水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統研制
王在滿,裴 娟,何 杰,張明華,楊文武,羅錫文
水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統研制
王在滿,裴 娟,何 杰,張明華,楊文武,羅錫文※
(華南農業大學南方農業機械與裝備關鍵技術教育部重點實驗室,廣州 510642)
播種量是水稻精量穴直播機的關鍵技術參數。為了實時監測水稻精量穴直播機的播種量,提高播種作業性能,該文以環形布置安裝于排種管的面源式光電傳感器為主要監測元件,設計了水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統。根據型孔式排種器結構與工作原理,確定了面源式光電傳感器和旋轉編碼器的安裝方式。采用高速攝像技術建立了水稻種子流通過監測區時種子數量與脈沖寬度之間的數學模型;通過時間分割節點得到穴粒數監測時間窗口,根據監測時間窗口內的脈沖寬度信息得到每穴播種粒數。選用南粳46和象牙香占2種具有代表性的水稻品種,對水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統進行試驗,將人工統計數據與監測系統統計數據進行對比分析,臺架試驗結果表明:對于南粳46(短粒型品種),平均穴粒數監測誤差不超過7.99%,穴數監測誤差不超過6.07%;對于象牙香占(長粒型品種),平均穴粒數監測誤差不超過24.07%,穴數監測誤差不超過5.66%。該系統基本滿足不同工作轉速下不同粒型的水稻播種量實時監測要求,可為后期實現水稻精量穴直播機大田作業參數監測提供了參考。
農業機械;水稻;穴播機;光電傳感器;播種量;監測系統;時間序列
0 引 言
精量播種技術是規模化生產實現節本增效的重要技術之一[1-2]。水稻精量穴直播已逐漸成為水稻輕簡化種植的主要研究方向[3-8]。播種量實時監測對提高直播機作業質量具有重要意義,可為播量實時調節、缺種實時補種以及水稻精量穴直播機作業管理系統等技術研發提供重要支撐[9-14]。
目前國外與播種機配套的監測裝置較為完善,美國的John Deere播種機采用光電傳感器配合信號采集電路,能夠監測播種機漏播、斷條等現象,利用圖形化處理技術對播種質量進行統計與分析,方便駕駛員實時了解播種機作業情況。Precision Planting研制的WaveVision 監測器采用高頻無線電波監測種子質量,克服了玉米播種機在排種過程中連續2 粒或多粒種子被認為1粒種子、塵土被監測為種子等技術難題,可實現對播種工況的全程監控[15]。意大利MC electronic研制的精準播種系統[16]能對大中粒徑種子進行播種監測。近年來,國內對于播種機的播種過程監測技術的研究取得了較大進展,丁幼春等[17-21]對種子與壓電薄膜的碰撞信號進行特征分析,實現了排種頻率與排種總量的實時監測。邱兆美等[22]采用光電傳感器和CMOS圖像傳感器設計的播種質量監測系統可實現對單粒播種的蔬菜種子播量監測。陳建國等[23-25]基于電容法建立了種子數量與電容變化量之間的線性關系,實現了對小麥播量的監測,但當種子通過電容傳感器引起的電容變化量較小時,監測精度會受到寄生電容和環境的影響。譚穗妍等[26-27]在育秧播種流水線上基于機器視覺和BP神經網絡對超級雜交稻的穴播量進行監測,實現了對穴播種量的精確監測的功能,平均準確率達94.4%。機器視覺法可以獲得排種過程全部的細節[28-32],但因圖像處理數據量大、設備昂貴等難以實時監測整個作業過程,不適合大田生產應用。
綜上所述,由于受田間作業環境條件差和設備成本高的限制,圖像法難以用于田間對播種量進行實時監測;電容法和光電法等對小顆粒多粒播種的播種量實時監測精度較低。因此,本文針對點陣式光電傳感器在監測高速稻種流過程中存在漏測、誤測等問題,以組合型孔式排種器為研究對象,采用面源式光電傳感器環形布置方式設計水稻精量穴直播機播量實時監測系統。該系統可多角度獲取稻種在排種管中的運動信息,并通過提取和處理脈沖信號后得到時間序列中的時間特征參數,以播種量判定指標中的“穴粒數”為監測目標,實現對水稻精量穴直播機播種量的實時精準監測。
1 監測系統基本原理
穴粒數是水稻精量穴直播機的重要性能指標。一般情況下,常規稻的每穴播種量在6~10粒,雜交稻每穴播種量為3~5粒[8]。作業時,排種器型孔內的水稻種子由彈性隨動護種機構護送至投種口在自身重力的作用下完成排種。如圖1所示,在排種過程中的各作業部件中,排種管結構形式簡單且靠近落種點,因此優選在排種管上設置播量監測傳感器;為保證排種器轉速監測的準確性,編碼器采用直聯式安裝結構,通過固定支架安裝于排種器的定位端蓋上。

1.種子 2.紅外發射器 3.監測區 4.紅外接收器 5.排種管 6.排種輪 7.固定支架 8.排種器 9.面源式光電傳感器 10.編碼器
排種管內的水稻種子流經過光電傳感器監測區時引起紅外光束強度的變化,從而導致接收端光敏電阻電壓變化。單片機控制器利用輸入捕獲中斷采集水稻種子流經面源式光電傳感器引起的脈沖信號,從而得到被監測的排種時間序列,通過排種時間序列與排種器轉速的同步監測,獲取時間分割節點,通過2個相鄰時間分割節點得到穴粒數監測時間窗口,每個監測時間窗口對應1穴;對監測時間窗口內的脈沖寬度進行特征分析,從而得到穴粒數。
時間分割節點與投種時間間隔有關。由于每穴種子在下落時具有分散性,導致實際投種時間間隔與理論投種時間間隔不一致,為保證監測的準確性,減少排種速度變化引起的監測誤差,對理論投種時間間隔進行加權處理。因投種時間間隔與轉速成反比,隨著排種速度變化,采用加權的方式修正理論投種時間間隔,可減少監測誤差。
在田間作業時排種輪轉速一般為30~60 r/min[8],因此本文設置了5個排種輪轉速,分別為25、35、45、55和65 r/min。根據前期預試驗確定了以上各轉速下對應的最優權重系數分別0.65、0.6、0.5、0.45、0.33。以權重系數為因變量,排種輪轉速為自變量,進行曲線擬合,如圖2所示。
擬合方程為

理論投種時間間隔T(s)的計算公式為

修正后投種時間間隔T(s)的計算公式為

聯立式(1)~(3)有:

式中為型孔數量,取8;為排種輪角速度,rad/s。

圖2 權重系數與排種輪轉速的關系
記排種時間序列為



式(5)~(7)中代表排種時間序列,s;(t)為第t個電平時長,s;集合代表脈沖寬度,s;q代表第個脈沖寬度,s;代表種子下落時間間隔,s;s代表第個下落時間間隔,s。
通過對排種時間序列中每一個新到達的數據元素s與修正后的投種時間間隔相比較,進行分割節點判斷,若s≥T,則該點即分割點,2個相鄰分割節點組成一個監測時間窗口,通過對監測時間窗口內的脈沖寬度進行特征分析,得出穴粒數。
2 監測系統設計
采用STM32H743IIT6微處理器作為主控芯片,該芯片主頻為400 MHz,內置2MB閃存、1MB 隨機存儲器,10個定時器、4路UART等I/O端口和外設接口,能夠滿足本文高速稻種流的監測功能。
針對目前點陣式光電傳感器在監測高速種子流過程中存在漏測、誤測等問題,以及田間作業時存在因灰塵堆積導致光電信息接收減弱等問題,本文采用面源式光電傳感器(SZ-JS系列)環形布置于排種管的安裝方式(如圖1c),實現無盲區監測,如圖1所示。面源式光電傳感器的監測范圍為25 mm×36 mm,感光面積大,能有效監測每穴通過傳感器的種子;響應速度小于0.5 ms,具備分辨每穴種子中不同種子產生的脈沖信號的能力,能有效監測每穴水稻種子粒數。面源式光電傳感器的工作面由透明外殼密封,保證了發射端發出的紅外光被接收端有效接收,同時能夠隔絕灰塵進入,避免光敏感器件的損傷,有效抑制了灰塵遮擋造成的接收電流不足。排種管(包括面源式傳感器的非工作面)采用非透明材料制成,有效地隔絕外界強光對面源式傳感器監測靈敏度的影響。為測量排種器的每穴實際投種時間間隔,采用歐姆龍E6B2-CWZ6C增量式旋轉編碼器(分辨率為2 000 P/R)獲取每穴的投種時間間隔。基于面源式光電傳感器的穴粒數監測系統硬件結構如圖3所示。

圖3 監測系統硬件結構圖
水稻種子流經面源式傳感器的光敏感區產生低電平脈沖,利用高速攝像儀觀察得到單粒種子通過監測區時的下落時間最短為3 ms。為保證監測精度,STM32控制器定時器的時間基準應小于3 ms,故設定為50s。當STM32接收到對應輸入捕獲中斷的觸發信號后開啟定時器,采用內部計數器對產生的相應信號進行計數,分別測出低電平時長Δ1和高電平時長Δ2,對修正后投種時間間隔T與高電平時長Δ2進行比較,判斷分割節點。通過計算監測時間窗口內低電平時長Δ1(脈沖寬度)對應的種子數量,實現對穴粒數的監測,計算方法如圖4所示。

圖4 穴粒數和穴數計算方法
按照上述方法,設計播量監測流程如圖5所示。
為驗證監測方法的可行性,選用排種輪常用工作轉速35、45和55 r/min,品種選用南粳46,啟動排種器使其轉動1圈(對應排種8穴),對水稻種子流經過面源式光電傳感器時的輸出脈沖信號進行采集,通過Matlab軟件對采集到的脈沖序列進行處理,結果如圖6所示,圖中局部放大圖代表一穴種子經過傳感器時的情況,相鄰2穴之間無明顯干擾信號,表明該方法可實現穴粒數與穴數的監測。

圖5 播量監測流程圖

圖6 不同排種輪轉速下南粳46的輸出電壓脈沖波形圖
3 試驗與結果分析
3.1 試驗材料
試驗在華南農業大學工程學院南方農業機械與裝備關鍵技術教育部重點實驗室進行。試驗設備主要有JPS-12計算機視覺精密排種器性能監測試驗臺、組合型孔排種器[20]、面源式光電傳感器、編碼器以及水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統。試驗裝置如圖7所示。
本文采用的組合型孔式排種器主要用于常規稻品種的播種,一般情況下,穴距10~25 cm可調,每穴播種粒數為6~10粒,短粒型品種與長粒型品種每穴播種粒數相差1粒左右。不同品種粒型和不同工作轉速對每穴播種粒數有一定的影響,因此,為考察不同品種的排種監測效果,試驗品種為短粒型稻種南粳46(常規粳稻,長寬厚為7.39 mm×3.16 mm×2.31 mm)和長粒型稻種象牙香占(常規秈稻,長寬厚為10.42 mm×2.55 mm× 1.82 mm),所選的稻種類別和外觀粒形具有代表性。

1.排種器 2.排種管 3.面源式光電傳感器傳感器 4.編碼器 5.種箱
3.2 試驗方法
3.2.1 種子數量與脈沖寬度標定
為研究監測區內不同種子數量與輸出脈沖寬度的關系,采用高速攝像對監測區內的種子數量與脈沖寬度之間的關系進行標定。選用南粳46品種作為標定對象,試驗轉速為25、35、45、55和65 r/min,通過回放高速攝像錄像統計種子下落時間,每組試驗統計100穴,重復3次。
采用日本PHOTRON公司生產的FASTCAMSUPER- 10K型高速攝像機進行種子下落過程攝像。試驗時相機拍攝幀率為1 000幀/s,分辨率為1 024×1 024。為準確記錄種子在投種過程中的下落時間,采用5 mm×5 mm網格的黑色背景板對種子下落時間進行標定,如圖8所示,建立坐標系,以排種器殼體最左端垂線為標準線,記作軸,距離排種器殼體最低端處的水平直線記作軸,并將黑色網格板中的水平線和垂直線與,軸重合。
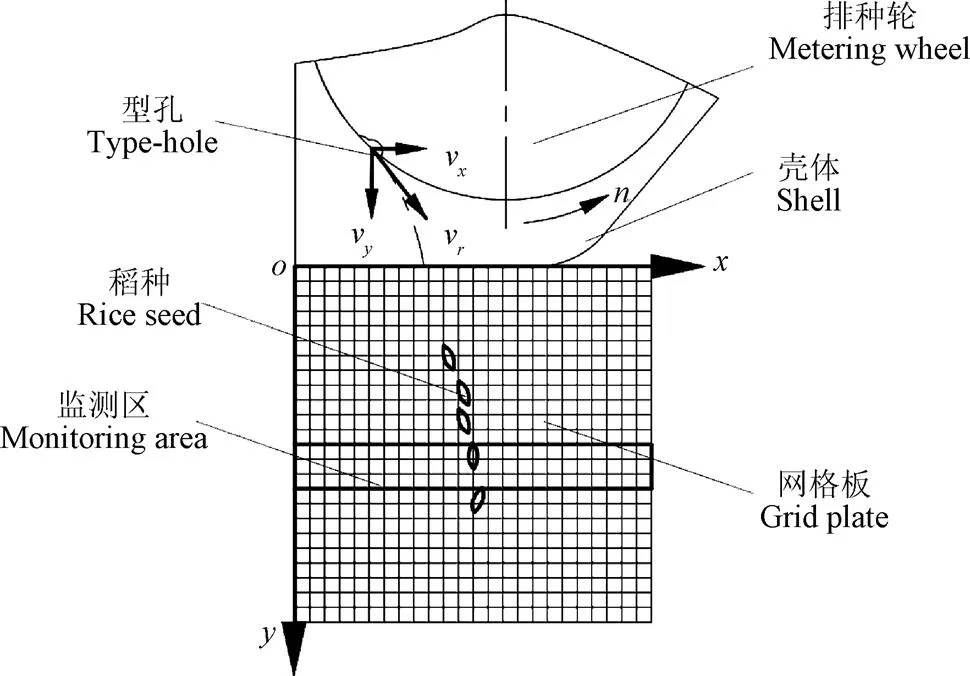
注:xoy為坐標系;vr為稻種脫離型孔時平行于排種輪平面的速度,m·s-1;vx為vr的水平分量,m·s-1;vy為vr的豎直分量,m·s-1;n為排種輪轉速,r·min-1。
3.2.2 監測系統適應性試驗
為研究監測系統對不同水稻品種粒型的適應性,選用南粳46和象牙香占2個品種,以平均穴粒數和變異系數為試驗指標,每個轉速重復3次,監測記錄200穴的穴粒數;同時采用錄像回放的方法,人工統計出輸送帶上的實際排種穴粒數和穴數,并進行數據對比分析。
3.3 結果與分析
3.3.1 種子數量與脈沖寬度標定結果
組合型孔式排種器具有多粒穴播的特點,排種輪轉速和監測區的種子數量對面源式光電傳感器輸出的脈沖寬度有影響。
為了分析種子在監測區的下落時間,連續提取水稻種子的瞬時運動圖像,圖像間的時間間隔為0.001 s。圖9為高速攝像拍攝的南梗46(短粒型品種)在不同轉速下其中1穴種子在落種區的運動狀態。

圖9 南粳46的投種過程高速攝像記錄結果
由圖9可知,在不同排種輪轉速下,當種子離開排種輪后,種子流在下落過程中以較小時間間隔的分散狀態為主。根據高速攝像拍攝到的水稻種子流在監測區內的種子數量與下落時間,結合人工統計結果,繪制不同轉速下種子數量與下落時間的曲線,如圖10所示。

圖10 不同排種輪轉速下南粳46的種子數量與下落時間關系曲線
由圖10可知,經過監測區的種子數量有1、2、3、4、5、6、7和7粒以上8種情況。在同一轉速下,在監測區的下落時間隨著種子數量的增加而增加;對于相同數量的種子,下落時間隨著轉速的增大略有降低,但降低的幅度不大,最大差值為0.003 s,表明轉速對種子的下落時間影響較小。
由監測系統工作原理可知,水稻種子流經面源式光電傳感器引起的脈沖寬度等于種子在監測區的下落時間。根據高速攝像試驗結果可計算出監測區內的種子數量及下落時間,對相同數量種子的下落時間取均值,作為相應數量的種子下落引起的面源式光電傳感器輸出脈沖寬度。對種子流引起的脈沖寬度與種子數量進行數據擬合,結果如圖11所示,兩者之間的關系式為

式中為種子數量;為粒種子通過監測區引起的脈沖寬度,s。
由圖11可知,當排種輪工作轉速一定時,種子經過監測區引起的脈沖寬度與種子數量呈單調遞增變化,線性相關系數為0.988 4,從擬合結果可看出,種子流引起的脈沖寬度與對應的種子數量之間線性關系良好。

圖11 南粳46種子數量與脈沖寬度標定曲線
3.3.2 監測系統對不同粒型水稻種子的適應性試驗結果
采用本文設計的監測系統安裝于水稻精量穴直播機組合型孔式排種器上,分別對穴數和穴粒數進行監測,試驗結果如表1所示。

表1 試驗結果與分析
由表1可知,對于南粳46(短粒型品種),平均穴粒數的監測誤差不超過7.99%,穴數的監測誤差不超過6.07%;對于象牙香占(長粒型品種),平均穴粒數的監測誤差不超過24.07%,穴數的監測誤差不超過5.66%。隨著排種輪工作轉速的升高,穴粒數的變異系數會增大,其中,當排種輪轉速在45 r/min以上時,每穴播種粒數監測值的變異系數較高,平均達到30%以上。
試驗結果表明:穴粒數監測值與實際值不一致,不同品種的監測結果也存在差異,主要原因是當2粒或者2粒以上種子經過監測區時,若存在全部或個別重疊的相鄰種子,不能產生明顯差異的脈沖寬度,故系統無法準確地監測到種子個數,造成對重疊種子的漏判,從而導致監測粒數與實際粒數存在一定的偏差;短粒型品種形狀偏橢圓形,充種與排種穩定性較好,且短粒型種子尺寸較小,故監測系統對短粒型稻種的監測精度較高。監測系統實際采集到的南粳46(短粒型品種)脈沖寬度數據結果如圖12所示。
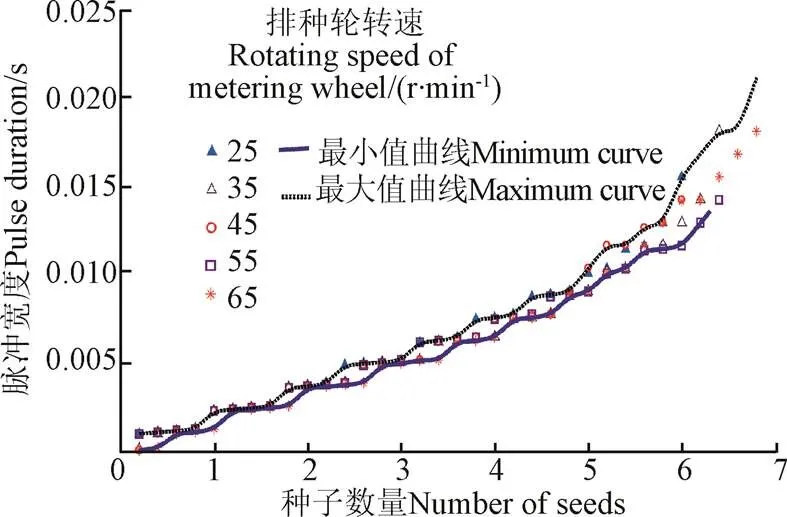
圖12 不同轉速下南粳46的種子數量與脈沖寬度關系
由圖12可知,在監測播量的過程中,由于排種器工作中會產生振動,系統的監測結果會伴有波動,波動范圍在0.002 s左右,導致系統的監測結果整體比高速攝像得到的結果偏小。
4 結 論
1)以組合型孔式排種器為研究對象,以面源式光電傳感器作為主要監測元件設計了水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統,確定了編碼器與面源式光電傳感器的安裝方式和播量基本監測原理。
2)采用高速攝像技術對種子在監測區內的下落過程進行了記錄,標定了監測區內種子數量與脈沖寬度之間的關系,為監測系統獲取播量信息提供了參考。確定了穴粒數和穴數監測算法;根據種子經過面源式光電傳感器引起的輸出脈沖信號,經控制器處理后從所產生的時間序列中提取時間值,計算得出直播機的平均穴粒數、穴數與排種器轉速的關系。
3)臺架試驗結果表明,在排種器轉速在25~65 r/min時,南粳46(短粒型品種)的平均穴粒數的監測誤差不超過7.99%,穴數的監測誤差不超過6.07%;象牙香占(長粒型品種)的平均穴粒數監測誤差不超過24.07%,穴數的監測誤差不超過5.66%;排種器工作轉速對平均穴粒數的監測精度影響較大,隨著排種器工作轉速的升高,平均穴粒數監測值的變異系數會增大。
在不同的排種輪工作轉速下,該監測系統對不同外觀粒型的水稻品種均具有較高的監測精度,可實現對水稻精量穴直播機播量的實時監測。
[1]楊麗,顏丙新,張東興,等. 玉米精密播種技術研究進展[J]. 農業機械學報,2016,47(11):38-48.
Yang Li, Yan Bingxin, Zhang Dongxing, et al. Research progress on precision planting technology of maize[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(11): 38-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2]苑嚴偉,張小超,吳才聰,等. 玉米免耕播種施肥機精準作業監控系統[J]. 農業工程學報,2011,27(8):222-226.
Yuan Yanwei, Zhang Xiaochao, Wu Caicong, et al. Precision control system of no-tillage corn planter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(8): 222-226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3]知谷,羅錫文. 開啟水稻機械化精量穴直播時代[J]. 農業機械,2018(2):57-58.
[4]Zhang Minghua, Wang Zaiman, Luo Xiwen, et al. Review of precision rice hill-drop drilling technology and machine for paddy[J]. Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2018, 11(3): 1-11.
[5]張明華,王在滿,羅錫文,等. 組合型孔排種器雙充種室結構對充種性能的影響[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(12):8-15.
Zhang Minghua, Wang Zaiman, Luo Xiwen, et al. Effect of double seed-filling chamber structure of combined type-hole metering device on filling properties[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(12): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6]王金武,李樹偉,張曌,等. 水稻精量穴直播機電驅式側深穴施肥系統設計與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(8):43-54.
Wang Jinwu, Li Shuwei, Zhang Zhao, et al. Design and experiment of electrical drive side deep hill-drop fertilization system for precision rice hill-direct-seeding machine [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(8): 43-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7]張明華,羅錫文,王在滿,等. 水稻精量穴直播機仿形與滑板機構的優化設計與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2017,33(6):18-26.
Zhang Minghua, Luo Xiwen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Optimization design and experiment of profiling and slide board mechanism of precision rice hill-drop drilling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(6): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8]張明華,羅錫文,王在滿,等. 水稻直播機組合型孔排種器設計與試驗[J]. 農業機械學報,2016,47(9):29-36.
Zhang Minghua, Luo Xiwen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Design and experiment of combined hole-type metering device of rice hill-drop drilling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9): 29-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9]車宇,偉利國,劉婞韜,等. 免耕播種機播種質量紅外監測系統設計與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2017,33(增刊1):11-16.
Che Yu, Wei Liguo, Liu Xingtao, et al. Design and experiment of seeding quality infrared monitoring system for no-tillage seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(Supp.1): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10]黃東巖,賈洪雷,祁悅,等. 基于聚偏二氟乙烯壓電薄膜的播種機排種監測系統[J]. 農業工程學報,2013,29(23):15-22.
Huang Dongyan, Jia Honglei, Qi Yue, et al. Seeding monitor system for planter based on polyvinylidence fluoride piezoelectric film[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(23): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11]王金武,張曌,王菲,等. 基于壓電沖擊法的水稻穴直播監測系統設計與試驗[J]. 農業機械學報,2019,50(6):74-84.
Wang Jinwu, Zhang Zhao, Wang Fei, et al. Design and experiment of monitoring system for rice hill-direct-seeding based on piezoelectric impact method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(6): 74-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12]趙立新,張增輝,王成義,等. 基于變距光電傳感器的小麥精播施肥一體機監測系統設計[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(13):27-34.
Zhao Lixin, Zhang Zenghui, Wang Chengyi, et al. Design of monitoring system for wheat precision seeding-fertilizing machine based on variable distance photoelectric sensor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(13): 27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13]Duan Lingfeng, Yang Wanneng, Bi Kun, et al. Fast discrimination and counting of filled/unfilled rice spikelets based on bi-modal imaging[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2011, 75(1): 196-203.
[14]賈洪雷,路云,齊江濤,等. 光電傳感器結合旋轉編碼器監測氣吸式排種器吸種性能[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(19):28-39.
Jia Honglei, Lu Yun, Qi Jiangtao, et al. Detecting seed suction performance of air suction feeder by photoelectric sensor combined with rotary encoder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(19): 28-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15]Precision Planting. WaveVision [EB/OL]. 2014-07-15 [2019-08-22]. https://www.precisionplanting.com/products /product/wavevision
[16]MC electronics. Sistema full semina [EB/OL]. 2019-06-28 [2019-12-29].https://www.mcelettronica.it/it/prodotti/semina/semina-a-righe/fotocellula-blockage-pro-seeder_256c28.html.
[17]丁幼春,王雪玲,廖慶喜. 基于時變窗口的油菜精量排種器漏播實時監測方法[J]. 農業工程學報,2014,30(24):11-21.
Ding Youchun, Wang Xueling, Liao Qingxi. Method of real-time loss sowing detection for rapeseed precision metering device based on time changed window[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(24): 11-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18]丁幼春,朱凱,王凱陽,等. 薄面激光-硅光電池中小粒徑種子流監測裝置研制[J]. 農業工程學報,2019,35(8):12-20.
Ding Youchun, Zhu Kai, Wang Kaiyang, et al. Development of monitoring device for medium and small size seed flow based on thin surface laser- silicon photocell[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(8): 12-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19]李明,劉曉輝,丁幼春,等. 基于排種頻率的油菜氣力式精量排種器漏播監測技術與裝置[C]//中國農業工程學會學術年會. 重慶:2011:299-304.
Li Ming, Liu Xiaohui, Ding Youchun, et al. Loss sowing test technology and equipment of rapeseed pneumatic precision seeder based on the seeding frequency[C]//Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, Chongqing: 2011: 299-304. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20]丁幼春,楊軍強,朱凱,等. 油菜精量排種器種子流傳感裝置設計與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2017,33(9):29-36.
Ding Youchun, Yang Junqiang, Zhu Kai, et al. Design and experiment on seed flow sensing device for rapeseed precision metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 29-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21]丁幼春,張莉莉,楊軍強,等. 油菜精量直播機播種監測系統傳感裝置改進及通信設計[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(14):19-26.
Ding Youchun, Zhang Lili, Yang Junqiang, et al. Sensing device improvement and communication design on sowing monitoring system of precision planter for rapeseed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(14): 19-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22]邱兆美,張巍朋,趙博,等. 小粒種子電動播種機作業質量監測系統設計與試驗[J]. 農業機械學報,2019,50(4):77-83.
Qiu Zhaomei, Zhang Weipeng, Zhao Bo, et al. Design and test of operation quality monitoring system for small grain electric seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(4): 77-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23]陳建國,李彥明,覃程錦,等. 小麥播種量電容法監測系統設計與試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(18):51-58.
Chen Jianguo, Li Yanming, Tan Chengjin, et al. Design and test of capacitive detection system for wheat seeding quantity[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(18): 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24]周利明,王書茂,張小超,等. 基于電容信號的玉米播種機排種性能監測系統[J]. 農業工程學報,2012,28(13):16-21.
Zhou Liming, Wang Shumao, Zhang Xiaochao, et al. Seed monitoring system for corn planter based on capacitance signal[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(13): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25]田雷. 基于電容傳感器的玉米精量播種機排種性能監測系統研究[D]. 大慶:黑龍江八一農墾大學,2018.
Tian Lei. Research on Monitoring System for Performance of Corn Precision Seeder Based on Capacitance Sensor Seeding[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26]譚穗妍,馬旭,吳露露,等. 基于機器視覺和BP神經網絡的超級雜交稻穴播量監測[J]. 農業工程學報,2014,30(21):201-208.
Tan Suiyan, Ma Xu, Wu Lulu, et al. Estimation on hole seeding quantity of super hybrid rice based on machine vision and BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(21): 201-208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27]趙鄭斌,劉昱程,劉忠軍,等. 基于機器視覺的穴盤精密播種性能監測系統[J]. 農業機械學報,2014,45(Z1):24-28.
Zhao Zhengbin, Liu Yucheng, Liu Zhongjun, et al. Performance detection system of tray precision seeder based on machine vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(Z1): 24-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28]張海娜,馬玉芳. 基于圖像處理的機器播種參數檢測方法研究[J]. 測控技術,2015,34(2):44-47.
Zhang Haina, Ma Yufang. Research on performance testing method of machine sowing based on image processing[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2015, 34(2): 44-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29]周茉,張學明,劉志剛. 基于高速攝像系統和圖像邊緣檢測的精密排種器設計[J]. 農機化研究,2016,38(9):108-112.
Zhou Mo, Zhang Xueming, Liu Zhigang. Designn metering devic for precisioe based on high—speed camera and image edge detection[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016,38(9): 108-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30]陳進,邊疆,李耀明,等. 基于高速攝像系統的精密排種器性能檢測試驗[J]. 農業工程學報,2009,25(9):90-95.
Chen Jin, Bian Jiang, Li Yaoming, et al. Performance detection experiment of precision seed metering device based on high-speed camera system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(9): 90-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31]趙學觀,徐麗明,王應彪,等. 基于Fluent與高速攝影的玉米種子定向吸附研究[J]. 農業機械學報,2014,45(10):103-109,128.
Zhao Xueguan, Xu Liming, Wang Yingbiao, et al. Directional adsorption characteristics of corn seed based on fluent and high-speed photography[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(10): 103-109, 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32]Karayel D, Wiesehoff M. Laboratory measurement of seed drill seed spacing and velocity of fall of seeds using high-speed camera system[J]. Computers & Electronics in Agriculture, 2006, 50(2): 89-96.
Development of the sowing rate monitoring system for precision rice hill-drop drilling machine
Wang Zaiman, Pei Juan, He Jie, Zhang Minghua, Yang Wenwu, Luo Xiwen※
(,,,510642,)
Precision seeding technology is one of the important technologies to realize cost saving and efficiency increasing in large-scale production. Precision direct seeding of rice has gradually become the main research direction of rice light and simplified planting. The real-time sowing monitoring system has an important contribution to improve the sowing quality of direct seeding machine, and can provide important support for the research and development of sowing rate real-time adjustment, real-time reseeding and the seeding evaluation quality system of rice precision direct seeding machine. At present, the methods of seeding monitoring are photoelectric-based, image-based and capacitance-based. However, image processing technology requires special equipment with high cost, and cameras are easy to be interfered by external light. For the capacitance-based method, when multiple small seeds fall simultaneously, the monitoring performance is not accurate enough. In order to monitor the sowing rate of precision rice hill-drop drilling machine in real time, in this paper, the surface-type photoelectric sensor installed in the seeding tube is used as the main monitoring element to design the monitoring system of precision rice hill-drop drilling machine. According to the structure and working principle of seed metering device, the installation modes of photoelectric sensor and rotary encoder are determined. In this system, the seeds flow in the seeding tube is taken as the research object. When the rice seeds pass through the photoelectric sensor monitoring area, it will cause the change of infrared beam intensity, which will lead to the change of photoresist voltage. The pulse signal from the photoelectric sensor is used as the time sequence to capture the interruption source, and then the monitored time sequence of rice seeds flow is obtained. The time division node is obtained by the synchronous monitoring of the seed metering time series and the rotation speed of the seed metering device. Based on the two adjacent time dividing nodes, the detecting time window of the seeds number per hill is obtained, each time window corresponds to one hill. The pulse width time of the rice seeds output in the monitoring time window is analyzed to get the seeds number per hill. Compared and analyzed the manual statistical data with the monitoring system statistical data, the test results show that the rotation speed of the seed metering device has a great influence on the monitoring accuracy of the average seeds number per hill, the variation coefficient of the monitored value of the average seeds number per hill grows up with the increase of the rotation speed of the seed metering device. When the rotation speed of seed metering device is 25-65 r/min, the relative error of seeds number per hill is less than 7.99% for Nanjing 46 (short grain variety), the monitoring errors of the number of hills is less than 6.07%; the relative errors of seeds number per hill is less than 24.07% for Xiangyaxiangzhan (long grain variety), the monitoring errors of the number of hills is less than 5.66%.The test results show that sowing rate monitoring system is applicable to different varieties of seed and has good detection accuracy, which can provide reference for improving the operation quality of precision rice direct seeder.
agricultural machinery; rice; hill-drop drilling machine; surface-type photoelectric sensor; sowing rate; monitoring system; time series
王在滿,裴娟,何杰,等. 水稻精量穴直播機播量監測系統研制[J]. 農業工程學報,2020,36(10):9-16.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.10.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Wang Zaiman, Pei Juan, He Jie, et al. Development of the sowing rate monitoring system for precision rice hill-drop drilling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(10): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.10.002 http://www.tcsae.org
2020-02-24
2020-04-27
國家重點研發計劃項目(2017YFD0700503);廣東省自然科學基金(2020B1515020034);現代農業產業技術體系建設專項資金(CARS-01-41)
王在滿,博士,副研究員,主要從事水稻生產機械化關鍵技術與裝備研究。Email:wangzaiman@scau.edu.cn
羅錫文,教授,中國工程院院士,主要從事農業機械化研究。Email:xwluo@scau.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.10.002
S223.25
A
1002-6819(2020)-10-0009-08

