Pleural effusion in an immunocompetent host with cryptococcal pneumonia:A case report
Huan-Huan Wu,Yan-Xiao Chen,Shuang-Yan Fang
Huan-Huan Wu,Shuang-Yan Fang,Department of Respiratory Medicine,Dongyang Hospital Affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University,Dongyang 322100,Zhejiang Province,China
Yan-Xiao Chen,Department of Evidence-base Medicine,Dongyang Hospital Affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University,Dongyang 322100,Zhejiang Province,China
Abstract
Key words: Pulmonary cryptococcosis;Immunocompetent;Computed tomography;Pleural effusion;Imaging findings;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Cryptococcosis mainly occurs as a result of inhalation of fungal spores in the environment.It has been reported that approximately 35% of patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis are immunocompetent[1].The imaging manifestations of pulmonary cryptococcosis vary considerably,depending on the immune status of the host.Most radiologic findings of pulmonary cryptococcosis in immunocompetent patients exhibit single or multiple peripheral nodule or masses,and localized pneumonia-like lesions[2,3].Nodular and masses with burrs and lobes can easily be misdiagnosed as lung cancer.Most of these lesions are located in the peripheral lung field,usually subpleural within the inferior lobes,often in the right lower lobe.However,immunocompromised patients have more extensive and varied imaging findings.Besides nodular and mass lesions,diffuse,disseminated pneumonia-like infiltration and consolidation are common,leading to the formation of cavities and the halo sign[4].Other changes on imaging include grid infiltration,hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy,pleural effusion,diffuse miliary shadows,and ground-glass opacity.In such cases,the diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis becomes very challenging;therefore,invasive examination is occasionally conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 29-year-old Asian male was admitted to our emergency department after complaining of cough and fever that had persisted for a month.
ICP-AES工作條件:等離子源頻率為27.12MHz;射頻發生器功率為1150W;冷卻氣流量為0.50L/min;霧化氣流量為0.50L/min;等離子炬觀測方向為水平方向;試液沖洗時間為25s;泵速為50r/min;積分時間為30s;Ar氣純度不低于99.999%。
History of present illness
The patient's symptoms started a month ago with cough and fever.At a local hospital,he underwent a chest computed tomography (CT) scan and oral antibiotics(unknown);however,his cough and fever were not relieved.
History of past illness
His history of past illness was negative.
Physical examination
Physical examination revealed crackle in the left lower lobe.Neurological examination was normal.On admission,he had a pulse of 106 beats/min,blood pressure of 130/70 mmHg,and a body temperature of 38.2°C.According to the patient's chest CT scan result,it was thought that he might have bacterial pneumonia and was prescribed cefoperazone as empirical treatment.
Laboratory examinations
Laboratory data,including white blood cell count,platelet count,renal and liver function,C-reactive protein,procalcitonin,and tumor markers,were all considered normal.Moreover,his human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) serology was negative and CD4 count was normal.
Imaging examinations
After a week of antibiotic therapy,his cough and fever still persisted,with additional chest pain.Therefore,he underwent another CT scan to evaluate the therapeutic effects.We observed that the lesions revealed in the previous CT scan had not resolved,and multiple cavities and pleural effusion were also visible (Figure 1),prompting another diagnosis.
Further diagnostic work-up
A tuberculosis infection T-cell spot test (T-SPOT.TB;Oxford Immunotec,Marlborough,MA,United States) was then performed,but yielded negative results.Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy was subsequently performed.Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) and serum cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) testing were positive for cryptococcosis.Cryptococcus capsules were observed on BAL ink stain (Figure 2).Furthermore,histopathological examination of a percutaneous lung biopsy from the left lower lobe revealed granulomatous inflammation,and periodic acid-Schiff staining showed red-colored yeast walls.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
According to the pathology and BAL ink stain,the diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis was confirmed.
TREATMENT
The patient was then treated with a daily dose of fluconazole (0.4 g),but exhibited unsatisfactory clinical outcome as cough and mild fever persisted,a week later.Therefore,the anti-fungal treatment was changed from fluconazole to voriconazole(0.2 g,twice a day)[5,6].
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
After 8 months of antifungal therapy,his cough and fever improved.A repeated chest CT scan showed significant absorption of the lesion.In addition,no recurrence was observed after follow-up (Figure 3).
DISCUSSION
As mentioned above,approximately 35% of patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis are immunocompetent,and there are also reports to show that more than 50% of patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis are immunocompetent[2,7].In addition,approximately 60% of patients with HIV-negative pulmonary cryptococcosis do not have underlying disease[4].The imaging findings of pulmonary cryptococcosis are often related to the patient's immune status.Liuet al[4]summarized the imaging findings of 88 patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis,and found that poorly-defined nodules,cavity,and the halo-sign were more frequent in immunosuppressed patients than in immunocompetent patients.Solitary and well-defined nodules were more common in patients with normal immune function.Zhanget al[2]summarized the imaging findings of 76 patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis,and found that pneumonia-like manifestations were more common in immunocompetent patients than in immunocompromised patients.Regardless of whether the patient's immune function was impaired,the most prevalent imaging findings in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients are nodules or masses located mainly in the peripheral lung field (outer third of the lung),and close to the pleura[8].In this study,we observed that missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis was highly likely as its CT images mimicked lung cancer,tuberculosis,and bacterial infection.

Figure1 Chest computed tomography images before antifungal therapy.
Testing for CrAg in serum and cerebrospinal fluid is an important diagnostic procedure for the detection of cryptococcosis.Although this non-invasive procedure has been reported to be sensitive,contrary reports have emerged showing that its sensitivity is insufficient in the diagnosis of isolated pulmonary cryptococcosis.A study reported that only 56% of patients with non-HIV related isolated pulmonary cryptococcosis tested positive for serum CrAg[9].Another recent study of 23 non-HIV related pulmonary cryptococcosis patients showed that the positive rate of CrAg testing in BAL was 82.6%,which was higher than the serum positive rate[10].In this study,we also found BAL CrAg testing to be more sensitive.Therefore,BAL CrAg detection can be used as an adjunctive diagnostic tool for patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis.
Fluconazole is the preferred drug for treating cryptococcosis that has not spread to the central nervous system.This antifungal therapy prevents or diminishes the risk of disease progression.However,increasing fluconazole resistance in Cryptococcus is a major drawback to this mode of treatment.For example,a recent study revealed fluconazole resistance of 10.6% in 4995 Cryptococcus isolates from HIV-positive patients[11],with the resistance rate set to increase over time.In cases where fluconazole is not available or contraindicated,oral voriconazole (200 mg twice a day)has been proposed as a suitable substitute[12].Unlike after fluconazole therapy,we observed a significant improvement in the patient's lung lesions after voriconazole treatment.
CONCLUSION
Pulmonary cryptococcosis also affects immunocompetent patients,and its clinical outcome is always satisfactory if the disease is diagnosed and treated early.Therefore,if a patient has a relatively slow progression of lesions,as well as a poor response to antibiotics,without the signs of inflammation caused by tuberculosis and lung cancer,then the possibility of pulmonary cryptococcosis should be considered.Clinicians should not disregard the possibility of cavities and pleural effusion occurring in immunocompetent hosts without underlying diseases.
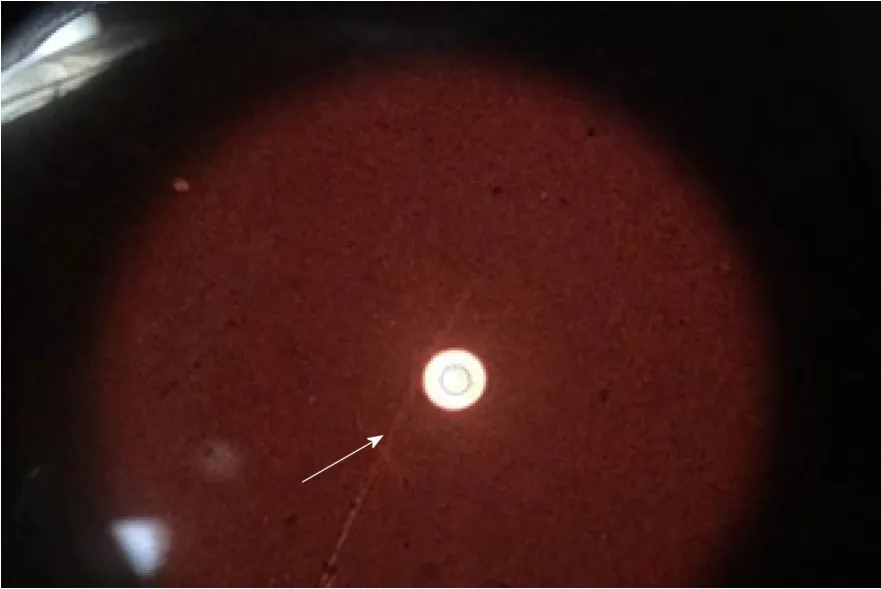
Figure2 Cryptococcus capsules observed in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid ink stain (white arrow).
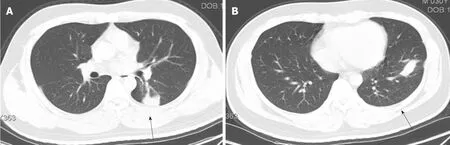
Figure3 Chest computed tomography images after antifungal therapy.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年7期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年7期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- CD56+ lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the lung:A case report and literature review
- Systemic treatment for severe concentrated sulfuric acid burns in an adult male at high altitude:A case report
- Clinical effects of apatinib mesylate for treatment of multiple brain micrometastases:Two case reports
- Disseminated histoplasmosis in primary Sj?gren syndrome:A case report
- Severe venous thromboembolism in the puerperal period caused by thrombosis:A case report
- Multiple neurofibromas plus fibrosarcoma with familial NF1 pathogenicity:A case report
