環丙沙星對豚鼠心電圖和乳頭肌動作電位的影響
劉芳,李宜培,師瑞紅,陳文超
(河南醫學高等專科學校,鄭州451191)
?
環丙沙星對豚鼠心電圖和乳頭肌動作電位的影響
劉芳,李宜培,師瑞紅,陳文超
(河南醫學高等專科學校,鄭州451191)
目的 觀察環丙沙星對豚鼠心電圖和乳頭肌動作電位的影響。方法 選擇豚鼠42只,隨機分為司帕沙星低、中、高劑量組,環丙沙星低、中、高劑量組及對照組,每組6只。司帕沙星低、中、高劑量組分別腹腔注射50、100、200 mg/kg的司帕沙星,環丙沙星低、中、高劑量組分別腹腔注射50、100、200 mg/kg的環丙沙星,對照組腹腔注射等量生理鹽水。采用RM-6240軟件記錄各組給藥前及給藥5、10、30 min時Ⅱ導聯心電圖,收集心電圖各參數,包括HR、P波高度、PR間期、R波高度、QRS波寬度、QT間期和T波高度。另取豚鼠18只,隨機分為司帕沙星組、環丙沙星組、對照組,每組6只,分別剪下右心室乳頭肌后灌流。對照組采用臺氏液恒溫、恒速灌流;司帕沙星組臺式液+司帕沙星灌流,采用累積濃度給藥法依次使藥物終濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L;環丙沙星組臺式液+環丙沙星灌流,采用累積濃度給藥法依次使藥物終濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L。采用RM-6240軟件記錄各組灌流15 min時的靜息電位(RP)、動作電位幅值(APA)、動作電位復極至50%的時程(APD50)及動作電位復極至90%的時程(APD90)。結果 腹腔注射100 mg/kg司帕沙星10、30 min時,QT間期均較給藥前及對照組延長(P均<0.01);腹腔注射200 mg/kg司帕沙星5、10、30 min時,QT間期均較給藥前及對照組延長(P均<0.01)。腹腔注射200 mg/kg環丙沙星10、30 min時,QT間期均較給藥前及對照組延長(P均<0.05)。環丙沙星中、高劑量組延長QT間期的作用均小于司帕沙星中、高劑量組(P<0.05或<0.01)。灌流液中司帕沙星濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L時,乳頭肌APD50、APD90與對照組比較均明顯延長(P均<0.01)。灌流液中環丙沙星濃度為100 μmol/L時,其乳頭肌APD90較對照組明顯延長(P<0.01)。100 μmol/L環丙沙星延長APD50、APD90的作用均小于100 μmol/L司帕沙星(P均<0.01)。結論 大劑量環丙沙星可引起豚鼠乳頭肌動作電位時程延長,明顯延長QT間期,具有潛在的心臟毒性。
環丙沙星;QT間期;乳頭肌;動作電位;豚鼠
環丙沙星是第三代人工合成喹諾酮類抗菌藥物,廣泛用于各種細菌感染性疾病[1],但近年來其不良反應的報道逐漸增多[2,3]。有報道認為,雖然環丙沙星導致心臟毒性的概率較低,但發病突然、猝死率高[4~6]。目前國內關于環丙沙星對心肌電生理方面的影響鮮見報道。2014年3~12月,本研究觀察了環丙沙星的心臟毒性,旨在為其臨床應用的安全性提供參考。
1 材料與方法
1.1 材料 健康成年豚鼠60只,雌雄不拘,體質量300~400 g,購自河南康達實驗動物有限公司,動物許可證號:SCXK(豫)2011-0001。環丙沙星、司帕沙星,購自大連美侖生物技術有限公司,用1 mol/L的NaOH配成10 mmol/L的母液,用時稀釋成需要濃度。烏拉坦,天津市光復化工精細研究所。臺氏液成分(mmol/L):NaCl 140、KCl 5.4、CaCl22、MgCl21、HEPES 10、Glucose 10,使用前用1 mol/L的NaOH調整pH至7.4。
1.2 豚鼠心電圖參數檢測 ①取42只豚鼠隨機分為對照組,司帕沙星低、中、高劑量組及環丙沙星低、中、高劑量組,每組6只。各組均腹腔注射20%烏拉坦(5 mL/kg)麻醉,仰臥位固定。將針形電極插入豚鼠四肢皮下,司帕沙星低、中、高劑量組分別腹腔注射50、100、200 mg/kg的司帕沙星,環丙沙星低、中、高劑量組分別腹腔注射50、100、200 mg/kg的環丙沙星,對照組腹腔注射等量生理鹽水。采用RM-6240軟件記錄各組給藥前及給藥5、10、30 min時Ⅱ導聯心電圖,收集各組心電圖各參數,包括HR、P波高度、PR間期、R波高度、QRS波寬度、QT間期和T波高度。
1.3 豚鼠乳頭肌動作電位參數檢測 取豚鼠18只,隨機分為對照組、司帕沙星組和環丙沙星組,每組6只。開胸取出各組心臟,剪下右心室乳頭肌,將乳頭肌置于肌槽底部,不銹鋼針固定。對照組乳頭肌臺氏液恒溫(35.5 ℃±0.5 ℃)、恒速(4 mL/min)灌流;司帕沙星組臺式液+司帕沙星灌流,采用累積濃度給藥法依次使藥物終濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L;環丙沙星組臺式液+環丙沙星灌流,采用累積濃度給藥法依次使藥物終濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L。采用刺激頻率為2 Hz、波寬為1 ms、強度為1.5倍閾刺激的方波信號,雙極起搏電極以場刺激驅動標本,產生動作電位。采用RM-6240軟件記錄各組灌流15 min時的靜息電位(RP)、動作電位幅值(APA)、動作電位復極至50%的時程(APD50)及動作電位復極至90%的時程(APD90)。
2 結果
2.1 各組心電圖參數比較 腹腔注射不同濃度司帕沙星時,心電圖各參數中僅QT間期出現延長。腹腔注射100 mg/kg司帕沙星10、30 min時,QT間期均較給藥前及對照組延長(P均<0.01);腹腔注射200 mg/kg司帕沙星5、10、30 min時,QT間期均較給藥前及對照組延長(P均<0.01),且豚鼠出現嘔吐、抽搐等中樞中毒癥狀,注射10 min時有2只豚鼠死亡,注射30 min時有4只豚鼠死亡。腹腔注射不同濃度環丙沙星時,心電圖各指標中亦僅QT間期出現延長。腹腔注射200 mg/kg環丙沙星10、30 min時,QT間期均較給藥前及對照組延長(P均<0.05),豚鼠出現煩躁、嘔吐、抽搐等中樞中毒癥狀,或出現室性心律失常,但無死亡。環丙沙星中、高劑量組QT間期短于司帕沙星中、高劑量組(P<0.05或P<0.01)。具體結果見表1及插頁Ⅰ圖3、4。

表1 各組心電圖QT間期比較
注:與同組給藥前及對照組同期比較,*P<0.05,△P<0.01;與司帕沙星中劑量組比較,#P<0.05;與司帕沙星高劑量組比較,▲P<0.01。
2.2 各組乳頭肌動作電位參數比較 灌流液中司帕沙星濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L時,豚鼠乳頭肌APD50和APD90與對照組比較均明顯延長(P均<0.01)。灌流液中環丙沙星濃度為100 μmol/L時,其乳頭肌APD90較對照組明顯延長(P<0.01)。100 μmol/L環丙沙星延長APD50和APD90的作用均小于100 μmol/L司帕沙星(P均<0.01)。見表2及圖1、2。
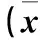
表2 各組乳頭肌動作電位參數比較±s)
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.01;與100 μmol/L司帕沙星比較,△P<0.05。

注:a為加藥前;b、c 為10、100 μmol/L司帕沙星作用15 min。
圖1 灌流液中加入司帕沙星時豚鼠乳頭肌動作電位時程(BCL=1 000 ms)
3 討論
近年來隨著環丙沙星的廣泛應用,其不良反應報道也明顯增多。環丙沙星的不良反應主要包括過敏反應、肝腎功能損害、中樞神經系統損害等。丁仲如等[5]報道,索他洛爾與環丙沙星聯合應用可引起尖端扭轉型室性心動過速;欒福起等[4]報道,環丙沙星可致小兒室性心動過速。但目前鮮見其對心肌電生理方面不良反應的報道。

注:a為加藥前;b、c 為10、100 μmol/L環丙沙星作用15 min。
圖2 灌流液中加入環丙沙星時豚鼠乳頭肌動作電位時程(BCL=1 000 ms)
司帕沙星是最早報道可誘發QT間期延長及致死性心律失常的氟喹諾酮類藥物。喹諾酮類藥物的臨床推薦使用劑量為200~400 mg/d[7],根據動物與人體表面積的折算[8],本研究選擇50、100、200 mg/kg司帕沙星和環丙沙星注射于豚鼠腹腔,結果顯示,腹腔注射50、100 mg/kg環丙沙星時,豚鼠QT間期與用藥前比較差異無統計學意義;注射100 mg/kg司帕沙星后QT間期比用藥前延長;腹腔注射200 mg/kg環丙沙星或司帕沙星,豚鼠心電圖QT間期均較用藥前明顯延長,但環丙沙星延長QT間期的作用小于司帕沙星。心電圖QT間期是心室肌去極化和復極化的總時間,其中去極化時間占20%~25%,對于QRS波時限正常的QT間期,主要反映心室肌復極化過程[9]。上述結果提示,50、100 mg/kg環丙沙星臨床應用較安全,200 mg/kg環丙沙星有引起QT間期延長而致心律失常的風險,與其他臨床報道[10~12]結果一致。
本研究對豚鼠右心室乳頭肌給予含累積濃度為1、10、100 μmol/L環丙沙星或司帕沙星的臺式液灌流, 結果僅100 μmol/L環丙沙星可延長APD90, 其余各濃度環丙沙星對RP、APA、APD50影響均較小;司帕沙星各濃度組對APD50和APD90均有延長作用;且100 μmol/L環丙沙星比100 μmol/L司帕沙星延長心室肌APD90的作用弱。提示1、10 μmol/L環丙沙星對乳頭肌動作電位時程影響較小,僅在100 μmol/L時才具有延長APD90的作用。Hagiwara等[13]研究發現,100 μmol/L的司帕沙星、加替沙星、格帕沙星、莫西沙星分別使動作電位時間延長41%、31%、24%、25%,而100 μmol/L左氧氟沙星、曲伐沙星、環丙沙星、吉米沙星不延長或極少延長動作電位時間,表明各種氟喹諾酮類抗生素使QT間期延長程度不同[14,15]。心室肌細胞的復極化過程非常復雜,包括Na+內流、K+外流、Ca2+內流等離子流動。在生理情況下,心肌細胞APA取決于Na+最大內流量,任何影響Na+流動的因素均可影響APA。心肌細胞動作電位復極2期離子流為L型鈣電流(ICa-L)和延遲整流鉀電流(Ik),復極3期的離子流主要為Ik。任何原因引起的ICa-L增強或Ik減弱均可使APD50延長,Ik減弱可使APD90延長。在本實驗中,環丙沙星可延長豚鼠乳頭肌的APD90,司帕沙星對APD50和APD90均有延長作用,提示這兩種藥物可影響復極化2期和3期的離子流,但目前尚未發現氟喹諾酮類抗菌藥影響ICa的報道,推測它們可能是通過抑制Ik而延長動作電位時程,但其具體機制還需進一步研究證實。本研究觀察到50、100、200 mg/kg環丙沙星對RP、APA均無明顯影響,提示環丙沙星對心室肌細胞的Na+通道無明顯影響。
綜上所述,環丙沙星在治療劑量下臨床應用較安全,但大劑量應用時可延長心室肌動作電位時程,有引起QT間期延長而致心律失常的風險。臨床對QT間期延長、心動過緩、低鉀血癥、老年患者以及同時應用其他可能影響QT間期藥物的患者應慎用或禁用環丙沙星等氟喹諾酮類藥物[16]。
[1] 張俊,李林虎,劉明亮.與氟喹諾酮類抗菌藥治療相關的風險[J].國外醫藥抗生素分冊,2014,35(6):250-254.
[2] 溫愛萍,賈國強.101例環丙沙星不良反應報告回顧性分析[J].中國藥物應用與監測,2014,11(1):34-37.
[3] 孟慶純.環丙沙星的臨床應用及不良反應分析研究[J].中國衛生標準管理,2015,6(17):97-98.
[4] 欒福起,梁爽,欒香梅.環丙沙星致小兒室性心動過速1 例[J].中華婦幼臨床醫學雜志,2006,2(4):222.
[5] 丁仲如,秦永文,丁繼軍,等.索他洛爾與環丙沙星并用引起尖端扭轉型室性心動過速一例[J].中華心血管病雜志,2006,34(4):374.
[6] Mehrzad R, Barza M. Weighing the adverse cardiac effects of fluoroquinolones: a risk perspective [J]. J Clin Pharmacol, 2015,55(11):1198-1206.
[7] Rubinstein E, Camm J. Cardiotoxicity of fluoroquinolones [J]. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2002,49(4):593-596.
[8] 秦川.醫學實驗動物學[M].2版.北京:人民衛生出版社,2015:272.
[9] Sesti F, Abbott GW, Wei J, et al. A common polymorphism associared with antibiotic-induced cardiac arrhythmia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2000, 97(19):10613-10618.
[10] 劉小康,周黎明,李黎明,等.喹諾酮類藥物對豚鼠心電圖的影響[J].中國抗生素雜志,2004,29(7):423-425.
[11] Noel GJ, Natarajan J, Chien S, et al. Effects of tree fluoroquinolones on QT interval in healthy adults after single doses[J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2003,73(4):292-303.
[12] 賈雪冬,王碩,劉明亮.與氟喹諾酮治療相關的心血管及代謝安全性[J].國外醫藥抗生素分冊,2013,34(3):123-128.
[13] Hagiwara T, Satoh S, Kasai Y, et al. A comparative study of the fluoroquinone antibacterial agents on the action potential duration in quinea pig ventricular myocardia[J]. Jpn J Pharmacol, 2001,87(3):231-234.
[14] Holmgren CM, Abdon NJ, Bergfeldt LB, et al. Changes in medication preceding out-of-hospital cardiac arrest where resuscitation was attempted [J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2014,63(6):497-503.
[15] Briasoulis A, Agarwal V, Pierce WJ. QT prolongation and torsade de pointes induced by fluoroquinolones: infrequent side effects from commonly used medications [J]. Cardiology, 2011,120(2):103-110.
[16] Stahlmann R, Lode HM. Risks associated with the therapeutic use of fluoroquinolones [J]. Expert Opin Drug Saf, 2013,12(4):497-505.
Effects of ciprofloxacin on QT interval of electrocardiogram and cardiac action potential in papillary muscles of guinea pigs
LIUFang,LIYipei,SHIRuihong,CHENWenchao
(HenanMedicalCollege,Zhengzhou451191,China)
Objective To observe the effects of ciprofloxacin on electrocardiogram (ECG) and action potential in papillary muscles of guinea pigs, and to investigate the cardio toxicity of ciprofloxacin in order to provide a reference for the safety of clinical application. Methods A total of 42 guinea pigs were randomly divided into 7 groups, with 6 guinea pigs in each group. 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg sparfloxacin were injected intraperitoneally into guinea pigs with the low, medium and high dose groups of sparfloxacin, while the low, middle and high dose ciprofloxacin groups were intraperitoneally injected with 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg ciprofloxacin. The control group was injected intraperitoneally with equal doses of NS. Ⅱ lead ECG were recorded before and after 5, 10, and 30 minutes of intraperitoneal injection by RM-6240 software. The parameters of ECG were measured, including heart rate, P wave height, PR interval, R wave height, QRS wave width, QT interval and T wave height. A total of 18 guinea pigs were cut off the right ventricular papillary muscle and randomly divided into 3 groups, with 6 guinea pigs in each group. The control group was treated with Tyrode′s solution at constant temperature and constant speed. Sparfloxacin was added to the Tyrode′s solution in the sparfloxacin group, and the concentration of sparfloxacin was increased to 1, 10 and 100 μmol/L, respectively. Ciprofloxacin was added to the Tyrode′s solution in ciprofloxacin group, and the final concentration of drug was 1, 10 and 100 μmol/L respectively. The time of resting potential (RP), amplitude of action potential (APA), action potential duration of 50% repolarization (APD50), and action potential duration of 90% repolarization (APD90) of guinea pigs′ papillary muscles were recorded by RM-6240 software after adding drugs in 15 min. Results At 10 and 30 min after injecting 100 mg/kg sparfloxacin, the QT interval of ECG were prolonged significantly, as compared with the data before injection and that of the control group (allP<0.01). After injecting 200 mg/kg sparfloxacin 5, 10, and 30 min, the QT interval of ECG were prolonged significantly, as compared with the data before injection and the control group (allP<0.01). After injecting 200 mg/kg ciprofloxacin 10, and 30 min, the QT interval of ECG were prolonged significantly as compared with the data before injection and that of the control group (allP<0.05). Ciprofloxacin of medium and high dose groups had a lighter prolonged effect on QT interval than sparfloxacin of medium and high dose groups (P<0.05 orP<0.01). When the concentration of sparfloxacin in perfusate were 1, 10, and 100 μmol/L, the APD50and APD90were prolonged significantly as compared with that of the control group (allP<0.01). When the concentration of ciprofloxacin in perfusate was 100 μmol/L, the APD90was prolonged as compared with that of the control group (P<0.01). The effect of 100 μmol/L ciprofloxacin in prolonging APD50as well as APD90was less than that of 100 μmol/L sparfloxacin (allP<0.01). Conclusions When ciprofloxacin is in high dose, it can cause action potential duration prolong in papillary muscles of guinea pigs, as well as elongate QT interval of ECG in guinea pigs, with potential cardiac toxicity.
ciprofloxacin; QT interval; papillary muscles; action potential; guinea pigs
河南省基礎與前沿技術研究計劃項目(142300410469)。
劉芳(1976-),女,副教授,研究方向為心臟電生理。E-mail: sincerelf@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.40.007
R331.3
A
1002-266X(2016)40-0025-04
2016-05-17)

