Cross electro-nape-acupuncture ameliorates cerebral hemorrhageinduced brain damage by inhibiting necroptosis
Guo-Feng Cai,Zhong-Ren Sun,Zhe Zhuang,Hai-Chun Zhou,Shan Gao,Kai Liu,Li-Li Shang,Kun-Ping Jia,Xiu-Zhen Wang,Hui Zhao,Guo-Liang Cai,Wen-Li Song,Sheng-Nan Xu
Guo-Feng Cai,Hai-Chun Zhou,Kai Liu,Kun-Ping Jia,Xiu-Zhen Wang,Hanan Branch of Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150001,Heilongjiang Province,China
Guo-Feng Cai, Postdoctoral Research Station of Heilongjiang Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150001,Heilongjiang Province,China
Zhong-Ren Sun, Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang Province,China
Zhe Zhuang,Li-Li Shang,Hui Zhao,Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150000,Heilongjiang Province,China
Shan Gao, First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang Province,China
Guo-Liang Cai,Wen-Li Song, Harbin Sport University,Harbin 150001,Heilongjiang Province,China
Sheng-Nan Xu,Graduate School of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang Province,China
Abstract
Key words:Cross electro-nape acupuncture;Cerebral hemorrhage;Receptor interacting protein kinase 1;Necroptosis;Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction;Enzymelinked immunosorbent assay
INTRODUCTION
Cerebral hemorrhage(CH)is one of the most common cerebrovascular emergencies with high mortality worldwide[1-3].Although surgery,especially minimally invasive surgery,has led to some progress in the treatment of CH,the long-term outcomes including inflammatory response and encephaledema after CH are not completely resolved.Moreover,there is a lack of a systematic therapeutic mode in the treatment of CH.Therefore,it is of necessity to determine the pathophysiological pathogenesis of CH and develop more effective treatments.
Necroptosis,a new-found programmed cell death,was originally nominated by Degterevet al[4],who found that this type of cell death could be triggered by the tumor necrosis factor receptor(TNFR)signaling pathway.Generally,once the TNFR signaling pathway is activated,receptor interacting protein kinase 1(RIPK1)is then recruited to the intracellular domain of TNFR to activate the downstream signaling pathway[5,6].When modified by ubiquitination,RIPK1 interacts with the IκB kinase(IKK)complex and transforming growth factor β-activated kinase-1(TAK1)to induce activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B(NF-κB)signaling pathway and the mitogenactivated protein kinases(MAPKs)signaling pathway[7,8].In the absence of caspase-8,RIPK1 interacts with RIPK3 to form a necrosome,resulting in auto-phosphorylation of RIPK3(p-RIPK3)[9].Furthermore,p-RIPK3 activates and phosphorylates mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase(MLKL),which translocates to the cell membrane and induces rupture of the cell membrane[10].Therefore,RIPK1 functions at the crossroad.Although the morphological features of necroptosis are indistinct from necrosis,genetic and pharmacological interventions could block necroptosis,which belongs to programmed cell death[11].It has been demonstrated that necroptosis is involved in a variety of diseases,including tumors[12],inflammatory diseases[13]and ischemic injury[14].Recently,Suet al[15]reported that targeting RIPK1 using the chemical necrostatin-1 could mitigate brain damage after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice.In addition,inhibiting necroptosis contributes to the improvement of synaptic injury induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage in the hippocampus[16].Therefore,overcoming necroptosis may be a novel approach for the treatment of CH.
Acupuncture,a traditional Chinese medicine for multiple diseases,acts on specific acupoints of the body to exert its functions,and is extensively used worldwide[17,18].It has been demonstrated that acupuncture ameliorates neurological impairments in rats with CH[19].A randomized controlled trial was carried out in patients with CH and showed that acupuncture improved neurological functions[20].Based on the effectiveness of acupuncture in CH,researchers have applied electric stimulus into acupuncture to assess the effects of electroacupuncture(EA)in CH,andin vivoexperiments show that EA inhibits expression of apoptosis-related proteins to reduce brain damage in rats with CH[21].Cross electro-nape-acupuncture(CENA)is a modified EA,and our previous clinical trial demonstrated that CENA promoted recovery of lung infection in patients with CH by remodeling the cough reflex[22],which suggested a potential therapy for CH.However,the underlying mechanism is still unknown.
選用于2016年1月至12月期間在本院接受糖尿病治療的100例患者作為研究對象進行分析,并根據其實施品管圈活動前后,將其平均分成兩組,即觀察組(實施品管圈活動后)與對照組(未實施實施品管圈活動)。在觀察組中,患者中,男性27例,女性23例;年齡55~70歲不等,平均年齡68.25±1.05歲,病程1~10年不等,平均年齡5.68±0.67年。在對照組患者中,男性26例,女性24例;年齡56~71歲不等,平均年齡68.52±1.20歲;病程1~11年不等,平均年齡5.57±0.54年。對比兩組的年齡、性別等臨床資料,其差異甚小,存在統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。
In the present study,we determined the protective effects of CENA on brain damage in rats with CH and investigated the underlying mechanism,in order to provide a theoretical foundation to better understand the pathogenesis of CH and to develop optimized treatments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and grouping
A total of one hundred and eight male Sprague-Dawley(SD)rats,weighing 300 ± 15 g,were obtained from Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine.The procedures were approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine.The rats were randomized into four groups:Sham group(n=27),CENA group(n=27),CH group(n=27)and CH+CENA group(n=27).To obtain brain tissues,we randomly chose 36 rats in total with 9 rats from each group on the third day after surgery and treatment.The remaining 72 rats continued to be treated with the experimental procedures.
Establishment of CH models
The rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium(40 mg/kg)and placed in stereotaxic apparatus.A hole was drilled through the skull and a microsyringe was injected into the basal ganglia region(5 mm to the left side of the bregma and 0.2 mm in front of the coronal suture)with a depth of 5 mm.A total of 50 μL autogenous femoral arterial blood was transfused at a speed of 20 μL/min.After 10 min,the microsyringe was slowly withdrawn.The hole was covered with Self Curing Denture Acrylic(Pearson,United States).Rats in the sham group underwent the same procedures without the transfusion.
Application of CENA
After surgery,all the rats were fixed.Rats in the CENA group and CH+CENA group were treated with CENA.The acupuncture needles(Hwato,China)were placed in the leftFengchiacupoint(GB20)and the rightYifengacupoint(TE17),and connected to the EA therapeutic apparatus(Hwato,China).Rats were treated with CENA for 30 min/d after the surgical procedures.Rats in the sham group and CH group were fixed without treatment.
Measurement of necrotic cells in vivo
Propidium iodide(PI,Abcam,United States)was used to monitor the necrotic cells in brain tissues of the experimental rats.The brain tissues were embedded with O.C.T.Compound(Sakura,United States)and then cut into sections 30 μm thick.The sections were incubated with PI solution for 30 min.After washing three times with PBS,images of the sections were captured by fluorescence microscopy(Olympus,Japan).
Immunofluorescence
Brain sections were incubated with p-MLKL primary antibodies(Abcam,United States)overnight at 4°C.NeuN(Abcam,United States)was used to label neurons.After washing,the sections were incubated with goat anti-mouse IgG-Cy3 Conjugated secondary antibodies(Beyotime,China)and goat anti-rabbit IgG-Alexa Fluor 488 Conjugated secondary antibodies(Beyotime,China)for 2 h.DAPI(Beyotime,China)was used to label cell nuclei.Images of the sections were visualized and captured by confocal microscopy.
Detection of neurological functions
Neurological functions were determined by estimating the neurological scores[23]and behavioral scores[24]as previously reported.For detection of neurological scores,the contributing factors consisted of six parts:Autonomic movement,tail-suspension four-limb movement,forelimb stretching,climbing and grasping ability,somatosensory response,and beard-touching response.Each factor was graded from 0(no response)to 3(normal).Lower neurological scores in the experimental rats represented impaired neurological function.For evaluation of the behavioral scores,the contributing factors included ipsilateral circling,bilateral grasp,and beam walking.Each factor was graded from 0(normal behavior)to 4(no response).Higher behavioral scores in the experimental rats represented damaged behavioral function.
Evaluation of water content in rat brain tissues
On the third day after surgery and treatment,the brain tissues of experimental rats(n=36)were harvested.Water content(edema)was measured as reported previously[23].Water content(%)=(wet weight - dry weight)/wet weight.
Western blot
Western blot analysis was carried out as reported previously[15].Total protein was extracted from brain tissues of experimental rats using RIPA Lysis Buffer(MultiSciences,China).The BCA Protein Quantification Kit(MultiSciences,China)was used to detect protein concentration.The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE gel(MultiSciences,China).Primary antibodies(RIPK1,RIPK3,p-RIPK3,MLKL,p-MLKL,GAPDH)were purchased from Abcam(United States).ChemDocTMXRS+System(Bio-Rad,United States)was used to detect the protein bands.GAPDH was the internal reference protein.
Immunoprecipitation assay
The immunoprecipitation(IP)assay was conducted using the Pierce Co-Immunoprecipitation Kit(Thermo Fisher Scientific,United States)according to the manufacturer's instructions.The brain tissues were cut into pieces and lysed by IP Lysis Buffer.Next,the RIPK1 primary antibody(Abcam,United States)was added to the lysis solution containing total protein,Sodium cyanoborohydride,Coupling Buffer,Elution Buffer and Loading Buffer were used in sequence to obtain the samples.The interaction between RIPK1 and RIPK3 was evaluated by western blot analysis.
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
Total RNA was extracted from the freshly isolated brains of rats using TRIzol(Ambion,United States).The acquisition of cDNA and the following quantitative realtime polymerase chain reaction(qRT-PCR)were performed using SuperScript III(Invitrogen,United States)and SYBR Premix Ex Taq II(Takara,Japan),respectively.The set procedures were as follow:95 °C,30 s;55 °C,30 s;72 °C,30 s.A total of 40 cycles were performed.The primers were obtained from Sangon(China).Interleukin(IL)-6 forward:5'-CCACTTGGATGTAACTGGCCT-3';IL-6reverse:5'-GGAAAAAGTGCTGCTACCCTG-3'.IL-8forward:5'-CATTAATATTTAACGATGT-GGATGC-3';IL-8reverse:5'-TAACACGTCAAATTTCTACCATCCG-3'.Tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α)forward:5'-TATCCGTCCAACCTCAGCAT-3';TNF-αreverse:5-'GCGAATGAACGAACAAGCGT-3'.GAPDHforward:5'-TGAAATGTGCACGCACCAAG-3';GAPDHreverse:5'-GGGAAGCAGCATTCAGGTCT-3'.GAPDH was the internal reference.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
On the seventh day after surgery and treatment,300 μL of cerebrospinal fluid(CSF)from each rat and 1.2 mL of fresh blood were collected.After centrifugation,the CSF samples and serum samples were added into plates to measure the concentration of IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α using a Rat IL-6 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)Kit(Beyotime,China),Rat IL-8 ELISA Kit(NeoScientific,United Kingdom)and Rat TNF-α ELISA Kit(Beyotime,China),respectively,in accordance with the manufacturers' guidelines.
Statistical analysis
All data are shown as mean ± SD,and were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 6.01 Software(GraphPad,United States).The statistical analysis methods used weret-test and two-way ANOVA.APvalue less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
CH induced necroptosis in brain
To investigate the involvement of necroptosis in CH,we first monitored the necrotic cells in brains by evaluating the PI positive rate.As shown in Figure 1A and B,the number of PI positive cells was significantly increased in rats with CH(cP<0.001),indicating that CH can induce necrosis.It has been reported that p-MLKL could be regarded as an indicator of necroptosis[25,26].Next,we performed immunofluorescence to determine the expression of p-MLKLin situ.The results showed that p-MLKL was not detectable in the neurons of rats in the sham group,whereas p-MLKL was positively expressed in the neurons of rats with CH(Figure 1C).These results demonstrated that necroptosis existed in CH.
CENA alleviated brain damage in rats with CH
To determine whether CENA exerted protective effects in rats with CH,we performed the following experiments.The neurological scores of rats in the CENA group showed a similar trend to that in the sham group;however,CENA reversed the decreased neurological score in rats with CH(Figure 2A,bP<0.01).In parallel,CENA ameliorated the damaging behavior of rats with CH by evaluating the behavioral score(Figure 2B,bP<0.01).Next,we measured brain tissue edema in the different groups.On the third day after surgery and treatment,rat brain tissues were collected,and it was found that the water content in the brain tissues of rats with CH was increased compared with that in the sham group,while CENA partially reduced water content in the brain tissues of rats with CH(Figure 2C,aP<0.05).These results suggested that CENA can alleviate brain damage.
CENA inhibited CH-mediated necrosome formation in vivo
Based on the above findings,we assessed whether CENA reduced cell death in the brains of rats with CH,especially necroptosis.Immunofluorescence analysisin situshowed that the number of PI positive cells in the CENA group was similar as that in the sham group(Figure 3A and B).Importantly,the increased PI positive cells in the CH group were reduced by CENA in the brains of rats with CH(Figure 3A and B,bP<0.01).As necroptosis is mediated by RIPK1,and executed by RIPK3 and MLKL,it is still unclear whether CENA affected the expression of necroptosis-related molecules in the brain tissues of these rats.Western blot analysis revealed that CENA treatment did not upregulate the expression of RIPK1,RIPK3 and MLKL,and did not activate RIPK3 and MLKL in normal brain tissues(Figure 3C-3H).It was also found that rat brain tissues in the CH group displayed a dramatically higher protein level of RIPK1,RIPK3,p-RIPK3 and p-MLKL,which was reversed by CENA treatment(Figure 3C-F and H,aP<0.05).However,the expression of MLKL showed no obvious change(Figure 3C and G).In addition,an IP assay was carried out to evaluate necrosome formation.The results showed that RIPK3 interacting with RIPK1 increased markedly in rat brain tissues after CH,and CENA treatment partially disturbed this interaction between RIPK1 and RIPK3(Figure 3I-K,aP<0.05).These results indicated that CENA reduced cell death by inhibiting necrosome formation in rat brain tissues after CH.
CENA ameliorated inflammatory cytokines in rats with cerebral hemorrhage
It has been demonstrated that CH is accompanied by inflammation[27,28].We first detected the expression of inflammatory factors IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α in the brain tissues of rats.qRT-PCR showed that rat brain tissues in the CH group displayed a significantly higher mRNA level of IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α,and CENA treatment partially decreased these three inflammatory factors(Figure 4A-C,aP<0.05).Next,we extracted CSF and measured the content of IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α using ELISA.Consistent with the results of qRT-PCR,increased concentrations of IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α were found in the CSF of CH model rats,which was reduced by CENA treatment(Figure 4D-F,aP<0.05).In parallel,the secretion of IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α in rat serum showed a similar trend to that detected in CSF(Figure 4G-I,aP<0.05).Thus,CENA can ameliorate local and systemic inflammation caused by CH.
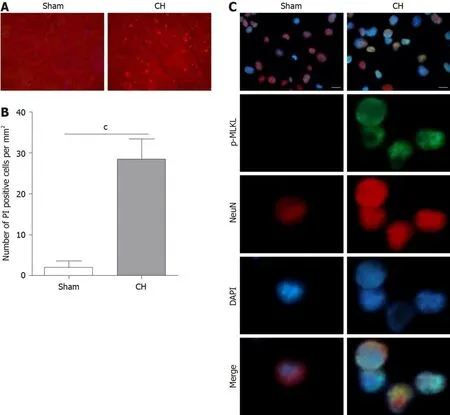
Figure 1 Cerebral hemorrhage induced necroptosis in brain tissue.A and B:Propidium iodide staining(A)and propidium iodide positive rate(B)in brain tissues of the experimental rats;C:Immunofluorescence assay showed the expression of the necroptotic marker p-MLKL in the experimental rats.Scale bar:20 μm.cP<0.001.CH:cerebral hemorrhage;PI:Propidium iodide;MLKL:mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase.
DISCUSSION
In the current study,we investigated the neuroprotective role of CENA in rats with CH and investigated the underlying mechanism.First,we found that a necroptotic marker was detectable in the brain of a CH rat model.The impaired neurological functions induced by CH were reversed by CENA.Furthermore,our results showed that necroptosis mediator RIPK1 was overexpressed in the brain tissues of the CH rat model.In addition,CH induced phosphorylation of RIPK3 and MLKL.Notably,CENA reduced the upregulation of RIPK1,p-RIPK3 and p-MLKL,and partially blocked the interaction between RIPK1 and RIPK3.Finally,CENA contributed to the amelioration of CH-induced inflammatory response in rats.
Although a variety of studies have focused on the pathogenesis of brain damage after CH,the complex mechanisms make it difficult to overcome the problem of ineffective treatments.Increasing evidence has demonstrated that apoptosis and necrosis play leading roles in neuron death after CH[29,30].Apoptosis belongs to programmed cell death;while necrosis is passive cell death and accompanied by inflammatory response[31].As necrosis cannot be regulated,there is little research on the role of necrosis in CH.A previous investigation reported that a new-found necrotic cell death,namely necroptosis,exists in ischemic brain damage,which could be suppressed by small molecule inhibitor necrostatin-1[4].Subsequently,RIPK1 was identified as the key mediator of necroptosis and the target of necrostatin-1[32].Accumulating evidence indicates that RIPK1 interacts with RIPK3 to form a necrosome,which phosphorylates the substrate molecule MLKL to break the integrity of the plasm membrane and cause cell death[5,8,10,26].In addition,genetic intervention of RIPK3[33]or MLKL inhibition with small interfering RNA and small molecule inhibitor necrosulfonamide[34]can prevent necroptosis.Therefore,targeting RIPK1,RIPK3 or MLKL is a promising strategy to treat necroptosis-related diseases.
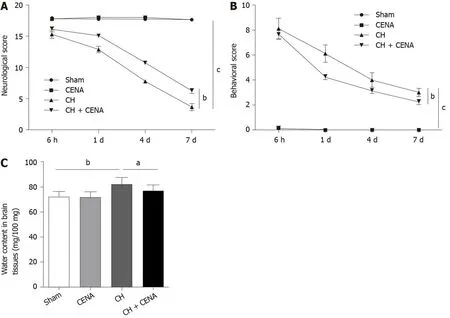
Figure 2 Cross electro-nape acupuncture alleviated brain damage in rats with cerebral hemorrhage.A:Neurological scores in the experimental rats;B:Behavioral scores in the experimental rats;C:Evaluation of cerebral edema in the brain tissues of experimental rats.aP<0.05,bP<0.01,cP<0.001.CENA:Cross electro-nape acupuncture;CH:cerebral hemorrhage.
It has been demonstrated that necroptosis is an alternative cell death in CH.Initially,Lairdet al[35]reported that the hemoglobin metabolite hemin resulted in oxidative injury,elevation of inflammatory cytokines and necroptosis of astrocytesin vitro,inferring that necroptosis might contribute to brain damage after CH.The application of RIPK1 inhibitor in mice after CH reduced the necrotic rate of neurons and ameliorated neurological impairment[15].Bothin vivoandin vitroexperiments further elucidated the crucial role of RIPK1 in necroptosis-mediated brain damage after CH,as RIPK1 overexpression in cultured neurons promoted necroptosis[36].In addition,necrostatin-1 treatment ameliorated blood-brain barrier damage in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage by inhibiting activation of the RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL cascade[37].As shown by Yuanet al[38],RIPK1 and RIPK3 were involved in brain damage after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats.In our study,we found that the neuroprotective effects of CENA targeted RIPK1,but not RIPK3 in rats after CH.
Similar to necrosis,necroptosis is accompanied by the release of inflammatory cytokines.Mechanistically,RIPK1 can induce an inflammatory response by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway and MAPKs signaling pathway[5,13].Accumulating evidence has shown that RIPK1 intervention using genetic and pharmacological approaches prevents severe inflammatory response during pathogen infection[39]and autoimmune diseases[40].In addition,NF-κB activation-induced production of IL-6 and TNF-α promotes neuroinflammation[41].It has been demonstrated that inflammation can aggravate brain damage after CH,and targeting inhibition of inflammation is a potential treatment for CH[42].Zhouet al[43]reported that patients with CH displayed a significantly higher level of IL-6 and IL-8,and ameliorating inflammation could reduce brain edema and improve outcomes.Our results suggested that CH-induced elevation of inflammatory cytokines(IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α)in brain tissue,serum and CSF of rats with CH could be partially controlled by CENA.Moreover,CENA suppressed the expression of RIPK1 in the brain tissues of rats with CH.Combined with the findings from other research groups,our study indicated that CENA inhibited RIPK1 to ameliorate necroptosis and inflammation in rats with CH.
Taken together,our findings suggested a potential protective effect of CENA on brain damage after CH,which involves the suppression of necroptosis.Further investigations are needed to determine the effectiveness of CENA in patients with CH,which might provide a novel treatment for CH.
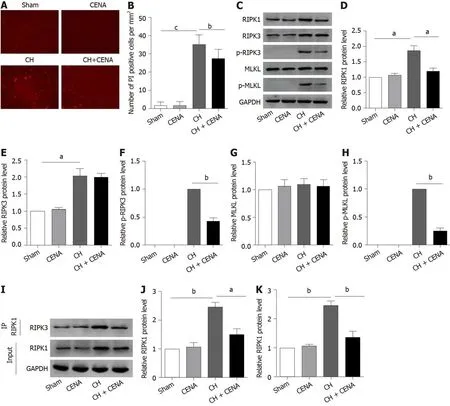
Figure 3 Cross electro-nape acupuncture inhibited cerebral hemorrhage -mediated necrosome formation in vivo.A and B:Propidium iodide staining(A)and propidium iodide positive rate(B)in the brain tissues of experimental rats;C:Protein level of RIPK1,RIPK3,p-RIPK3,MLKL and p-MLKL in the brain tissues of experimental rats;D-H:Quantitative analysis of RIPK1(D),RIPK3(E),p-RIPK3(F),MLKL(G)and p-MLKL(H);I-K:RIPK1 and RIPK3 interaction in the brain tissues of experimental rats using IP assay(J)and quantitative analysis(K)of the IP assay.aP<0.05,bP<0.01,cP<0.001.CENA:Cross electro-nape acupuncture;CH:cerebral hemorrhage;RIPK:Receptor interacting protein kinase;MLKL:mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase.
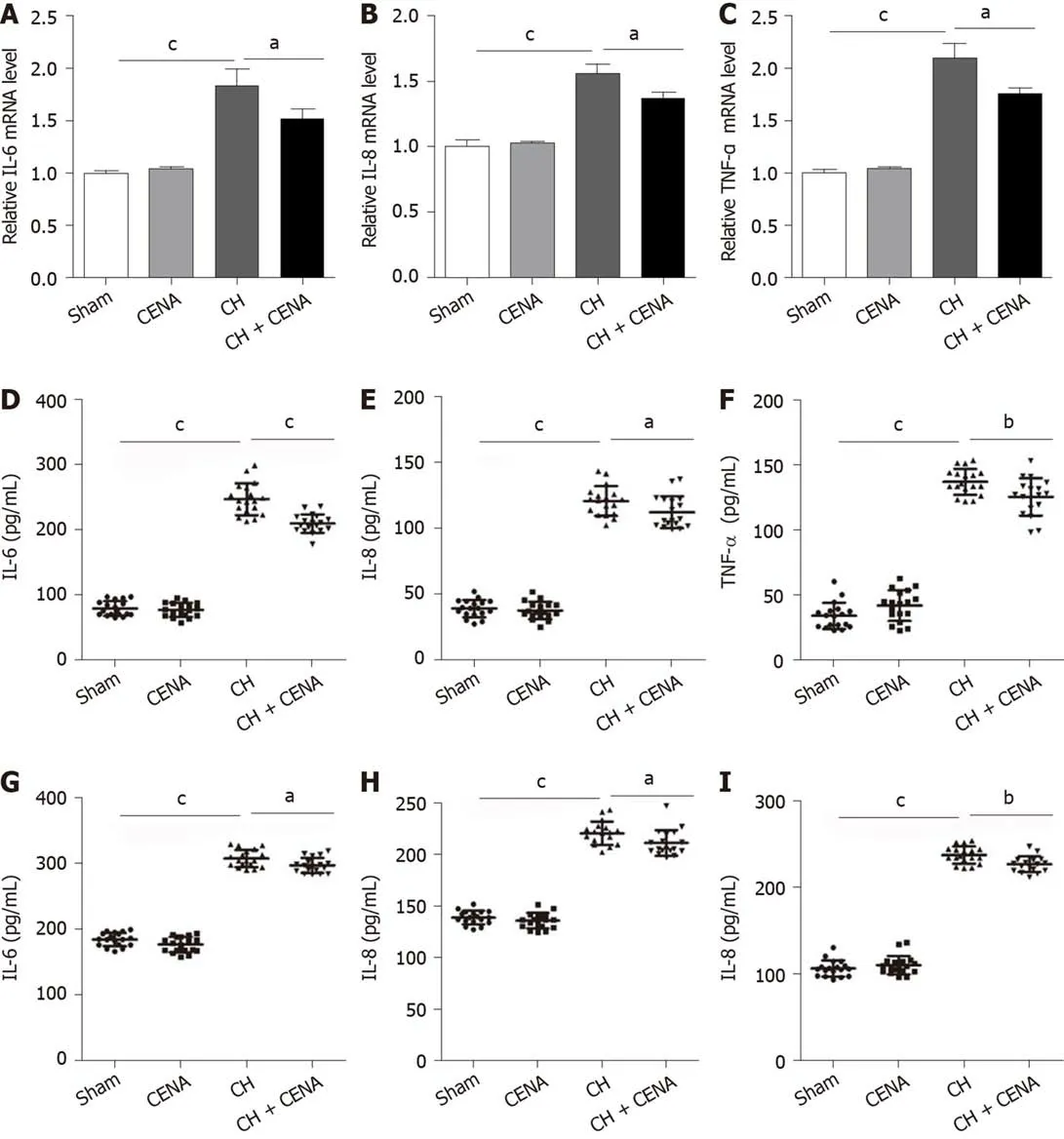
Figure 4 Cross electro-nape acupuncture ameliorated inflammatory cytokines in rats with cerebral hemorrhage.A-C:The mRNA level of IL-6(A),IL-8(B)and TNF-α(C)in the brain tissues of experimental rats;D-F:The concentration of IL-6(D),IL-8(E)and TNF-α(F)in the CSF of rats;G-I:The secretion level of IL-6(G),IL-8(H)and TNF-α(I)in the serum of rats.aP<0.05,bP<0.01,cP<0.001.CENA:Cross electro-nape acupuncture;CH:cerebral hemorrhage;IL:Interleukin;TNF:Tumor necrosis factor.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Cerebral hemorrhage(CH)is a severe disease worldwide.Although accumulating evidence has demonstrated that cell death is the dominant event in the pathogenesis of CH,there is still a lack of preferred treatment.Therefore,developing novel methods to treat CH is currently an urgent issue.
Research motivation
Our previous study showed that cross electro-nape acupuncture(CENA),a modified electroacupuncture,could ameliorate lung infection in patients with CH.However,the role of CENA in brain damage in patients with CH and the underlying mechanism are still unclear.
Research objectives
The aim of this work was to investigate the exact effect of CENA on rats with CH and its underlying mechanism.
Research methods
Rats were surgically treated to mimic CH and received CENA treatment.Propidium iodide staining and immunofluorescence analysis were performed to determine cell death.Neurological score,behavioral score and brain water content were calculated to evaluate brain damage.Western blot,immunoprecipitation assay,quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were conducted to determine the underlying mechanism.
Research results
The present study identified the presence of necroptotic marker p-MLKL in the brain tissues of rats with CH.CENA decreased neurological score,behavioral score and brain water content in rats with CH.Further investigation revealed that CENA inhibited necrosome formation and the expression of IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α in rats with CH.
Research conclusions
Our research found that receptor interacting protein kinase 1(RIPK1)-mediated necroptosis was involved in brain damage in rats with CH.CENA treatment suppressed necroptosis and the inflammatory response to ameliorate brain damage in rats with CH,providing a novel strategy for CH treatment.
Research perspectives
Based on the clinical findings andin vivoexperiments,RIPK1 could be a novel therapeutic target for CH-induced brain damage,and CENA improved brain damage by targeting RIPK1 and inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors.Furtherin vivoassays in primates are necessary to clarify the protective effects of CENA on CH-induced brain damage,which is very meaningful and would contribute to the clinical application of CENA.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年10期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年10期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Needs and concerns of patients in isolation care units - learnings from COVID-19:A reflection
- Successful use of plasma exchange in fulminant lupus myocarditis coexisting with pneumonia:A case report
- Robot-assisted retroperitoneal laparoscopic excision of perirenal vascular tumor:A case report
- Ileocecal intussusception caused by two different tumors - which is the culprit lesion? A case report
- Cryptococcal pneumonia in a human immunodeficiency virusnegative patient:A case report
- Treating severe periodontitis with staged load applied implant restoration:A case report
