Magnetoresistance hysteresis in topological Kondo insulator SmB6 nanowire?
Ling-Jian Kong(孔令劍),Yong Zhou(周勇),Hua-Ding Song(宋化鼎),Da-Peng Yu(俞大鵬),and Zhi-Min Liao(廖志敏),3,4,?
1State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics,School of Physics,Peking University,Beijing 100871,China
2Shenzhen Institute for Quantum Science and Engineering and Department of Physics,Southern University of Science and Technology,Shenzhen 518055,China
3Beijing Key Laboratory of Quantum Devices,Peking University,Beijing 100871,China
4Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter,Beijing 100871,China
Keywords:topological Kondo insulator,magnetocaloric effect,magnetoresistance hysteresis
1.Introduction
SmB6,a Kondo insulator that had been investigated for several decades,was recently predicted theoretically and confirmed experimentally to be a candidate of topological Kondo insulator.[1–12]In this strongly correlated system, the hybridization of 5f electrons and 4d electrons opens a bulk gap and the spin-momentum-locked topological surface state emerges.[13,14]The spin-texture of surface states has been observed by spin-resolved angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy(SRARPES).[15–17]Moreover,the Fermi level always lies in the gap by its Kondo insulator nature,leading to the transport behaviors dominated by surface states.[3,18–23]The transport properties of SmB6in a low temperature range have been studied extensively,showing that the surface states dominate the transport.However,the detailed investigations in the temperature range,where both surface and bulk states contribute to transport,are still desirable.In a temperature range from 10 K to 4 K,the bulk channel is gradually closed,and the surface states emerge to remarkably influence the transport properties.
Here in this paper,we report the magnetotransport properties of individual SmB6nanowire at temperatures ranging from 10 K to 4 K,where the resistance is very sensitive to temperature.A hysteresis loop in magnetoresistance(MR)is observed,when magnetic field direction is along the nanowire axis.When the magnetic field changes from forward to backward sweep,a sudden increase of resistance occurs.Such a resistance jump is detected both at a bias current of 0.1μA,where the MR is negative,and at 5μA,where the MR is positive.The magnitude of the resistance variation is proportional to the slope of the resistance–temperature(R–T)curve.The experimental results are well understood by considering the magnetocaloric effect(MCE).The backward sweep of magnetic field results in the sample cooling and increase of resistance. The MCE has been reported in many materials with Lanthanide atoms.[24–27]Since Sm is also a lanthanide,[28]the MCE may also be significant in SmB6.
2.Experiment
The SmB6nanowires were grown by chemical vapor deposition(CVD)method in a tube furnace.[29,30]SmB6nanowires were first transferred onto a Si substrate with a 285-nm-thick SiO2layer.The Ti/Au electrodes were deposited on individual SmB6nanowire by electron beam evaporation after removing the oxide layer from the nanowire surface by Ar-ion etching.Four terminal measurements were carried out in an Oxford cryostat via lock-in technique with a current source of 17.777 Hz.
3.Results
Figure 1(a)shows the scanning electron microscope(SEM)image of SmB6nanowires with lengths ranging from 10μm to 20μm. The transmission electron microscopy(TEM)image shown in Fig.1(b)indicates that the nanowire possesses high crystal quality grown along the[001]direction with lattice constant ~0.41 nm. The inset of Fig.1(b)shows the electron diffraction pattern of the nanowire in the selected area. The SEM image of a typical device is shown in Fig.1(c).The variation of nanowire resistance with temperature is shown in Fig.1(d). Below 20 K,the resistance increases sharply with temperature decreasing and finally is saturated at 3 K.The saturated resistances at low temperatures are well consistent with the fact that the bulk state is insulating and only the surface state is conductive.By fitting the resistance at 4 K–10 K,we obtain the bulk transport gap to be about 3.2 meV.

Fig.1.(a)SEM image of SmB6 nanowires grown by CVD method.(b)TEM image of SmB6 nanowire,with inset showing corresponding diffraction pattern.(c)SEM image of typical device.(d)Variation of resistance of SmB6 nanowire with temperature.
Figure 2(a)shows the schematic diagram of the measurement setup. Magnetic field is directed along the nanowire axis. The bias current is 0.1μA.As shown in Fig.2(b),the MR curve exhibits no hysteresis behavior at 1.5 K,because the transport is only carried out by the surface states.The parabolic negative MR is observed,which is attributed to the decrease of spin-related scattering with magnetic field increasing.[30]Figures 2(c)–2(f)show the MR values of the same sample at 4 K–7 K,respectively. As temperature increases,the magnitude of negative MR decreases monotonically.The negative MR starts to deviate from parabolic curve and double-shoulder structures emerge at 5 T–7 T:the lowfield part of the negative MR curve even changes into positive MR.All these phenomena originate from the fact that bulk states play a more and more important role as temperature increases.The topological surface states with spin–momentum locking are responsible for the negative MR due to the spinpolarized transport.On the other hand,the trivial bulk states result in a positive MR.
It is worth noting that the MR curves show obvious hysteresis behaviors at temperatures ranging from 4 K to 7 K as shown in Figs.2(c)–2(f). The MR hysteresis occurs as the magnetic field reverses from forward to backward sweep.The hysteresis loop becomes larger and larger with temperature increasing.At 7 K,as shown in Fig.2(f),the sudden change of MR at the turning point from forward to backward sweep of magnetic field reaches as large as 0.3%.

Fig.2.Plots of MR of SmB6 nanowire versus B,measured at different temperatures.The magnetic field is parallel to SmB6 nanowire.The bias current is 0.1μA.(a)Schematic diagram of the nanowire device,(b)MR at 1.5 K without hysteresis behavior.(c)–(f)The MR values versus B at 4 K,5 K,6 K,and 7 K,respectively.The hysteresis behavior gradually becomes obvious.
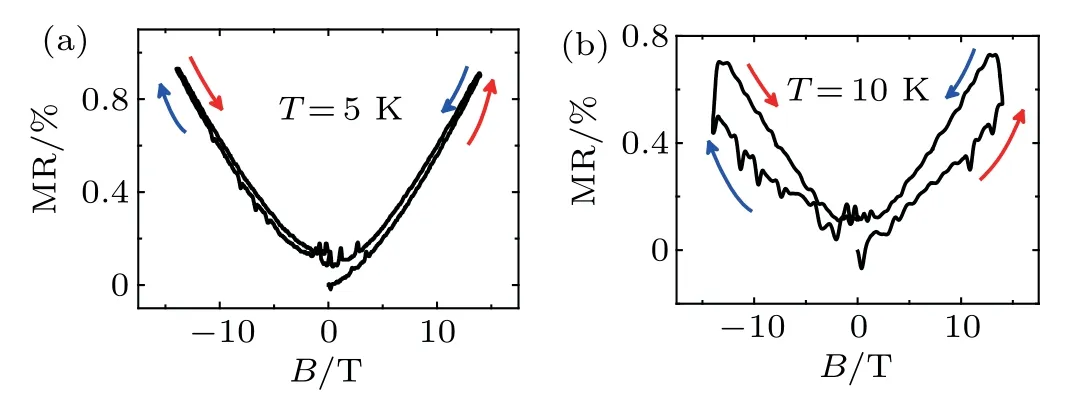
Fig.3. Variations of MR with B of SmB6 nanowire measured at different temperatures.Magnetic field is parallel to SmB6 nanowire.Bias current is 5μA.(a)Variations of MR with B at 5 K and(b)at 10 K.Although the MR is positive,the hysteresis behavior is still observed.
To further investigate the hysteresis behavior,we perform the measurements under a bias current of 5μA.At this large current,bulk states can be activated even at 1.5 K and a positive MR is induced.[30]At 5 K,as shown in Fig.3(a),the MR curve still exhibits slight hysteresis behavior even the MR becomes positive.It is interesting to note that the resistance is still larger in the backward sweep process than that in the forward sweep process.The MR curve at 10 K shows more obvious hysteresis behavior(Fig.3(b)).
The MR under a magnetic field perpendicular to both the substrate and the nanowire is further investigated. The measurement schematic diagram is shown in Fig.4(a).With 0.1-μA current bias,a negative MR is observed at both 5 K(Fig.4(b))and 10 K(Fig.4(c)),which is attributed to the magnetic field reduced spin-related scattering of the spin-polarized topological surface states.[30]Besides the overall negative MR,an MR dip is observed near the zero magnetic field,which results from the weak antilocalization effect.Furthermore,the hysteresis MR under a perpendicular magnetic field can still be observed(Figs.4(b)and 4(c)),while the hysteresis loop is much smaller than that under a parallel magnetic field.

Fig.4.(a)Schematic diagram of device;variations of MR with B at(b)5 K and(c)10 K of SmB6 nanowire measured at different temperatures with a perpendicular magnetic field and 0.1-μA bias current.The hysteresis loop is small.
We should first point out that SmB6does not have a ferromagnetic order,so the hysteresis behavior should not originate from the sample magnetism.We suggest an MCE mechanism to explain the MR hysteresis.When magnetic field is applied,the magnetic moments in SmB6tend to be aligned and the entropy of magnetism decreases.When the magnetic field is removed,the increase of the magnetism entropy is compensated for by absorbing the phonon energy,thus leading the temperature to decrease.This makes the system temperature in the magnetic field backward sweep process lower than that in the forward sweep process.On the other hand,the SmB6resistance increases sharply with temperature decreasing from 10 K to 4 K.This is why the hysteresis loop is much remarkable in that temperature range.Moreover,the hysteresis loop shows the same tendency under large(5μA)and small(0.1μA)bias current.Because even the bulk states are activated with large current bias,the MCE still exists.Besides,the MCE is symmetric for positive and negative magnetic field,which is also in accordance with our results. Nevertheless,an little MR hysteresis under a perpendicular magnetic field indicates the anisotropy of the MCE.
To verify the mechanism of MCE,we extracted the increments in resistance(?R)at the turning point of 14 T at different temperatures. The slopes of the R–T curve(dR/dT)at different temperatures are also extracted. The plot of ?R versus dR/dT is presented in Fig.5,which shows a linear dependence.The MCE leads to a change of temperature ?T,thus a change of resistance ?R.This is well consistent with the dR/dT in the R–T curve.

Fig.5.Plot of ?R versus dR/dT.?R is extracted as resistance increases at 14 T with reversing the magnetic field sweep direction at different temperatures.dR/dT values are extracted from slope of R–T curve at different temperatures.
4.Conclusions
In this work,we have observed a hysteresis behavior of MR of SmB6nanowire at temperature ranging from 10 K to 4 K.When magnetic field is parallel to SmB6nanowire,the resistance of SmB6nanowire exhibits a sudden increase at the turning point from forward to backward sweep of magnetic field. We suggest an MCE mechanism to explain this phenomenon.That is,the demagnetization induces a cooling process of the system,and thus the resistance increases with temperature decreasing.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Theoretical analyses of stock correlations affected by subprime crisis and total assets:Network properties and corresponding physical mechanisms?
- Influence of matrigel on the shape and dynamics of cancer cells
- Benefit community promotes evolution of cooperation in prisoners’dilemma game?
- Theory and method of dual-energy x-ray grating phase-contrast imaging?
- Quantitative heterogeneity and subgroup classification based on motility of breast cancer cells?
- Designing of spin filter devices based on zigzag zinc oxide nanoribbon modified by edge defect?

