Non-adiabatic quantum dynamical studies of Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction?
Yue-Pei Wen(溫月佩),Bayaer Buren(布仁巴雅爾),and Mao-Du Chen(陳茂篤)
Key Laboratory of Materials Modi fication by Laser,Electron,and Ion Beams(Ministry of Education),School of Physics,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
Keywords:time-dependent wave packet method,non-adiabatic reaction,integral cross section,differential cross section
1.Introduction
The reactions of excited-state alkali atoms with hydrogen molecule have received much attention because of their unique advantages for studying non-adiabatic processes in reaction dynamics.[1-17]As the most intriguing characteristic,the alkali-hydrogen reactions are highly endoergic in their ground state.The energy to initiate the reaction is easily achieved via electronic excitation of the alkali atom,therefore the transitions of electronic states necessarily occur when the reaction proceeds from the excited entrance valley to the ground exit valley.[13]
For the Na+H2→NaH+H reaction,several excited states(32P,42S,42P,32D,and 62S)of sodium atom were considered in previous studies.Regarding the collision of Na(32P)+H2,both quenching[17-24](Na(3p)+H2→Na(3s)+H2)and reactive[15-20](Na(3p)+H2→NaH+H)processes were investigated.Motzkus et al.[15]demonstrated twostep collision process for the formation of sodium hydride from the collision of Na(3p)+H2,where the vibrationally excited hydrogen molecule from first quenching process plays a signi ficant role.The rate for NaH formation was determined by rate-equation-model based on the two-step reaction model,and other reaction schemes were ruled out.Regarding the Na(4p)+H2→NaH+H reaction,Bililign et al.[1,2]observed a bimodal rotational state distribution for the NaH products,which was attributed to the two different reaction pathways.The side-on-attack mechanism leads to highly rotationally excited products,while the end-on-attack mechanism generates products with low-rotational excitation.Motzkus et al.[17]performed comparative studies for the two previous reactions using several nonlinear techniques.Consequently,vibrational state distributions of NaH from two reactions were determined.The time scale of NaH formation revealed that the Na(4p)+H2→NaH+H reaction is direct.Chang et al.[4]obtained rotational and vibrational state distributions of NaH from the reactions of Na(42S,32D and 62S)plus H2.A bimodal rotational feature was found in the 42S and 32D reaction,which is similar to the 42P reaction.However,rotationally cold but vibrationally hot product population was found in the 62S reaction which was explained by the collinear abstraction mechanism.The results conclude that the increasing atomic size of Na may hinder the insertion reaction mechanism.
In this work,we intend to investigate the dynamics of the Na(3p)+HD(ν =1,j=0)→ NaH/NaD+D/H reaction.The reaction involves two coupled potential energy surfaces(PESs),thus diabatic PESs should be considered in the dynamical calculations.Recently,a new set of highly accurate diabatic PESs(called WYYC[16]PESs)of the NaH2system was developed by Wang et al.[16]and the dynamic studies were carried out for the Na(3p)+H2(ν =0,j=0)→ NaH+H reaction.For dynamical calculations of state-to-state reactions,the quasi-classical-trajectory[25-28]method and timedependent wave packet[29-37](TDWP)method have been used widely.The TDWP method has unique advantage for the dynamical study of non-adiabatic reactions.In the present work,the dynamical calculations of the Na(3p)+HD(ν=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction are carried out by using TDWP method based on the WYYC diabatic PESs.The rest of this paper is organized as follows.A brief description regarding TDWP method is presented in Section 2.Dynamic results and detailed discussion are performed in Section 3.Fi-nally,some conclusions are drawn from the present study in Section 4.
2.TDWP method
The TDWP method is particularly powerful for studying the dynamics of state-to-state reactions and has been used to study many atom-diatom reactions[29-32]and reactions involving polyatom.[33-37]This method is also effective to study the dynamic of non-adiabatic reactions,[10,16,32]which involve several coupled PESs.The basic principle of the TDWP method is to solve the time-dependent Schr¨odinger equation.The initial wave packet containing all the information about reactants propagates on the PES,and the dynamic information can be extracted from total wave function after propagating for enough time.The solution of wave function at time t is given by
For an atom-diatom reaction of A+BC→AB+C,the timeindependent Hamiltonian operator in the body- fixed reactant Jacobi coordinates R(distance of A from the center of mass of BC),r(bond length of BC)and γ(the angle between R and r)can be written as

The initial wave function ψ(t=0)can be written as
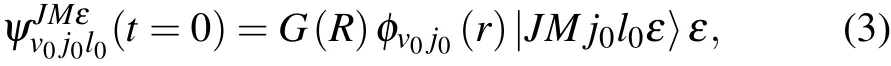
where|JMj0l0ε〉ε isthespace- fixed rotational basis,G(R)isa Gaussian wave packet,and φv0j0(r)is the rovibrational eigenfunction of the BC molecule.
The second order split operator[38]is used to propagate the wave packet.During the propagation of the wave packet,the absorbing potential expressed by the R and r coordinate is used to avoid the re flection of the wave packet from the boundaries.The absorbing potential used in the TDWP calculations is in the following form:
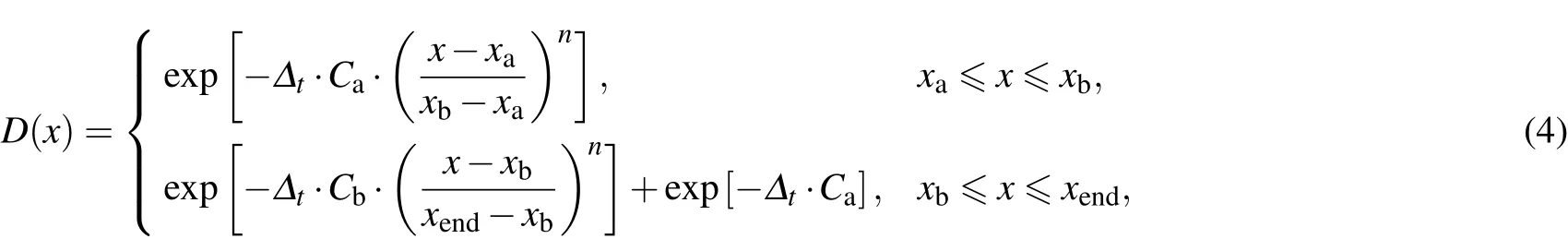
where x represents the R or r coordinate;xa,xb,and xendare the positions of absorbing potentials;Ca,Cb,and n determines the strength of the absorbing potential.
After propagating for enough time,the state-to-state S-matrix SJεvjK←v0j0K0(E)is obtained by using the reactant coordinate-based(RCB)[40]method.
The state-to-state reaction probability is obtained by using
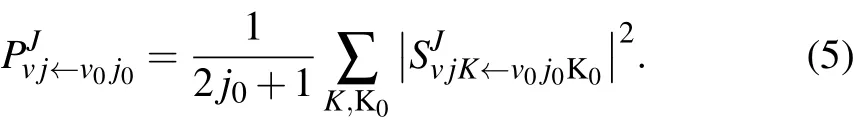
The state-to-state integral cross section(ICS)is calculated from
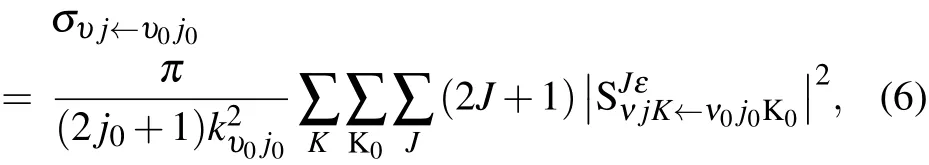
where kυ0j0is the momentum in the entrance channel.The state-to-state differential cross section(DCS)is obtained from
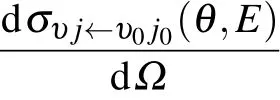
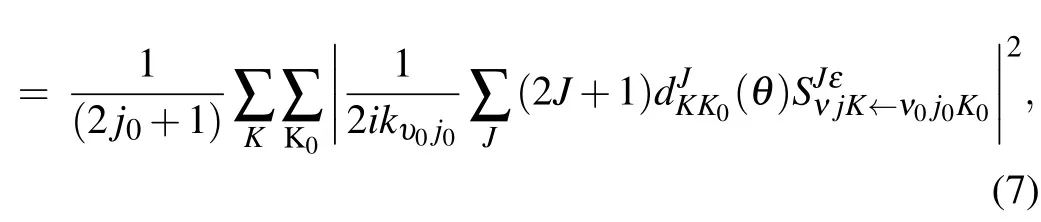
where θ is the scattering angle,and dJKK0(θ )is the reduced Wigner rotation matrix.
For a non-adiabatic reaction correlated with two electronic states,diabatic PESs should be considered in the TDWP calculations.The,r,γ)in Eq.(2)can be written as a 2×2 Hermitian matrix
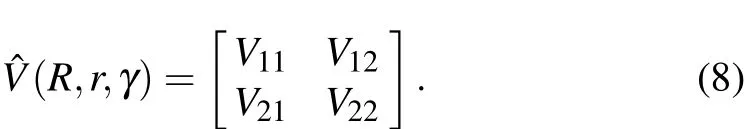
In this work,the WYYC[16]diabatic PESs are employed in the TDWP dynamical calculations for the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction.A more detailed description regarding the TDWP method can be found in the relevant literature.[39-42]
3.Results and discussion
In this work,state-to-state quantum dynamical calculations of the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H re-action are carried out by using the TDWP method.The initial rotational-vibrational states of reagent are set to be v0=1,and j0=0.The full Coriolis-coupling is involved in the TDWP calculations.A lot of tests were carried out on the reaction probability of different total angular momentum values to obtain appropriate numerical parameters for the TDWP calculations,which are listed in Table 1.The state-to-state reaction probabilities,ICSs and DCSs are calculated for two reaction channels.
For the non-adiabatic Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction,electronic states of reactants and products correlate with the first excited and ground electronic states of NaH2system,respectively.This indicates that the transition between two electronic states occurs along the reaction path.In the present work,the WYYC[16]diabatic PESs are used in the TDWP calculations.Regarding the WYYC[16]PESs,the ab initio single-point energy is calculated by the multi-reference con figuration interaction method with large basis sets(cc-pw-CVQZ for Na atom and aug-cc-PVQZ for H atom),and the neural network method is used to fit the PESs.The V22surface of WYYC[16]PESs connects elecelectronicstates of reactant and products of the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction.Therefore,the initial wave packet is constructed on the V22surface and product information was collected at the V22surface after propagating for enough time in the TDWP calculations.For a better description of the non-adiabatic dynamics in the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction,a schematic energy diagram of the reactants and products is shown in Fig.1 based on the WYYC[16]PESs.Blue and red lines represent V11and V22surface of WYYC[16]diabatic PESs,respectively.The cross of V11and V22curves indicates the transition between two electronic states along the reaction path.As seen from product energy diagram,the product channel of NaD+H opens easier than that of NaH+D,because vibrational constant of NaD molecule is smaller than that of NaH.There still exists a threshold in reaction when HD is excited to v=1 state;however,the threshold disappears when HD is excited above the v=2 state.Moreover,it should be noted that there is a potential well along the reaction path,which may generate a longlived complex.A more detailed description regarding WYYC diabatic PESs could be found in Ref.[16].
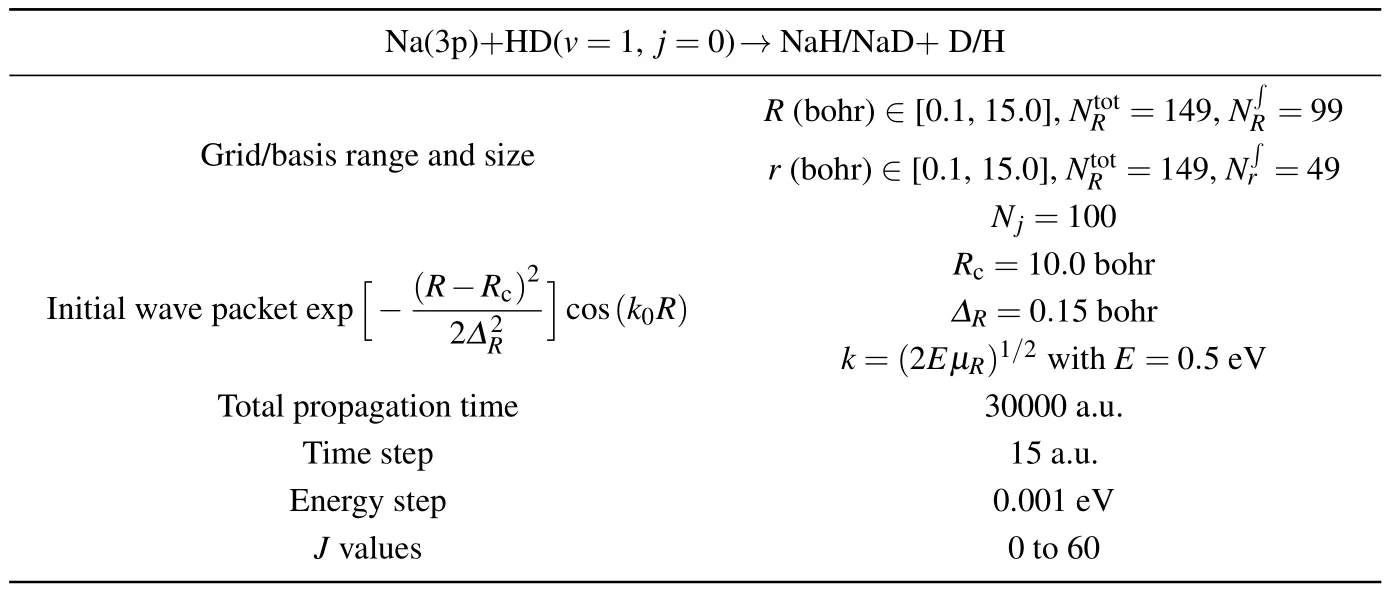
Table 1.Numerical parameters used in TDWP calculations.
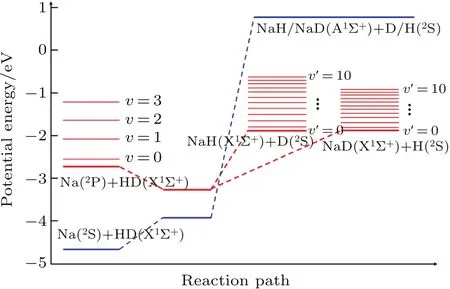
Fig.1.Energy diagram of reactants,products,and the most possible reaction path on WYYC diabatic PESs.Blue and red line represent V11 andV22elements of WYYC PESs,respectively.
The reaction probabilities of two reaction channels from the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction are shown in Fig.2 each as a function of collision energy at several selected J values.Many oscillation peaks are found in reaction probability curves,which can be attributed to the dynamical resonances.The reaction threshold becomes larger and the values of reaction probabilities decrease as the J value increases,which is attributed to the increasing centrifugal potential energy in the total Hamiltonian.Due to the fact that the increased centrifugal potential energy can reduce the depth of potential well in the reaction path,the oscillations in the reaction probabilities gradually subside as the J value increases.In addition to these similarities,there are also some differences in reaction probability between two reaction channels.The reaction threshold of NaD+H channel(almost 0.186 eV)is lower than that of NaH+D channel(almost 0.206 eV)because of the difference in zero-energy point between NaD(almost 0.057 eV)and NaH(almost 0.077 eV)molecule.This is consistent with the energy diagram as shown in Fig.1.Moreover,the threshold of the J=60 partial wave for the NaD+H product channel is approximately 0.45 eV,which is higher than that of NaH+D product channel(approximately 0.4 eV).The convergence of reaction probability for the NaD+H channel is faster than that of NaH+D channel,which may be attributed to the different reduced mass in centrifugal potential at product Jacobi coordinates.
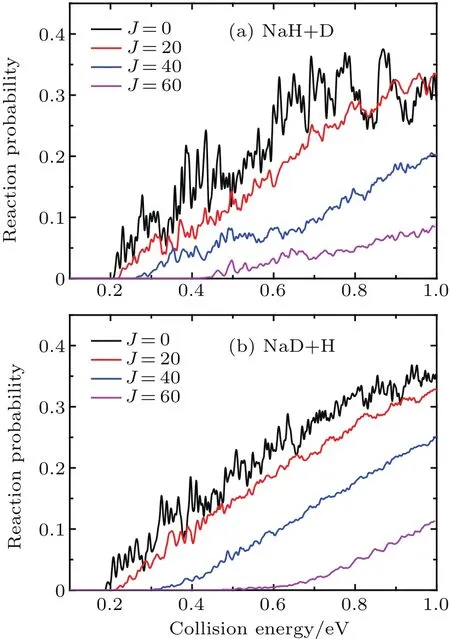
Fig.2.The reaction probabilities of the two reaction channels for Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction at several selected J values.
The state-to-state ICSs and DCSs are calculated for collision energy up to 0.4 eV based on the convergence of reaction probability at the maximum value of J.The total and product vibrationally state-resolved ICSs of two product channels from the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction are shown in Fig.3.The ICS curves are very smooth and increase monotonically as the collision energy increases.The vibrationally excited products rise with the increase of collision energy.Due to the vibrational constant of NaD being smaller than that of NaH,the opened channels for NaD+H are more than for NaH+D.Thresholds of ICSs are consistent with those shown in the reactant and product energy diagram.From the product’s vibrational state-resolved ICSs,the NaD and NaH products both prefer to form in the vibrational ground state in the whole range of the calculated collision energy.As seen from total ICSs,the NaD+H reaction channel opens easier than the NaH+D reaction channel.However,the NaH+D channel gradually overtakes the dominant position as collision energy increases.To clarify this competition,the cross-section branching ratio ICS(NaH)/ICS(NaD) is shown in Fig.4as a function of collision energy. At low collision energy(<0.227 eV),branching ratio is lower than 1.0 and increases monotonically with collision energy increasing.For high collision energy(>0.227 eV),branching ratio is larger than 1.0 and fluctuates around 1.3.Therefore,the NaD+H product channel is dominant in the Na(3p)+HD(v=1)reaction at low collision energy(<0.227 eV),and it is surpassed by NaH+D channel as collision energy increases.A similar competition between two reaction channels was found in the Au+HD reaction[43]anditwas explainedas thefactthattheDatomcan easily get away from the potential well because of its larger mass than that of the H atom.This explanation is also applicable to the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction.
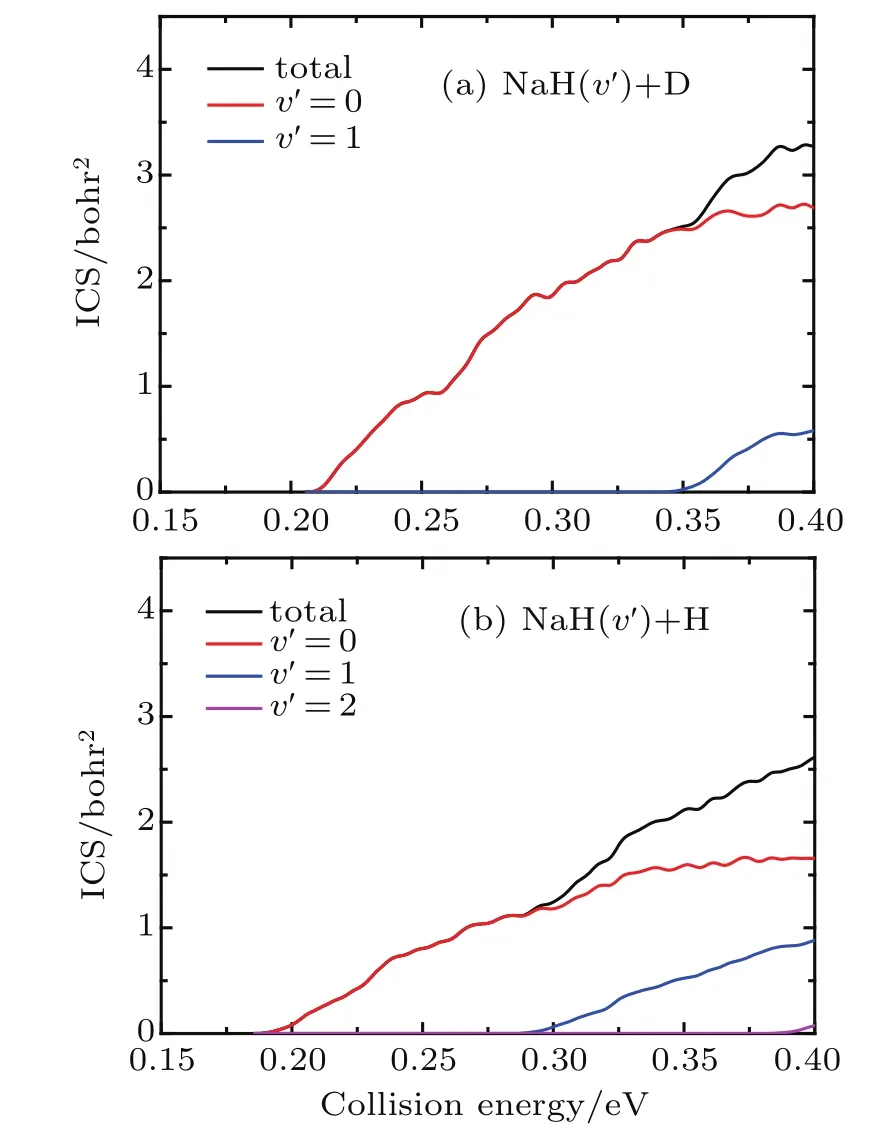
Fig.3.Total and product vibrational state-resolved ICSs of two reaction channels for Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction.
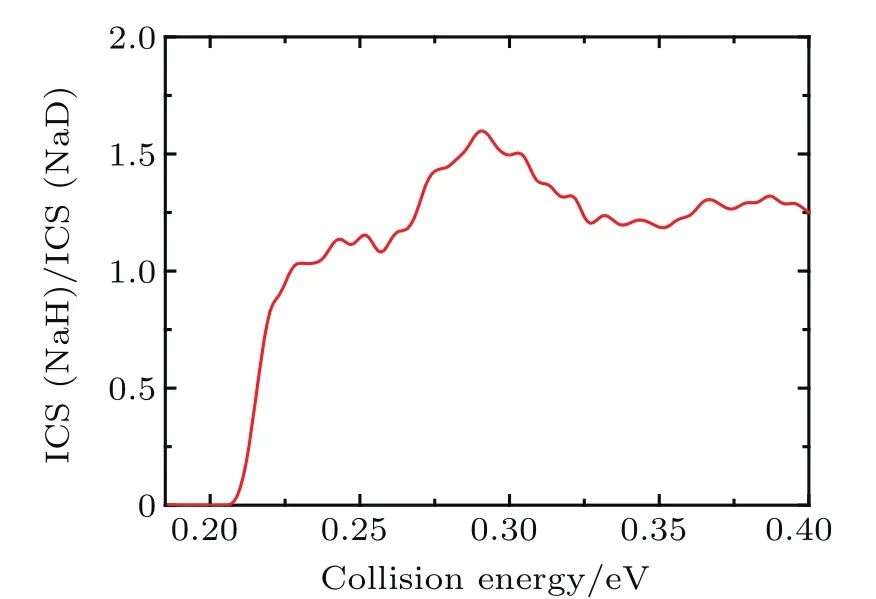
Fig.4.The cross-section branching ratio ICS(NaH)/ICS(NaD)of the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction versus collision energy.
To obtain more details regarding energy distribution of products from the Na(3p)+HD(v=1)reaction,rotational state distributions of products at some values of selected collision energy are shown in Fig.5.Only vibrational ground state products are depicted in Fig.5 because products primarily form in the vibrational ground state,as mentioned above.As seen from Fig.5,products of two reaction channels both prefer to form in rotationally excited states that are different from the vibrationally exited states.The product rotational states’distributions become broader and the maximum populations of j′become larger as collision energy increases.The rotational state distribution of NaD is broader than that of NaH and the maximum population of j′in the NaD is larger than that in the NaH at the same collision energy.This is attributed to fact that the rotational constant of NaD is smaller than that of NaH,therefore,the more the channels are opened for NaD,the larger the product rotational state density will be than that of NaH at the same collision energy.

Fig.5. Rotational state distributions of products from the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction respectively at four values of collision energy(0.25,0.30,0.35,and 0.40 eV).
The three-dimensional total DCSs of two reaction channels from the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction are shown in Fig.6.There are many peaks at extreme angles 0°and 180°which are corresponding to forward and backward scattering,respectively.The products of two reaction channels both prefer forward scattering,especially at low collision energy.Signi ficant forward scattering peaks reveal that the reaction is dominated by the direct reaction mechanism.Small backward scattering peaks rise as the collision energy increases,which may be attributed to the opening collinear abstraction reaction channel.To understand the information regarding product scattering direction in depth,the product state-resolved angular distributions of two product channels at several values of selected collision energy are shown in Fig.7.The forward scattering products from the NaH+D channel are mainly at lower rotational states(j′< 5).However,the forward scattering products from the NaD+H channel each have a wide rotational state distribution.The forward scattering products from two reaction channels both can be excited to higher rotational excited states as the collision energy increases,which is consistent with the above discussion.Moreover,many oscillations are found along the scattering angle.A similar phenomenon was observed in the H+HD→H2+D reaction,[44]and the observed forward angular oscillations were explained by the contribution of partial waves.The period Δθ in the angular oscillation can be used to estimate which J partial wave has primary contribution by using J=180°/Δθ -1/2.[44]As seen from Fig.7,the period Δθ decreases as the collision energy increases.This indicates that the J value of partial wave contributing to the oscillations increases as the collision energy increases.
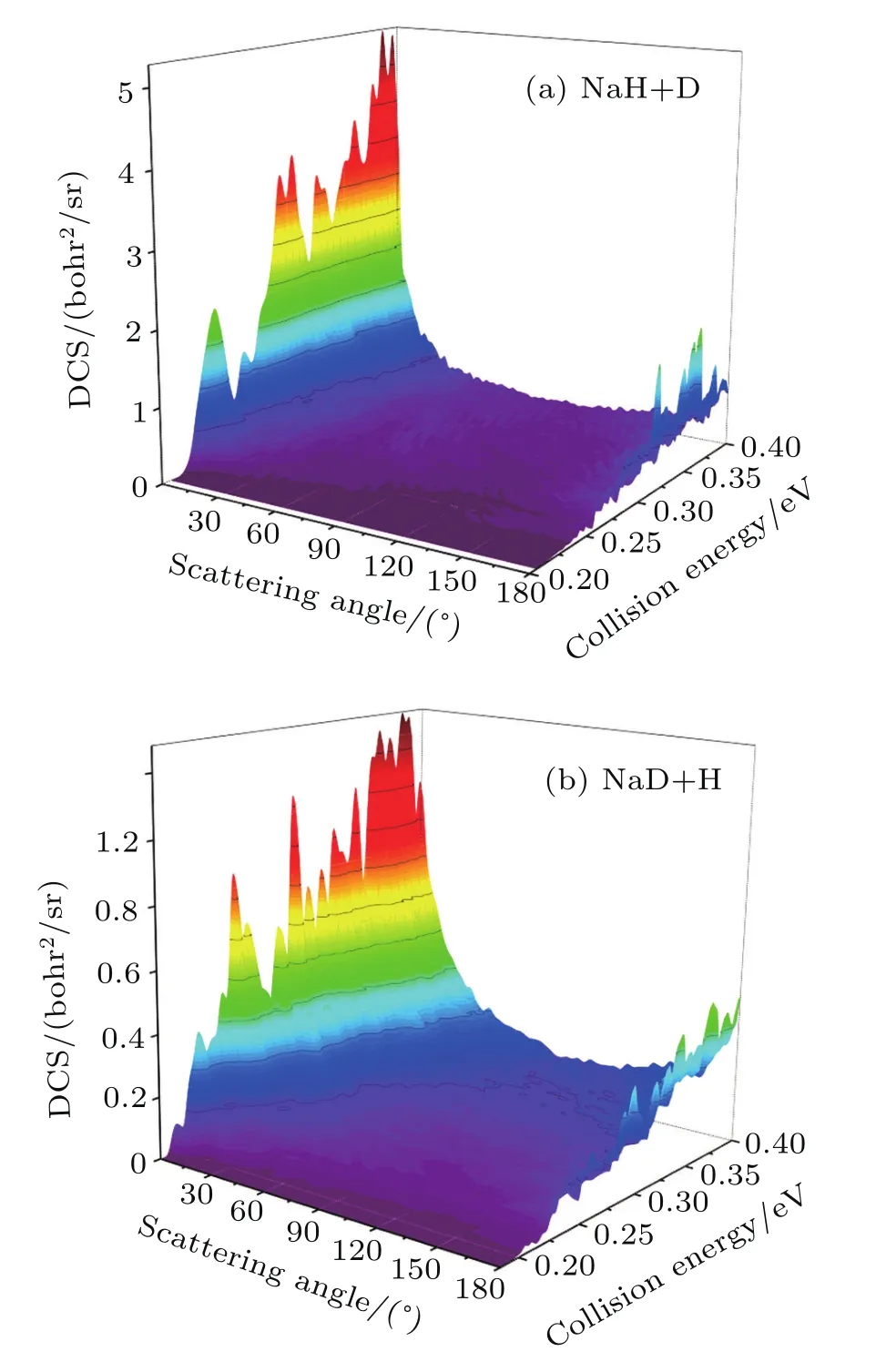
Fig.6. Three-dimensional DCSs of two reaction channels for Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction versus collision energy and scattering angle.
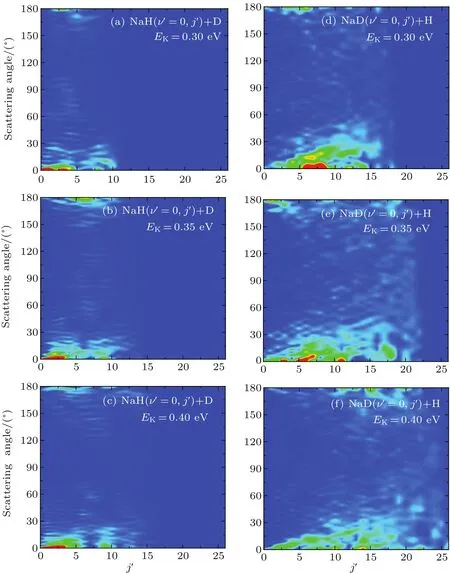
Fig.7.State-to-state DCSs of two reaction channels for Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction at three collision energies(0.3,0.35,and 0.4 eV).
4.Conclusions
In this work,the dynamics of the non-adiabatic Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)→NaH/NaD+D/H reaction are investigated using the TDWP method.The state-to-state reaction probabilities,ICSs and DCSs of two product channels from the Na(3p)+HD(v=1,j=0)reaction are calculated.The threshold of the NaD+H product channel is lower than that of NaH+D because of the difference in zero-point energy between NaD and NaH.The product vibrational-state resolved ICSs show that the products of two reaction channels both prefer to form in vibrational ground state.However,distributions of product rotational states have peaks at excited states.The curves of total ICS indicate that there is a competition between the two product channels with collision energy changing.From the cross-section branching ratio it follows that the NaD+Hchannel dominates the Na(3p)+HD(v=1)reactionat the collision energy lower than 0.227 eV,and then the NaH+D channel gradually becomes dominant as the collision energy increases.Total DCSs show that the products of two reaction channels both prefer forward scattering.The forward scattering NaH products mainly populate at lower rotational excited sates,while NaD products have a broad rotational state distribution.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Theoretical study of overstretching DNA-RNA hybrid duplex?
- influence of carbon coating on the electrochemical performance of SiO@C/graphite composite anode materials?
- Spin glassy behavior and large exchange bias effect in cubic perovskite Ba0.8Sr0.2FeO3-δ?
- Aging mechanism of GaN-based yellow LEDs with V-pits?
- Magnetotransport properties of graphene layers decorated with colloid quantum dots?
- Temperature-dependent subband mobility characteristics in n-doped silicon junctionless nanowire transistor?

