攪拌摩擦焊對接面附近材料流變行為研究
楊誠樂 陳高強(qiáng) 劉瞿 史清宇


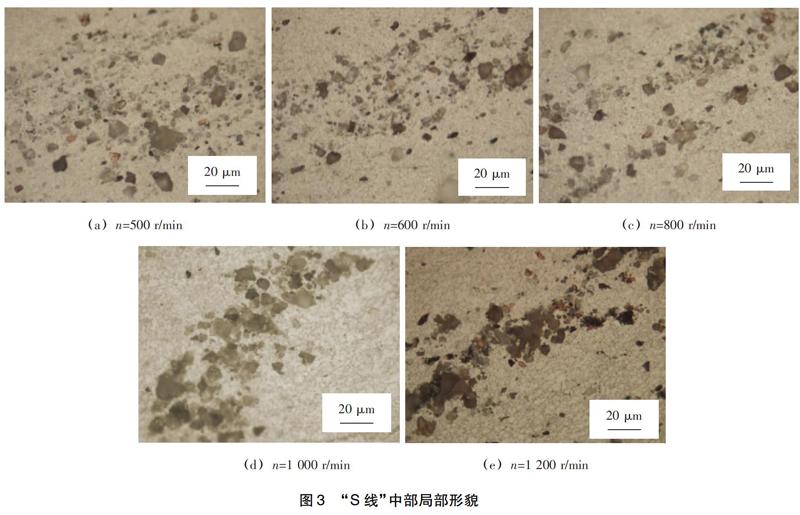
摘要: 攪拌摩擦焊(FSW)過程中的對接面附近工件材料流動變形行為與許多缺陷的形成密切相關(guān)。通過開展攪拌摩擦焊試驗(yàn),研究對接面附近材料在FSW過程中的流動與變形行為。針對AA2024T3鋁合金進(jìn)行研究,通過采用預(yù)制氧化膜為標(biāo)示材料的方法進(jìn)行標(biāo)示,并采用不同的焊接參數(shù)進(jìn)行FSW試驗(yàn)。結(jié)果表明,預(yù)制氧化膜在焊接過程中完全破碎,在焊縫中以氧化鋁顆粒的形式呈有規(guī)律的“S線”分布,并且隨著攪拌頭轉(zhuǎn)速的上升,宏觀上“S線”分布寬度降低,局部上氧化鋁顆粒尺寸越大,分布越緊密。標(biāo)示材料在接頭中的沉積特征體現(xiàn)出,在較低的攪拌頭轉(zhuǎn)速下,對接面附近工件材料在FSW過程中經(jīng)歷了劇烈的應(yīng)變,而隨著攪拌頭轉(zhuǎn)速的提高,總應(yīng)變量反而減小。
關(guān)鍵詞: 攪拌摩擦焊;對接面;材料流動;材料應(yīng)變
中圖分類號:TG 453
Research on the material flow and strain behavior near the initial butt surface in friction stir welding
Yang Chengle1,2, Chen Gaoqiang1,2, Liu Qu1,2, Shi Qingyu1,2
(1.State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;2.Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: During friction stir welding (FSW) , the flow and deformation of parent material near the butt surface is closely related to the formation of many defects. The flow and deformation behavior of initial butt surface material were studied by carrying out an experiment of FSW. AA2024T3 aluminium alloy was utilized as parent material and processed under different welding condition. Oxide film was prefabricated on butt surfaces as marker material. All oxide films were broken into particles, deposited into the weld and formed a regular line named lazy S. The increasing rotation rate of the tool results in the decreasing of the width of the macro spread of lazy S, and meanwhile, in a specified area, the particles size is coarser and the spread of them is narrower. The deposition pattern of the marker material reveals that low rotation rate of the tool introduces severe strain to the parent material near the butt surface during FSW process. However, as the rotation rate increasing, the total strain in the same area decreases.
Key words: friction stir welding; butt surface; material flow; material strain
0 前言
攪拌摩擦焊(FSW)是一種環(huán)保、無消耗的固相焊焊接工藝[1-6]。經(jīng)過20多年的發(fā)展,F(xiàn)SW已從工藝開發(fā)逐漸走向大規(guī)模工業(yè)應(yīng)用[7-8]。學(xué)術(shù)界與工程界普遍認(rèn)識到,F(xiàn)SW接頭中的一些特有的組織特點(diǎn)及缺陷形式,如對接面表面的氧化物在焊縫中富集形成的“S線”[9-14]、接頭底部材料焊合不充分形成的根部缺陷[15-19]等,均與對接面附近的材料流動變形行為密切相關(guān)。因此,為了縮短焊接工藝的開發(fā)周期,有必要專門針對FSW中對接面附近材料的流動變形行為及規(guī)律進(jìn)行深入研究。
由于FSW過程中固態(tài)金屬在高速旋轉(zhuǎn)攪拌頭周圍毫米級的薄層內(nèi)發(fā)生劇烈的塑性流變,因此采用試驗(yàn)手段直接獲取FSW過程中的材料塑性流變行為十分困難。……

