang H,Du Y,et al.Curcumin inhibits transforming growth factor-beta activity via inhibition of Smad signaling in HK-2 cells[J].Am JNephrol,2010,31(4):332-41.
▲通訊作者
[中圖分類號]R285.5
[文獻標識碼]A
[文章編號]1673-9701(2016)19-0034-04
收稿日期:(2016-03-18)
[基金項目]浙江省溫州市科技局科技計劃項目(Y2013 0233);浙江省自然科學基金(LY13H150005)
Effects of curcumin on the airway smooth musle cell by inhibiting TGFβ1 in asthmatic rats
YANG Nengli1LIANG Yafeng2LI Changchong3ZHANG Weixi3PAN Guoquan2
1.Department of Anesthesiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University,Wenzhou325000,China;2.Department of Pediatric Intensive Care Unit,Yuying Children's Hospital,the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University,Wenzhou325000,China;3.Department of Children's Respiratory Disease,Yuying Children's Hospital,the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University,Wenzhou325000,China
[Abstract]Objective To study the role of curcumin on proliferation mechanism of airway smooth musle cell(ASMC)and TGFβ1 expression in asthmatic rats.Methods A total of 24 Sprague-Dawley(SD)rats were sensitized and challenged by OVA to establish asthmatic model were divided into three groups with 8 rats in each group.The total bronchial wall thickness(Wat)and the airway smooth musle thickness(Wam)were measured by image analysis system.The TGFβ1 expressions were determined by immunohistochemistry.Vitro experiments were conducted to determine the direct effect of curcumin on TGFβ1 expression by ASMC.Real-time PCR was employed to detect the expression of TGFβ1 mRNA levels.TGFβ1 concentrations were determined by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA).Cell Counting Kit-8(CCK-8)was used to detect ASMC proliferation.Results Wat and Wam of curcumin group were significantly thiner than asthma group(P<0.01);but those were significantly thicker than control group(P<0.01).The TGFβ1 expressions in the curcumin group was significantly lower than those of the asthmatic group(P<0.01);but they were higher than the control group(P<0.01).Compared to control group,curcumin decreased the protein expressions and mRNA expressions of TGFβ1 of ASMC(P<0.01),inhibited ASMC proliferation(P<0.01).Conclusion Curcumin could inhibit ASMC proliferation in asthmatic rats,which is associated withthe decrease of TGFβ1.
[Key words]TGFβ1;Rat;Asthma;Airway remodeling;Curcumin

