西格列汀對胰島素抵抗的2型糖尿病患者HOMA-IR影響的真實世界研究
葉堯瑤 曹琴 阮泓寅

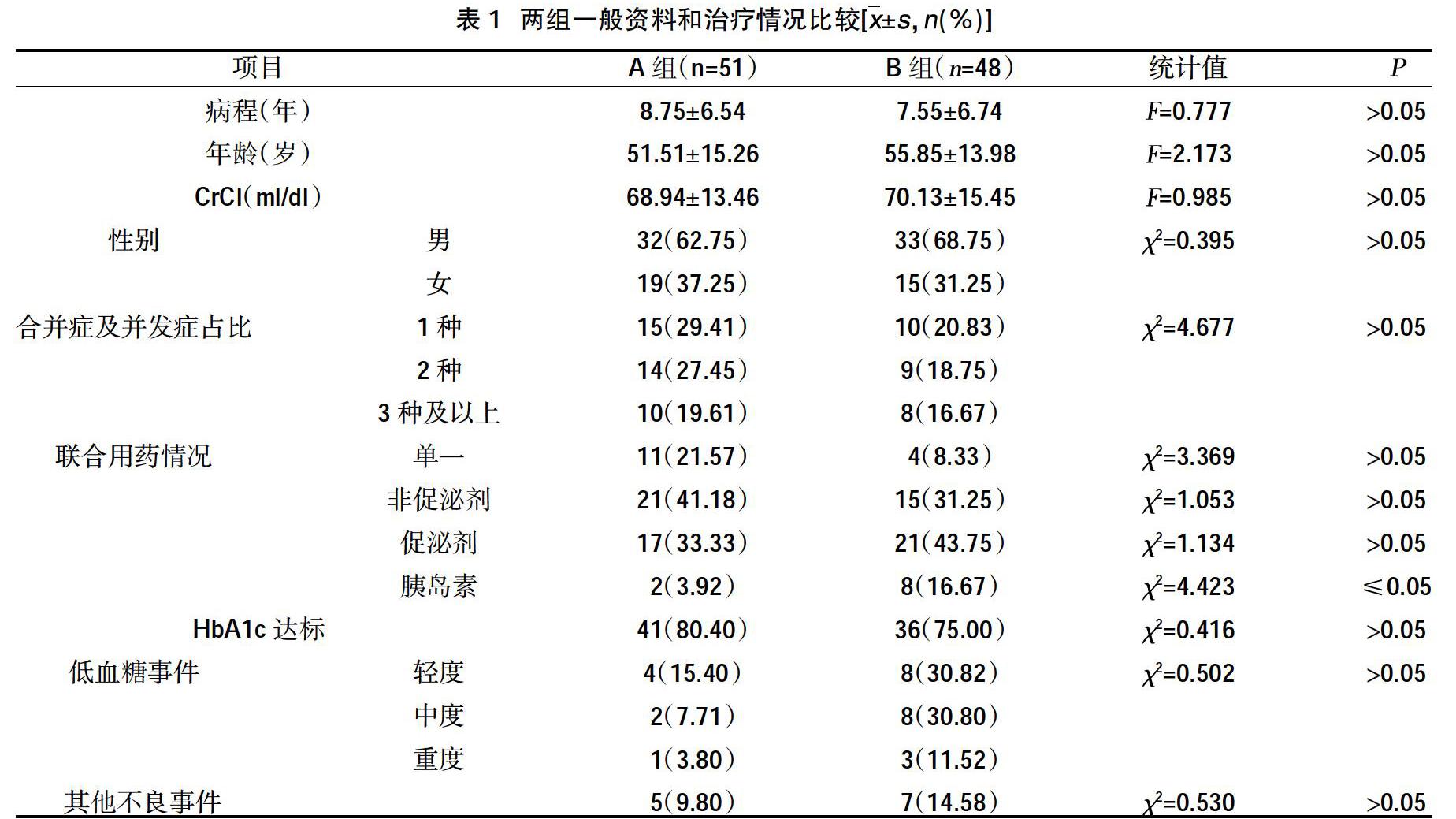
摘要:目的 ?觀察臨床實踐中西格列汀單一或聯合治療對存在胰島素抵抗的2型糖尿病(T2DM)穩態模型胰島素抵抗指數(HOMA-IR)的影響。方法 ?選取2018年3月~2019年10月在合肥市第八人民醫院就診的T2DM患者99例,采用隨機數字表法分為A組(51例)和B組(48例)。A組采用西格列汀單一或聯合其他口服降糖藥或甘精胰島素治療,B組采用非西格列汀治療,比較兩組治療前后的HOMA-IR、HbA1c、體重、血脂、HbA1c≤7%達標率、胰島素使用率及低血糖事件發生率。結果 ?兩組治療前后HbA1c、甘油三脂比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);A組治療前后體重、HOMA-IR比較,差異有統計學意義(P≤0.05),B組治療前后體重、HOMA-IR比較,差異無統計學意義(P≥0.05);組間比較顯示:治療后兩組HbA1C和體重比較,差異無統計學意義(P≥0.05),但A組HbA1c和體重的下降幅度優于B組;治療后兩組甘油三酯和HOMA-IR比較,差異有統計學意義(P≤0.05)。相關分析顯示,HOMA-IR改善與體重下降和甘油三酯下降呈正相關(r=0.631,P=0.000;r=0.451,P=0.030),與HbA1c的下降無相關性(r=0.061,P=0.671)。結論 ?西格列汀可改善胰島素抵抗的T2MD患者的HOMA-IR,這種作用與體重的下降和甘油三酯改善有關,與HbA1c的下降無關。
關鍵詞:西格列汀;HOMA-IR;2型糖尿病
中圖分類號::R587.1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.17.025
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)17-0089-04
Abstract:Objective ?To observe the effect of sitagliptin single or combined treatment in clinical practice on the insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) homeostasis model with insulin resistance.Methods ?A total of 99 patients with T2DM who were treated at Hefei Eighth People's Hospital from March 2018 to October 2019 were selected and divided into group A (51 cases) and group B (48 cases) by random number table. Group A was treated with sitagliptin alone or in combination with other oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin glargine, and group B was treated with non-sitagliptin. The HOMA-IR, HbA1c, body weight, blood lipids,HbA1c≤7% compliance rate, insulin usage rate and incidence of hypoglycemia events.Results ?The comparison of HbA1c and triglycerides before and after treatment between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05); the differences in body weight and HOMA-IR before and after treatment in group A were statistically significant (P≤0.05).There was no statistically significant difference in body weight and HOMA-IR of group B before and after treatment (P≥0.05); comparison between groups showed that there was no significant difference in HbA1C and body weight between the two groups after treatment (P≥0.05), but group A the reduction of HbA1c and body weight was better than that of group B; after treatment, the difference in triglyceride and HOMA-IR between the two groups was statistically significant (P≤0.05). Correlation analysis showed that HOMA-IR improvement was positively correlated with weight loss and triglyceride reduction (r=0.631,P=0.000;r=0.451,P=0.030), no correlated with HbA1c reduction(r=0.061,P=0.671).Conclusion ?Sitagliptin could improve HOMA-IR in patients with insulin resistance and T2MD. This effect was related to weight loss and triglyceride improvement, was not related to the decrease of HbA1c.
Key words:Sitagliptin;HOMA-IR;Type 2 diabetes
西格列汀是一種二肽基肽酶4(DDP-IV)抑制劑,上市已十余年,安全性和耐受性已得到廣泛地認證[1],其降低糖化血紅蛋白(HbA1c)和血糖的作用得到肯定。胰島素抵抗和β細胞衰退是2型糖尿病(T2DM)病理基礎。研究顯示[2],新發2型糖尿病患者使用西格列汀治療后可改善胰島素抵抗。真實世界為了血糖控制達標患者常多種降糖藥或抗高血糖的藥物聯合應用,病情的復雜化和治療方案的多樣化與隨機對照試驗中患者變化因素可控性存在較大差異。本研究從臨床實際應用角度探討西格列汀對存在胰島素抵抗的T2DM患者HOMA-IR的影響,旨在為該病的臨床治療提供參考,現報道如下。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料 ?選擇2018年3月~2019年10月在合肥市第八人民醫院內分泌科就診的T2DM患者99例為研究對象。納入標準:血糖控制未達標(HbA1c>7%),穩態模型胰島素抵抗指數(HOMA-IR)≥2.70;排除標準……

