pH值和劑量對腹腔注射L-精氨酸誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型的影響
肖魯瑤 張 杰* 鄭 帥 梅少帥
(1.首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院消化內科,北京 100029;2.首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院心肺血管疾病研究所,北京 100029;3.首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院病理科,北京 100029)
·基礎研究·
pH值和劑量對腹腔注射L-精氨酸誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型的影響
肖魯瑤1張 杰1*鄭 帥2梅少帥3
(1.首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院消化內科,北京 100029;2.首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院心肺血管疾病研究所,北京 100029;3.首都醫科大學附屬北京安貞醫院病理科,北京 100029)
目的探討L-精氨酸(L-arginine)不同給藥方法誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型的效果。方法L-精氨酸溶液以不同pH值、不同劑量誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型,造模后2、4、12、24 h統計小鼠病死率,采集小鼠血漿以淀粉-碘比色法檢測淀粉酶活性,取胰腺及肺組織行石蠟切片HE染色觀察組織損傷嚴重程度。結果pH值為11高劑量組小鼠2 h病死率100%,其余各組各時間點小鼠均存活。3個模型組與對照組相比血漿淀粉酶活性、胰腺組織病理評分均升高,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。模型組之間比較,pH值為7高劑量組胰腺及肺組織損傷最重。結論L-精氨酸溶液的 pH值及給藥劑量對胰腺損傷程度有不同程度的影響,20%L-精氨酸溶液pH值為7按4 g/kg的劑量間隔1 h連續2次腹腔注射誘導的小鼠急性胰腺炎模型組織損傷重,且小鼠存活率高。
小鼠;L-精氨酸;急性胰腺炎;動物模型
急性胰腺炎是臨床常見病,急性重癥胰腺炎病情進展快,病死率高[1]。動物模型是研究其病理機制、治療療效的重要途徑。小鼠急性胰腺炎模型的建立方法很多,藥物腹腔注射的方法具有操作簡單、降低感染風險、對內環境影響小等優勢,應用L-精氨酸腹腔注射是誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎的重要造模方法之一。大多數研究采用間隔1 h連續兩次腹腔注射給藥的方式[2-4],但不同文獻對L-精氨酸溶液的單次給藥劑量及溶液pH值報道并不統一[5-7]。為了找到最佳造模條件,本研究對比了L-精氨酸溶液不同pH值、不同劑量的給藥方案所誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型的效果。
1 材料與方法
1.1材料
1)動物:健康C57BL/6J雄性小鼠102只,體質量20~25 g,SPF級,購自北京華阜康生物科技有限公司,實驗動物許可證號:11401500012660。
2)儀器與試劑:高精度電子天平(瑞士Mettler公司),高速低溫離心機(美國Thermo公司),Biotek Synergy4全波長多功能酶標儀(美國Gene公司),Eclipse TE2000-S顯微鏡(日本Nikon公司),PB-10 pH計(德國Sartorius公司)。L-精氨酸(L-arginine, L-Arg)(Solarbio,貨號A0013)純度≥98%,使用時用0.9%(質量分數)氯化鈉注射液配成20%(質量分數)溶液,pH值計測定溶液pH值,鹽酸溶液調節pH值。α-淀粉酶 (amylase, AMS) 試劑盒(南京建成生物工程研究所,貨號C016),其余試劑均為國產分析純級。
1.2實驗方法
1.2.1 分組
C57BL/6J小鼠102只,采用數字表法隨機分為5組: pH值為7低劑量組24只、pH值為7高劑量組24只、pH值為11低劑量組24只、pH值為11高劑量組24只及對照組6只。
1.2.2 實驗方法
實驗前各組小鼠禁食12 h、不禁水,各模型組以不同pH值、不同劑量L-精氨酸溶液間隔1 h連續2次小鼠腹腔注射,詳見表1。對照組用等體積0.9%(質量分數)氯化鈉注射液間隔 1 h連續 2次腹腔內注射。各模型組均在第2次腹腔注射給藥后2、4、12、24 h 4個時間點觀察小鼠血漿淀粉酶活性、胰腺及肺組織病理,并統計小鼠病死率,每個時間點6只小鼠;對照組第2次腹腔注射給藥后12 h觀察上述指標。

表1 各模型組L-精氨酸給藥方法Tab.1 Injection methods of L-arginine in model groups
1.2.3 標本收集及處理
在2、4、12、24 h以1%(質量分數)戊巴比妥鈉0.009 mL/g麻醉小鼠,右心房取血于肝素鈉抗凝的EP管,立即低溫離心3 000 r/min 15 min,分離血漿,淀粉-碘比色法檢測血漿淀粉酶活性;留取胰腺及肺組織浸于4%(質量分數)多聚甲醛溶液中固定24 h,經過脫水、石蠟包埋后切片并 HE染色,請專業人員進行病理分析。采用胰腺組織病理Rongione評分指標[8]。
1.3統計學方法
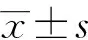
2 結果
2.1各模型組成功構建急性胰腺炎模型
pH值為11高劑量組小鼠2 h病死率為100%,其余3個模型組各觀察時間點小鼠均存活。造模后12 h,模型組與對照組相比,小鼠血淀粉酶活性、胰腺組織病理Rongione評分均升高,且差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),3個模型組均成功構建急性胰腺炎模型(圖1)。
2.2各模型組胰腺炎程度隨時間變化
各模型組在造模后2、4、12、24 h觀察血淀粉酶活性和胰腺組織病理評分變化。pH值為7低劑量組小鼠造模后4 h血淀粉酶活性開始升高,12 h達到高峰,24 h后開始回落,而pH值為7高劑量組及pH值為11低劑量組小鼠造模后2 h血淀粉酶活性開始升高,同樣12 h達高峰,24 h回落;各模型組胰腺組織病理評分在2 h開始升高,12 h達到高峰,24 h開始下降(圖2)。
2.3各模型組急性胰腺炎嚴重程度比較
比較各模型組在造模后12 h血淀粉酶活性,由高到低依次為pH值為7高劑量組(14 579±1 267)U/dL、pH值為11低劑量組(8 179±1 167)U/dL、pH值為7低劑量組(4 657±349.5)U/dL(圖2A);各模型組造模后12 h胰腺組織石蠟切片HE染色,pH值為7低劑量組可見局灶腺泡細胞空泡變性,葉間水腫,未見明顯炎細胞浸潤、腺泡細胞壞死;pH值為7高劑量組可見葉間水腫,擴散性腺泡細胞空泡變性,小葉邊緣大量炎細胞浸潤、腺泡細胞壞死、核固縮;pH值為11低劑量組可見擴散性腺泡細胞空泡變性,葉間水腫,未見明顯炎細胞浸潤及腺泡細胞壞死;肺組織石蠟切片HE染色,各模型組肺組織肺泡壁增厚,肺泡上皮增生,炎細胞浸潤,其中pH值為7高劑量組最為明顯,肺組織結構明顯紊亂(圖3)。

圖1 不同模型組造模后12 h誘導的小鼠急性胰腺炎效果評價Fig.1 Evaluation of mice acute pancreatitis 12 h after last injection in different model conditions
A: plasma amylase activity;B: Rongione score of pancreas pathological indicators;n=6,**P<0.01vscontrol group,***P=0.000vscontrol group.

圖2 各模型組急性胰腺炎程度隨時間變化Fig.2 Time dependent changes of mice acute pancreatitis severity in different model conditionsA: plasma amylase activity; B: Rongione score of pancreas pathological indicators(,n=6).
3 討論
L-精氨酸1984年首次用于誘導急性胰腺炎模型[9],大劑量 L-精氨酸溶液能減少多胺合成從而抑制細胞核酸及蛋白質合成,而胰腺腺泡細胞的蛋白質合成最為活躍,因此出現損傷[10]。目前L-精氨酸用于誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型的給藥方案在不同文獻報道不一,L-精氨酸溶液濃度、pH值、給藥劑量影響造模效果[11-14]。使用8%(質量分數)L-精氨酸溶液誘導模型使小鼠液體負荷增加,可能增加小鼠病死率,20%(質量分數)L-精氨酸溶液可明顯減低小鼠液體負荷。由于L-精氨酸溶液強堿性(pH值為11)的特點,對腹腔具有較強的化學刺激作用,使得小鼠急性胰腺炎模型不穩定,增加小鼠病死率,石占利等[15]比較了不同pH的L-精氨酸溶液所誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型效果,pH值為11時胰腺損傷較pH為8時嚴重,小鼠病死率增加;調整L-精氨酸溶液pH值后小鼠存活率增加,但胰腺組織損傷減輕。此外不同給藥劑量也影響胰腺組織損傷效果[16]。本研究比較L-精氨酸兩種不同pH值及不同給藥劑量誘導的小鼠急性胰腺炎模型效果,結果顯示,不調節L-精氨酸溶液pH值的情況下,高劑量給藥方案小鼠病死率高,不適合用于造模;而低劑量給藥方案小鼠胰腺組織主要表現擴散性腺泡細胞空泡變性及胰腺組織葉間水腫,炎細胞浸潤、腺泡細胞壞死不明顯,血淀粉酶水平較對照組升高2倍余;調整L-精氨酸溶液pH值至7,小鼠存活率提高,低劑量給藥方案小鼠胰腺表現局灶腺泡細胞空泡變性,葉間水腫,血淀粉酶水平較對照組升高不到2倍,胰腺炎性反應相對輕;提高給藥劑量后胰腺組織損傷明顯加重,表現葉間水腫,擴散性腺泡細胞空泡變性,小葉邊緣大量炎細胞浸潤、腺泡細胞壞死、核固縮,血淀粉酶水平較對照組升高達3倍以上,胰腺炎性反應明顯加重。由此可見,調整精氨酸溶液pH值后增加給藥劑量所誘導的小鼠急性胰腺炎模型胰腺組織損傷最重。同時,不同給藥方案肺組織病理改變與胰腺組織病理改變具有一致性,pH值為7高劑量組小鼠肺組織損傷最重,可用于急性胰腺炎肺損傷相關研究。
綜上所述,L-精氨酸可以誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型,但不同的給藥方案誘導的小鼠急性胰腺炎模型胰腺組織損傷效果不同,甚至導致小鼠病死率不同。本研究對比4種給藥方案,20%(質量分數)L-精氨酸調整pH值為7后以4 g/kg間隔1 h連續2次腹腔注射的給藥方案誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎可以達到滿意效果,胰腺組織出現水腫、炎細胞浸潤、空泡變性、壞死,且小鼠存活率100%,能較好滿足科研需求。
[1] Tenner S, Baillie J, Dewitt J, et al. American college of gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis.[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2014, 109(2):302-302.
[2] Hongwei Z, Xiao Y, Shaihong Z, et al. The fusion of autophagosome with lysosome is impaired in L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(9):11164-11170.
[3] Aziz N M, Kamel M Y, Rifaai R A. Effects of hemin, a heme oxygenase-1 inducer in L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury in adult male albino rats.[J]. Endocrine Regulat, 2017, 51(1):20-30.
[4] 張曉芹, 賈曉云, 李濤,等. 清胰湯對L-精氨酸誘發的重癥急性胰腺炎小鼠胰腺p-STAT3表達的影響[J]. 中國病理生理雜志, 2011, 27(11):2175-2179.
[5] Qiao Y Y, Liu X U, Xu CQ, et al. Interleukin-22 ameliorates acute severe pancreatitisassociated lung injury in mice[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(21):5023-5032.
[6] Chen J, Cai Q P, Shen P J, et al. Netrin-1 protects against L-Arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(9):1-9.
[7] Merza M, Hartman H, Rahman M, et al. NeutropHil extracellular traps induce trypsin activation, inflammation, and tissue damage in mice with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015,149(7):1920-1931.
[8] Yu Q H, Guo J F, Chen Y, et al. Captopril pretreatment protects the lung against severe acute pancreatitis induced injury via inhibiting angiotensin II production and suppressing Rho/ROCK pathway[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2016, 32(9):439-445.
[9] Mizunuma T, Kawamura S, Kishino Y. Effects of injecting excess arginine on rat pancreas[J]. J Nutr, 1984, 114(3):467-471.
[10] Tani S, Itoh H, Okabayashi Y, et al. New model of acute necrotizing pancreatitis induced by excessive doses of arginine in rats[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 1990,35(3):367-374.
[11] Bettaieb A, Koike S, Chahed S, et al. Pancreatic protein tyrosine pHospHatase 1B deficiency exacerbates acute pancreatitis in mice[J]. Am J Pathol, 2016,186( 8):2043-2054.
[12] Yu L, Yang M, Liu J, et al. Recombinant Reg3α protein protects against experimental acute pancreatitis in mice[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2016,422:150-159.
[13] Zhu H, Huang L, Zhu S, et al. Regulation of autopHagy by systemic admission of microRNA-141 to target HMGB1 in l-arginine-induced acute pancreatitisinvivo[J]. Pancreatology, 2016,16(3):337-346.
[14] 魏國麗, 鄭學寶, 劉強, 等. 腹腔內注射L-精氨酸誘導法建立急性胰腺炎小鼠模型的評價[J]. 中國實驗診斷學, 2011,15(10):1631-1634.
[15] 石占利, 陳芝蕓, 高凱. 不同pH值L-精氨酸誘導小鼠急性胰腺炎模型效果觀察[J]. 浙江中西醫結合雜志, 2013,23(4):265-268.
[16] 程禮, 胡國勇, 韓偉, 等. 左旋鹽酸精氨酸誘導重癥急性胰腺炎模型的建議[J]. 胃腸病學和肝病學雜志, 2009,18(5):459-462.
EffectsofpHvaluesanddosesonintraperitonealinjectionofL-arginineinducedacutepancreatitisinmice
Xiao Luyao1, Zhang Jie1*, Zheng Shuai2, Mei Shaoshuai3
(1.DepartmentofGastroenterology,BeijingAnzhenHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100029,China; 2.BeijingInstituteofHeartLungandBloodVesselDiseases,BeijingAnzhenHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100029,China; 3.DepartmentofPathology,BeijingAnzhenHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100029,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of different methods of L-arginine injection on acute pancreatitis model mice.MethodsMice suffering from acute pancreatitis were induced by different pH values and different doses of L-arginine, then mortality was calculated, and plasma amylase activity was detected by starch-iodine colorimetry, and pancreas and lung tissue injury severity was observed by paraffin section of HE staining at the time of 2, 4, 12, 24 h after last injection.ResultsMortality in pH11 high-dose group was 100% at 2 h, and mice in other groups all survived. Compared with the control group, the plasma amylase activity and pancreas pathological score were significantly increased in all model groups (P<0.001).Compared with the other model groups, pancreas and lung tissue injury was the most severe in pH7 high-dose group.ConclusionThe pH value and dosage of L-arginine solution have significant impacts on the degree of pancreatic injury. Acute pancreatitis mice model induced by 2 i.p. injections of L-arginine (400 mg/kg body weight) in 0.9% sodium chloride (pH7) at 1-hour intervals was the most severe compared with the other model groups, and with high survival rate.
mice; L-arginine; acute pancreatitis; animal model
國家自然科學基金 (81470889)。This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(81470889).
*Corresponding author, E-mail:zhangjie4155@sina.com
時間:2017-10-14 16∶06
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.R.20171014.1606.014.html
10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2017.05.014]
R576
2017-06-20)
編輯 慕 萌

