腦梗死患者血清腱糖蛋白-C與梗死體積的關系
路陽 陸敏艷

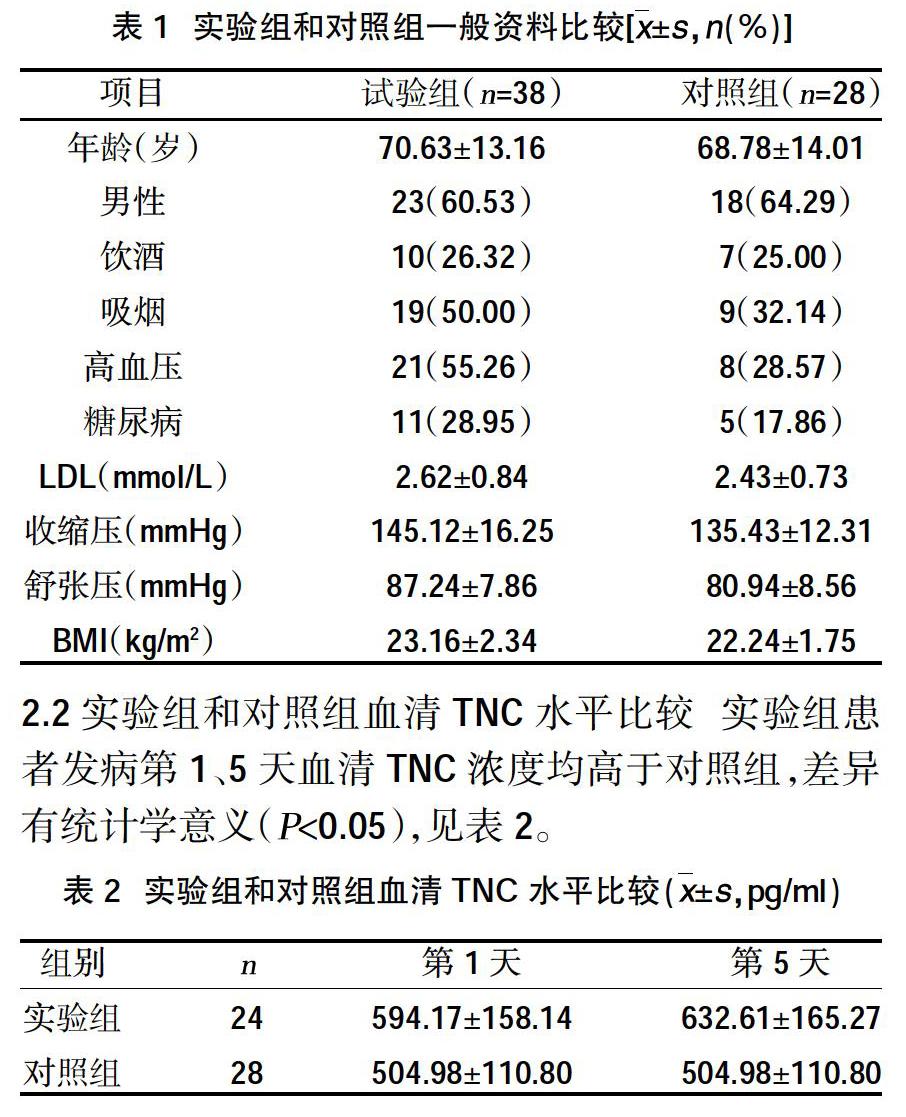
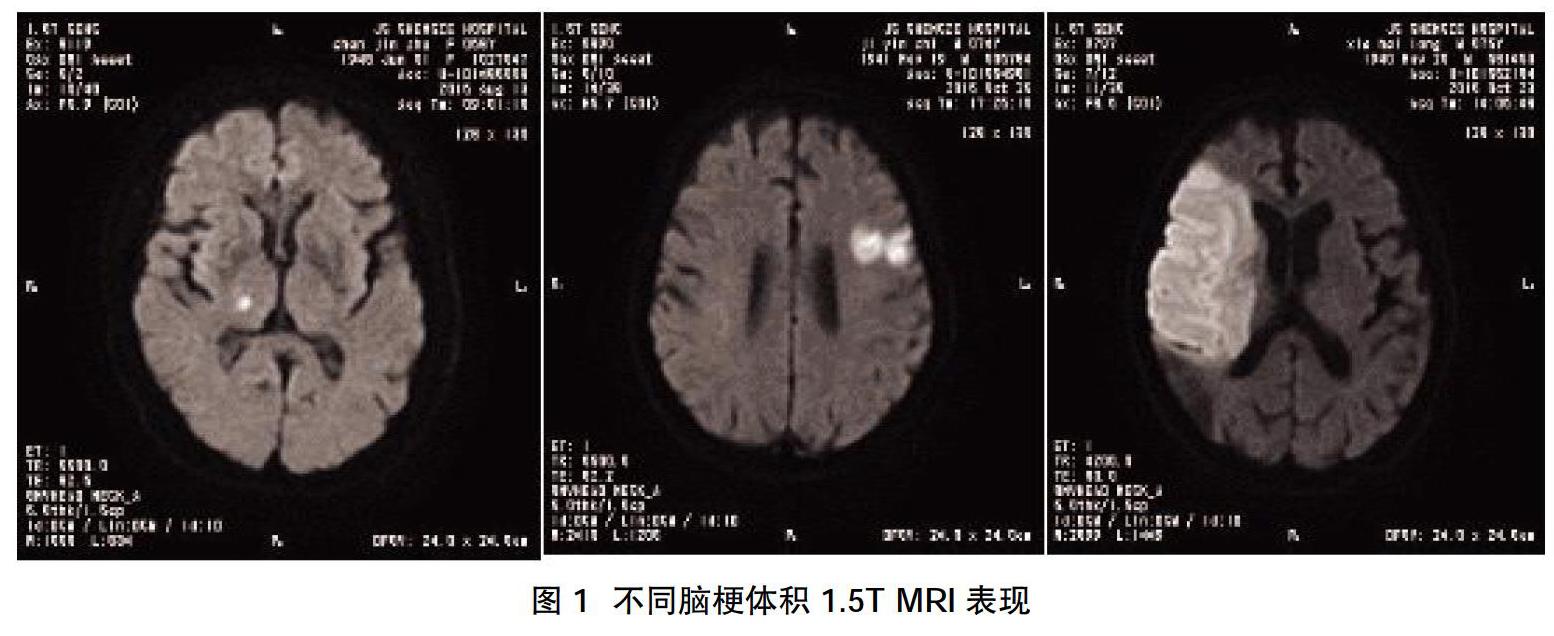
摘要:目的 ?探討血清腱糖蛋白-C(TNC)與急性腦梗死患者梗死體積及神經功能缺損程度的相關性。方法 ?選擇2016年7~10月我院神經內科住院的38例急性腦梗死患者作為實驗組,另外選取同期健康體檢者28名作為健康對照組。根據腦梗死體積將實驗組分為小、中、大梗死組,根據神經功能缺損程度將實驗組分為輕、中、重度損傷組,比較實驗組和健康對照組年齡、性別、高血壓、糖尿病、吸煙構成比、飲酒構成比、平均收縮壓(SBP)、平均舒張壓(DBP)、血清低密度脂蛋白濃度、發病第1、5天血清TNC濃度;比較不同梗死體積、神經功能損傷程度患者的血清TNC濃度。結果 ?實驗組高血壓、糖尿病、吸煙構成比、SBP、DBP均高于健康對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);兩組性別、飲酒構成比、年齡、血清低密度脂蛋白水平比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);發病第1、5天,實驗組血清TNC濃度高于健康對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);發病第1天,小、中、大梗死組及輕、中、重度損傷組血清TNC濃度均高于健康對照組,且小、中、大梗死組血清TNC濃度比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);輕、中、重度損傷組血清TNC濃度比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 ?血清TNC水平與缺血性卒中密切相關,可反映急性腦梗死梗死灶的大小及患者神經功能缺損的嚴重程度。
關鍵詞:急性腦梗死;血清腱糖蛋白-C;梗死體積;神經功能
中圖分類號:R743.3 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.17.020
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)17-0070-04
Abstract:Objective ?To investigate the correlation between serum tenascin-C (TNC) and infarct volume and neurological deficit in patients with acute cerebral infarction.Methods ?38 patients with acute cerebral infarction who were hospitalized in the Department of Neurology of our hospital from July to October 2016 were selected as the experimental group, and 28 healthy subjects were selected as the healthy control group. According to the cerebral infarction volume, the experimental groups were divided into small, medium, and large infarction groups, and the experimental groups were divided into mild, moderate, and severe injury groups according to the degree of neurological impairment. Compare the experimental group and the healthy control group in terms of age, gender, hypertension, and diabetes,smoking composition ratio, drinking composition ratio, mean systolic blood pressure (SBP), mean diastolic blood pressure (DBP), serum low-density lipoprotein concentration, serum TNC concentration on the first and fifth days of onset; compare patients with different infarct volume and neurological impairment the serum TNC concentration.Results ?The composition ratio of hypertension, diabetes, smoking, SBP, and DBP in the experimental group were higher than those in the healthy control group,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); comparison of gender, drinking composition, age, and serum low-density lipoprotein levels between the two groups,the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05); the serum TNC concentration of the experimental group was higher than that of the healthy control group on the first and fifth days of onset,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); on the first day of onset, small, medium and large The serum TNC concentration of the infarct group and the mild, moderate, and severe injury group was higher than that of the healthy control group,the difference in the serum TNC concentration of the small, medium, and large infarction group was statistically significant (P<0.05); light, moderate, and severe injury there was a statistically significant difference in serum TNC concentration between the groups (P<0.05).Conclusion ?Serum TNC level is closely related to ischemic stroke, and could reflect the size of acute cerebral infarction and the severity of the patient's neurological deficit.
Key words:Acute cerebral infarction;Serum tenascin-C;Infarct volume;Neural function
腦梗死(cerebral infarction)是因腦部血流循環障礙,缺血缺氧引起的局限性腦組織壞死或軟化。血管壁病變、血流成份病變和血液動力學改變是引起腦梗死的主要原因。腦梗死體積反映了病情嚴重程度,但是目前急性腦梗死體積計算主要依賴影像學檢查比如頭顱CT、MRI及腦血管造影等,檢查程序繁瑣,經濟成本高,患者負擔重,目前尚沒有完全可靠成熟的血清學指標。腱糖蛋白-C(TNC)是一種特殊的蛋白,在慢性炎癥過程中發揮著巨大的作用,近年關于血清TNC在心血管系統的研究較多,Sato A等[1]研究了急性心……

