RFH-NPT在肝硬化患者營養評估中的應用
王娜 彭瓊 戴夫
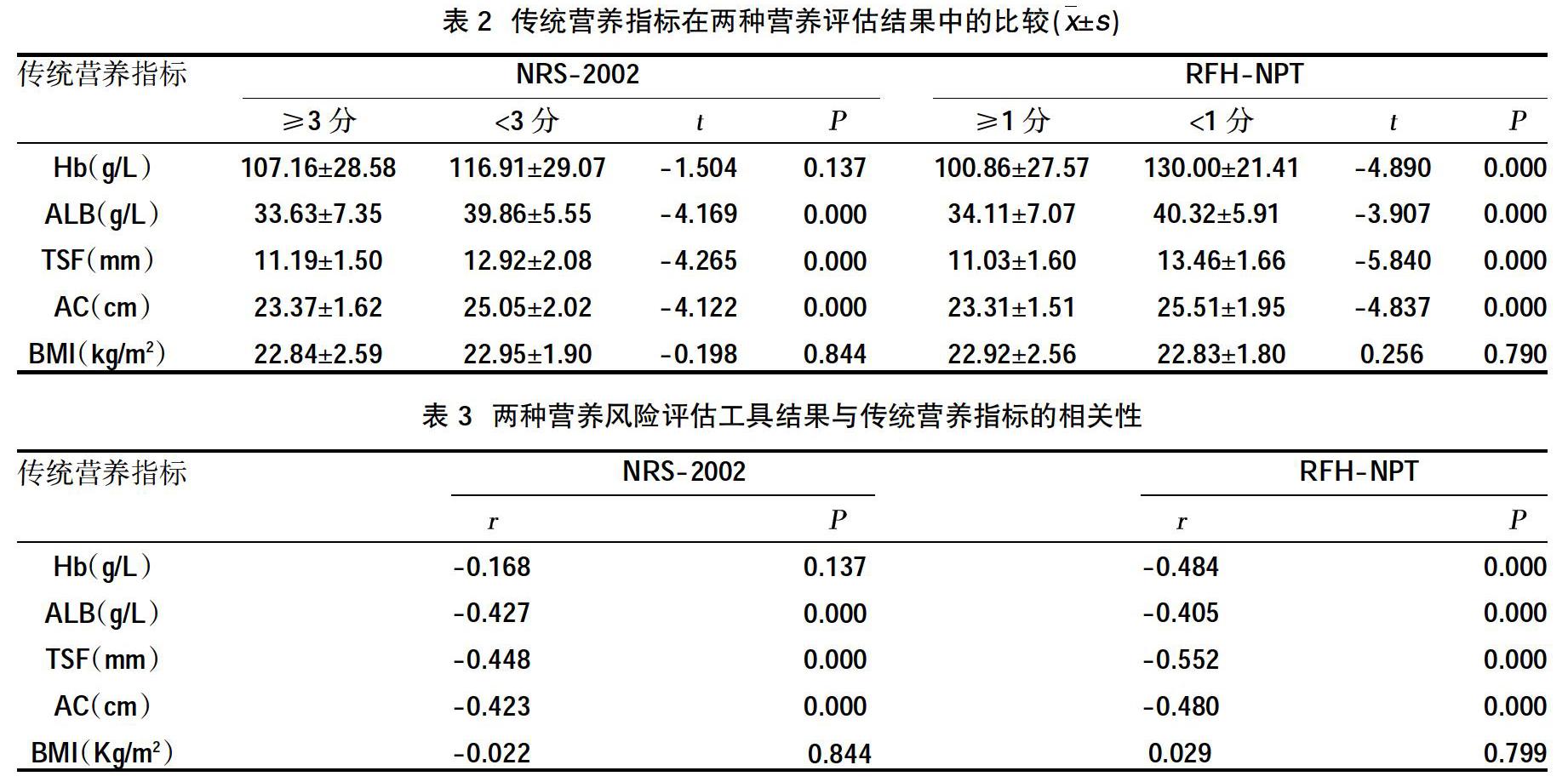
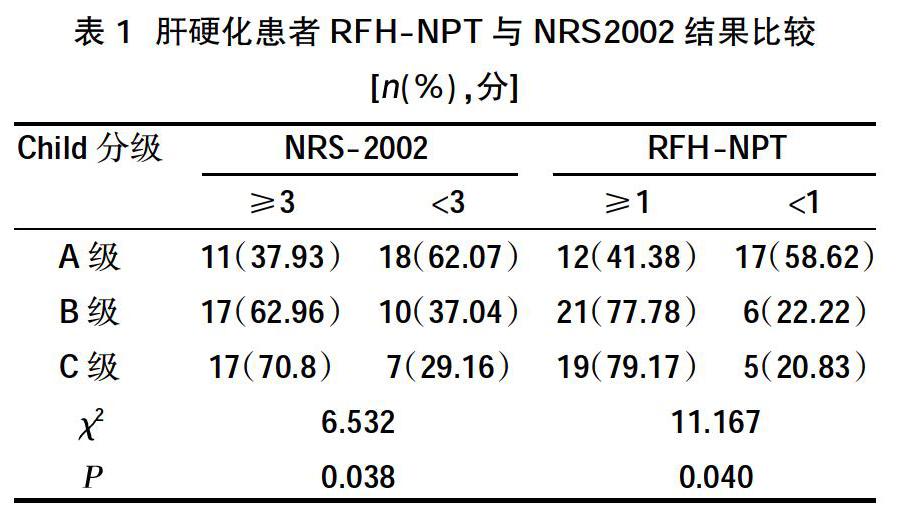
摘要:目的 ?比較皇家自由醫院-營養優先排序工具(RFH-NPT)與營養風險篩查2002(NRS-2002)在肝硬化患者營養評估中應用價值。方法 ?收集安徽醫科大學第三附屬醫院2018年6月~2019年6月消化科及感染科住院肝硬化患者80例,入院后24 h內完成性別、年齡、吸煙飲酒史的登記,測量計算體質指數(BMI)、肱三頭肌皮褶厚度(TSF)、上臂肌圍(AC),收集實驗室指標,包括白蛋白(ALB)、血紅蛋白(Hb)、谷丙轉氨酶(ALT)、谷草轉氨酶(AST)、肌酐(BUN)、凝血酶原時間(PT)、國際標準化比值(INR),應用Child-Pugh 評分將所有患者分為 A、B、C3級,使用RFH-NPT及NRS-2002分別對患者進行營養風險評估,分別比較傳統營養指標結果、RFH-NPT評估結果、NRS-2002評估結果三者之間的關系。結果 ?RFH-NPT和NRS-2002分別篩選出65.00%、56.26%的肝硬化患者存在營養不良;營養不良風險隨著肝臟儲備功能的下降而升高,RFH-NPT與NRS-2002相比醫院風險篩出率更(?字2NRS-2002=6.532,PNRS-2002=0.038;?字2RFH-NPT=11.167,PRFH-NPT=0.040);RFH-NPT評估時營養不良組ALB、肱三頭肌皮褶厚度、AC、Hb水平均低于正常營養組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩組BMI比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);NRS-2002評估時營養不良組ALB、TSF、AC水平均低于正常營養組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),而兩組之間Hb、BMI分別比較時,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論 ?RFH-NPT在住院肝硬化患者營養評估篩查中價值高于NRS2002,是肝硬化患者營養評估的更為有效的工具,避免了SGA與NRS2002所存在的影響因素的作用,并且其操作簡單、靈敏度高等特點有助于臨床醫師對肝硬化患者營養不良的早期發現,但仍需要大量樣本進行反復驗證。
關鍵詞:肝硬化;營養不良;RFH-NPT;NRS-2002
中圖分類號:R575.2 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.17.024
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)17-0085-04
Abstract:Objective ?To compare the value of Royal Free Hospital-Nutrition Prioritization Tool (RFH-NPT) and Nutrition Risk Screening 2002 (NRS-2002) in nutritional assessment of patients with liver cirrhosis.Methods ?A total of 80 patients with liver cirrhosis in the Department of Gastroenterology and Infectious Diseases from June 2018 to June 2019 in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University were collected. The registration of gender, age, smoking and drinking history was completed within 24 hours after admission, and the body mass index was measured and calculated (BMI), triceps skinfold thickness (TSF), upper arm muscle circumference (AC), collect laboratory indicators, including albumin (ALB), hemoglobin (Hb), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), creatinine (BUN), prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), all patients were divided into A, B, C3 grades using Child-Pugh score, and RFH-NPT and NRS-2002 were used to treat patients respectively carry out nutritional risk assessment and compare the relationship between the results of traditional nutritional indicators, the results of RFH-NPT, and the results of NRS-2002.Results ?RFH-NPT and NRS-2002 respectively screened 65.00% and 56.26% of patients with liver cirrhosis to have malnutrition; the risk of malnutrition increases with the decline of liver reserve function. Compared with NRS-2002, RFH-NPT screens out the hospital risk rate was even higher (?字2NRS-2002=6.532, PNRS-2002=0.038;?字2RFH-NPT=11.167, PRFH-NPT=0.040); the malnutrition group ALB, TSF, AC, Hb level in the RFH-NPT assessment was lower than the normal nutrition group,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in BMI between the two groups (P>0.05); the levels of ALB, TSF, and AC in the malnutrition group were lower than those in the normal nutrition group when assessed by NRS-2002. There was statistical significance (P<0.05), but when Hb and BMI were compared between the two groups, the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05).Conclusion ?RFH-NPT was more valuable than NRS2002 in the nutritional assessment and screening of inpatients with liver cirrhosis. It was a more effective tool for nutritional assessment of patients with liver cirrhosis. It avoided the effects of the influencing factors of SGA and NRS2002, and its operation was simple,the high sensitivity and other features were helpful for clinicians in the early detection of malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis, but a large number of samples were still needed for repeated verification.
Key words:Liver cirrhosis;Malnutrition;RFH-NPT;NRS-2002
肝硬化(liver cirrhosis)是一種常見的慢性疾病,由于肝臟功能的下降,患者會出現蛋白質合成不足、營養吸收障礙以及營養消耗等疾病狀態,會導致部分患者出現不同程度營養不良,從而對患者本身的治療及遠期預后產生不良影響。……

