Recovery of injured corticoreticulospinal tract following cranioplasty in an ischemic stroke patient: a diffusion tensor tractography study
The corticoreticular pathway (CRP), which mainly mediates proximal and axial muscles, is an important neural tract for gait and postural stability, whereas the corticospinal tract is mainly involved in control of the distal muscles (Jang et al., 2005). Since development of diffusion tensor tractography (DTT), which is derived from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), a few studies have demonstrated injury of neural tracts following cranioplasty in patients with stroke. In the current study, we report on a stroke patient who underwent decompressive craniectomy showed recovery of the CRP, using DTT.
A 48-year-old right-handed male was diagnosed with infarction in the left middle cerebral artery (Figure 1A). He underwent decompressive craniectomy for management of brain swelling at 2 days after onset. Three weeks later, he was transferred to the rehabilitation department of the same hospital. The patient exhibited right hemiplegia (shoulder abductor: 0, elbow flexor: 0, finger flexor:0, hip flexor: 0, knee extensor: 0, ankle dorsiflexor: 0) (Patermostro-Sluga et al.,2008). He underwent comprehensive rehabilitation for 5 weeks, however, his right hemiplegia was not recovered (shoulder abductor: 0, elbow flexor: 0, finger flexor: 0, hip flexor: 0, knee extensor: 0, ankle dorsiflexor: 0). The patient underwent cranioplasty using auto-bone 8 weeks after onset. After cranioplasty, his motor weakness of the right leg recovered as follows without motor recovery of the right arm: 10 weeks after onset (2 weeks after cranioplasty): hip flexor: 2-, knee extensor:2-, ankle dorsiflexor: 2-. He received comprehensive rehabilitative management(movement therapy — physical and occupational therapy, neuromuscular electrical stimulation etc.) in the same university hospital and a local rehabilitation hospital.At 6 months after onset (4 months after cranioplasty), he showed motor recovery of the right leg without recovery of the right arm (hip flexor: 3, knee extensor: 3,ankle dorsiflexor: 2). As a result, he became able to walk with mild assistance. This study was conducted retrospectively, and approval for the study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Yeungnam University Hospital (YUMC 2015-07-065-011) on August 28, 2015. The patient signed informed consent.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was performed twice (2 days before and 10 days after cranioplasty) using a 6-channel head coil on a 1.5T Philips Gyroscan Intera (Philips, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) with single-shot echo-planar imaging.For analysis of the corticoreticulospinal tract (CRT) — the first region of interest(ROI) was placed on the reticular formation and second ROI was placed on the tegmentum. Termination criteria used for fiber tracking were fractional anisotropy (FA) < 0.15, and angle < 27°.
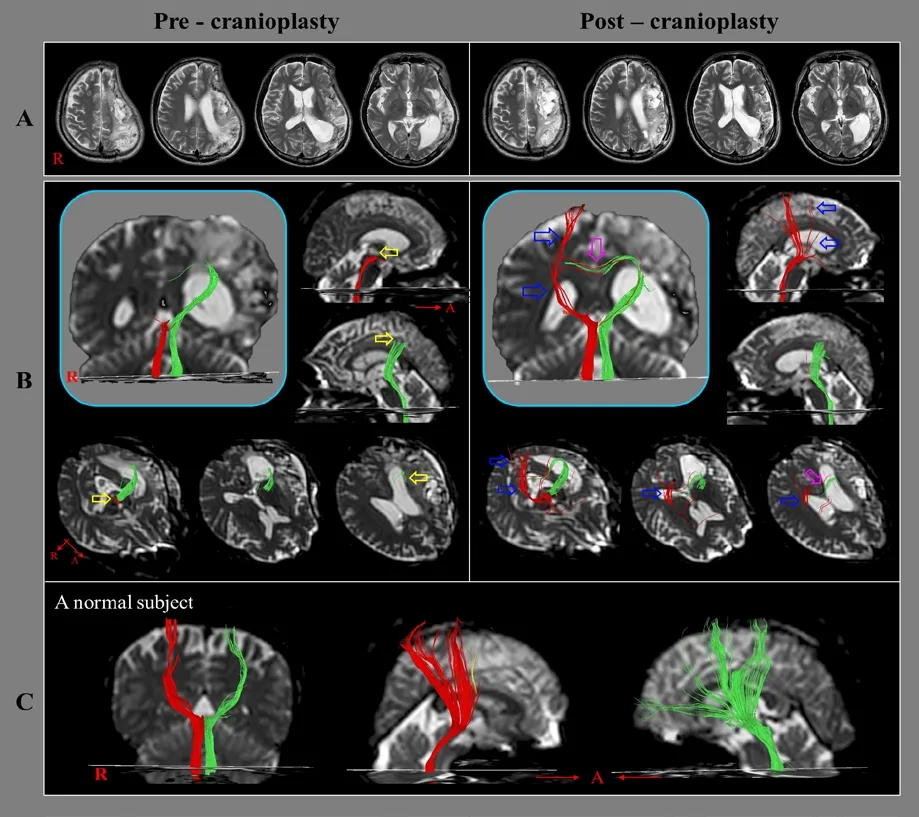
Figure 1 Diffusion tensor tractography for the corticoreticulospinal tract(CRT) of the patient with infarction in the left middle cerebral artery.(A) Brain MR images taken at 8 (pre-cranioplasty) and 10 (post-cranioplasty)weeks after onset show leukomalactic lesions in the left fronto-parieto-temporal lobes (orange arrows). (B) Results of diffusion tensor tractography(DTT) for the corticoreticulospinal tract (CRT). On the pre-cranioplasty DTT, discontinuations in both CRTs (the right CRT (red fiber): the brain stem level, and the left CRT (green fiber): the subcortical white matter level, yellow arrows) are observed. On the post-cranioplasty DTT, the discontinued right CRT is extended to the cerebral cortex level (blue arrows) and the transcallosal fibers of the discontinued left CRT are thickened (sky-pink arrows). (C)DTT results for the CRT in a normal subject (49-year-old male).
On the pre-cranioplasty diffusion tensor tractography (DTT), discontinuations of the CRTs (the right CRT: the brain stem level, and the left CRT: the subcortical white matter level) were observed compared with a normal subject (49-year-old male). On the post-cranioplasty DTT, the discontinued right CRT was extended to the cerebral cortex level and the transcallosal fibers of the discontinued left CRT were thickened (Figure 1B).
In this study, on follow-up DTTs, because the right CRT was extended to the cerebral cortex with thickening of transcallosal fibers of the left CRT concurrently with the motor recovery of the right leg, which is the main function of the CRT, it appeared that the changes of both CRTs mainly contributed to the patient's motor recovery of the right leg (Miyai et al., 2002; Jang and Seo, 2014). Cranioplasty can restore physiological intracranial dynamics by restoration of the contour of the skull. Thus, it is plausible that the reconstructed skull improves cerebral perfusion of the underlying lobes (Shahid et al., 2018). As a result, we think that cranioplasy contributed at least partly to the recovery of the right CRT in this patient. However, the limitations of DTT should be considered. Because regions of fiber complexity and crossing can prevent full reflection of the underlying fiber architecture,DTT may underestimate or overestimate the fiber tracts (Yamada et al., 2009).
In conclusion, the injured CRTs were recovered concurrently with motor recovery of the affected leg after cranioplasty in a stroke patient who underwent decompressive craniectomy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate recovery of an injured CRT following cranioplasty in stroke patients.
Sung Ho Jang1,Han Do Lee2,*
1 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine,Yeungnam University, Daegu, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Physical Therapy, Ulsan College University, Ulsan, Republic of Korea
*Correspondence to:Han Do Lee, PhD, lhd890221@hanmail.net.
orcid:0000-0002-1668-2187 (Han Do Lee)
Received:March 12, 2019
Peer review started:March 25, 2019
Accepted:September 19, 2019
Published online:January 6, 2020
doi:10.4103/1673-5374.272625
Author contributions:Study concept and design: SHJ and HDL; manuscript development and writing: SHJ; data acquisition and analysis and manuscript authorization:HDL. Both authors approved the final version of this paper.
Financial support:This work was supported by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (19-BD-0401).
Conflicts of interest:The authors reported no disclosures relevant to the manuscript.
Institutional review board statement:Approval for the study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Yeungnam University Hospital (YUMC 2015-07-065-011)on August 28, 2015.
Declaration of participant consent:The authors certify that they have obtained the appropriate participant consent forms. In the forms, the participants have given their consent for their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The participants understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity.
Reporting statement:This study followed the Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals developed by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors.
Biostatistics statement:No statistical method was used in this study.
Copyright license agreement:The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by both authors before publication.
Data sharing statement:Datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Plagiarism check:Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review:Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Diabetic retinopathy: a matter of retinal ganglion cell homeostasis
- Insights from human sleep research on neural mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease
- Protective effects of pharmacological therapies in animal models of multiple sclerosis: a review of studies 2014-2019
- EDITORIAL BOARD
- Temporal changes in the spinal cord transcriptome after peripheral nerve injury
- Neurotoxic role of interleukin-17 in neural stem cell differentiation after intracerebral hemorrhage