Therapeutic efficacy observation on auricular point sticking therapy for cardiac syndrome X in women
Zhang Ya-mei(張亞梅), Wang Jun (王俊)
1Xiaoshan Hospital of Zhejiang Province,Hangzhou 310013,China
2Hangzhou Red CrossHospital,Hangzhou 310003,China
Abstract
Keywords:Acupoint Therapy; Auricular Point Sticking; Otopoint, Heart (CO15); Otopoint, Liver (CO12); Otopoint, Kidney (CO10); Microvascular Angina;Cardiac Syndrome X;Women
CardiacsyndromeX (CSX),alsonamedas microvascular angina[1], is usually manifested as effort angina with a transient depression of ST segment in electro- cardiogram (ECG) test or positive treadmill test, while coronary angiogram shows no abnormity. Nearly 60% of the affected group are women in menopause period[2-3].The cause of CSX remains unclear, and is regarded to be linked withmicrovascular endothelial dysfunction,shortage of coronary artery supply, insulin resistance,inflammation and shortness of estrogen[4-5]. Speaking the treatment of CSX, medicines including nitrate esters,beta-receptor-blocking agents, calcium ion antagonist,statin and hormone have been recommended in guides of different versions[6-8], though with a wide range of selection, the therapeutic effect remains unsatisfactory.We treated CSX in women with auricular point sticking therapy on thebasis of conventional treatment. The report is now given as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
Usually manifested as effort angina, with a transient depressionof ST segment inECGtest or positive treadmill test,whilecoronary angiogramshowedno abnormity[1].
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Conformed to the diagnostic criteria of CSX; women aged between 45 and 60 years old; without auricular point sticking therapy in the past 6 months; informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Myocardial infarction or other heart diseases; those didn't finish the whole treatment scheme.
1.4 Statistical methods
TheSPSS version19.0 softwarewas usedfor statisticalanalysis.The enumerationdatawere comparedusing Chi-squaretest;measurement data were described as mean ± standard deviation (±s)and compared usingt-test.P<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
1.5 General data
All CSX patients in this study were recruited between March 2016 and March 2018 in Xiaoshan Hospital of Zhejiang Province. All 64 cases were randomized into 2 groups by the random number table method, with 32casesineachgroup.Thepatients wereaged between 45 and 59 years in the control group, and their disease duration ranged between 6 and 21 months. The caseswereagedbetween45and59years inthe treatment group,andtheir diseasedurationranged between 7 and 20 months. There was no dropout case during the treatment. Between-group comparisons of the age and duration showed no statistical significance(bothP>0.05), indicating the comparability (Table 1).
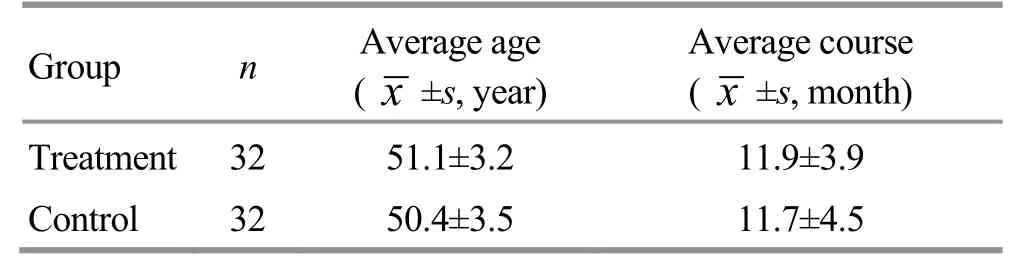
Table 1. Comparison of the general data
2 Treatment Methods
2.1Controlgroup
Thepatients inthe controlgroupreceived conventionalmedicinetreatmentfor angina,including aspirin,statinandbeta-receptor-blocking agents.
2.2 Treatment group
Patients inthetreatment groupreceivedauricular point sticking therapy onthebasisof conventional treatment sameas thatinthecontrolgroup.
Auricular points:Heart(CO15),Liver (CO12)andKidney (CO10).
Methods:Locatedauricular pointsintheconcha regionof thetwo earswithaprobing stick.Then sterilizedconcharegionwith75% alcohol,and fixedWang Bu Liu Xing(SemenVaccariae) onto the point with a piece of tape (6 mm×6 mm). At last, pressed each point for 1 min to generate endurable feeling of soreness, distention or pain in the local area. Each point was pressed three times a day for 3 min in the morning,at noon and in the evening, respectively. Changed the auricular point sticker every other day, and the whole treatment lasted for 8 weeks.
3 Therapeutic Efficacy Evaluation
3.1 Observation items
3.1.1 Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) symptoms score
This was based on theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicinesand symptoms grading criteria[9-10],inwhichsymptomsincluding chest pain and tightness, palpitations, weakness and shortness of breath were graded. No symptom scored 0 point, a mild symptom scored2points,amoderate onescored 4 points, and a severe symptom scored 6 points. At last,the total symptom score was calculated.
3.1.2 Blood sample test
Beforeandafter treatment,fasting venous blood sample was taken in the morning to test estradiol (E2),nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium-1(ET-1)levels,in which ET-1 was tested by nitrate reductase method.
3.2 Therapeutic efficacy evaluation
Markedly effective: No occurrence of angina, or the occurrence frequency reduced by >80%.
Effective:Theoccurrence frequency reducedby 50%-80%.
Invalid: The occurrence frequency reduced by <50%.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of clinical efficacy
The markedly effective rate was 53.1% and the total effective rate was 93.8% in the treatment group, which were higher thanthose inthecontrolgroup,with statistical significance (bothP<0.05), (Table 2).
3.3.2 Comparison of the TCM symptoms score
After treatment, the chest pain and tightness scores decreased significantly in the treatment group, and the intra-group comparisons showed statistical significance(bothP<0.05). The chest pain, tightness, palpitations,weakness andshortnessof breathscoresdecreased significantly after treatment in the treatment group,with statistical significance (allP<0.05), and the intergroup comparisons of chest pain and tightness scores showed statistical significance (bothP<0.05), (Table 3).
3.3.3 Comparison of serum E2, NO and ET-1 levels
After treatment,theintra-groupcomparisons of serumE2,NOandET-1levels showednostatistical significance in the control group (allP>0.05), while the E2, NO and ET-1 levels in the treatment group changed significantly, and were significantly different from those in the control group (allP<0.05), (Table 4).

Table 2. Comparison of the clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)
Table 3. Comparisons of TCM symptoms scores between the twogroups (±s, point)
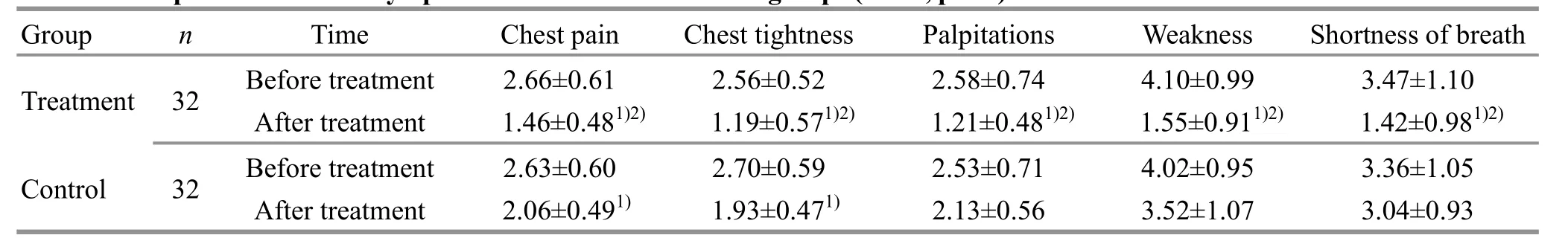
Table 3. Comparisons of TCM symptoms scores between the twogroups (±s, point)
Note:Intra-groupcomparison,1) P<0.05; between-groupcomparison after treatment,2) P<0.05
GroupnTime Chest pain Chest tightnessPalpitationsWeaknessShortness of breath Treatment 32Beforetreatment 2.66±0.612.56±0.522.58±0.744.10±0.993.47±1.10 After treatment 1.46±0.481)2)1.19±0.571)2)1.21±0.481)2)1.55±0.911)2) 1.42±0.981)2)Control 32Beforetreatment 2.63±0.602.70±0.592.53±0.714.02±0.953.36±1.05 After treatment 2.06±0.491) 1.93±0.471)2.13±0.563.52±1.073.04±0.93
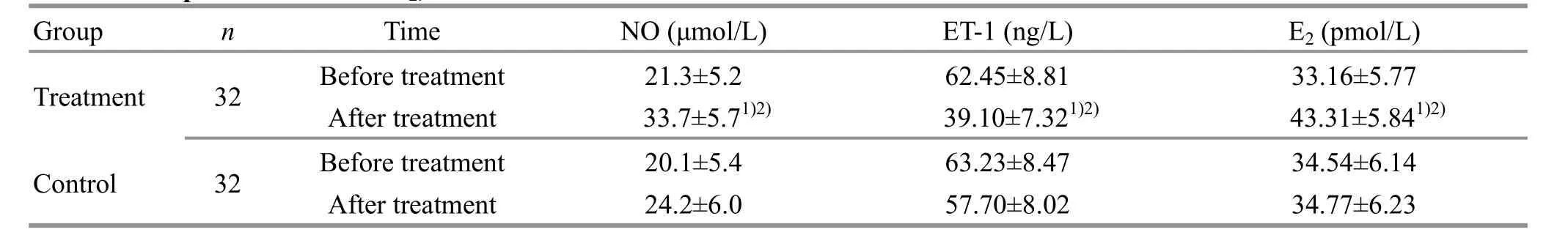
Table 4. Comparisons of serum E2, NO and ET-1 levels
4 Discussion
The cause of CSX remains unclear, and it is generally considered to be linked with microvascular endothelial dysfunction.TheimbalancebetweenNOfrom endothelial cells and endothelial marker ET-1 may be the major pathogenesis[11-12]. Scholars found serum E2levelclosely relatedto vascular endothelialgrowth factor (VEGF) in menopausal CSX women[13]. Therefore,we chose women aged 45-60 years, and used serum NO,ET-1 and E2that can reflect endothelial function as the main observation items.
CSX pertainsto chestBi-impedimentinTCM according toits clinicalsymptoms.Thoughformer research gained certain clinical efficacy, the relapse rate remained high[14-15]. We hold that the main cause of CSX shouldberoot deficiency andsuperficialexcess,in which deficiency of liver and kidney works as the root cause, and blood stasis in the Heart Meridian works as the superficial cause. Moreover, the high-risk group of CSX is women during menopausal period, which further indicates the cause of liver and kidney deficiency. As for the physiologicalcharacteristicsof Zang-fuorgans,kidney stores essence, liver stores blood and governs dredging. Dysfunction of liver and kidney, deficiency of essence and blood and failure of dredging will lead to blood stasis in heart vessels and thus cause chest pain.
Auricular pointstickingtherapy is animportant component of acupuncture-moxibustion therapy, and is widely used. Yu YT,et al[16]found the concha region was theonly areaonbody surfacewherevagusnerve afferent fiber distributedinmammalian,andby transcutaneous electrical stimulation, vagus nerves in the concha region could regulate central nerve system,which was constructive to treatment of hypertension[17],diabetes[18-19],epilepsy[20-21],depression[22]and insomnia[23-24],etc.Besides,onaccount of TCM pathogenesis of CSX: the liver and kidney deficiency as the root cause, and blood stasis in the Heart Meridian as the superficial cause, we chose Heart (CO15), Liver (CO12) and Kidney (CO10) to promote the vagus nerve tension, and improve vascular endothelial cell function to reduce the angina attack frequency.
The results showed that auricular point sticking at Heart (CO15), Liver (CO12) and Kidney (CO10) can reduce angina attack frequency in CSX patients, reduce TCM symptoms, decrease serum ET-1 level, and increase NO and E2secretions, and thus revealed the mechanism of auricular point sticking therapy for CSX.
Aboveall,conventionalmedicine treatment plus auricular point sticking therapy to stimulatevagus nerves in the concha region can effectively treat CSX in women, and the mechanism may be multi-target and multi-layer, which might link with vascular endothelial functionandE2level.Our researchstillhadmany limitations including biased investigation target for male patients, small-sample size, and single center. We hope a multi-center research with a large-sample size can be conducted in the future.

C onflict of Interest Theauthorsdeclare that there isnoconflict of interest.Acknowledgments Thiswork wassupported by ScientificResearch Fund of Hangzhou Red CrossHospital,Zhejiang Province(浙江省杭州市紅十字會醫院院內科研基金, No. hhyn201702).Statement of Informed Consent Informed consent wasobtained from all individual participants.
Received:1July 2019/Accepted:15 August 2019
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年3期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年3期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Analysis of clinical application patterns in acupuncture-moxibustion treatment of Alzheimer disease
- Therapeutic observation of manipulation plus exercise therapy in treating upper crossed syndrome postures of primary school students
- Therapeutic observation on lung-clearing and spleen-strengthening tuina in children with exogenous cough
- Clinical observation on heat-sensitive moxibustion plus lactulose for postoperative constipation of mixed hemorrhoid due to spleen deficiency
- Therapeutic effect of heat-sensitive moxibustion plus medications for senile osteoporosis and its effect on serum BMP-2 and OPG levels
- Effects of electroacupuncture plus drug anesthesia on pain and stress response in patients after radical surgery for stomach cancer
