等厚度三維單元在薄板-土動力接觸中的應用
劉文武,陸念力,胡長勝
(哈爾濱工業大學機電工程學院,黑龍江哈爾濱150001)
等厚度三維單元在薄板-土動力接觸中的應用
劉文武,陸念力,胡長勝
(哈爾濱工業大學機電工程學院,黑龍江哈爾濱150001)
針對薄板與土體的動力接觸問題,根據土體小變形和基于薄板理論,對土體和薄板分別采用一階基函數和零階基函數進行建模,建立了一種基于一階數值流形方法的等厚度三維接觸單元。采用虛位移原理和剛塑性本構模型,推導了接觸單元的剛度矩陣。通過引入阻尼單元和采用等價線性模型,建立了接觸系統的二階動力微分方程,并利用四階Runge-Kutta顯式方法編程求解得到了薄板與土體動力接觸過程中的位移與應力值。相比于Goodman單元,在系統單元數相同條件下,當接觸單元厚度為其寬度的0.06倍時,文中結果更符合試驗值。通過和原位試驗結果比較分析表明,文中建立的接觸單元不僅建模方便,而且精度更高。
薄板-土相互作用;數值流形方法;接觸單元;等厚度;原位試驗;剛度矩陣;阻尼單元;本構模型
眾所周知,薄板結構已廣泛應用于力學和土木工程等領域,薄板-土相互作用分析在各種結構基礎設計中也越來越重要,并成為近年來國內外探討的熱門問題[1-2]。薄板與土體之間接觸應力和位移的分布在其動力相互作用過程中至關重要。因此,研究薄板-土動力相互作用中的接觸關系具有非常重要的理論和工程價值。
接觸問題的非線性特征,使得解析方法難于處理應用力學中的土-結構邊值問題。有限元[3-5]和邊界元[6-8]等數值分析方法由于通用性而在接觸問題中被普遍采用,但高計算消耗是這些數值方法的共同缺點。R.E.Goodman等[9]首先提出了無厚度的接觸單元對平面問題進行仿真。苗雨等[10]提出了用改進薄層單元來解決樁與土三維接觸問題。齊良鋒等[11]提出了在樁與土界面建立接觸單元來模擬其相互間的共同作用,雷曉燕等[12]在其基礎上進行了改進,通過將節點接觸力作為基本未知量,并利用虛位移原理推導了等價接觸單元剛度矩陣。為改善接觸單元精度,Desai C S等[13]在Goodman單元基礎上提出薄層單元,考慮了厚度對接觸分析的影響。L.Gaul等[14]提出了一種片段之間的接觸單元來模擬多自由度的復雜系統。上述基于有限元等方法所建立的接觸單元,均無法在保持單元數不變的條件下增加接觸分析的精度。K.Alexander等[15-16]指出階數提高對描述接觸問題能夠帶來更高的精度。系統單元數保持不變情況下,數值流形方法由于采用有限覆蓋技術,只須提高基函數的階數則能提高求解精度,且對于擁有不規則邊界的實體進行建模更加方便[17-21]。
鑒于現有方法或建立的單元很難兼顧求解精度和計算耗費,本文提出基于一階數值流形方法的等厚度三維接觸單元。
1 接觸單元結構
在薄板-土接觸模型中建立長度和寬度分別為a和b的等厚度接觸單元如圖1所示,接觸單元的厚度為h,有1~8共八個節點。其中,節點1~4為八節點土體等參單元的表面節點,節點5~8為薄板單元的表面節點,節點9~12分別為薄板單元的中面節點。板單元每個節點有3個轉動自由度和3個移動自由度,土體等參單元每個節點具有3個移動自由度。

圖1 接觸模型和接觸單元Fig.1 Contact model and contact element
圖1中OXYZ為接觸系統全局坐標系,O1ζηξ為接觸單元和土體單元局部坐標系,O2xyz為薄板單元局部坐標系,薄板單元的厚度為2t。各個局部坐標系原點均位于相應單元的幾何中心。
2 接觸單元剛度矩陣
土體和薄板單元分別基于一階和零階數值流形方法進行建模,則土體單元每個節點位移可表示為

式中:Si采用數值流形方法中的一階基函數,具體方程表示為

式中:Ni為每個數學覆蓋的權函數,ξi、ηi和ζi為中間自由度。di={dij}(i=1,2,3,4;j=1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12),I為3×3單位矩陣。其中,
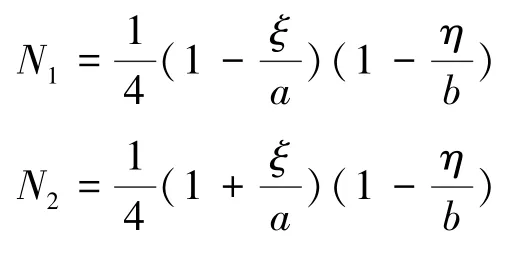

式中:ζ、η分別為單元長度和寬度方向的物理坐標。
薄板單元每個節點的位移方程表示為

式中:Sj矩陣能將薄板單元轉動自由度轉化為移動自由度,具體如方程表示為
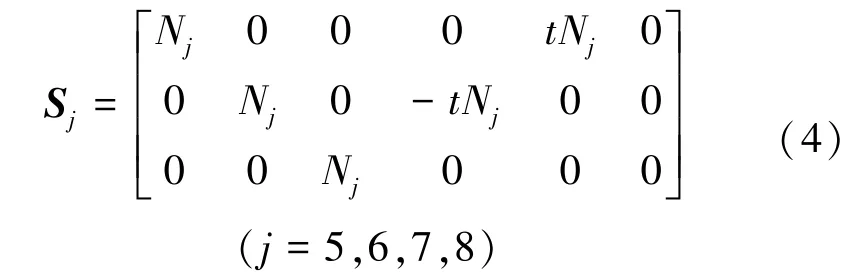
式中:Nj為接觸單元每個數學覆蓋的權函數,di={dij}(i=9,10,11,12;j=1,2,3,4,5,6)。


因此,接觸單元每個節點的相對位移方程:

式中:Se=[S1S2S3S4-S5-S6-S7-S8]為接觸單元的相對應變矩陣。
由于接觸單元厚度較小,故假設沿厚度方向的應變分量沒有變化,根據虛位移原理:

則等厚度接觸單元的剛度矩陣方程表示為

式中:h和D分別為接觸單元厚度和本構關系矩陣。

式中:W=(1+kn)(1+kt)-μ2,kn、kt分別為法向和切向剛度,取值可參考文獻[22]。E、μ和Cs分別為接觸材料的彈性模量、泊松比和引入參數。
則整個接觸系統的剛度矩陣方程表示為
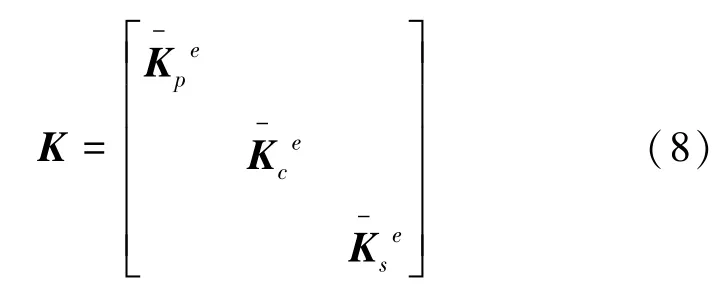
3 動力接觸模型
采用等價線性模型作為土體動力本構關系模型,則系統的動力方程為

式中:

其中,K、C和M分別為接觸單元的剛度、阻尼和質量矩陣,F(t)和U分別為動力接觸系統的力向量和位移向量,Ds和ω分別為土體的阻尼比和固有頻率。
將接觸單元阻尼矩陣組裝到系統阻尼矩陣當中,假設在短時間間隔內系統的平均加速度為定值,采用四階Runge-Kutta顯示方法求解動力方程并編寫動力接觸關系程序則可求得動力作用下,薄板與土體之間的接觸應力和接觸位移。
4 試驗驗證
在哈爾濱市王崗地區對薄板-土體動力接觸關系進行現場試驗,試驗裝置如圖2(a)所示。液壓系統壓力為12 MPa,試驗裝置的力學分析過程見文獻[23]。孔壁土體中測試點的布置如圖2(b)所示。薄板的長度為hp=0.7 m,外半徑R=0.75 m,中心角φ=50°,厚度為tp=0.01 m,彈性模量E和泊松比νp分別為2 100 GPa和0.3。試驗中樁孔的半徑R= 1.35 m,深度h=2.0 m,土體分析模型的半徑R0= 6.75 m,深度為H=10.0 m,表1列出了土體的其他參數。
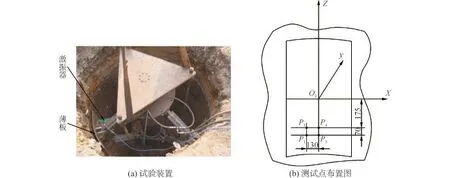
圖2 試驗裝置和測試點布置圖Fig.2 Experimental device and site layout of test points

表1 試驗區土體參數Table 1 Parameters of the soil of the test area
4.1 數值分析模型
六面體作為系統的數學覆蓋,數值模型建模過程如圖3(a)所示。由數值流形方法建模原理,得到系統的物理覆蓋如圖3(b)所示。最終系統的數值分析模型如圖4所示,其中虛線區域表示接觸單元。考慮剪切波速和土體-薄板的相互作用頻率較小,模型水平和豎直方向單元尺寸分別為50 mm和100 mm。接觸區域單元尺寸為50×50 mm2。最終薄板結構由64個流形元組成,每個流形元有4個數學覆蓋,土體由23 000個流形元組成,每個流形元有8個數學覆蓋,薄板與土體之間共有64個接觸單元。土體模型四周為粘彈性邊界,避免產生過大反射波[24],土體底部為固定約束。
4.2 動力接觸分析
在激振器作用下,由文獻[23]中的力學分析可知,F2(t)=230sin(0.1πt)。數值仿真過程中,討論厚度h分別等于0.01、0.02…0.1倍接觸單元寬度b時的本文解,并與試驗值和Goodman單元解相比較,Goodman單元法向和切向剛度按文獻[9]均取為20 MPa/m。最終P1、P3的接觸位移和P2、P4的接觸應力如圖5~8所示,其中循環時間為60 s,采樣頻率為1 Hz。
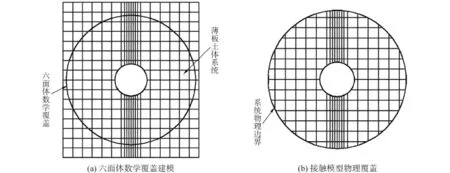
圖3 數值模型的建模過程Fig.3 Modeling process of the numerical model

圖4 數值模型軸向剖視圖Fig.4 Axial cross-sectional view of the numerical model
由圖5和圖6分析可知,在不同接觸單元的厚度下,本文解的結果相差較大。當接觸單元厚度h為其寬度b的0.06倍時,本文解相比于Goodman單元解更加接近試驗值。在整個循環時間內P1點接觸位移的本文解相對于試驗值的最小誤差為5.57%,P2點接觸應力的本文解相對于試驗值的最小誤差為5.68%。結果表明,在系統單元數相同條件下,增加覆蓋函數的階次能夠獲得更高的求解精度。

圖5 測試點P1的接觸位移Fig.5 Contact displacement of point P1

圖6 測試點P2的接觸應力Fig.6 Contact stress of point P2

圖7 測試點P3的接觸位移Fig.7 Contact displacement of point P3

圖8 測試點P4的接觸應力Fig.8 Contact stress of point P4
由圖7和圖8分析可知,不同接觸單元的厚度下,本文解的值也存在較大差異。同樣當接觸單元厚度為其寬度的0.06倍時,本文解相比于Goodman單元解更加接近試驗值。試驗過程中激振器將激振力傳遞給連桿,由于測試點P3和P4位于薄板軸向中間線上,在軸向連桿組的共同作用下,P3點的接觸位移和P4點的接觸應力都將產生拍振。在整個循環時間內P3點接觸位移的本文解相對于試驗值的最小誤差為6.58%,P4點接觸應力的本文解相對于試驗值的最小誤差為6.78%。對比結果也表明,在系統單元數相同條件下,增加覆蓋函數的階次能夠獲得更高的求解精度。
5 結論
本文提出一種基于一階數值流形方法的等厚度三維接觸單元來模擬薄板與土體之間的動力接觸關系。采用剛塑性本構關系模型和根據虛位移原理,推導了接觸單元的剛度矩陣。引入Rayleigh阻尼反應薄板-土體系統在動力接觸過程中的能量耗散。通過現場試驗驗證了本文所建立單元的有效性和精確性。具體結論如下:
1)采用數值流形方法通過規則的六面體對不規則的接觸系統進行建模,簡化了建模過程。
2)針對薄板-土體接觸模型,接觸單元厚度為其寬度的0.06倍時,仿真效果更符合試驗值,并提出了厚度公式,其正確性需后續進一步驗證。
3)通過和現場試驗結果比較,表明在單元數相同條件時所建立接觸單元比Goodman單元精度更高。
[1]MOONEY M,BOUTON C.Vibratory plate loading of compacted and instrumented field soil beds[J].Geotechnical testing journal,2005,28(3):221-230.
[2]AUERSCH L.Response to harmonic wave excitation of finite or infinite elastic plates on a homogeneous or layered halfspace[J].Computers and geotechnics,2013,51:50-59.
[3]MAO Jianqiang.A finite element approach to solve contact problems in geotechnical engineering[J].International journal for numerical and analytical methods in geomechanics,2005,29(5):525-550.
[4]GINER E,SUKUMAR N,FUENMAYOR F J,et al.Singularity enrichment for complete sliding contact using the partition of unity finite element method[J].International journal for numerical methods in engineering,2008,76(9):1402-1418.
[5]SEGURA J M,CAROL I.On zero-thickness interface elements for diffusion problems[J].International journal for numerical and analytical methods in geomechanics,2004,28(9):947-962.
[6]GUN H.Boundary element analysis of 3-D elasto-plastic con-tact problems with friction[J].Computers&structures,2004,82(7/8):555-566.
[7]PADRóN L A,MYLONAKIS G,BESKOS D E.Simple superposition approach for dynamic analysis of piled embedded footings[J].International journal for numerical and analytical methods in geomechanics,2012,36(12):1523-1534.
[8]李志富,任慧龍,石玉云,等.Laguerre函數在時域匹配邊界元中的應用研究[J].哈爾濱工程大學學報,2016,37(5):629-633.LI Zhifu,REN Huilong,SHI Yuyun,et al.Research on the application of Laguerre function in the time domain Rankine-Green panel method[J].Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2016,37(5):629-633.
[9]GOODMAN R E,TAYLOR R L,BREKKE T L.A model for the mechanics of jointed rock[J].Journal of the soil mechanics and foundations division,1968,94(3):637-660.
[10]苗雨,李威,鄭俊杰,等.改進的薄層單元在樁-土動力相互作用中的應用[J].巖土力學,2015,36(11): 3223-3228.MIAO Yu,LI Wei,ZHENG Junjie,et al.Application of modified thin layer element to the analysis of dynamic pilesoil interaction[J].Rock and soil mechanics,2015,36(11):3223-3228.
[11]齊良鋒,簡浩,唐麗云.引入接觸單元模擬樁土共同作用[J].巖土力學,2005,26(1):127-130.QI Liangfeng,JIAN Hao,TANG Liyun.The computing model of adopting contact element to simulate the pile-soil’s reciprocity[J].Rock and soil mechanics,2005,26(1): 127-130.
[12]LEI Xiaoyan.Contact friction analysis with a simple interface element[J].Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering,2001,190(15-17):1955-1965.
[13]DESAI C S,ZAMAN M M,LIGHTNER J G,et al.Thinlayer element for interfaces and joints[J].International journal for numerical and analytical methods in geomechanics,1984,8(1):19-43.
[14]MAYER M H,GAUL L.Segment-to-segment contact elements for modelling joint interfaces in finite element analysis[J].Mechanical systems and signal processing,2007,21(2):724-734.
[15]KONYUKHOV A,SCHWEIZERHOF K.Incorporation of contact for high-order finite elements in covariant form[J].Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering,2009,198(13/14):1213-1223.
[16]NGUYEN D T,RAUCHS G,PONTHOT J P.The impact of surface higher order differentiability in two-dimensional contact elements[J].Journal of computational and applied mathematics,2013,246:195-205.
[17]PABISEK E.Self-learning FEM/NMM approach to identification of equivalent material models for plane stress problem[J].Computer assisted mechanics and engineering sciences,2008,15(1):67-78.
[18]ZHANG H W,ZHOU L.Numerical manifold method for dynamic nonlinear analysis of saturated porous media[J].International journal for numerical and analytical methods in geomechanics,2006,30(9):927-951.
[19]MA Guowei,AN Xinmei,HE Lei.The numerical manifold method:a review[J].International journal of computational methods,2010,7(1):1-32.
[20]QU X L,FU G Y,MA G W.An explicit time integration scheme of numerical manifold method[J].Engineering analysis with boundary elements,2014,48:53-62.
[21]ZHENG Hong,XU Dongdong.New strategies for some issues of numerical manifold method in simulation of crack propagation[J].International journal for numerical methods in engineering,2014,97(13):986-1010.
[22]劉晶波,谷音,杜義欣.一致粘彈性人工邊界及粘彈性邊界單元[J].巖土工程學報,2006,28(9):1070-1075.LIU Jingbo,GU Yin,DU Yixin.Consistent viscous-spring artificial boundaries and viscous-spring boundary elements[J].Chinese journal of geotechnical engineering,2006,28(9):1070-1075.
[23]LIU Wenwu,HU Changsheng,LU Nianli.Bearing board’s force analysis of the rodless drilling set and its prototype test[J].Applied mechanics and materials,2014,446-447:526-531.
[24]TAO Guilan,ZHANG Li.Dynamic response analysis of docking chamber structure considering viscoelastic boundary condition[J].Applied mechanics and materials,2013,405-408:1939-1944.
Application of a 3D constant-thickness element in thin-plate-soil dynamic contact interaction
LIU Wenwu,LU Nianli,HU Changsheng
(School of Mechatronics Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150001,China)
To solve the dynamic contact problem between a thin plate and soil,a new 3D constant-thickness contact element based on the first-order numerical manifold method is proposed.In this method,the soil is modeled by a firstorder basic function and the thin plate is modeled by a zero-order basic function.Using the principle of virtual displacement and a rigid-plastic constitutive model,the stiffness matrix of the new contact element was deduced.By adding a damping component and equivalent linear model,the second-order differential dynamic equation of the contact system was built.Then,the displacement and stress values of the dynamic contact process were solved using the four-order Runge-Kutta explicit method.Compared with the Goodman results,the new contact element agrees better with the experimental results when the thickness of the contact element is 0.06 times its width.Comparison with the field test shows that the new contact element is not only convenient for modeling but also has higher accuracy.
thin-plate-soil interaction;numerical manifold method;contact element;constant thickness;field test;stiffness matrix;damping component;constitutive model
10.11990/jheu.201510020
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1390.u.20160928.0936.034.html
TU67
A
1006-7043(2016)12-1698-06
劉文武,陸念力,胡長勝.等厚度三維單元在薄板-土動力接觸中的應用[J].哈爾濱工程大學學報,2016,37(12):1698-1703.
2015-10-12.
2016-09-28.
國家國際科技合作專項項目(2013DFA71120,2015DFA70100);中央高校基礎研發基金項目(HIT.NSRIF.2013049).
劉文武(1985-),男,博士研究生;
陸念力(1955-),男,教授,博士生導師;
胡長勝(1971-),男,副教授.
胡長勝,E-mail:hit_liuwenwu@163.com.
LIU Wenwu,LU Nianli,HU Changsheng.Application of a 3D constant-thickness element in thin-plate-soil dynamic contact interaction[J].Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2016,37(12):1698-1703.

