改進的分段主成分分析算法及其在前列腺分割中的應用
宋建萍 石勇濤

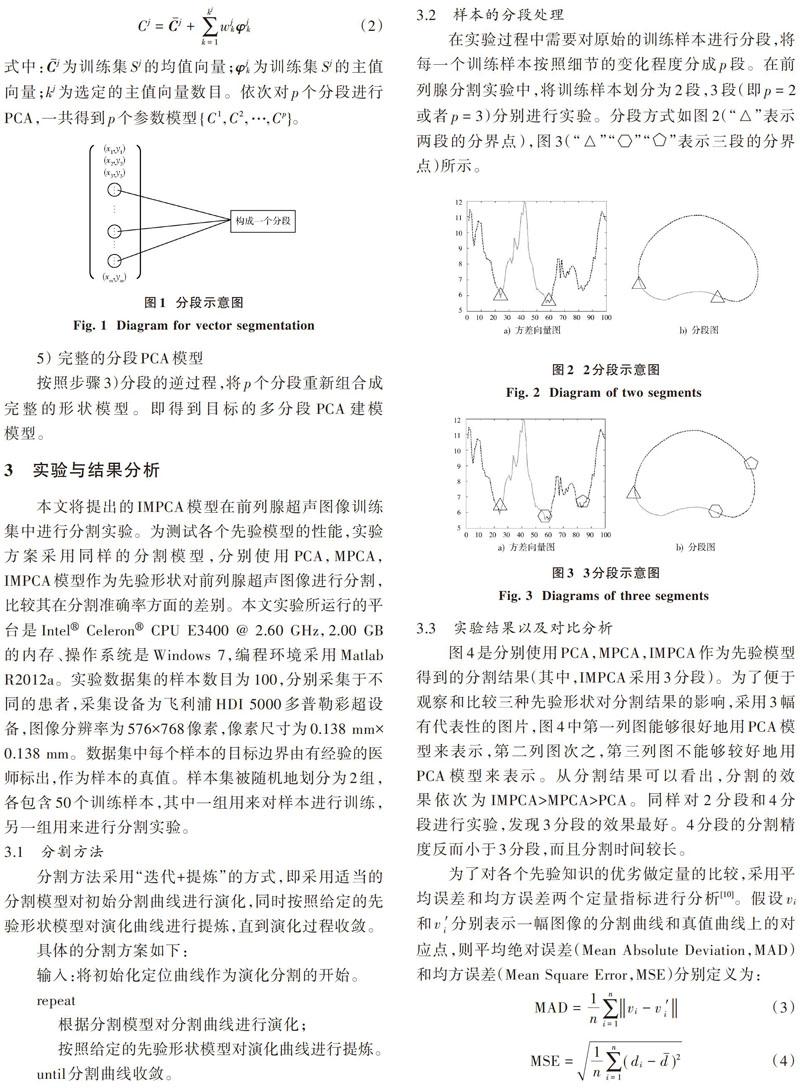
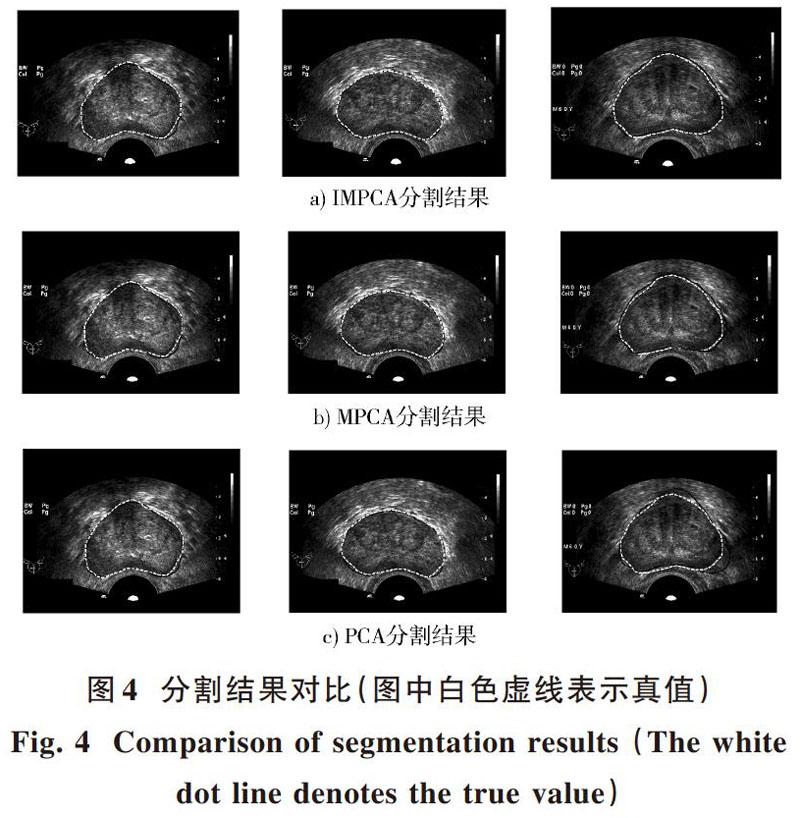
摘 要: 主成分分析(PCA)作為形狀建模中的經典算法,在訓練階段考慮訓練樣本的整體信息,而忽略了樣本的局部細節信息。分段主成分分析(MPCA)針對PCA的不足改進了算法,在人臉識別應用中獲得了比傳統PCA更好的識別效果。但在MPCA中樣本一般都被劃分為同樣大小的子樣本塊,沒有考慮到實際的樣本局部動態變化信息。這里根據初始樣本的方差信息對MPCA算法進行改進,將樣本劃分成尺寸大小不一的多類樣本(分段樣本),然后分別對分段樣本做主成分分析,得到原始樣本的分段PCA模型。將該模型應用于前列腺超聲圖像分割實驗,結果表明其分割效果優于傳統的PCA算法和MPCA算法。
關鍵詞: 醫學超聲圖像分割; 先驗形狀; 分段樣本; 分段主成分分析; 前列腺圖像分割; 信息提取
中圖分類號: TN911.73?34; TP391.4 文獻標識碼: A 文章編號: 1004?373X(2018)13?0061?04
Abstract: The whole information of the training samples is considered in the training stage, but the local detailed information is ignored in principal component analysis (PCA), which is regarded as a classical algorithm of shape modeling. The modular PCA (MPCA) can make up for the deficiency of PCA, and obtain better recognition results than the conventional PCA in the application of face recognition, but in MPCA, the training example is generally divided into subsamples with the same size, and the local dynamic variation information of the practical sample isn′t considered. On the basis of the variance information of the initial information, the MPCA algorithm is improved, and the sample is divided into segmented samples with different size. The PCA is performed for the segmented samples to get the MPCA model of the initial sample. The model was applied to the segmentation experiment of prostate ultrasonic image. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is superior to the classical PCA and modular PCA algorithms.
Keywords: medical ultrasonic image segmentation; prior shape; segmented example; modular PCA; prostate image segmentation; information extraction
0 引 言
超聲圖像分割能夠為負責診斷和治療疾病的醫師提供患者精確且全面的各種定量分析數據,并以此作為依據展開相關的醫療工作。但是,由于醫學超聲圖像的成像原理和器官組織本身的特性差異,導致得到的醫學超聲圖像與普通圖像相比,不可避免地具有模糊、不均勻性等特點[1]。因此,在超聲圖像的分割中必須要加入待分割對象的先驗知識才能保證分割的正常進行[2]。
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)法是先驗形狀建模中的一種經典算法[3],它采用線性變換方法尋找一組最優的正交向量基,通過它們的線性組合來重構原始樣本,并使得重構后的樣本和原樣本的均方誤差最小[4],因此被國外學者率先運用于先驗形狀建模。PCA通常將整個訓練樣本作為操作對象,主要考慮樣本的全局特征,且樣本中的各個分量被同等對待,由此忽略了樣本的局部細節。為解決該問題,一些學者提出改進的PCA模型[5?8]。文獻[7]提出通過使用權值矩陣將待加強信息的比重提高來突出原始樣本中的微小信息;Rajkiran Gottumukkal提出將MPCA(Modular Principal Component Analysis)算法用于人臉識別,可以有效地提取圖像中重要的局部信息。MPCA與傳統PCA相比,在局部細節信息方面的效果會更好[6],但是,該算法還很少被用于形狀建模,且在分塊時,一般將原始樣本劃分成同樣大小的多塊子樣本[8?9],這雖然能在提取細節特征方面起到一定效果,但更為理想的方式是根據樣本不同部分的變化程度將樣本動態地劃分為不同大小的分塊,使得所建的先驗模型能更好地表達目標的形狀信息。
基于上述分析,本文提出一種改進的分塊主成分分析(Improved Modular Principal Component Analysis,IMPCA)方法并用于圖像目標的形狀建模,且將該先驗形狀模型在前列腺超聲圖像中進行分割實驗。實驗結果表明,所提出的IMPCA方法的分割效果要優于MPCA方法和傳統的PCA方法。
1 MPCA算法
MPCA算法的基本思想是將圖像劃分成同樣尺寸的多塊子圖像,比如[m×n]大小的原始圖像[U],將被劃分為[P×Q]塊同樣大小的子圖像矩陣,即:

表1是分別采用三種不同先驗模型得到的定量分析結果。
4 結 語
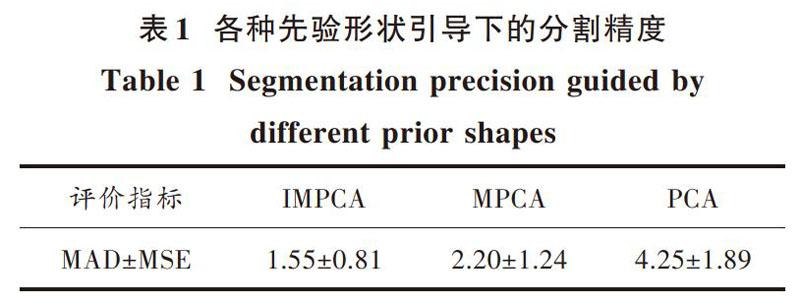
MPCA在提取目標的局部特征信息方面比傳統的PCA更為理想,但是均勻分塊則對原始信息的局部變化同等對待,還不能較好地根據原始信息的局部變化細節對目標進行分塊。本文提出的IMPCA方法能夠很好地克服這一點,使得分塊后的PCA建模能夠更好地逼近原始細節信息。因此,取得了比MPCA方法更好的分割結果。但是,并不是分段越多越好,需要根據具體情況尋找合適的分段。
參考文獻
[1] 黃建波,倪東,汪天富.基于先驗概率和統計形狀的前列腺超聲圖像自動分割方法[J].生物醫學工程研究,2015,34(1):15?19.
HUANG Jianbo, NI Dong, WANG Tianfu. Automatic segmentation method based on probability priors and statistical shape for prostate TRUS images [J]. Journal of biomedical engineering research, 2015, 34(1): 15?19.
[2] RATHI Y, VASWANI N, TANNENBAUM A. A generic framework for tracking using particle filter with dynamic shape prior [J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2007, 16(5): 1370?1382.
[3] BOUWMANS T, ZAHZAH E H. Robust PCA via principal component pursuit: a review for a comparative evaluation in video surveillance [J]. Computer vision and image understanding, 2014, 122: 22?34.
[4] 謝佩,吳小俊.分塊多線性主成分分析及其在人臉識別中的應用研究[J].計算機科學,2015,42(3):274?279.
XIE Pei, WU Xiaojun. Modular multilinear principal component analysis and application in face recognition [J]. Computer science, 2015, 42(3): 274?279.
[5] CREMERS Daniel, KOHLBERGER Timo, SCHN?RR Christoph. Shape statistics in kernel space for variational image segmentation [J]. Pattern recognition, 2003, 36(9): 1929?1943.
[6] GOTTUMUKKAL R, ASARI V K. An improved face recognition technique based on modular PCA approach [J]. Pattern recognition letters, 2004, 25(4): 429?436.
[7] SHEN D G, DAVATZIKOS C. An adaptive?focus deformable model using statistical and geometric information [J]. IEEE transactions on pattern recognition and machine intelligence, 2007, 22(7): 1?8.
[8] YANG J, ZHANG D, FRANGI A F, et al. Two?dimensional PCA: a new approach to appearance?based face representation and recognition [J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2004, 26(1): 131?137.
[9] ZHANG L, ZHU P, HU Q, et al. A linear subspace learning approach via sparse coding [C]// 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2011: 755?761.
[10] YAN P, XU S, TURKBEY B, et al. Discrete deformable model guided by partial active shape model for trus image segmentation [J]. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering, 2010, 57(5): 1158?1166.

