某地區(qū)慢病管理人員2型糖尿病合理用藥認知性調(diào)研
成昌娟 李莉 李美芳


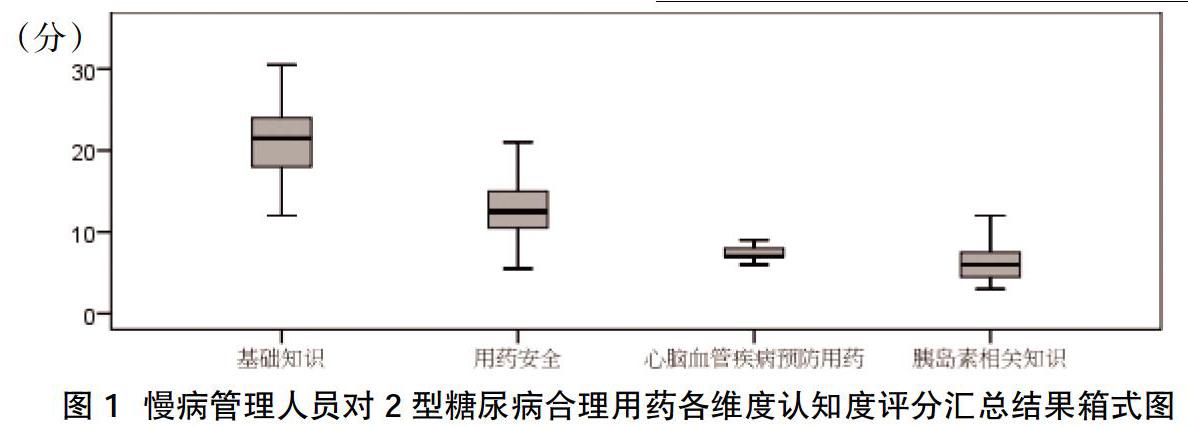
摘要:目的 ?了解某地區(qū)慢病管理人員2型糖尿病合理用藥水平及相關(guān)影響因素,為后續(xù)進行相關(guān)培訓提供參考。方法 ?于2018年4月~2019年2月對本地區(qū)衛(wèi)生服務站慢病管理人員進行2型糖尿病合理用藥認知度的問卷調(diào)研,了解慢病管理人員年齡、職業(yè)、職稱、學歷等特點,分析慢病管理人員不同特征與2型糖尿病合理用藥認知度的相關(guān)性。結(jié)果 ?14.78%的慢病管理人員T2DM合理用藥認知水平為良,34.78%的慢病管理人員T2DM合理用藥認知水平為中,50.43%的慢病管理人員T2DM合理用藥認知水平為差;單因素分析顯示,不同職業(yè)慢病管理人員T2DM合理用藥認知水平比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05);不同職稱、年齡、學歷水平的慢病管理人員T2DM合理用藥認知水平比較,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);衛(wèi)生服務站慢病管理人員認知總分為(47.02±8.62)分,慢病管理人員對T2DM合理用藥知識需求高,學習意愿強烈。結(jié)論 ?慢病管理人員對2型糖尿病合理用藥認知水平總體偏低,在分級診療、慢病逐漸下沉至基層的大背景下,應進一步提高本地區(qū)慢病管理人員的慢病合理用藥水平,對于2型糖尿病二代合理用藥,需開展有針對性的T2DM合理用藥知識培訓。
關(guān)鍵詞:慢病管理人員;2型糖尿病;合理用藥;認知度
中圖分類號:R587.1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.17.035
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)17-0122-04
Abstract:Objective ?To understand the level of rational use of type 2 diabetes and related influencing factors for chronic disease managers in a certain area, and to provide reference for follow-up related training.Methods ?From April 2018 to February 2019, a questionnaire survey was conducted on chronic disease management personnel in local health service stations on the awareness of the rational use of drugs for type 2 diabetes, to understand the characteristics of chronic disease management personnels age, occupation, title, and educational background, and to analyze chronic disease management personnel. The correlation between the different characteristics of disease managers and the awareness of rational use of type 2 diabetes.Results ?14.78% of chronic disease managers had a good level of knowledge of T2DM rational use of drugs, 34.78% of chronic disease managers had a moderate level of T2DM rational use of drugs, and 50.43% of chronic disease managers had a poor level of T2DM rational use of drugs; single factor the analysis showed that there was no statistically significant difference in the cognition level of T2DM rational drug use among chronic disease managers of different occupations (P>0.05);There was a statistically significant difference in the cognition level of chronic disease managers with different professional titles, ages, and educational backgrounds in the rational use of T2DM (P<0.05); the total score of chronic disease managers in health service stations was (47.02±8.62), chronic disease managers have a high demand for knowledge of the rational use of T2DM and a strong willingness to learn.Conclusion ?Chronic disease managers generally had a low level of awareness of the rational use of drugs for type 2 diabetes. Under the background of graded diagnosis and treatment and chronic diseases gradually sinking to the grassroots level, the level of chronic disease managers in the region should be further improved. For the second-generation rational use of type 2 diabetes, it was necessary to carry out targeted training on the rational use of T2DM.
Key words:Chronic disease management personnel;Type 2 diabetes;Rational drug use;Awareness
國際糖尿病聯(lián)盟(international diabetes federation,IDF)報道2017年全球糖尿病總?cè)藬?shù)已達4.25億,我國為糖尿病患病人數(shù)最多的國家,糖尿病患者為1.14億,患病率達10.9%[1]。《中國防治慢性病中長期規(guī)劃(2017—2025年)》提出要積極推進高血壓、糖尿病、慢性呼吸系統(tǒng)疾病等患者的分級診療,形成基層首診、雙向轉(zhuǎn)診、上下聯(lián)動、急慢分治的合理就醫(yī)體系[2]。然而有研究顯示,我國68.3%的受訪者不信任社區(qū)醫(yī)療機構(gòu)的醫(yī)療水平,61.2%的患者會首選二級以上醫(yī)院進行就診[3]。基層、社區(qū)醫(yī)務人員的診療水平成為患者參與慢病管理依從性的重要影響因素。為了解本地區(qū)慢病管理人員合理用藥水平,發(fā)現(xiàn)用藥短板,本研究對本地區(qū)衛(wèi)生服務站慢病管理人員進行2型糖尿病合理用藥認知度的問卷調(diào)研,旨在通過專業(yè)及有針對性的培訓提高慢病管理人員專科用藥水平,是提高其慢病診療水平的重要環(huán)節(jié)。

