BIS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼在婦科腔鏡手術(shù)中的應(yīng)用及對麻醉效果的影響
林海榮 邱晨
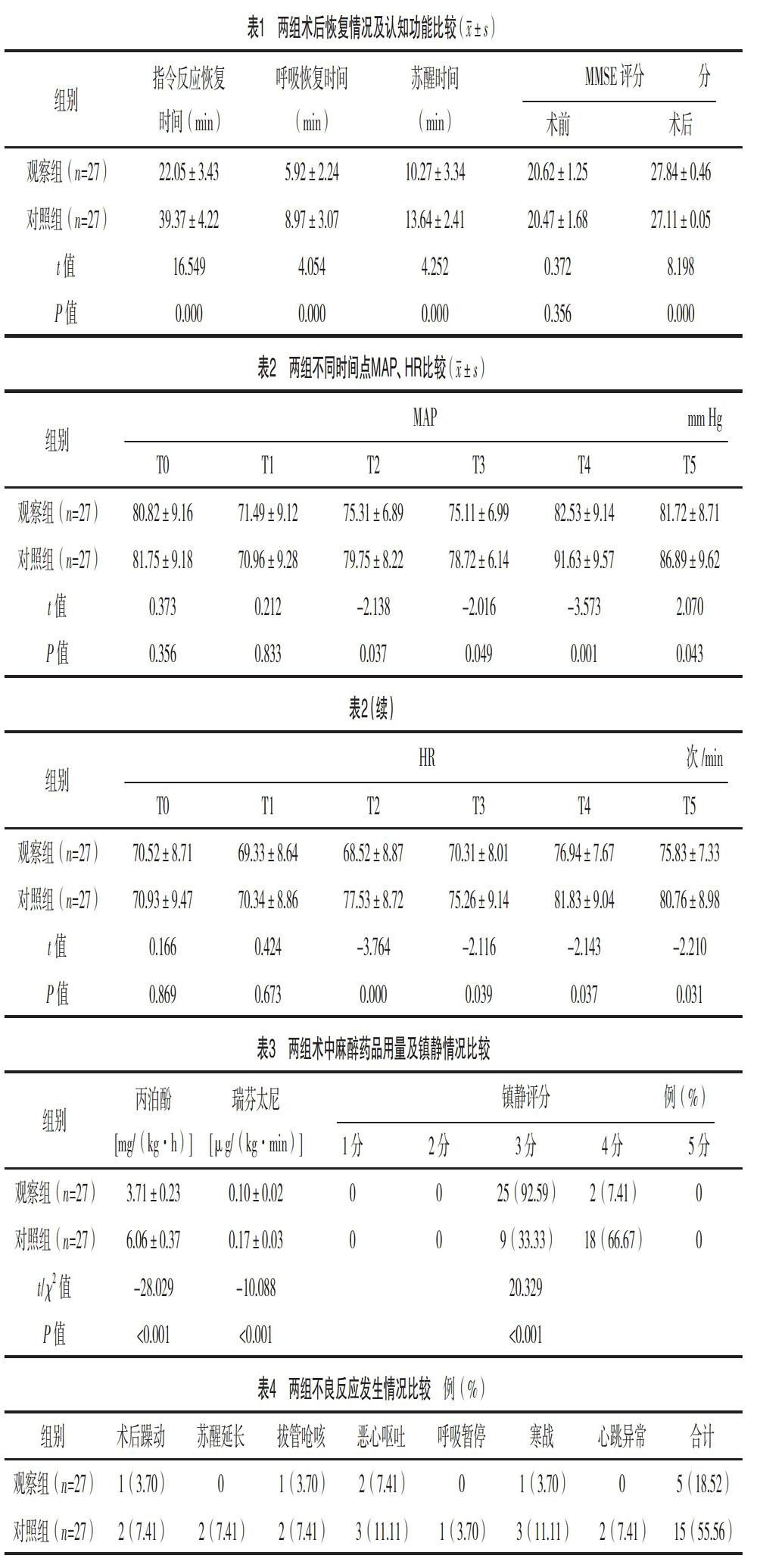
【摘要】 目的:探討B(tài)IS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼在婦科腔鏡手術(shù)中的應(yīng)用及對麻醉效果的影響。方法:選取2018年4月-2019年4月本院收治的54例婦科腔鏡下子宮全切除術(shù)患者為研究對象,按照隨機數(shù)字表法將患者分為觀察組和對照組,每組27例。對照組給予丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼進行麻醉,觀察組在BIS監(jiān)測下給予右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼進行麻醉。比較兩組術(shù)后恢復(fù)情況及認(rèn)知功能,比較兩組不同時間點MAP、HR,術(shù)中麻醉藥品用量、鎮(zhèn)靜情況及不良反應(yīng)發(fā)生情況。結(jié)果:觀察組指令反應(yīng)恢復(fù)時間、呼吸恢復(fù)時間、蘇醒時間均短于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組術(shù)后MMSE評分高于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組在T2、T3、T4、T5時點的MAP及HR均低于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組術(shù)中丙泊酚與瑞芬太尼用量均低于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組的鎮(zhèn)靜情況好于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組術(shù)后不良反應(yīng)發(fā)生率18.51%,低于對照組55.55%(P<0.05)。結(jié)論:BIS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和芬太尼麻醉效果顯著,能有效促進婦科腔鏡手術(shù)患者術(shù)后認(rèn)知功能的恢復(fù),有利于手術(shù)順利完成且安全性較高,具有臨床推廣應(yīng)用價值。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 BIS監(jiān)測下 右美托咪啶 丙泊酚 瑞芬太尼 婦科腔鏡手術(shù) 麻醉效果
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the application of Dexmedetomidine combined with Propofol and Remifentanil in gynecological endoscopic surgery under BIS monitoring and its effect on anesthesia. Method: From April 2018 to April 2019, 54 patients who underwent gynecological laparoscopic hysterectomy were selected as subjects. They were divided into observation group and control group according to the random number table method, 27 cases in each group. The control group was given Propofol with Remifentanil, the observation group was given Dexmedetomidine combined with Propofol and Remifentanil under BIS monitoring. The postoperative recovery and cognitive function were compared, and the MAP and HR at different time points were compared, the amount of narcotic drugs, sedation and adverse reactions during the operation were compared between the two groups. Result: The response recovery time, breathing recovery time and wake-up time of the observation group were lower than those of the control group (P<0.05). The postoperative MMSE score of the observation group was higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). The MAP and HR at T3, T4, and T5 in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The amount of Propofol and Remifentanil in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The sedation in the observation group was better than that in the control group (P<0.05). The incidence of adverse reactions in the observation group was 18.51%, lower than 55.55% in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: Under BIS monitoring, Dexmedetomidine combined with Propofol and Remifentanil has a significant anesthetic effect, which can effectively promote the recovery of postoperative cognitive function in patients undergoing gynecologic endoscopic surgery, and is conducive to the smooth completion of surgery and high safety, and has clinical application value.
本研究中,觀察組與對照組在T0、T1時點的MAP、HR比較,差異均無統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P>0.05),觀察組在T2、T3、T4、T5時點的MAP及HR均低于對照組(P<0.05),主要是因為BIS作為一種新型技術(shù),采用電腦雙頻指數(shù)實時、動態(tài)地監(jiān)測血流動力學(xué)變化,能夠幫助手術(shù)醫(yī)生科學(xué)的把握術(shù)中麻醉深度,提升麻醉效果[15]。右美托咪啶能通過抑制去甲腎上腺素遞質(zhì),終止傳導(dǎo)疼痛信號。并通過抑制交感神經(jīng)元活性,從而有效控制術(shù)中MAP和心率水平,鎮(zhèn)靜鎮(zhèn)痛和抗交感效果顯著[16]。BIS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼能有效控制婦科腔鏡手術(shù)患者平均動脈壓、心率變化,維持血流動力學(xué)的穩(wěn)定狀態(tài),有利于手術(shù)成功完成。
本研究中,觀察組術(shù)中丙泊酚與瑞芬太尼用量均低于對照組(P<0.05),鎮(zhèn)靜情況好于對照組(P<0.05),主要是因為婦科腹腔鏡下子宮全切除術(shù)時間較短,需要患者在術(shù)前盡快進入理想麻醉狀態(tài),如麻醉深度不夠,術(shù)中出現(xiàn)知曉的概率較高。如麻醉深度過深,術(shù)后蘇醒時間過長則會影響術(shù)后恢復(fù)質(zhì)量[17]。BIS是監(jiān)測觀察婦科腹腔鏡手術(shù)麻醉用藥的重要手段,通過對術(shù)中監(jiān)測觀察的數(shù)值變化進行判斷,在保障術(shù)中不知曉的情況下,合理調(diào)控并有效控制術(shù)中麻醉用藥量。右美托咪定是具有較高的選擇性的新型腎上腺素能受體激動劑,作為局部麻醉時的輔助藥物,可有效減少局部麻醉藥物的用量[18-19],BIS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼,可顯著降低術(shù)中丙泊酚與瑞芬太尼用量,有利于提升麻醉效果。
本研究中觀察組術(shù)后不良反應(yīng)發(fā)生率18.52%,低于對照組55.56%(P<0.05),主要是因為本研究中婦科腔鏡術(shù)后不良反應(yīng)與術(shù)中鎮(zhèn)靜效果和丙泊酚與瑞芬太尼的用量有關(guān)。BIS通過監(jiān)測術(shù)中麻醉深度,科學(xué)合理地調(diào)整和控制丙泊酚與瑞芬太尼用量,從而降低惡心嘔吐、拔管嗆咳等不良反應(yīng)。右美托咪啶是α2受體激動藥,能有效抑制手術(shù)刺激引起的交感神經(jīng)系統(tǒng)興奮,明顯降低術(shù)后寒戰(zhàn)的發(fā)生,鎮(zhèn)靜鎮(zhèn)痛作用顯著且對阿片類藥的呼吸抑制無協(xié)同作用[20],有效減少了術(shù)后躁動、呼吸暫停、心跳異常等不良反應(yīng)。BIS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼能起到良好的協(xié)同鎮(zhèn)痛效應(yīng),降低不良反應(yīng)發(fā)生,有利于術(shù)后恢復(fù)。
綜上所述,BIS監(jiān)測下右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼麻醉效果顯著,能有效促進婦科腔鏡手術(shù)患者術(shù)后認(rèn)知功能的恢復(fù),有利于手術(shù)順利完成且安全性較高,具有臨床推廣應(yīng)用價值。
參考文獻
[1]張浩.腹腔鏡手術(shù)患者應(yīng)用七氟烷或異丙酚復(fù)合瑞芬太尼麻醉的臨床觀察[J].中國醫(yī)學(xué)創(chuàng)新,2019,16(5):156-159.
[2]章云飛,李長生,盧錫華,等.右美托咪啶復(fù)合丙泊酚或七氟烷全麻對胃腸腫瘤腹腔鏡手術(shù)患者應(yīng)激和術(shù)后恢復(fù)質(zhì)量的影響[J].中華醫(yī)學(xué)雜志,2019,99(17):1302-1306.
[3]張小偉.右美托咪定復(fù)合舒芬太尼用于術(shù)后鎮(zhèn)痛對婦科腹腔鏡手術(shù)患者睡眠質(zhì)量的影響[J].國際麻醉學(xué)與復(fù)蘇雜志,2019,40(4):294-297.
[4]章良.右美托咪啶復(fù)合舒芬太尼全身麻醉對剖宮產(chǎn)術(shù)中新生兒氧攝取率的影響[J].中國全科醫(yī)學(xué),2017,20(s1):158-160.
[5]張輝,朱詠,嚴(yán)彬,等.靜吸復(fù)合麻醉下右美托咪定對老年患者頸椎手術(shù)運動誘發(fā)電位監(jiān)測及術(shù)后躁動的影響[J].中華麻醉學(xué)雜志,2018,38(8):964.
[6] Ding J,Chen Y,Gao Y.Effect of propofol, midazolam and dexmedetomidine on ICU patients with sepsis and on arterial blood gas[J].Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,2019,18(6):4340-4346.
[7] Hu B,Zhong Y,Zou X.Propofol vs. thiopental in hypotention after GA induction[J].Journal of Anesthesia,2019,33(6):705.
[8] Chaki T,Hirata N,Yoshikawa Y,et al.Lipid emulsion, but not propofol, induces skeletal muscle damage and lipid peroxidation[J].Journal of Anesthesia,2019,33(6):628-635.
[9] Uuskula A,Jarlais D D,Vorobjov S.The fentanyl epidemic in Estonia: opportunities for a comprehensive public health response[J].The Lancet Psychiatry,2019,6(12):985.
[10] Walia C,Gupta R,Kaur M,et al.Propofol sparing effect of dexmedetomidine and magnesium sulfate during BIS targeted anesthesia: A prospective, randomized, placebo controlled trial[J].J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol,2018,34(3):335-340.
[11]陳淼,韓雪萍,尚學(xué)棟,等.右美托咪定對頸內(nèi)動脈球囊閉塞試驗患者術(shù)中喚醒試驗質(zhì)量的影響[J].中華麻醉學(xué)雜志,2017,37(5):601-605.
[12]謝東武.依托咪酯復(fù)合丙泊酚方案對無痛胃腸鏡檢查過程中應(yīng)激及炎癥反應(yīng)的影響[J].海南醫(yī)學(xué)院學(xué)報,2017,23(22):3176-3179.
[13]李長生,劉素芳,周一,等.右美托咪啶對胸腹腔鏡下食管癌根治術(shù)患者圍手術(shù)期應(yīng)激和術(shù)后疼痛的影響[J].中華醫(yī)學(xué)雜志,2018,98(46):3778-3783.
[14]王欣,孫媛,魏硯硯,等.不同靶控輸注瑞芬太尼復(fù)合丙泊酚、右美托咪定用于精神分裂癥剖宮產(chǎn)手術(shù)的影響[J].中國地方病防治雜志,2017,32(8):900-901,908.
[15]趙勤峰,呂衛(wèi)兵,朱曉紅,等.丙泊酚聯(lián)合右美托咪啶與芬太尼在無痛氣管鏡檢查中的應(yīng)用價值[J].西部醫(yī)學(xué),2018,30(1):77-80.
[16]劉沖,董龍,張德利,等.右美托咪定與瑞芬太尼靜脈復(fù)合對臂叢阻滯下老年肩關(guān)節(jié)鏡手術(shù)VAS評分、BIS值及不良反應(yīng)的影響[J].解放軍預(yù)防醫(yī)學(xué)雜志,2018,36(6):732-735.
[17]石泉,李敏,唐志清,等.酮咯酸氨丁三醇復(fù)合右美托咪定對瑞芬太尼致婦科腹腔鏡患者術(shù)后痛覺過敏的影響[J].福建醫(yī)科大學(xué)學(xué)報,2018,52(6):421-424.
[18]張海亮,郝靜靜,白延斌,等.靜吸復(fù)合與全憑靜脈麻醉在婦科腹腔鏡手術(shù)中的臨床應(yīng)用研究[J].陜西醫(yī)學(xué)雜志,2019,48(8):1038-1041.
[19]馬龍,侯俊德,王志剛,等.硬膜外麻醉聯(lián)合全麻復(fù)合右美托咪定對腹腔鏡結(jié)直腸癌根治術(shù)患者免疫功能及應(yīng)激反應(yīng)的影響[J].廣西醫(yī)科大學(xué)學(xué)報,2018,35(8):1076-1079.
[20]呂國棟,齊超,馬改霞,等.丙泊酚復(fù)合瑞芬太尼對剖宮產(chǎn)孕婦血流動力學(xué)的影響[J].中國婦產(chǎn)科臨床雜志,2019,20(3):256-257.
(收稿日期:2020-02-28) (本文編輯:張爽)
 中國醫(yī)學(xué)創(chuàng)新2020年12期
中國醫(yī)學(xué)創(chuàng)新2020年12期
- 中國醫(yī)學(xué)創(chuàng)新的其它文章
- 特發(fā)性脊柱側(cè)凸后路手術(shù)的研究進展
- BI-RADS分級系統(tǒng)在臨床觸診陰性乳腺病灶微創(chuàng)活檢術(shù)前評估中的應(yīng)用
- 髕骨傾斜角動態(tài)變化分析對髕股關(guān)節(jié)不穩(wěn)定癥的診斷價值
- 早產(chǎn)兒與足月兒發(fā)生新生兒持續(xù)性肺動脈高壓的特點分析
- H型高血壓患者脈搏波傳導(dǎo)速度、踝臂指數(shù)在頸動脈粥樣硬化中的預(yù)測價值
- 腰硬聯(lián)合麻醉對無痛分娩中轉(zhuǎn)剖宮產(chǎn)患者的鎮(zhèn)痛效果及應(yīng)激反應(yīng)的影響
