Duodenal mature teratoma causing partial intestinal obstruction: A first case report in an adult
Tharintorn Chansoon, Napat Angkathunyakul, Rangsima Aroonroch, Department of Pathology,Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand
Jakrapan Jirasiritham, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital,Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand
Abstract
BACKGROUND
A teratoma is a germ cell tumor that is composed of tissue derived from two or three germ layers. Duodenal teratomas are extremely rare and have been exclusively reported in neonates and children. This is the third case of a teratoma primarily arising in the duodenum and the first case that occurred in an adult.
CASE SUMMARY
A 31-year-old male presented with clinical partial gut obstruction (epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting). The physical examination showed a palpable illdefined mass on the left side of the abdomen. The computed tomography scan revealed a multiseptated cystic tumor at the retroperitoneal area. First, he underwent gastrojejunostomy to relieve the symptoms and was referred to a tertiary-care hospital. The second operation revealed a 10-cm solid-cystic mass originating from the third part of the duodenum and adhering to the abdominal aorta and pancreas. Segmental duodenectomy was performed. The pathological diagnosis was a mature cystic teratoma. The patient was asymptomatic at 5 mo after the operation.
CONCLUSION
Duodenal teratomas are extremely rare but should be included in the differential diagnosis in patients who present with intestinal obstruction. Radiological imaging is helpful to reach the preoperative diagnosis. Multidisciplinary team planning is essential to avoid injury to the adjacent organ in duodenal operation.
Key words: Duodenal teratoma; Mature cystic teratoma; Intestinal obstruction; Germ cell tumor; Retroperitoneal mass; Case report
INTRODUCTION
A teratoma is a tumor composed of tissue derived from two or three germ layers(ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). Teratomas are mostly found in children and young adults and are usually located in gonadal tissue and the midline region.Extragonadal sites have also been reported, such as the sacrococcygeal region, head and neck, retroperitoneum, mediastinum, brain, liver and abdominal wall[1].Duodenal teratomas are extremely rare and have been reported in only two cases in neonates and children. We report the first case to occur in an adult as a cause of partial intestinal obstruction. Clinicopathological features and a literature review are included in this paper.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 31-year-old male presented with abdominal pain which had increased in the last 3 mo.
History of present illness
He had intermittent epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting for 1 year. Abdominal pain had increased in the last 3 mo, urging him to go to the hospital. He also had weight loss of 2 kg in 1 mo. He was diagnosed with partial gut obstruction. Exploratory laparotomy revealed a 10-cm duodenal mass occupying the retroperitoneal region close to the aorta. He underwent gastrojejunostomy only. The mass was not removed because of the high risk of aortic injury. Lymph node biopsy was performed, and the histopathology demonstrated reactive lymphoid hyperplasia. The patient was referred to our hospital.
History of past illness
He did not have any underlying disease or medication history.
Physical examination
The physical examination at our hospital showed a well-healed midabdominal surgical scar and a palpable ill-defined mass on the left side of the abdomen with mild tenderness. The other organs are within normal limits.
Laboratory examinations
All his blood tests were within normal limits.
Imaging examinations
The computed tomography scan revealed a multiseptated cystic tumor at the retroperitoneal area, adhering to the duodenum and close to the abdominal aorta and left renal vein, compressing the left ureter (Figure 1). No bony structure was detected.
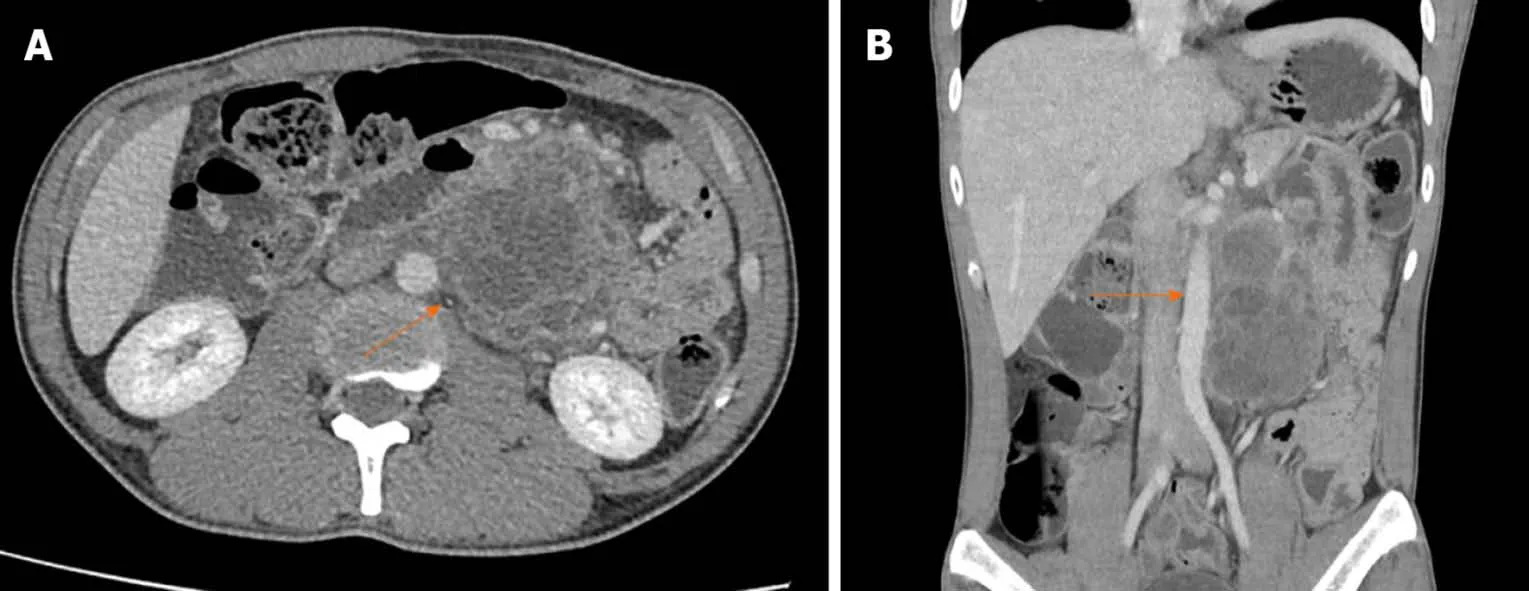
Figure 1 Computed tomography scan of the abdomen. A: Axial enhanced computed tomography image demonstrated a multiseptated cystic tumor (arrow) in the retroperitoneal region, adhering to the duodenum and close to the abdominal aorta and left renal vein; B: coronal enhanced computed tomography reconstruction demonstrating a tumor close to the abdominal aorta (arrow).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The final diagnosis was mature cystic teratoma of the duodenum. The pathological examination revealed a 12 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm oval-shaped soft tan-brown mass attached to a segment of the duodenum. Serial sections showed a multiloculated cystic lesion with multiple white-yellow solid nodules measuring 0.3-1.4 cm in diameter. The cyst wall was 0.1-0.3 cm thick. The duodenal mucosa was smooth without ulcers or masses. The microscopic examination demonstrated multiloculated cysts that were located between the inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of the duodenal muscularis propria (Figure 2A). The cysts lined by stratified squamous cell epithelium with sebaceous glands, simple-to-stratified columnar epithelium, and intestinal-type epithelium intermixed with irregular bundles of smooth muscle, fat and hyaline cartilage (Figure 2B) and communicated with the duodenal lumen. Some of the cysts contained keratin material. No atypia, immature elements or other germ cell components were identified. The duodenal mucosa adjacent to the opening site displayed erosion and inflammation. The pathological diagnosis was mature cystic teratoma. The physical examination of the testis and imaging of intrathoracic and intraabdominal organs were unremarkable, metastatic teratomas from other organs were excluded.
TREATMENT
The urology surgeon was consulted for standing by in case injury to the ureter occurred. The second exploratory laparotomy showed a 10-cm solid-cystic mass originating from the third part of the duodenum, adhering to the abdominal aorta and pancreas. The feeding artery was from the abdominal aorta. The prior gastrojejunostomy was patent. Segmental duodenectomy and tumor removal were performed.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
The postoperative course was uneventful. The patient recovered and was discharged to his home. At 5 mo after the operation, the patient was asymptomatic.
DISCUSSION
Duodenal teratomas are extremely rare, and to the best of our knowledge, only two cases have been reported in the English-language literature. The first case was reported by Joshiet al[2]and occurred in a neonate with exomphalos minor[3]. The second case was reported in a 2-year-old girl with an incidentally found upper abdominal mass[4]. Therefore, this is the third case of teratoma primarily arising in the duodenum and the first case that occurred in an adult. The summaries of reported cases of primary duodenal teratoma are shown in Table 1.

Figure 2 Histopathological findings (hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification ×100). A: Teratoma located between the inner circular and the outer longitudinal layers of the duodenal muscularis propria (arrow) and communicate with the normal duodenal mucosa (arrowhead); B: the tumor consists of stratified squamous cell epithelium, simple cuboidal epithelium, and irregular bundles of smooth muscle, fat and hyaline cartilage.
A teratoma is a tumor composed of tissue derived from two or three germ layers(ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). Teratomas are divided into three categories:Mature teratomas, immature teratomas, and monodermal teratomas. Mature teratomas are tumors composed exclusively of mature tissue. Immature teratomas contain variable amounts of immature tissue, typically primitive or embryonal ectodermal tissue, while monodermal teratomas are almost exclusively composed of one type of germ layer[5]. Totipotent stem cell lines have been implicated as progenitor teratoma cells. Molecular biology and karyotyping suggest that extragonadal teratomas are thought to arise from primordial germ cells or early embryonic cells,while gonadal teratomas arise from germ cells in which parthenogenesis has occurred[6].
Teratomas can occur in a wide range of ages but exhibits two peaks in incidence.The first is at approximately 2 years of age, and the second is in late adolescence or early young adulthood[5]. The location of teratomas is usually gonadal tissue and the midline region. Extragonadal teratomas are very rare. The most common site in the extragonadal group is the sacrococcygeal region, followed by the head and neck,retroperitoneum, mediastinum, brain, liver, and abdominal wall[1]. Gastrointestinal teratomas have been occasionally reported, including in the stomach, terminal ileum,cecum, rectum, and pancreas[2]. Gastrointestinal teratomas have a higher frequency in females and in the hindgut. There seems to be no association between mature teratomas of the gastrointestinal tract and developmental anomalies of the urogenital tract, spine or sacrum[7]. According to the rare location of teratomas, local spreading or metastasis from other organs should be excluded. Ovarian cystic teratomas can rupture or undergo iatrogenic epidermal implantation into the peritoneal cavity, and rarely into the intestine, during surgery[8-10].
Gastrointestinal teratomas have variable clinical presentations depending on the organ of origin and compression symptoms. The symptoms include asymptomatic,abdominal pain with or without nausea, constipation and intestinal obstruction.Physical examination may reveal a palpable abdominal mass[7]. Because some part of the duodenum is in the retroperitoneal region, a duodenal teratoma can present as a retroperitoneal mass that should be differentially diagnosed as a mesenchymal tumor,lymphoma or other germ cell tumor[11]. Malignant teratomas tend to progress rapidly and may be diagnosed in an advanced stage at first presentation[5].
Radiological imaging is a useful tool for the diagnosis of these tumors, not only to locate the precise site of the tumor but also to display the adjacent structure near the tumor, which can guide preoperative planning. Mature teratomas have some characteristic imaging features. A plain film may show rim calcification or teeth-like components. Ultrasonography can reveal an anechoic or hyperechoic mass due to the presence of fluid, hair, fat and calcification[1]. Computed tomography often reveals the complex, predominantly cystic masses that often contain fat and calcifications. The presence of a fat-containing cyst with mural calcifications is highly suggestive of a mature teratoma, but it may be difficult to distinguish between immature and mature teratomas on the basis of imaging alone[12]. The duodenum lies adjacent to many structures, such as the aorta, inferior vena cava, superior mesenteric artery, common bile duct, and ureters. Hence, to remove the tumor, preoperative planning with a multidisciplinary team is critically important to avoid incidental injury to the adjacent structures.
Macroscopic features of mature teratomas are usually cystic lesions containing hair and sebaceous material. The wall is thin and usually lined by an opaque white-graywrinkled epidermis. There may be a solid component within the cyst that frequently contains dermal appendages, fat, teeth, cartilage or bone. Interestingly, all of the reported duodenal teratoma cases, including our case, have a communicating tract between the tumor and duodenal wall. Immature teratomas are usually larger than their mature counterparts. The microscopic features of mature teratoma are the presence of only mature tissue from three germ layers. The ectodermal derivative, the most abundant component, is represented by squamous epithelium, skin adnexal structures, and brain tissue. Mesodermal tissue includes fat, cartilage, bone, and smooth muscle tissue. Endodermal tissue is represented by the gastrointestinal epithelium, respiratory tract epithelium and thyroid tissue[5]. The presence of immature embryonal-type tissue, including neuroectodermal tubules or rosettes, is the criterion for the diagnosis of an immature teratoma, which is a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, careful tumor sampling and thorough histological examination are highly recommended to avoid underdiagnosis, especially in tumors that have a large area of the solid component.

Table 1 Reported cases of primary duodenal teratoma
It has been reported that 1% of teratomas undergo a malignant transformation. The most common malignancy developing in teratomas is squamous cell carcinoma. It usually metastasized at presentation, which has a high recurrence rate and is more aggressive than pure teratoma alone[6]. It has been postulated that the mechanism underlying the malignant transformation is the differentiation of totipotent embryonal carcinoma cells into a somatic-type neoplasm or the malignant transformation of a mature benign teratoma elements[13].
The mainstay treatment of teratoma is surgery. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy have relatively small roles in management unless the tumor has a malignant counterpart. The prognosis of benign teratomas is excellent after complete surgical resection[6].
CONCLUSION
We report the first case of a duodenal teratoma occurring in an adult. Teratomas,although extremely rare, should be one of the differential diagnoses in patients who present with intestinal obstruction. Radiological imaging is helpful to preoperative diagnosis and planning. Multidisciplinary surgical team planning is also essential to avoid injury to the adjacent organs in duodenal teratoma operation. Complete surgical excision is the treatment of choice, and the prognosis of mature teratomas is excellent.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年8期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年8期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Clinicopathological differences and correlations between right and left colon cancer
- Bedside score predicting retained common bile duct stone in acute biliary pancreatitis
- Stability and infectivity of coronaviruses in inanimate environments
- Status, challenges, and future prospects of stem cell therapy in pelvic floor disorders
- Unusual presentation of congenital radioulnar synostosis with osteoporosis, fragility fracture and nonunion: A case report and review of literature
- Predictive factors for central lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
