Serial computed tomographic findings and specific clinical features of pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia: A case report
Xing Chen, Xiao-Jie Zou, Zhen Xu
Xing Chen, Xiao-Jie Zou, Zhen Xu, Department of Pediatrics, Huzhou Central Hospital,Affiliated Cent Hospital HuZhou University, Huzhou 313000, Zhejiang Province, China
Abstract
Key words: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Pediatric patient; Computed tomographic; Fecaloral transmission; Case report
INTRODUCTION
In December 2019, the first suspected case of novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection was reported in a seafood wholesale market in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China[1].According to virus typing, the 2019-nCoV was identified as the causative agent on January 7, 2020[2]. The disease was officially named as coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19) by the World Health Organization. To date, according to the analysis of virus genotypes, the outbreak of pneumonia occurred just a few months after the large congregation of the 7thInternational Military Sports Council Military World Games held in Wuhan. Therefore, it is reasonable to suggest that the novel coronavirus may have been imported from the United States or other countries[3,4]. The clinical symptoms and therapeutic measures of patients with COVID-19 need to be further explored, especially in infants, young children and immunodeficient populations. There are few reports of chest computed tomography (CT) findings and other clinical features in pediatric patients with COVID-19 compared with those in adult patients[5,6]. In this article, we report a 7-year-old girl with confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia in Huzhou Central Hospital, as well as the results of CT images and radiographs at initial and serial follow-up related to the clinical course. As far as we know, this is the first batch of chest CT manifestations and therapeutic measures in a pediatric patient with COVID-19 in China. This report was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Huzhou Central Hospital.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
On January 30, 2020, a 7-year-old girl (height: 120 cm, body weight: 25 kg), presented with irregular fever (body temperature of 39.0°C) for 1 d. She was admitted to the Emergency Department of Huzhou Central Hospital.
History of present illness
The patient showed irregular fever for 1 d, with a body temperature of 39.0°C.
History of past illness
The patient was in good health, without potential or congenital diseases, and returned to Huzhou, Zhejiang Province, with her parents from Wuhan 1 wk ago.
Personal and family history
The patient was living in an almost smoke-free environment, and her parents showed no symptoms of infection and negative laboratory test results for viral RNA during her period of infection.
Physical examination
When the patient presented to our hospital, her physical examination on admission revealed that vital signs were within normal limits, except for irregular fever and a sore throat.
Laboratory examinations
Blood counts on admission indicated leukocytosis (white blood cell count > 12.5 ×109/L), increased neutrophils (10.2 × 109/L) and elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (10.2 mg/L). Her blood urea nitrogen was abnormally low (2.19 mmol/L),suggesting that children infected with the novel coronavirus may develop kidney injury. This clinical phenomenon is different to adult patients. Her vital signs on admission are summarized in Table 1.
Imaging examinations
CT imaging showed multiple patchy consolidations and ground-glass opacities with an unclear boundary in both lungs. The lesions were distributed in the bronchial bundles or subpleural areas of both lungs (Figure 1). Localized pleural thickening was detected, with patchy increased opacity in both the left and right lower lungs. No characteristic changes in abdominal and pelvic organs were found on abdominal CT.However, she presented with diarrhea during her hospital stay, and this symptom was relieved after antiviral therapy. Live virus was also abundant in her feces. After 3 d of antiviral therapy, no significant shadow was found in both lung lobes. The patient exhibited rapid focal absorption in the area of pulmonary infection after antiviral therapy (Figure 1D).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Eight common respiratory pathogens in this pediatric patient were negative,includingMycoplasma pneumoniae, respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus,influenza B virus,Chlamydia pneumoniae, adenovirus, influenza A virus, andLegionella pneumophila. In addition, influenza A antigen screening was also negative. She was finally diagnosed with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV-2 infection according to real-time polymerase chain reaction amplification of viral DNA from sputum samples in Huzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
TREATMENT
On the second day after admission, the patient was treated with antiviral agents(lopinavir and ritonavir), twice daily. Her fever disappeared after 3 d of antiviral and symptomatic treatment. The patient recovered uneventfully and was discharged 5 d after admission.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Daily follow-up radiography evaluated disease progression. The patient did not show any fever or other abnormal symptoms. However, the patient had diarrhea on day 5 after discharge, but no virus or viral RNA was detected in her excrement.
DISCUSSION
COVID-19 is caused by infection with the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. The original source of SARS-CoV-2 still requires further study, but bats are thought to be the primary animal host[7]. Interpersonal transmission has been confirmed to occur,and possible modes include aerosol and contact transmission[8]. To date (March 16,2020), 81 099 confirmed cases of COVID-19 have been reported among hospital contacts in China, with 89 793 cases overseas. The mortality in China is 3.94% and 3.81% in other countries. In this case, no human-to-human transmission occurred within a single family. The patient was infected with SARS-CoV-2, but her parents who lived with her were not infected. This suggests that children and other individuals who may have weak immune systems are susceptible to infection with the novel coronavirus.
Our young female patient initially showed irregular fever, followed by swelling and pain in the throat, without symptoms such as stomachache, emesis or headache.According to a previous report[9], common symptoms of COVID-19 in adults at presentation are fever (98%), cough (76%) and dyspnea (55%), and gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea (3%) or vomiting are infrequent. The proportion of COVID-19 patients with diarrhea is significantly lower than that in patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome[10]. However, our pediatric patient showed gastrointestinal signs and symptoms, and live coronavirus was found in her feces,indicating that she may also have had mild kidney injury. In addition, she had diarrhea on day 5 after discharge, but no virus or viral RNA was detected in her feces,suggesting that the digestive tract may be more susceptible in pediatric patient than inadults. These results suggest that the clinical symptoms in pediatric patients with COVID-19 may be different to those in adult patients, and fecal excretions in pediatric patients should be monitored and detected until the viral RNA test results of infected patients are negative.
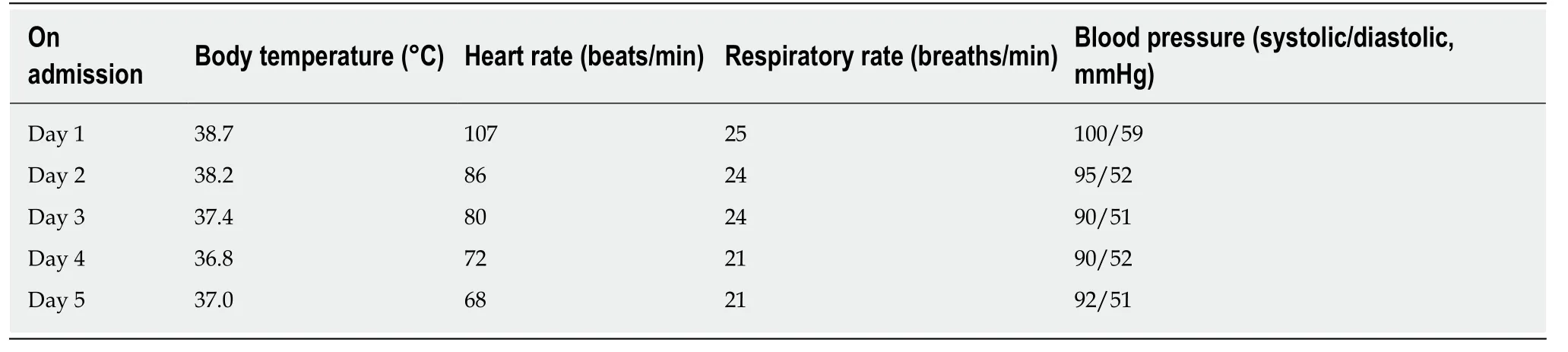
Table 1 Vital signs of the patient on admission
The CT results showed that the patient had multiple patchy consolidations and ground-glass opacities of both lungs, and the lesions were mostly distributed in the bronchial bundles or subpleural areas, especially in the right lower lobe. No pleural effusion or lymphadenopathy was found in the patient. Her fever disappeared after 3 d of antiviral and symptomatic treatment, indicating that compared to adult patients with COVID-19, children may exhibit rapid recovery after antiviral therapy. No diffuse infiltration, mediastinal emphysema or “white lungs” were found in our case.Furthermore, there was no obvious pulmonary fibrosis in this patient, which may be correlated with the short course and mild intensity. The objective clinical symptoms and CT findings in pediatric patients with COVID-19 require further investigation in subsequent large-scale studies.
CONCLUSION
We report serial chest CT findings and clinical symptoms before and after antiviral treatment, correlated with the clinical course of COVID-19 in a 7-year-old girl. Chest CT showed multiple regions of patchy consolidation and ground-glass opacities, and the lesions were mainly distributed in the bronchial bundles or subpleural areas of both lungs, particularly in the right lower lobe. Interestingly, unlike infected adult patients, this child exhibited rapid recovery after antiviral treatment. In addition, live coronavirus was found in her feces. Blood tests showed mild kidney injury during the infection. In pediatric patients with COVID-19, the novel coronavirus needs to be detected in time to ensure early diagnosis and treatment, and fecal excretions need to be monitored and detected to prevent fecal–oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
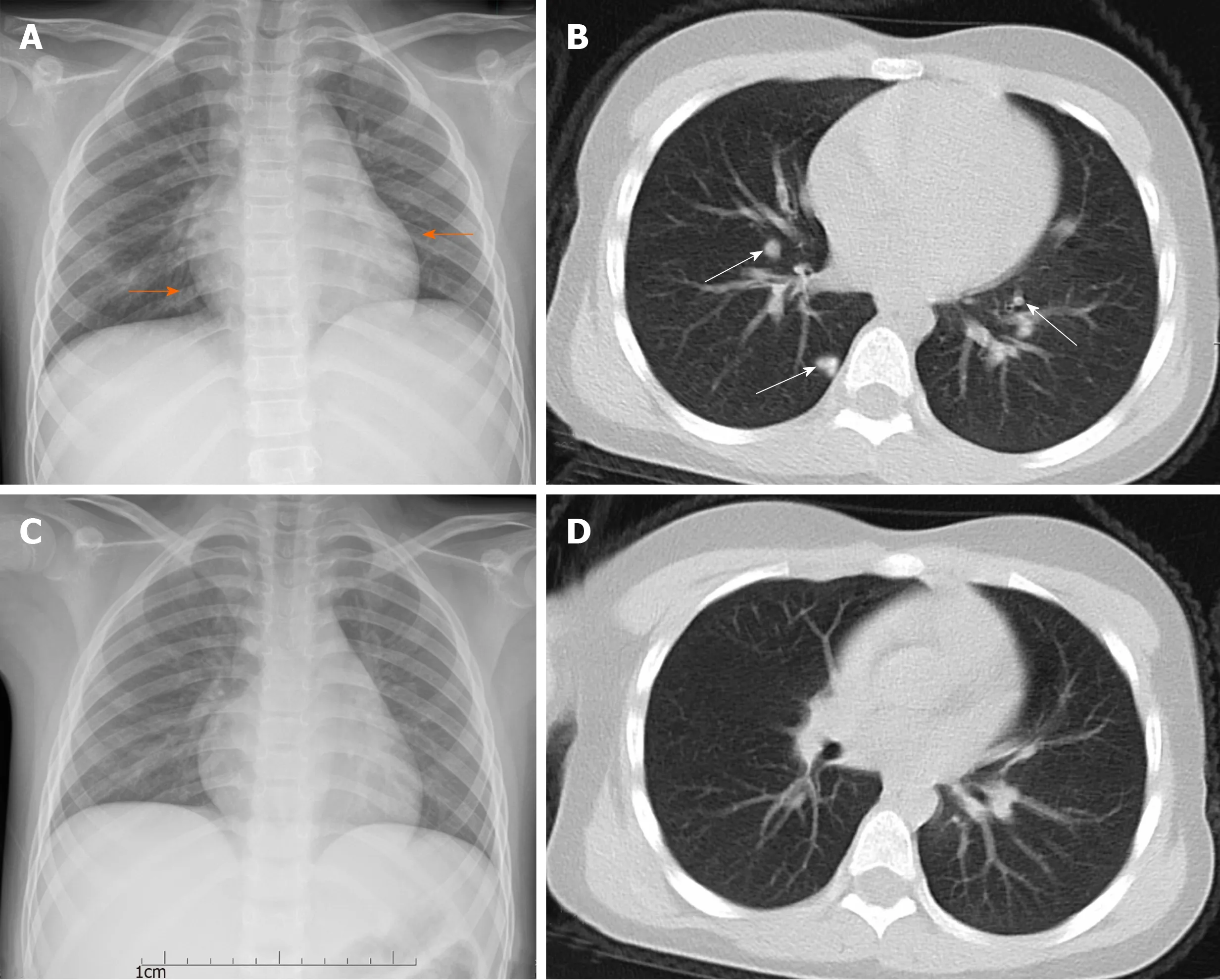
Figure 1 Seven-year-old girl with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. The posteroanterior chest radiograph and pectoral computed tomography (CT) scan were carried out in Huzhou Central Hospital on the first day of admission (1 d after fever) (A and B) and 3 d after antiviral therapy (C and D). A: Chest radiograph showed a patchy increase in the opacity of the left lower lung area located in the retrocardiac region (orange arrows); B: CT scan showed multiple patchy consolidations in both upper lobes with a ground-glass opacity halo and nodular lesions (white arrows); C: Chest radiograph showed the newly discovered unclear patchy area increase in the opacity of the right upper lung area; D: Coronal reformation CT showed rapid focal absorption in the area of pulmonary infection after 3 d of antiviral therapy.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年11期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年11期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Macrophage activation syndrome as an initial presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Optical coherence tomography guided treatment avoids stenting in an antiphospholipid syndrome patient: A case report
- Uterine incision dehiscence 3 mo after cesarean section causing massive bleeding: A case report
- Ataxia-telangiectasia complicated with Hodgkin's lymphoma: A case report
- Gastric pyloric gland adenoma resembling a submucosal tumor: A case report
- Reduced delay in diagnosis of odontogenic keratocysts with malignant transformation: A case report
