Development Progress of China’s First Mars Exploration Mission: Its Scientific Objectives and Payloads*
JIA Yingzhuo ZOU Yongliao ZHU Yan DU Qingguo FAN Yu CHEN Yuesong WANG Chi
Development Progress of China’s First Mars Exploration Mission: Its Scientific Objectives and Payloads*
JIA Yingzhuo ZOU Yongliao ZHU Yan DU Qingguo FAN Yu CHEN Yuesong WANG Chi
(100190)
China’s first Mars exploration mission is scheduled to be launched in 2020. It aims not only to conduct global and comprehensive exploration of Mars by use of an orbiter but also to carry out in situ observation of key sites on Mars with a rover. This mission focuses on the following studies: topography, geomorphology, geological structure, soil characteristics, water-ice distribution, material composition, atmosphere and ionosphere, surface climate, environmental characteristics, Mars internal structure, and Martian magnetic field. It is comprised of an orbiter, a lander, and a rover equipped with 13 scientific payloads. This article will give an introduction to the mission including mission plan, scientific objectives, scientific payloads, and its recent development progress.
China’s first Mars exploration mission, Scientific objectives, Scientific payloads
1 Overview of China’s First Mars Exploration Mission
China’s first Mars exploration mission got approval in 2016. It is comprised of five systems, which are the probe system, the launch vehicle system, the launching site system, the TT&C (Tracking, Telemetry and Command) system, and ground research and application system.
The probe system consists of an orbiter, a lander platform, and a rover. The mission is scheduled to make a soft landing after the lander carrying the rover separates from the orbiter. The orbiter provides the service of communication relay links for the rover on the relay communication orbit as well as to conduct its own exploration mission[1]. The launch vehicle system will use Long March 5 launch vehicle, which will send the probe to the Earth-Mars transfer orbit directly in July 2020. The launch site system is expected to work at Wenchang satellite launch center, located in Hainan province.
Based on the existing spaceflight TT&C network and deep-space TT&C network, the TT&C system has additionally constructed three 35 m aperture antenna in Kashgar deep-space station to implement the TT&C task with assistance of the VLBI network. Ground research and application system will receive the scientific data while completing the observation tasks, and subsequently, carry out the work of data analysis.
The mission is designed to implement a sequence of spacecraft orbiting, landing, and roving on Mars with only a single launch. This mission is scheduled to be launched in July 2020 and expected to reach Mars in 2021. The project objectives of the mission include the following key technology tasks: Mars orbit braking and capture, entering/descending/landing, long-term independent management, long-distance Tracking, Telemetry, and Command (TT&C) and communication, roving on the Martian surface.
2 Scientific Objectives and Payloads
The orbiter of the mission is scheduled to conduct Mars global survey. The rover is to carry out a detailed comprehensive investigation in some critical areas. The scientific objectives of China’s first Mars mission are as follows[2].
(1) To study the characteristics of Martian topography and geomorphology, acquire the data with high-precision to characterize global terrain of Mars and conduct the study on the processes that formed and modified the geologic record within a field exploration area on Mars.
(2) To study the characteristic of soil on the Mar-tian surface and the distribution of water ice, characterize a variety of soils, rocks, and global distribu-tion, search for the clue to past water activity to con-duct the study on the surface layer of the Martian soil.
(3) To investigate the composition of the Martian surface, identify the types of rocks and search for the secondary mineral to analyze the mineral composition on the Martian surface.
(4) To study atmosphere and ionosphere, surface climate, and environmental characteristics of Mars; monitor space environmental conditions, temperature, air pressure, and wind field to study the Martian ionosphere structure and the seasonal variation of surface weather.
(5) To study the Martian internal structure and magnetic field, investigate the Mars magnetic field to carry out the study on the history of early geological evolution, internal mass distribution, and gravity field.
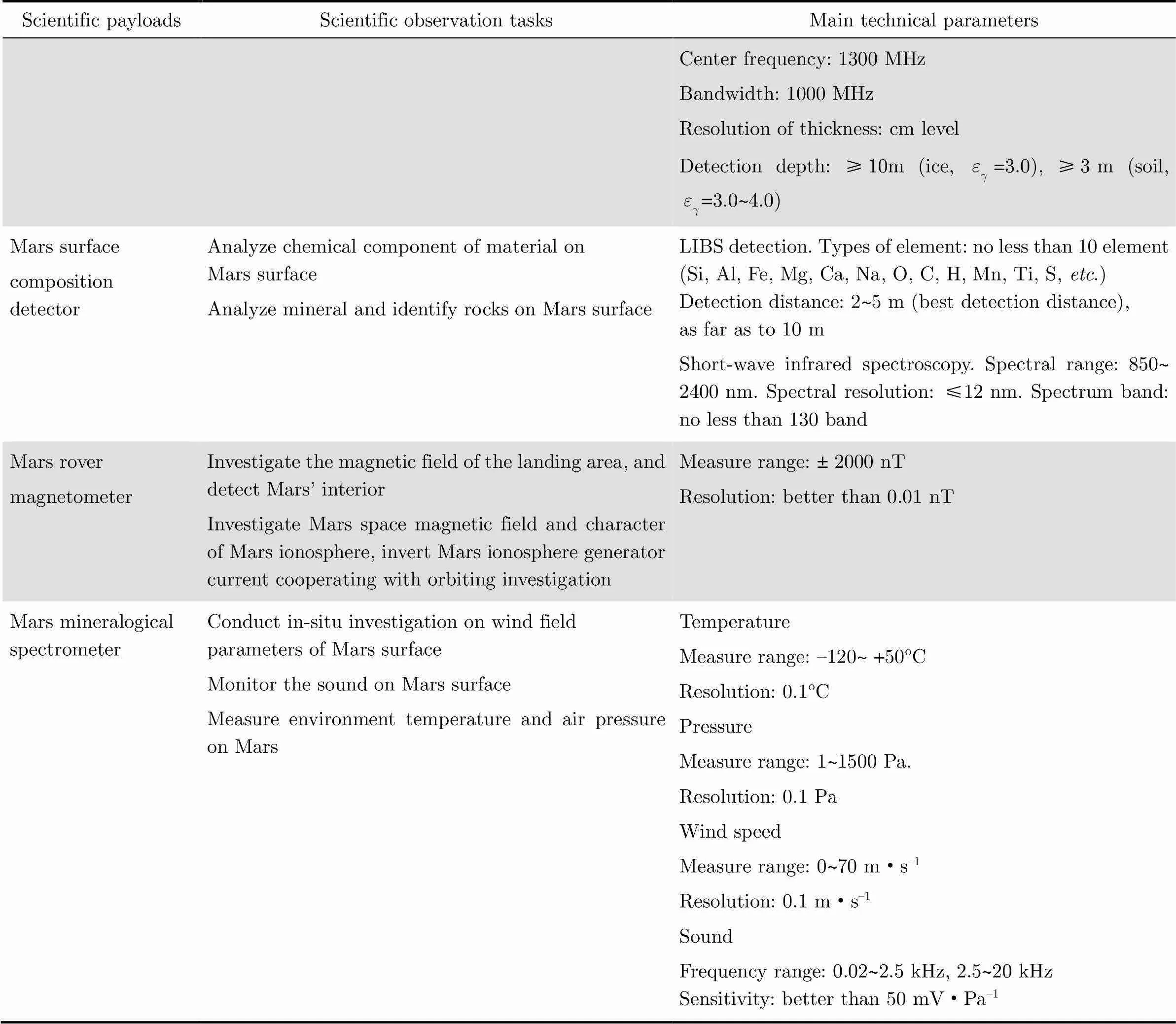
There are 13 scientific payloads equipped for the mission, 7 scientific payloads installed on the orbiter including Moderate Resolution Imaging Camera, High Resolution Imaging Camera, Mars Orbiter Scientific Investigation Radar, Mars Mineralogical Spectrometer, Mars Orbiter Magnetometer, Mars Ions and Neutral Particle Analyzer, Mars Energetic Particles Analyzer; 6 scientific payloads installed on the rover including Multispectral Camera, Navigation and Terrain Camera, Mars Rover Penetrating Radar, Mars Surface Composition Detector, Mars Rover Magnetometer, and Mars Mineralogical Spectrometer. There are two payload controllers separately installed on the orbiter and the rover, combined to command the payloads power supply, instruction control, data acquisition, and data processing[3]. The main technical parameters of scientific payloads and their scientific tasks are shown in Table 1.

Table1 Main technical parameters of scientific payloads
(Continued)
3 Key Technologies of Scientific Payloads
After over four years’ development, breakthroughs in the following key technologies have been achieved in scientific payloads.
(1) High resolution imaging camera: aiming at high elliptic orbit, it breaks through the real-time image motion compensation calculation of push- broom imaging and attitude control technology, so as to realize sub-meter level fine imaging observation.
(2) Mars orbiter scientific investigation radar: the technology of dual-frequency and dual-polariza-tion Linear Frequency Modulation (LFM) pulse is used to realize the layered structure detection of diff-erent geological targets.
(3) Mars mineralogical spectrometer: it uses Off- axis three reflective mirrors telescope, free-formed surface plane reflection grating technology to realize a wide band, compact and efficient spectrometer, and makes breakthroughs in the key technologies in infrared wide band light detector components.
(4) Mars rover penetrating radar: it uses ultra- wideband frequency Modulated Interrupting Continuous Wave (FMICW) to realize time-shared receiving/transmitting and solve receiving and transmitting channel segregation.
(5) Mars surface composition detector: it breaks Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectros (LIBS) quantitative inversion technology.
4 Summary
At present, the scientific payloads have been completely manufactured and will be transported to the launching site for installation and test as planned in April 2020. The five systems of the Mars mission schedule to be completed all the research and man-ufacture works before July 2020. The scientific data processing methods and application research will con-tinue to proceed. The scientific payloads aim at a global investigation of Mars such as terrain, geomo-r-phology, atmosphere, and magnetic fields. Chinese scientists are making efforts to deepen the study on methods and applications of scientific data, and eager to obtain a new understanding of Mars, such as Mars atmosphere, ionosphere, and Mars surface composition.
With the development of the Mars mission, China makes efforts to promote more missions in deep-space exploration such as the asteroid exploration, sample-return from Mars, Jupiter system and beyond exploration. CNSA (China National Space Administration) attaches great importance to international cooperation and has openly announced “Announcement of Opportunities for Scientific Pay-loads and Projects onboard Asteroid Exploration Mission” in April 2019. Currently, CNSA has received the relevant proposals from some countries, for instance, Russia, Italy, Sweden, Germany, Belgium, and so forth. In the near future, the selection process organized by CNSA will be underway.
[1] GENG Y, ZHOU J S, LI S,. Review of first Mars exploration mission in China [J]., 2018, 5(5):399-405
[2] LI C L, LIU J J, GENG Y,. Scientific objectives and payload configuration of China’s first Mars exploration mission [J]., 2018, 5(5):406-413
[3] ZHU Y, BAI Y F, WANG L G,. Integral technical scheme of payloads system for Chinese Mars-1 exploration [J]., 2017, 4(6):510-514
V 524, P 35
JIA Yingzhuo, ZOU Yongliao, ZHU Yan, DU Qingguo, FAN Yu, CHEN Yuesong, WANG Chi. Development Progress of China’s First Mars Exploration Mission: Its Scientific Objectives and Payloads., 2020, 40(5): 693-697. DOI:10.11728/ cjss2020.05.693
* Supported by the Major Program of the National Science Foundation of China (41590851) and the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Z181100002918003)
March 10, 2020
E-mail: fanyu@nssc.ac.cn

