地下儲氣庫井管柱沿程流體狀態數值模擬
劉銘剛王建軍閆怡飛謝巍楊秀娟閆相禎張艷茹
1.中國石油大學(華東);2.中國石油集團石油管工程技術研究院;3.中國石油華北油田分公司
地下儲氣庫井管柱沿程流體狀態數值模擬
劉銘剛1王建軍2閆怡飛1謝巍3楊秀娟1閆相禎1張艷茹3
1.中國石油大學(華東);2.中國石油集團石油管工程技術研究院;3.中國石油華北油田分公司
確定注采過程中天然氣在油管柱內的運動狀態是分析儲氣庫井管柱受力、確定沖蝕位置的關鍵。根據井身結構和運行參數建立天然氣流經儲氣庫定向井油管柱過程的物理模型,通過數值試驗研究造斜段管柱內沿程速度、渦量和近壁壓力分布;分析注采壓差、井斜角及油管內徑對管柱近壁壓力的影響規律。結果表明:油管柱內流體狀態受注采壓差和井身結構影響,天然氣流速和近壁壓力在流入流出造斜段時發生波動;管柱沿程速度和動壓隨井深增大而減小,沖蝕點位置出現在造斜段流入端和流出端管柱中心線與最大狗腿角位置徑向線的連線上;隨著注采壓差增大,流入端和流出端彎曲外側和內側平均壓程比均明顯增大;隨著井斜角增大,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比增大,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比減小;隨著油管內徑增大,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比減小,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比增大。
地下儲氣庫; 定向井; 造斜段; 沖蝕; 計算流體力學
目前國內地下儲氣庫類型以衰竭油氣藏型為主,其中定向儲氣庫井所占比例很大。生產管柱作為油氣生產中的關鍵工具,面對儲氣庫循環注采的復雜工況,其功能、結構完整性對儲氣庫作業效率甚至安全都有直接影響。其中封隔器管柱作為儲氣庫“又采又注”作業方式的控制樞紐,其在注采過程中承受高速氣流的作用,其質量對全井管柱的壽命和安全產生影響。由于流體在管路內的運動狀態和壓力變化主要受管路結構及截面特性影響[1-3],因此研究地下儲氣庫注采過程中油管柱內流體狀態和氣體沖蝕位置,研究不同工況參數下的速度、壓力分布規律,對儲氣庫井設計、施工和管柱選材具有重要意義。
國內外學者在彎曲管流的理論、試驗及計算方面做了許多工作:Jeffery L(1988)[4]等推導了理想氣體音速流動時運動狀態方程并與低速流進行了比較;Elling Sletfjerding(2003)[5]設計了氣體在粗糙管路中的流動狀態對比試驗,給出了管路沿程近壁壓力分布基本規律;Mazumder(2008a,2008b)和Deng(2005)[6-8]提出并改進了確定彎曲管路沖蝕位置的試驗方法;Stack and Abdurrahman(2011)、Zhang(2012)、Tan(2012)、Li(2010)、Suzuki(2008)和 Zeng(2014)[3,9-13]利用計算流體力學仿真(CFD)技術就彎曲管路流體沖蝕問題開展了一系列遞進的工作,提出高速管流的常用計算模型和參數取值依據;Ferng Y M(2008,2010)[14-15]和 Zhu(2012,2014a,2014b)[16-18]利用 CFD 技術對輸氣薄壁管道及氣體鉆井中的沖蝕問題進行了研究,國內的練章華等(2012)和王嘉淮等(2015)[19-20]對高壓氣井和地下儲氣庫井管柱的氣體沖蝕問題進行了初步研究。本文將上述研究作如下補充:根據井身結構和運行參數建立天然氣流經定向儲氣庫井油管柱的流體力學模型,通過數值試驗研究一定工況下定向井造斜段管柱內沿程速度和近壁壓力分布,并對比不同日注采量、井斜角和油管內徑對管柱近壁壓力的影響規律。
1 模型建立
Modeling
1.1 數學模型
Mathematical model
地下儲氣庫井處于注入工況時天然氣經壓縮機壓縮后注入井底,處于采出工況時天然氣自井底流向井口,可假設油管柱內運動流體為單相可壓縮流體。在ANSYS CFX/CFD模塊中選擇Renormalizationgroup(RNG) k-ε渦黏湍流模型進行數值計算,該模型的連續方程和運動方程分別為

式中,xi,j,k對應空間坐標系中的i、j、k方向的距離,m;Ui,j,k表示流體在 i、j、k 方向上的瞬時速度分量,m/s;SM為體積力,N;ρ為相對密度,kg/m3;μeff為有效動力黏度,數值上等于分子(動力) 黏度μ與湍流黏度 μt的和,μPa·s;p 為靜壓,MPa;對實際可壓縮流體作如下修正
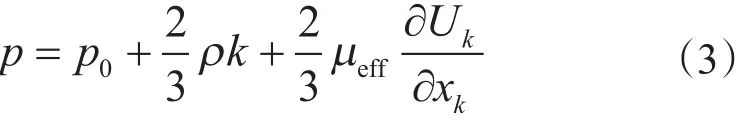
式中,p0為流體不可壓縮時的靜壓,本文中對應計算工況中的入口壓力,MPa。

式中,Kronecker積分項 δij在 i=j時,ρuiuj為正應力,為切應力,MPa。
湍動能k和湍動能耗散率ε分別由式(5)、(6)描述的傳遞方程得到,至此方程(1)、(2)封閉。
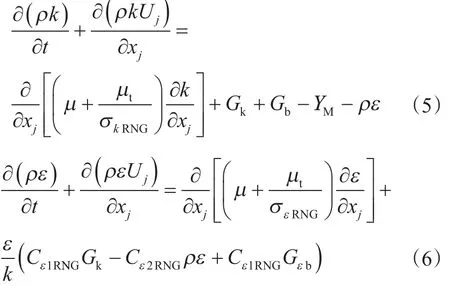
式中,i和j表示坐標方向;k表示單位質量氣體的湍動能,J;ε表示相對湍動能耗散率;σkRNG為k方程湍流模型常數,取0.7179;σεRNG為ε方程湍流模型常數,取 0.7179;Cε1RNG、Cε2RNG是湍流模型常數,分別取1.42、1.68;Gk是跟平均速度梯度有關的湍動能生成項;Gb和Gεb是與浮力有關的湍動能生成項;Gk為黏度引起的渦量項,由下式求得
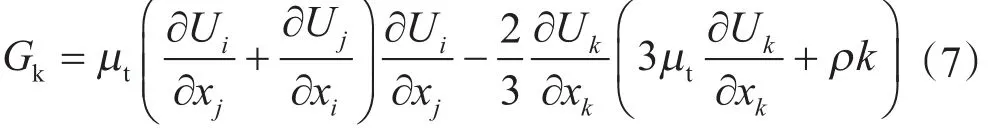
YM是流體可壓縮性引起的相對湍動能耗散率改變量,由下式求得


1.2 物理模型
Physical model
為保證數值計算結果與實際工況具有可比性,以某地下儲氣庫試驗井井身結構為物理模型基礎,根據實際井身數據,建立直井段、造斜段和帶封隔器管柱段數值模型。模型以入口端面為源面,采用六面體網格進行單元劃分,彎曲管柱段采用楔形網格過渡和加密。
在ANSYS CFX/CFD流體分析模塊中設置管柱流入、流出端為壓力邊界,以注氣工況為例進行分析,計算時壓縮機出口(流入端)壓力恒定,初始井底(流出端)壓力為20 MPa,參考環境溫度為56.25 ℃,按充分發展的湍流進行初始化設置。假定油管壁面無滑移,計算模型和湍流模型常數按1.1節描述的Renormalization-group(RNG)k-ε渦黏湍流模型設置,選擇Segregated Solver算法求解。數值模型(局部)如圖1所示。

圖1 數值計算模型Fig. 1 Numerical calculation model
2 算例分析
Analysis on calculation example
2.1 計算參數和工況設置
Calucation parameters and working condition setting
地下儲氣庫S-4試驗井的表層套管長202.74 m、技術套管長3 386.94 m、生產套管長4 598.08 m、篩管長204.21 m,下入深度分別為213.45 m、3 398.29 m、4 607 m和4 805 m;表層套管、技術套管、生產套管的補心距分別為10.71 m、11.35 m、8.92 m,最大井斜深度為2 890.44 m,井斜角、方位角分別23.60o和290.81o。油管采用壁厚/內徑為3.920 mm/99.56 mm、扣型為4-1/2in 13.5# JFEBEAR B×P的JFEHP1-13Cr-110型油管;封隔器采用壁厚/內徑為3.85 mm/97.79 mm、長為2 590 mm、壓力等級51.7 MPa、扣型為 5-1/4 -6 Acme Latch ×5in18.00#JFEBEAR P的S13Cr-110型封隔器。
本文計算工況設置如表1所示,其中日注采量、管柱規格和狗腿度在數值試驗時分別由注采壓差、油管內徑和井斜角控制,對應取值如表2所示。采用控制變量法,以注采氣量40×104m3/d、管柱規格?114.3 mm×7.37 mm、狗腿度9 (o)/30 m為基礎工況,分別對不同注采壓差、油管內徑和井斜角進行對比分析。算例井井筒內天然氣物理力學參數:流體為天然氣(主要成分為甲烷),密度為0.587 kg/m3,動力黏度為 16.06 μPa·s,運動黏度為 22.07×10-7m2/s,定壓比熱 2.23 kJ/(kg·K),定容比熱 1.704 kJ/(kg·K)。
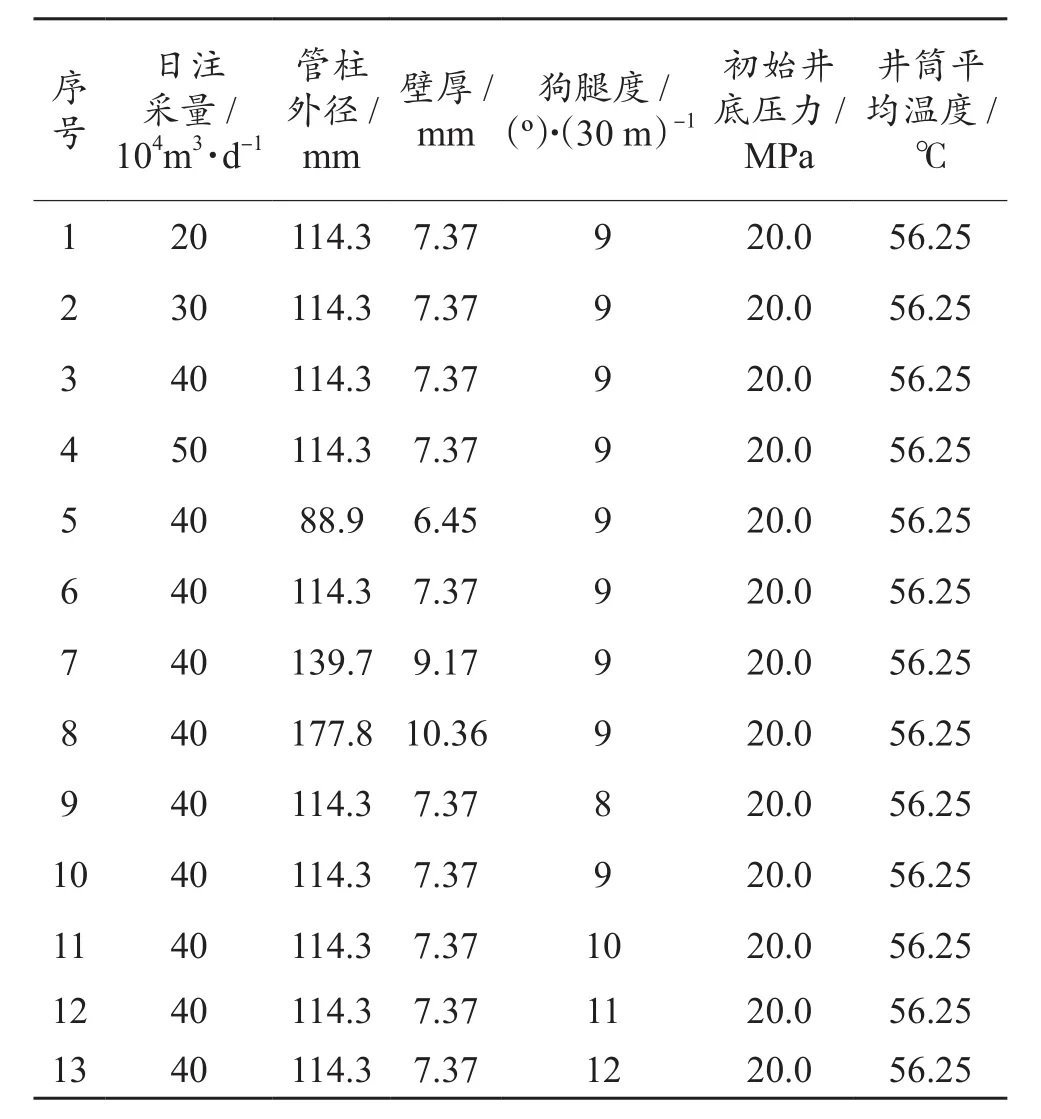
表1 算例工況設置Table 1 Working condition setting
2.2 計算結果分析
Analysis on calculation results
當不考慮固體顆粒沖蝕時,儲氣庫油管柱沖蝕損壞的原因是天然氣在高速流動和壓力變化條件下引起局部洞穴型腐蝕。儲氣庫注氣過程中,除由注采壓差引起的近壁靜壓外,管柱彎曲將導致管壁法向方向的氣體速度分量迅速減小,此時氣體動能轉化為作用于管壁的機械能,表現為管柱近壁壓力增大,該壓力稱為全受阻壓力(簡稱全壓或總壓,p總),它與未受擾動處的壓力(即靜壓,p靜)之差,稱為動壓(p動),動壓是管柱產生壓力沖蝕的重要原因。日注采量為40×104m3/d,井斜角為23.6o(最大狗腿度9(o)/30 m),采用 ?114.3 mm×7.37 mm 油管時,油管柱內天然氣的截面速度、渦量及近壁壓力計算結果如圖2所示。
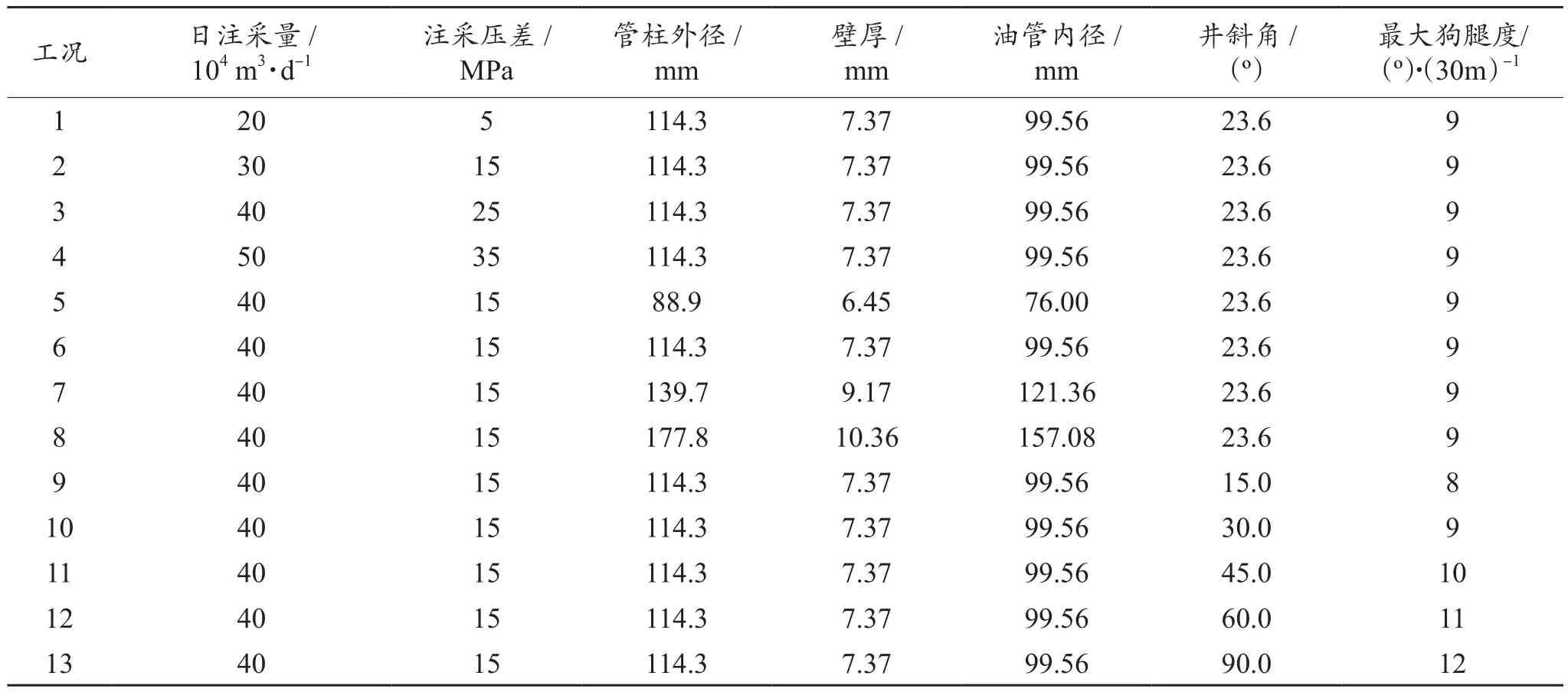
表2 模擬試驗工況Table 2 Working condition of simulation experiment
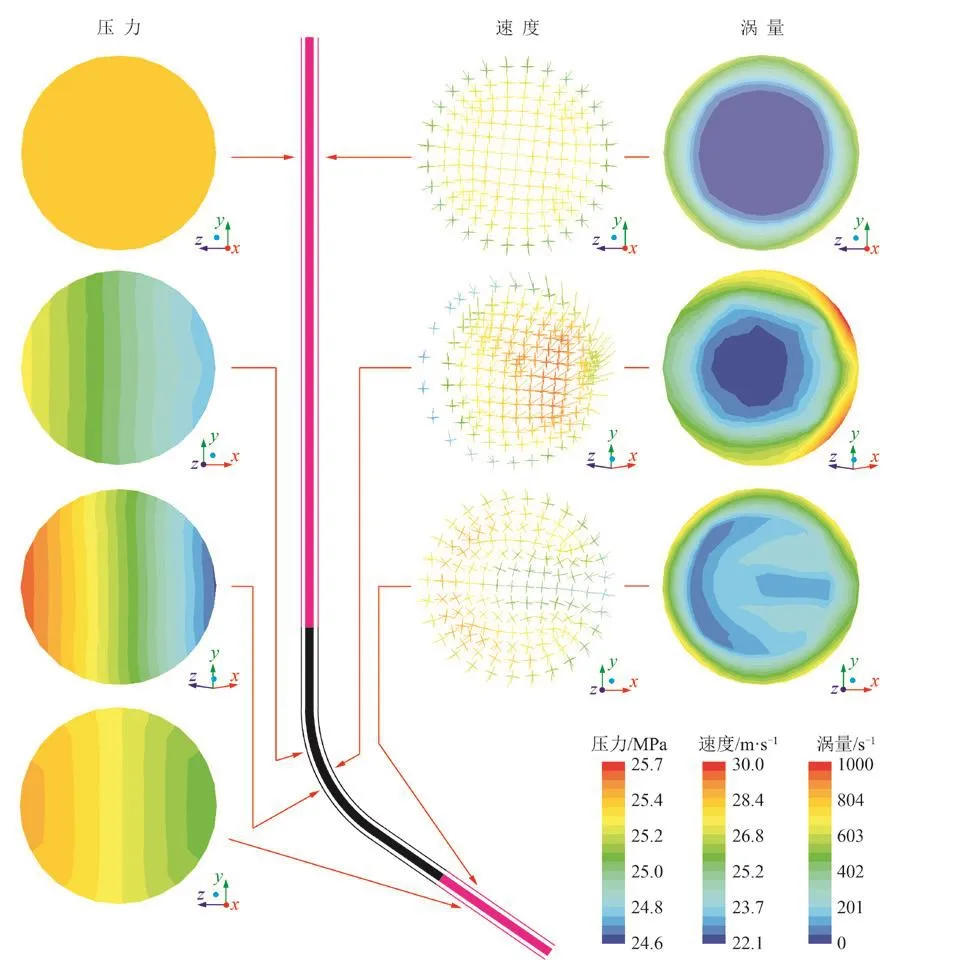
圖2 油管內天然氣速度(a)、渦量(b)及靜壓(c)截面云圖Fig. 2 Cross-section cloud chart of gas velocity (a), vorticity (b)and static pressure (c) inside the tubing
從圖2可以看出:(1)油管柱內氣體截面速度自油管中心到管壁逐漸減小;氣體從流入端到流出端過程中,彎曲內側速度先增大后減小,彎曲外側速度先減小后增大。(2) 油管柱內氣體截面渦量自中心到管壁逐漸增大;進入造斜段后,管柱內側渦量明顯增大,這是因為離心作用形成二次旋流在此處產生的壓力真空,形成漩渦分布,漩渦的存在使分子碰撞加劇,造成機械能損失。(3)儲氣庫管柱近壁壓力沿程分布受井身結構影響。天然氣流入造斜段時,管柱彎曲外側壁壓力增大,彎曲內側壁壓力減小;流出造斜段時,管柱彎曲外側壁壓力減小,彎曲內側壁壓力增大,并隨狗腿度減小逐漸趨于平穩。(4)天然氣進入造斜段后,靜壓得到釋放,速度增加,動壓隨之增大。(5) 沖蝕位置出現在造斜段管柱彎曲外側。
2.3 影響因素分析
Analysis on in fl uential factors
2.3.1 壓差 研究管柱規格和井身結構一定(井斜角23.6o,?114.3 mm×7.37 mm油管)時管柱近壁壓力隨注采壓差的變化規律。圖3為地下儲氣庫井筒底部壓力恒定(20 MPa),注采壓差分別為5 MPa、10 MPa、15 MPa和20 MPa時的造斜段油管柱壓程比變化規律曲線。從圖3可以看出,試驗壓差從5 MPa提高到20 MPa的過程中,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比明顯增大,變化率為325%和257%,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比明顯增大,變化率為425%和322%。
2.3.2 井斜角 研究管柱規格和日注采量一定(?114.3 mm×7.37 mm油管,注氣量40×104m3/d)時管柱近壁壓力隨井斜角變化的規律。圖 4為井斜角分別為 0o(直井)、15o、30o、45o、60o和 90o(水平井)時的造斜段油管柱壓程比變化規律。從圖4可以看出,井斜角從0o(直井)增大到90o(水平井)過程中,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比增大,變化率分別為14.7%和57.5%,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比減小,變化率分別為-12.8%和-69.2%。
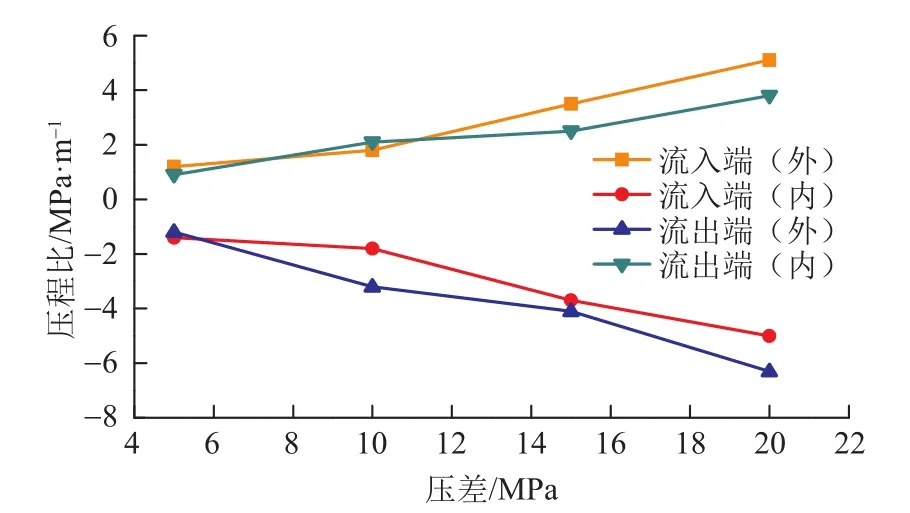
圖3 管柱造斜彎曲段流入流出端壓程比隨壓差變化規律Fig. 3 Effect of pressure difference on the pressure range ratio between the infow end and the outfow end of the defecting bend section in the string
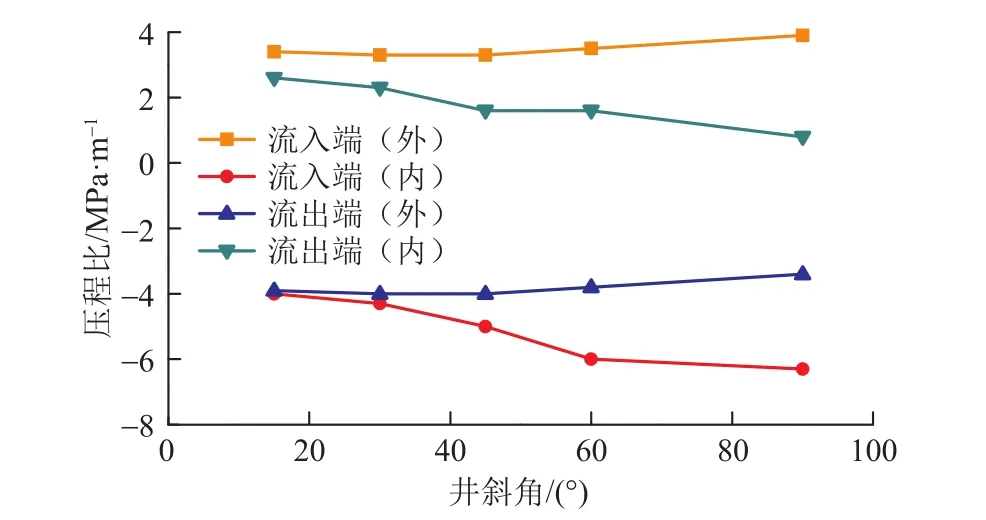
圖4 管柱造斜彎曲段流入流出端壓程比隨井斜角變化規律Fig. 4 Effect of hole deviation angle on the pressure range ratio between the infow end and the outfow end of the defecting bend section in the string
2.3.3 油管內徑 研究井斜角為23.6o(最大狗腿度9(o)/30 m)、注氣量 40×104m3/d 時,油管內徑變化(取油管規格分別為?88.9 mm×6.45 mm、?114.3 mm×7.37 mm、?139.7 mm×9.17 mm、?177.8 mm×10.36 mm)對氣體壓程比的影響規律,如圖5所示。
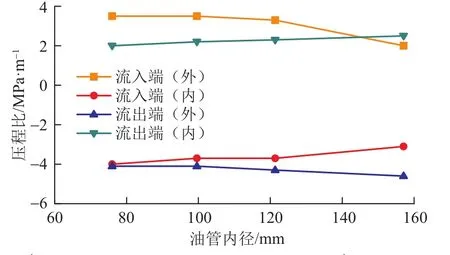
圖5 管柱造斜彎曲段流入流出端壓程比隨油管內徑變化規律Fig. 5 Effect of tubing ID on the pressure range ratio between the infow end and the outfow end of the defecting bend section in the string
從圖5可以看出,油管內徑從76 mm增加到157 mm時,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比減小,變化率分別為42.9%和22.5%,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比增大,變化率分別為12.2%和25.0%。
3 結論
Conclusions
(1) 油管柱內氣體截面速度自油管中心到管壁逐漸減小;氣體從流入端到流出端過程中,彎曲內側速度先增大后減小,彎曲外側速度先減小后增大。油管柱內氣體截面渦量自中心到管壁逐漸增大;進入造斜段后,管柱內側渦量明顯增大。天然氣流入造斜段時,管柱彎曲外側壁壓力增大,彎曲內側壁壓力減小;流出造斜段時,管柱彎曲外側壁壓力減小,彎曲內側壁壓力增大,并隨狗腿度減小逐漸趨于平穩。氣體沖蝕位置出現造斜段管柱彎曲外側壁上。
(2) 隨著注采壓差增大,流入端和流出端彎曲外側和內側平均壓程比均明顯增大;隨著井斜角增大,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比增大,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比減小;隨著油管內徑增大,流入端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比減小,流出端彎曲外側和內側的平均壓程比增大。
(3) 過高的日注采氣量將引起定向儲氣庫井造斜段管柱整體載荷水平的提高,過大的狗腿度和過大的油管內徑將分別造成造斜段管柱流入端和流出端的壓程比上升,造成該位置出現氣體沖蝕現象。實際生產中,建議采用“低產量、穩壓差”的生產理念,滿足產量要求的情況下優先選擇小尺寸油管,對狗腿度較大的井下油管氣蝕情況應進行重點監控。
[1] PATANKAR SV. Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow[M]. Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Fremont, CA,1980.
[2] WILCOX D C. Turbulence modeling for CFD[M].DCW Industries, La Canada, CA, 2006.
[3] STACK M M, ABDELRAHMAN S M. A CFD model of particle concentration effects on erosion–corrosion of Fe in aqueous conditions[J]. Wear, 2011, 273(1): 38-42.
[4] SAVIDGE J L, STARLING K E, MCFALL R L. Sound speed of natural: SPE Gas Technology Symposium[C].Alberta, Canada, Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1988.
[5] SLETFJERDING, ELLING, GUDMUNDSSON, JON STEINAR. Friction factor directly from roughness measurements[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, Transactions of the ASME, 2003, 125(2):126-130.
[6] MAZUMDER Q H, SHIRAZI S A, MCLAURY B.Experimental investigation of the location of maximum erosive wear damage in elbows[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 2008, 130(1): 244-254.
[7] MAZUMDER Q H, SHIRAZI S A, MCLAURY B.Mazumder Q H, Shirazi S A, Mclaury B S. Prediction of solid particle erosive wear of elbows in multiphase annular fow-model development and experimental validations[J].Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2008, 130(2):220-254.
[8] DENG T, PATEL M, HUTCHINGS I, BRADLEY M A. Effect of bend orientation on life and puncture point location due to solid particle erosion of a high concentration flow in pneumatic conveyors[J]. Wear,2005, 258(1): 426-433.
[9] ZHANG H, TAN Y Q, YANG D M, TRIAS F X, JIANG S Q, SHENG Y, Oliva A. Numerical investigation of the location of maximum erosive wear damage in elbow:Effect of slurry velocity, bend orientation and angle of elbow[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217(3): 467-476.
[10] TAN Y Q, ZHANG H, YANG D M, JIANG S Q, SONG J H, SHENG Y. Numerical simulation of concrete pumping process and investigation of wear mechanism of the piping wall[J]. Tribology International, 2012,46(1): 137-144.
[11] LI R, YAMAGUCHI A, NINOKATA H. Computational fluid dynamics study of liquid droplet impingement erosion in the inner wall of a bent pipe[J]. Journal of Power & Energy Systems, 2010, 4(2): 327-336.
[12] SUZUK M, INABA K, YAMAMOTO M. Numerical simulation of sand erosion in a square-section 90-degree bend[J]. Journal of Fluid Science & Technology,2008, 3(7): 868-880.
[13] ZENG L, ZHANG G A, GUO X P. Erosion–corrosion at different locations of X65 carbon steel elbow[J].Corrosion Science, 2014, 85(4): 318-330.
[14] FERNG Y M. Predicting local distributions of erosion–corrosion wear sites for the piping in the nuclear power plant using CFD models[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2008, 35(2): 304-313.
[15] FERNG Y M, LIN B H. Predicting the wall thinning engendered by erosion–corrosion using CFD methodology[J]. Nuclear Engineering & Design,2010, 240(10): 2836-2841.
[16] ZHU H J, LIN Y H, ZENG D Z, ZHOU Y, XIE J, WU Y P. Numerical analysis of fow erosion on drill pipe in gas drilling[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2012, 22(1):83-91.
[17] ZHU H J, WANG J, CHEN X Y, SHE J. Numerical analysis of the effects of fluctuations of discharge capacity on transient fow feld in gas well relief line[J].Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries,2014, 31(31): 105-112.
[18] ZHU H J, Pan Q, ZHANG W L, FENG G, Li X. CFD simulations of fow erosion and fow-induced deformation of needle valve: Effects of operation, structure and fuid parameters[J]. Nuclear Engineering & Design, 2014,273(1): 396-411.
[19] 練章華,魏臣興,宋周成,丁亮亮,李鋒,韓瑋. 高壓高產氣井屈曲管柱沖蝕損傷機理研究[J]. 石油鉆采工藝,2012,34(1):6-9.LIAN Zhanghua, WEI Chenxing, SONG Zhoucheng,DING Liangliang, LI Feng , HAN Wei. Erosion damage mechanism of buckled tubing in high pressure and high production gas wells[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2012, 34(1): 6-9.
[20] 王嘉淮,羅天雨,呂毓剛,薛承文,趙麗萍. 呼圖壁地下儲氣庫氣井沖蝕產量模型及其應用[J]. 天然氣工業,2012,32(2):57-59.WANG Jiahuai, LUO Tianyu, LV Yugang, XUE Chengwen, ZHAO Liping. Research and application of model of gas well erosion output of the Hutubi underground gas storage[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2012, 32(2): 57-59.
(修改稿收到日期 2017-05-25)
(編輯 景 暖)
Numerical simulation on the state of fl uids along the string of gas storage well
LIU Minggang1, WANG Jianjun2, YAN Yifei1, XIE Wei3, YANG Xiujuan1, YAN Xiangzhen1, ZHANG Yanru3
1. China University of Petroleum (Huadong), Qingdao 266580, Shandong, China;2. CNPC Tubular Goods Research Institute, Xi’an 710077, Shaanxi, China; 3. CNPC Huabei Oil field Company, Renqiu 062552, Hebei, China
To analyze the force applied on the string of gas storage well and determine the erosion position, it is crucial to fgure out the motion state of natural gas in the tubing string in the process of gas injection and production. In this paper, a physical model used to simulate the fowing process of natural gas along the tubing string of directional gas storage well was established on the basis of casing program and operation parameters. Then, the velocity and vorticity along the string and the distribution of pressure close to the wall in the defecting section were researched by means of numerical experiment. And fnally, the infuential laws of injection-production pressure difference, hole deviation angle and tubing ID on the pressure close to the wall of string were analyzed. It is indicated that the state of fuids inside the tubing string is affected by injection-production pressure difference and casing program, and the fow velocity of natural gas and its pressure close to the wall fuctuate the moment it fows into and out of the defecting section. The velocity and dynamic pressure along the string decrease as the well gets deep. Erosion point is located at the connection line between the radial line at the maximum dogleg angle and the central line of string from the infow end to the outfow end of defecting section. As the injection-production pressure difference increases, the average pressure range ratio between the outside and the inside of the bend at infow and outfow ends increases obviously. With the increasing of hole deviation angle, the average pressure range ratio between the outside and the inside ofthe bend at the infow end increases while that at the outfow end decreases. And with the increasing of tubing ID, the average pressure range ratio between the outside and the inside of the bend at the infow end decreases while that at the outfow end increases.
underground gas storage; directional well; defecting section; erosion; fuid mechanics calculation
劉銘剛,王建軍,閆怡飛,謝巍,楊秀娟,閆相禎,張艷茹.地下儲氣庫井管柱沿程流體狀態數值模擬[J] .石油鉆采工藝,2017,39(4):449-454.
TE38
A
1000 – 7393( 2017 ) 04 – 0449 – 06
10.13639/j.odpt.2017.04.010
:LIU Minggang, WANG Jianjun, YAN Yifei, XIE Wei, YANG Xiujuan, YAN Xiangzhen, ZHANG Yanru. Numerical simulation on the state of fuids along the string of gas storage well[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2017, 39(4): 449-454.
國家自然科學基金資助課題“基于應變控制的熱采井套管試驗及安全可靠性研究”(編號:51274231);國家自然科學基金資助課題“基于多目標約束優化方法的頁巖氣儲層微裂縫分析及壓裂縫網擴展機理研究”(編號:51374228)。
劉銘剛(1990-),博士研究生,從事油氣工程力學、機械強度及可靠性方面的研究工作。通訊地址:(266580)山東省青島市黃島區長江西路66號中國石油大學(華東)儲運與建筑工程學院。E-mail: liuminggang0303@126.com

