MSCT和CTPI在外傷性彌漫腦腫脹中的應用效果對比
張可+柳少光+張建華
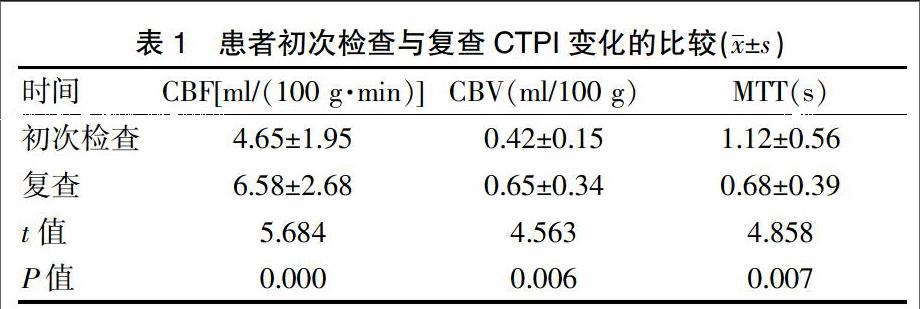
[摘要]目的 比較顱腦多排螺旋CT(MSCT)和CT腦灌注成像(CTPI)在外傷性彌漫腦腫脹(DBS)中的應用效果。方法 選取2015年1月~2016年10月收治的100例DBS患者作為研究對象,使用GE light speed 64排螺旋CT機掃描,在傷后2~6 h內行常規MSCT檢查和CTPI檢查,72 h內再次復查CTPI。比較MSCT與CTPI的DBS檢出率,分析腦血流量(CBF)、腦血容量(CBV)、平均通過時間(MTT)和超清彩色圖像與DBS預后的關系。結果 MSCT對DBS的檢出率為88.0%,低于CTPI的96.0%(P<0.01)。治療后,患者的CBF、CBV呈升高趨勢,初次檢查與復查CBF、CBV、MTT值比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。結論 MSCT和CTPI在DBS中具有較好的應用效果,但CTPI能夠有效評估患者的預后情況,通過超前彩色圖像可直觀觀察和評價患者的病情變化,值得在臨床中推廣應用。
[關鍵詞]多排螺旋CT;CT腦灌注成像;外傷性彌漫腦腫脹
[中圖分類號] R816.1 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1674-4721(2017)03(a)-0145-03
[Abstract]Objective To compare the application effect of brain multi-slice spiral CT (MSCT) and CT perfusion imaging (CTPI) in evaluation of traumatic diffuse brain swelling (DBS).Methods Altogether 100 cases of patients with DBS from January 2015 to October 2016 were selected as study object.All the patients were scanned by using GE light speed 64-slice spiral CT machine and underwent conventional MSCT and CTPI examinations at 2 to 6 hours after injury and CTPI re-examinations within 72 hours.The detection rate of DBS by using MSCT and CTPI were compared,cerebral blood flow (CBF),cerebral blood volume (CBV),mean transit time (MTT) and the relationship between ultra clear color images and prognosis of DBS were analyzed.Results The detection rate of DBS by using MSCT was 88.0%,significantly lower than that of CTPI (96.0%)(P<0.01);after treatment,CBF and CBV was increased,while MTT was decreased,the difference of CBF,CBV and MTT between initial examination and reexamination was statistically significant (P<0.01).Conclusion MSCT and CTPI have good application effect in evaluation of DBS,but CTPI can effectively assess the prognosis of patients.By using the color image,disease change can be directly evaluated and observed,which is worthy of clinical application.
[Key words]Multi-slice spiral CT;CT perfusion imaging;Traumatic diffuse brain swelling
隨著我國現代化進程的高速發展,各類工業和交通事故等導致的人身傷害逐年增多,僅顱腦外傷(traumatic brain injury,TBI)的發生率>100/10萬[1]。TBI的特點是重型腦外傷逐年增多,彌漫性腦損傷(diffuse brain injury,DBI)是TBI常見的急癥之一[2]。它可單獨存在或與各種類型的TBI同時并存,由于DBI的治療困難,死亡率>60%,預后極差,也是影響重型TBI預后的重要因素之一[3]。因此,本次研究旨在研究多排螺旋(Multi-slice spiral CT,MSCT)和CT腦灌注成像(computed tomographic perfusion imaging,CTPI)在外傷性彌漫腦腫脹(diffuse brain swelling,DBS)中的應用價值,為DBS患者早期診斷和治療方案的選擇以及預后判斷提供可靠依據,找到一種“金標準”,為重型TBI的診斷提供一種新的思路和方法,現報道如下。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料
選取2015年1月~2016年10月收治的100例DBS患者作為研究對象,其中男性52例,女性48例;年齡為26~62歲,平均(57.8±1.5)歲。本次研究經醫院醫學倫理委員會審批。入選標準:①年齡18~70歲;②受傷至入院時間<2 h;③無重大疾病史;④家屬對本次研究知情并能配合隨訪調查。排除標準:合并其他嚴重創傷、低血壓、窒息、低氧血癥、失血性休克等疾病。

